2021年第一次blog总结
一、前言
经过第一个月学习,已经了初步了解到面向对象的程序设计的一些特点。下面将总结三次习题集的一些要点。
1.习题集一 总共8题:
1-6题分别考察Java的各基础语法(输入,输出,各数据类型,循环,选择,数组等),7题考查排序方法,8题通过一个三角形的判断来考察我们的逻辑思维。
2.习题集二 总共5题:
1题考察对字符串的处理,2题考查有序数组的合并,3-5题通过对日期的处理来让我们感知类的定义以及对方法的构造
3.习题集三 总共3题:
1-3题都考查对类的设计与构造,前两题给予类设计的提示,第三题还考察了正则表达式对字符串的处理。
二、设计与分析
1.习题集一
全部八题非常基础为从C语言到Java的适应期题目,在此仅对有一定难度的第八题分析
题目:输入三角形三条边,判断该三角形为什么类型的三角形。
输入格式
(在一行中输入三角形的三条边的值(实型数),可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔,其中三条边的取值范围均为[1,200]。)
输出格式
((1)如果输入数据非法,则输出“Wrong Format”; (2)如果输入数据合法,但三条边不能构成三角形,则输出“Not a triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等 边三角形,则输出“Equilateral triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰直角三角形,则输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”; (5)如果输入数据合法且 能够成等腰三角形,则输出“Isosceles triangle”; (6)如果输入数据合法且能够成直角三角形,则输出“Right-angled triangle”; (7)如果输入数据合法且能够成一 般三角形,则输出“General triangle”。)
下面为提交源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 double a,b,c,d,e,f; 6 7 a= in.nextDouble(); 8 b= in.nextDouble(); 9 c= in.nextDouble(); 10 11 12 13 14 15 if((a>=1&&a<=200) &&(b>=1&&b<=200) && (c>=1&&c<=200)) { 16 if((a+b<=c)||(a+c<=b)||(b+c<=a)) 17 System.out.print("Not a triangle"); 18 19 else if(a==b&&b==c) 20 System.out.print("Equilateral triangle"); 21 else if((a==b&&(Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)<=1e-1))||(a==c&&(Math.abs((a*a)*2-b*b)<=1e-1))||(c==b&&(Math.abs((b*b)*2-a*a)<=1e-1))) 22 System.out.print("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); 23 else if(((a==b)&&(a!=c))||((a==c)&&(a!=b))||((c==b)&&(c!=a))) 24 System.out.print("Isosceles triangle"); 25 else if(((a*a+b*b)==c*c||((a*a+c*c)==b*b))||((b*b+c*c)==a*a)) 26 System.out.print("Right-angled triangle"); 27 else 28 System.out.print("General triangle"); 29 } 30 31 else { 32 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 33 } 34 35 36 37 } 38 }
由于在输出格式中已经提示了基本算法,按照提示要求,写出各三角形的判定条件即可。
但是关于等腰直角三角形的判定出了比较大的问题
1 else if((a==b&&(Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)<=1e-1))||(a==c&&(Math.abs((a*a)*2-b*b)<=1e-1))||(c==b&&(Math.abs((b*b)*2-a*a)<=1e-1))) 2 System.out.print("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
其中的 (Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)=1e-1),其转化成数学语言即 ![]() 。但根式在计算机中的存储不是以无理数来存储,而是被化简为一个有理数,即需要用(Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)<=1e-1)
。但根式在计算机中的存储不是以无理数来存储,而是被化简为一个有理数,即需要用(Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)<=1e-1)
来判断。
2.习题集二
1,2题较为基础,在此不分析。3-5题都关于日期处理。
第三题题目:输入年月日的值(均为整型数),输出该年份是否为闰年,同时输出该日期为星期几。 其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1820,2020] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取 值范围为[1,31] ; 判断星期几的算法如下:假定公元0001年1月1日为星期一,因此只要计算出当前输入日期离0001年1月1日所差的天数,然后拿这个天数除以7求余数,当余数为0时,为星 期日,当余数为1时,为星期一,以此类推,当余数为6时,为星期六。
下面为提交源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 8 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 9 int year=0,month=0,date=0; 10 year=sc.nextInt(); 11 month=sc.nextInt(); 12 date=sc.nextInt(); 13 14 if(year<1820||year>2020) { 15 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 16 System.exit(0); 17 } 18 19 if(month<1||month>12) { 20 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 21 System.exit(0); 22 } 23 24 if(date>31||date<1) { 25 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 26 System.exit(0); 27 } 28 29 else if(date==31) { 30 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 31 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 32 System.exit(0); 33 } 34 } 35 36 else if(date==29) { 37 