C# 表达式目录树解析--上篇
表达式目录树,在C#中是Expression来定义的,它是一种语法树,或者说是一种数据结构。其主要用于存储需要计算、运算的一种结构,它只提供存储功能,不进行运算。
1、lambda表达式和表达式目录树的区别
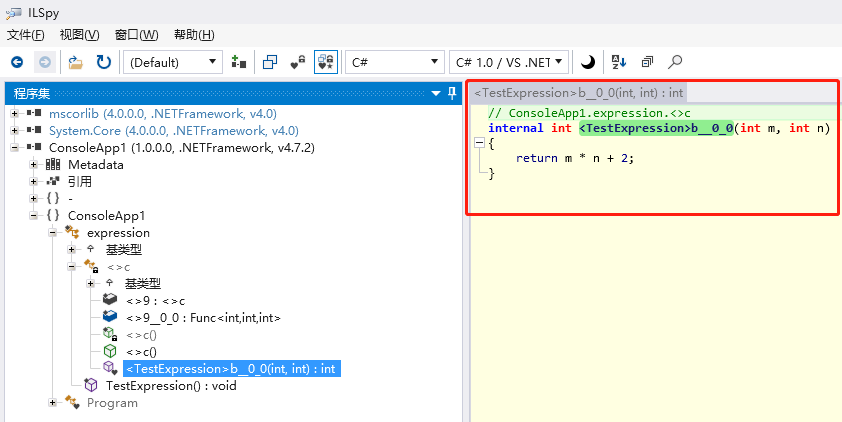
public static void TestExpression() { Func<int, int, int> func = (m, n) => m * n + 2; //:lambda表达式,匿名方法 Console.WriteLine("表达式目录树exp"); Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (m, n) => m * n + 2;//lambda表达式声明表达式目录树,exp是一种数据结构,并不是一个方法 Console.WriteLine("表达式目录树exp"); //上述func和exp执行结果相同: int s = func.Invoke(12, 4); int e= exp.Compile().Invoke(12, 4); //:表达式目录树可以被Compile成一个委托 }
通过ILSpy反编译工具,可以查看 Func<int, int, int> func = (m, n) => m * n + 2; 被编译成了一个方法。
2、手动拼装表达式目录树