if(isLeapYear(year)==false) { 38 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 39 System.exit(0); 40 } 41 42 43 } 44 45 if(isLeapYear(year)==true) { 46 System.out.println(year+" is a leap year" +"." ); 47 } 48 else { 49 System.out.println(year+" is not a leap year" +"." ); 50 } 51 52 int z=numOfDays(year,month ,date); 53 String A=getWhatDay(z); 54 System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+date+" is "+A+"."); 55 56 } 57 58 private static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { 59 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 60 boolean x=false; 61 62 if (year % 4 == 0){ 63 if (year % 100 == 0){ 64 if (year % 400 == 0){ 65 x=true; 66 } 67 68 } 69 else{ 70 x=true; 71 } 72 } 73 74 return x; 75 } 76 77 public static int numOfDays(int year,int month ,int day) { 78 int t=0; 79 int a=year-1,r=0,b=0; 80 for(int i=a;i>0;i--) { 81 if(isLeapYear(i)==true) { 82 r++; 83 } 84 } 85 b=a-r; 86 t=365*b+366*r; 87 88 int m=0, n=0,s=0,p=0; 89 if (month +1<= 8) 90 { 91 for (int i = 1; i < month; i = i + 2) { 92 m++; 93 } 94 95 for (int j = 4; j < month; j = j + 2) { 96 n++; 97 } 98 99 } 100 else 101 { 102 m = 4; 103 n = 2; 104 for (int i = 8; i < month; i = i + 2) { 105 m++; 106 } 107 108 for (int j = 9; j < month; j = j + 2) { 109 n++; 110 } 111 112 } 113 if(month>2) { 114 if(isLeapYear(year)==true) { 115 p=29; 116 } 117 else { 118 p=28; 119 } 120 } 121 s = 31 * m + 30 * n + day+p; 122 t+=s; 123 return t; 124 } 125 126 public static String getWhatDay(int days) { 127 int sum=days%7; 128 String end=""; 129 switch(sum) { 130 case 0:{ 131 end="Sunday"; 132 break; 133 } 134 135 case 1:{ 136 end="Monday"; 137 break; 138 } 139 140 case 2:{ 141 end="Tuesday"; 142 break; 143 } 144 145 case 3:{ 146 end="Wednesday"; 147 break; 148 } 149 150 case 4:{ 151 end="Thursday"; 152 break; 153 } 154 155 case 5:{ 156 end="Friday"; 157 break; 158 } 159 160 case 6:{ 161 end="Saturday"; 162 break; 163 } 164 165 166 167 } 168 return end; 169 } 170 }
判断具体星期几的算法已给,那本题核心为求出具体距公元0001年1月1日的具体天数
首先:
1 int t=0; 2 int a=year-1,r=0,b=0; 3 for(int i=a;i>0;i--) { 4 if(isLeapYear(i)==true) { 5 r++; 6 } 7 } 8 b=a-r; 9 t=365*b+366*r;
a为除本年以外距0001年的年数,通过循环判断出其中具体有多少闰年。从而得出除本年外的所有天数。
其次:
1 int m=0, n=0,s=0,p=0; 2 if (month +1<= 8) 3 { 4 for (int i = 1; i < month; i = i + 2) { 5 m++; 6 } 7 8 for (int j = 4; j < month; j = j + 2) { 9 n++; 10 } 11 12 } 13 else 14 { 15 m = 4; 16 n = 2; 17 for (int i = 8; i < month; i = i + 2) { 18 m++; 19 } 20 21 for (int j = 9; j < month; j = j + 2) { 22 n++; 23 } 24 25 }
这里算出除去二月的本年天数
具体以7,8月份为界。
上半部分 1,3,5,7(31天)与4,6(30天)。
下半部分8,10,12(31天)与9,11 (30天)。(其中,划分开的月份都是公差为2的等差数列,可以用循环处理)
最后:
1 if(month>2) { 2 if(isLeapYear(year)==true) { 3 p=29; 4 } 5 else { 6 p=28; 7 } 8 } 9 s = 31 * m + 30 * n + day+p; 10 t+=s;
判断闰年是否,完成天数的计算。
第四题题目:输入年月日的值(均为整型数),输出该日期的下一天。 其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1820,2020] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。
下面为提交源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 8 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 9 int year=0,month=0,day=0; 10 year=sc.nextInt(); 11 month=sc.nextInt(); 12 day=sc.nextInt(); 13 14 if(checkInputValidity( year, month, day)==false) { 15 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 16 System.exit(0); 17 } 18 19 20 nextDate( year, month, day); 21 22 } 23 24 private static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { 25 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 26 boolean x=false; 27 28 if (year % 4 == 0){ 29 if (year % 100 == 0){ 30 if (year % 400 == 0){ 31 x=true; 32 } 33 34 } 35 else{ 36 x=true; 37 } 38 } 39 40 return x; 41 } 42 43 44 public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { 45 46 boolean x=true; 47 48 if(year<1820||year>2020) { 49 x=false; 50 } 51 52 if(month<1||month>12) { 53 x=false; 54 } 55 56 if(day>31||day<1) { 57 x=false; 58 } 59 60 else if(day==31) { 61 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 62 x=false; 63 } 64 } 65 66 else if(day==29) { 67 if(isLeapYear(year)==false) { 68 x=false; 69 } 70 71 72 } 73 return x; 74 } 75 76 public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) { 77 if(day==31) { 78 if(month==12) { 79 year++; 80 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+1+"-"+1); 81 } 82 else { 83 month++; 84 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 85 } 86 } 87 88 else if(day==30) { 89 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 90 month++; 91 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 92 } 93 94 else { 95 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+31); 96 } 97 98 } 99 100 else if(day==29) { 101 if(month==2) { 102 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 103 } 104 105 else { 106 day++; 107 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 108 } 109 110 } 111 112 else if(day==28) { 113 if(month==2) { 114 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 115 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+2+"-"+29); 116 } 117 else { 118 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 119 } 120 } 121 122 else { 123 day++; 124 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 125 } 126 } 127 128 else { 129 day++; 130 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 131 } 132 133 } 134 }
本体核心就是跨月份时的处理
1 public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) { 2 if(day==31) { 3 if(month==12) { 4 year++; 5 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+1+"-"+1); 6 } 7 else { 8 month++; 9 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 10 } 11 } 12 13 else if(day==30) { 14 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 15 month++; 16 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 17 } 18 19 else { 20 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+31); 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 else if(day==29) { 26 if(month==2) { 27 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 28 } 29 30 else { 31 day++; 32 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 33 } 34 35 } 36 37 else if(day==28) { 38 if(month==2) { 39 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 40 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+2+"-"+29); 41 } 42 else { 43 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 44 } 45 } 46 47 else { 48 day++; 49 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 50 } 51 } 52 53 else { 54 day++; 55 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 56 } 57 58 } 59 }
先是以day为基准判断 ,即31,30,29,28,以及其他
31日:
1 if(month==12) { 2 year++; 3 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+1+"-"+1); 4 } 5 else { 6 month++; 7 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 8 9 }
主要是12月的跨年处理,及其他月份的跨月处理
30日:
1 else if(day==30) { 2 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 3 month++; 4 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 5 } 6 7 else { 8 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+31); 9 } 10 11 }
主要是判断30号是否为该月最后一天,然后在做跨月处理或通常处理。
29日:
1 else if(day==29) { 2 if(month==2) { 3 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 4 } 5 6 else { 7 day++; 8 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 9 } 10 11 }
主要是判断29号是否为该月最后一天,然后在做2月跨月处理或通常处理。(由于前方做过输入校验,所以此处不需要在做闰年判断)
28日:
1 else if(day==28) { 2 if(month==2) { 3 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 4 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+2+"-"+29); 5 } 6 else { 7 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 8 } 9 } 10 11 else { 12 day++; 13 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 14 } 15 }
主要是判断是否为闰年二月,然后在做2月跨月处理或通常处理。
最后其他情况为通常处理。
第五题题目:输入年月日的值(均为整型数),同时输入一个取值范围在[-10,10] 之间的整型数n,输出该日期的前n天(当n > 0时)、该日期的后n天(当n<0时)。
其中年份取值范围为 [1820,2020] ,月份取值范围为[1,12] ,日期取值范围为[1,31] 。
下面为提交源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 8 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 9 int year=0,month=0,day=0,n=0; 10 year=sc.nextInt(); 11 month=sc.nextInt(); 12 day=sc.nextInt(); 13 n=sc.nextInt(); 14 if(checkInputValidity( year, month, day)==false) { 15 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 16 System.exit(0); 17 } 18 19 if(n>10&&n<-10){ 20 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 21 System.exit(0); 22 } 23 if(n<0) { 24 n=Math.abs(n); 25 nextnDate(year,month,day,n); 26 } 27 28 else if(n>0){ 29 lastnDate(year,month,day,n); 30 } 31 else { 32 System.out.println(n+ " days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 33 } 34 } 35 36 private static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { 37 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 38 boolean x=false; 39 40 if (year % 4 == 0){ 41 if (year % 100 == 0){ 42 if (year % 400 == 0){ 43 x=true; 44 } 45 46 } 47 else{ 48 x=true; 49 } 50 } 51 52 return x; 53 } 54 55 56 public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { 57 58 boolean x=true; 59 60 if(year<1820||year>2020) { 61 x=false; 62 } 63 64 if(month<1||month>12) { 65 x=false; 66 } 67 68 if(day>31||day<1) { 69 x=false; 70 } 71 72 else if(day==31) { 73 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 74 x=false; 75 } 76 } 77 78 else if(day==29) { 79 if(isLeapYear(year)==false) { 80 x=false; 81 } 82 83 84 } 85 return x; 86 } 87 88 public static void nextnDate(int year,int month,int day,int n) { 89 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { 90 if(day==31) { 91 if(month==12) { 92 year++; 93 month=1; 94 day=1; 95 } 96 else { 97 month++; 98 day=1; 99 } 100 } 101 102 else if(day==30) { 103 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 104 month++; 105 day=1; 106 } 107 108 else { 109 day++; 110 } 111 112 } 113 114 else if(day==29) { 115 if(month==2) { 116 month++; 117 day=1; 118 } 119 120 else { 121 day++; 122 } 123 124 } 125 126 else if(day==28) { 127 if(month==2) { 128 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 129 day++; 130 } 131 else { 132 month++; 133 day=1; 134 } 135 } 136 137 else { 138 day++; 139 } 140 } 141 142 else { 143 day++; 144 } 145 } 146 System.out.println(-n+ " days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 147 148 } 149 150 public static void lastnDate(int year,int month,int day,int n) { 151 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { 152 if(day==1) { 153 if(month==1) { 154 month=12; 155 year--; 156 day=31; 157 } 158 else if(month==2||month==4||month==6||month==8||month==9||month==11) { 159 day=31; 160 month--; 161 } 162 else if(month==3) { 163 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 164 day=29; 165 month--; 166 } 167 else { 168 day=28; 169 month--; 170 } 171 } 172 } 173 else { 174 day--; 175 } 176 } 177 System.out.println(n+ " days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 178 } 179 180 }
本题实际就是上题的进阶版,n次求下一天和n次求上一天。 即将上题求下一天放入一个循环结构即可。
n次求下一天:
1 public static void nextnDate(int year,int month,int day,int n) { 2 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { 3 if(day==31) { 4 if(month==12) { 5 year++; 6 month=1; 7 day=1; 8 } 9 else { 10 month++; 11 day=1; 12 } 13 } 14 15 else if(day==30) { 16 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 17 month++; 18 day=1; 19 } 20 21 else { 22 day++; 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 else if(day==29) { 28 if(month==2) { 29 month++; 30 day=1; 31 } 32 33 else { 34 day++; 35 } 36 37 } 38 39 else if(day==28) { 40 if(month==2) { 41 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 42 day++; 43 } 44 else { 45 month++; 46 day=1; 47 } 48 } 49 50 else { 51 day++; 52 } 53 } 54 55 else { 56 day++; 57 } 58 } 59 System.out.println(-n+ " days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 60 61 }
n次求上一天:
1 public static void lastnDate(int year,int month,int day,int n) { 2 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { 3 if(day==1) { 4 if(month==1) { 5 month=12; 6 year--; 7 day=31; 8 } 9 else if(month==2||month==4||month==6||month==8||month==9||month==11) { 10 day=31; 11 month--; 12 } 13 else if(month==3) { 14 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 15 day=29; 16 month--; 17 } 18 else { 19 day=28; 20 month--; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 else { 25 day--; 26 } 27 } 28 System.out.println(n+ " days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 29 }
3.习题集三
全部三题都需要对与类的设计,第一题关于设计提示非常详细这里不分析。
第二题题目:
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注 意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法,否则按0分处理。
要求:Date类结构如下图所示
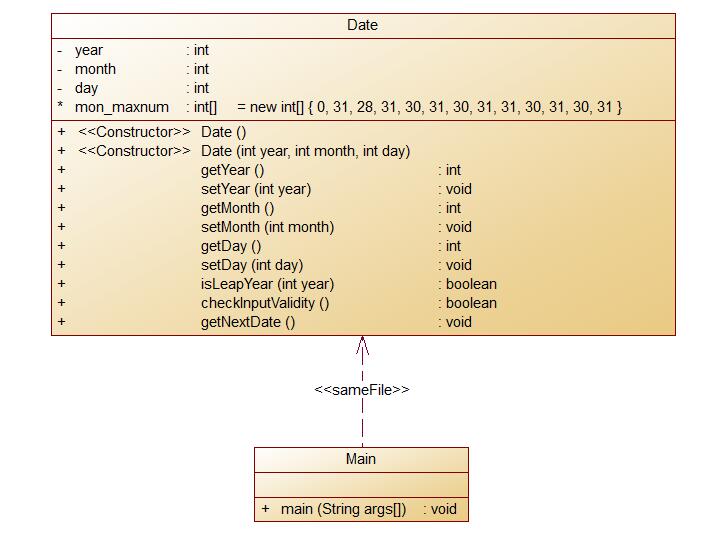
下面为提交源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 8 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 9 int year=sc.nextInt(); 10 int month=sc.nextInt(); 11 int day=sc.nextInt(); 12 Date date=new Date(); 13 date.setDay(day); 14 date.setMonth(month); 15 date.setYear(year); 16 if(date.checkInputValidity( year, month, day)==false) { 17 System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong"); 18 } 19 else { 20 date.getNextDay(); 21 System.out.println("Next day is:"+date.getYear()+"-"+date.getMonth()+"-"+date.getDay()); 22 } 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 class Date { 28 29 private int year=1900; 30 private int month=1; 31 private int day=1; 32 int[]mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 33 34 public Date() { 35 36 } 37 38 39 public Date(int year,int month,int day) { 40 this.year=year; 41 this.month=month; 42 this.day=day; 43 44 } 45 46 47 public int getYear() { 48 return year; 49 } 50 51 52 public void setYear(int year) { 53 this.year = year; 54 } 55 56 57 public int getMonth() { 58 return month; 59 } 60 61 62 public void setMonth(int month) { 63 this.month = month; 64 } 65 66 67 public int getDay() { 68 return day; 69 } 70 71 72 public void setDay(int day) { 73 this.day = day; 74 } 75 76 public boolean isLeapyear(int year) { 77 boolean flag=false; 78 if (year % 4 == 0){ 79 if (year % 100 == 0){ 80 if (year % 400 == 0){ 81 flag=true; 82 } 83 }else{ 84 flag=true; 85 } 86 }return flag; 87 } 88 89 public boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { 90 91 boolean x=true; 92 93 if(year<1900||year>2000) { 94 x=false; 95 96 } 97 98 else if(month<1||month>12) { 99 x=false; 100 101 } 102 103 else if(day>mon_maxnum[month]) { 104 if((month==2&&day==29&&isLeapyear(year)==true)== false){ 105 x=false; 106 107 } 108 109 } 110 else if(day<1) { 111 x=false; 112 } 113 114 return x; 115 } 116 public void getNextDay() { 117 if(getMonth()==2&&isLeapyear(year)==true) { 118 if(getDay()==29) { 119 setMonth(3); 120 setDay(1); 121 }else { 122 setDay(getDay()+1); 123 } 124 }else{ 125 if(getDay()==mon_maxnum[month]) { 126 if(getMonth()==12) { 127 setYear(getYear()+1); 128 setMonth(1); 129 }else { 130 setMonth(getMonth()+1); 131 }setDay(1); 132 }else { 133 setDay(getDay()+1); 134 } 135 } 136 } 137 138 }
其中关于Date类的设计:
属性为Year,Month,Day。并设置了mon_maxnum数组来方便判断天数,并来减少其复杂度。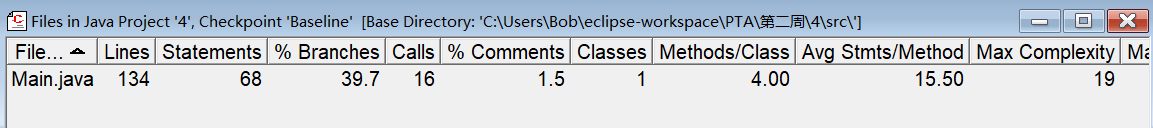
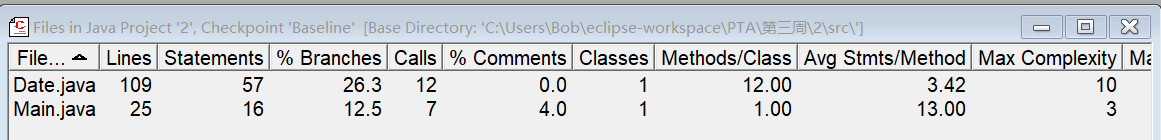
通过对比二者Max Complexity可以发现mon_maxnum数组的设置帮助还是很高的
第三题题目:一元多项式求导(类设计)

下面为提交源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 import java.util.regex.Matcher; 3 import java.util.regex.Pattern; 4 5 public class Main { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 int nOi=0,s=0; 10 Scanner sc=new Scanner (System.in); 11 String nextLine = sc.nextLine(); 12 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll(" ", ""); 13 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("x\\+", "x\\^1\\+"); 14 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\+x", "\\+1\\*x"); 15 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\-x", "\\-1\\*x"); 16 String pattern = "[+-]?[0-9]+\\*x\\^[+-]?[0-9]+|[+-]?[0-9]+"; 17 Derivate derivate=new Derivate(); 18 19 Pattern r = Pattern.compile(pattern); 20 Matcher m = r.matcher(nextLine); 21 Matcher d = r.matcher(nextLine); 22 while (d.find()) { 23 nOi++; 24 } 25 long[] coeFFicient=new long[nOi];//系数 26 long[] inDex=new long[nOi];//指数 27 derivate.setnOi(nOi); 28 String []end= new String[nOi]; 29 String []nEw= new String[nOi]; 30 while (m.find()) { 31 end[s]=m.group(); 32 s++; 33 } 34 for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 35 if(end[i].matches("[+-]?\\d+")) { 36 end[i]=end[i]+"*x^0"; 37 } 38 else if(end[i].matches("[+-]?\\d+\\*x")) { 39 end[i]=end[i]+"^1"; 40 } 41 } 42 43 44 for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 45 end[i] = end[i].replaceAll("\\*x\\^", " "); 46 } 47 48 // for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 49 // System.out.println(end[i]); 50 // } 51 52 for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 53 String []split=end[i].split(" "); 54 coeFFicient[i]=Integer.parseInt(split[0]); 55 inDex[i]=Integer.parseInt(split[1]); 56 }//前戏 57 for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 58 if(coeFFicient[i]==0) { 59 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 60 System.exit(0); 61 } 62 } 63 64 65 66 derivate.setCoeFFicient(coeFFicient); 67 derivate.setInDex(inDex); 68 derivate.Derivation(); 69 coeFFicient=derivate.getCoeFFicient();//系数 70 inDex=derivate.getInDex();//指数 71 72 73 ouTPut( coeFFicient, inDex, nOi,nEw); 74 75 } 76 public static void ouTPut( long[] coeFFicient, long[] inDex,int nOi,String []nEw) { 77 78 int m=0; 79 for(int i=0;i<nOi;i++) { 80 81 if(coeFFicient[i]==0) { 82 nEw[i]=""; 83 } 84 else if(coeFFicient[i]==1) { 85 nEw[i]="x^"+inDex[i]; 86 } 87 else { 88 if(inDex[i]==0) { 89 nEw[i]=""+coeFFicient[i]; 90 } 91 else if(inDex[i]==1) { 92 nEw[i]=coeFFicient[i]+"*x"; 93 } 94 else { 95 nEw[i]=coeFFicient[i]+"*x^"+inDex[i]; 96 m=m+nEw[i].length(); 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 // for(int i=0;i<nOi;i++) { 101 // System.out.println(nEw[i]); 102 // } 103 104 String nextLine = "" ; 105 for(int i=0;i<nOi;i++) { 106 107 nextLine+="+"+nEw[i]; 108 } 109 110 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\+\\-", "\\-"); 111 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("^\\+", ""); 112 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\+$", ""); 113 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\+\\-", "\\-"); 114 // nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\+0\\*x\\^0", "");//除求导前的常数项 115 // nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\*x\\^0", "");//化简求导前的一次项 116 117 118 if(nextLine=="") { 119 nextLine="0"; 120 } 121 122 System.out.print(nextLine); 123 } 124 125 126 } 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 class Derivate { 135 136 private int nOi=0;//项数 137 private long[] coeFFicient=new long[nOi];//系数 138 private long[] inDex=new long[nOi];//指数 139 public Derivate() { 140 super(); 141 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 142 } 143 public Derivate(int nOi, long[] coeFFicient, long[] inDex) { 144 super(); 145 this.nOi = nOi; 146 this.coeFFicient = coeFFicient; 147 this.inDex = inDex; 148 } 149 public int getnOi() { 150 return nOi; 151 } 152 public void setnOi(int nOi) { 153 this.nOi = nOi; 154 } 155 public long[] getCoeFFicient() { 156 return coeFFicient; 157 } 158 public void setCoeFFicient(long[] coeFFicient) { 159 this.coeFFicient = coeFFicient; 160 } 161 public long[] getInDex() { 162 return inDex; 163 } 164 public void setInDex(long[] inDex) { 165 this.inDex = inDex; 166 }//指数 167 public void Derivation() { 168 long[]z=getInDex(); 169 long[]x=getCoeFFicient(); 170 for(int i=0;i<getnOi();i++) { 171 172 173 x[i]*=z[i]; 174 z[i]--; 175 } 176 177 setCoeFFicient(x); 178 setInDex(z); 179 180 } 181 182 }
其中设计了Derivate类
属性为:
1 private int nOi=0;//项数 2 private long[] coeFFicient=new long[nOi];//系数 3 private long[] inDex=new long[nOi];//指数
以及求导方法:
1 public void Derivation() { 2 long[]z=getInDex(); 3 long[]x=getCoeFFicient(); 4 for(int i=0;i<getnOi();i++) { 5 6 7 x[i]*=z[i]; 8 z[i]--; 9 } 10 11 setCoeFFicient(x); 12 setInDex(z); 13 14 }
对输入字符串处理
1 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll(" ", "");
去除空格
1 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("x\\+", "x\\^1\\+"); 2 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\+x", "\\+1\\*x"); 3 nextLine = nextLine.replaceAll("\\-x", "\\-1\\*x");
将一些省略在系数与指数中的1添加上
1 String pattern = "[+-]?[0-9]+\\*x\\^[+-]?[0-9]+|[+-]?[0-9]+"; 2 Derivate derivate=new Derivate(); 3 4 Pattern r = Pattern.compile(pattern); 5 Matcher m = r.matcher(nextLine); 6 Matcher d = r.matcher(nextLine); 7 while (d.find()) { 8 nOi++; 9 } 10 long[] coeFFicient=new long[nOi];//系数 11 long[] inDex=new long[nOi];//指数 12 derivate.setnOi(nOi); 13 String []end= new String[nOi]; 14 String []nEw= new String[nOi]; 15 while (m.find()) { 16 end[s]=m.group(); 17 s++; 18 } 19 for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 20 if(end[i].matches("[+-]?\\d+")) { 21 end[i]=end[i]+"*x^0"; 22 } 23 else if(end[i].matches("[+-]?\\d+\\*x")) { 24 end[i]=end[i]+"^1"; 25 }
通过正则表达式将多项式分解成单项式,并常数项处理成a*x^0的形式。
1 for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 2 end[i] = end[i].replaceAll("\\*x\\^", " "); 3 } 4 5 // for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 6 // System.out.println(end[i]); 7 // } 8 9 for(int i=0;i<end.length;i++) { 10 String []split=end[i].split(" "); 11 coeFFicient[i]=Integer.parseInt(split[0]); 12 inDex[i]=Integer.parseInt(split[1]); 13 }//前戏
分离各项的系数与指数。
结果该题化简输出与输入校验还没有完成。
三、采坑心得:
1.首当其冲的就是三角形判断,其中等腰直角三角形判断过于考虑实际没有联想计算机的存储方法
其中的 (Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)=1e-1),其转化成数学语言即 ![]() 。但根式在计算机中的存储不是以无理数来存储,而是被化简为一个有理数,即需要用(Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)<=1e-1)
。但根式在计算机中的存储不是以无理数来存储,而是被化简为一个有理数,即需要用(Math.abs((a*a)*2-c*c)<=1e-1)
来判断。这就导致没有任何一个三角形可以符合等腰直角三角形的判断条件。
2.其次关于有序数组的合并
1 int z=x+y; 2 3 int[]c=new int[z]; 4 5 int t=0; 6 int j=0,i=0; 7 for(;j<y&&i<x;t++) { 8 if(a[i]>b[j]) { 9 c[t]=b[j]; 10 j++; 11 } 12 13 else { 14 c[t]=a[i]; 15 i++; 16 } 17 } 18 19 20 21 22 if(j==y) { 23 24 for(;i<x;i++,t++) { 25 c[t]=a[i]; 26 } 27 } 28 29 else if(i==x){ 30 31 for(;j<y;j++,t++) { 32 c[t]=b[j]; 33 } 34 }
后面这种排序判定会导致有些数字会排不进新数组。
/*for(int j=0;j<z;j++) { if(a[m]>=b[n]&&m<x&&n<y) { c[j]=b[n]; n++; } else if(a[m]<b[n]&&m<x&&n<y) { c[j]=a[m]; m++; } else if(a[m]>=b[n]&&n==y) { c[j]=b[n]; j++; while(m<=x) { c[j]=a[m]; m++; j++; } break; } else if(a[m]<=b[n]&&m==x) { c[j]=a[m]; j++; while(n<=y) { c[j]=b[n]; n++; j++; } break; } }*/
3.在求下一天 中,对于跨年月份时,
最好以天为基准来判断,以闰年来判断的话只会徒增代码复杂度时维护更加困难。
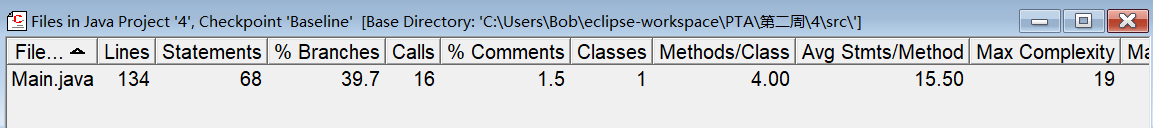

这里明显可以发现,Max Complexity瞬间增加了许多。
四、改进建议:
1. 这几次作业让我理解最深刻的是 if-else结构劣于switch结构,switch结构劣于数组结构
1 if(day==31) { 2 if(month==12) { 3 year++; 4 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+1+"-"+1); 5 } 6 else { 7 month++; 8 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 9 } 10 } 11 12 else if(day==30) { 13 if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) { 14 month++; 15 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+1); 16 } 17 18 else { 19 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+31); 20 } 21 22 } 23 24 else if(day==29) { 25 if(month==2) { 26 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 27 } 28 29 else { 30 day++; 31 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 32 } 33 34 } 35 36 else if(day==28) { 37 if(month==2) { 38 if(isLeapYear( year)) { 39 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+2+"-"+29); 40 } 41 else { 42 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+3+"-"+1); 43 } 44 } 45 46 else { 47 day++; 48 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 49 } 50 } 51 52 else { 53 day++; 54 System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 55 }
1 int[]mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 2 public void getNextDay() { 3 if(getMonth()==2&&isLeapyear(year)==true) { 4 if(getDay()==29) { 5 setMonth(3); 6 setDay(1); 7 }else { 8 setDay(getDay()+1); 9 } 10 }else{ 11 if(getDay()==mon_maxnum[month]) { 12 if(getMonth()==12) { 13 setYear(getYear()+1); 14 setMonth(1); 15 }else { 16 setMonth(getMonth()+1); 17 }setDay(1); 18 }else { 19 setDay(getDay()+1); 20 } 21 } 22 }
这样的改进使其复杂度下降,在算法出现错误时,前者修改的时间起码比后者修改时间多了一倍有余。
2.其次是正则表达式,
起初我本想通过
String 类中的
- String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement):将该字符串中所有匹配 regex 的子串替换成 replacement。
- String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement):将该字符串中第一个匹配 regex 的子串替换成 replacement。
- String[] split(String regex):以 regex 作为分隔符,把该字符串分割成多个子串。
这三个方法来解决多项式分解为单项式。最后发现用Pattern 类Matcher类中的find()方法和group()方法即可轻松解决。
五、总结:
本次的收获:
1.要养成良好的编程素养(书写要规范,写括号时要成对,字母大小写要区分,单词拼写要准确等等)。
2.不仅仅停留在java表层,不是抄例子运行出结果就可以。即便对一个简单的例子也要有耐心去琢磨、调试、改动。
3.一定要动手做、试着写代码,哪怕是照着范本多打几遍,很多东西和体会必须自己动手才能真正属于自己。
4.在Java的学习过程中,可能会遇到形形色色的问题不容易解决,多去专业论坛了解相关的知识,学会从网上搜索有用的信息加以整理,促进学习的深入和知识水平的提高。
5.了解了面向对象的设计思路。
本次的不足:
1.没有危机意识,每次都要在习题快结束前开始写,导致很多题目理解不深。
2.缺乏交流,关于正则表达式一开始因为只学会了String 类中的几个方法,就想利用他们去解决问题。最终是同学告诉我用Pattern 类Matcher类中的find()方法和group()方法即可轻松解决。结果导致我浪费了许多时间。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号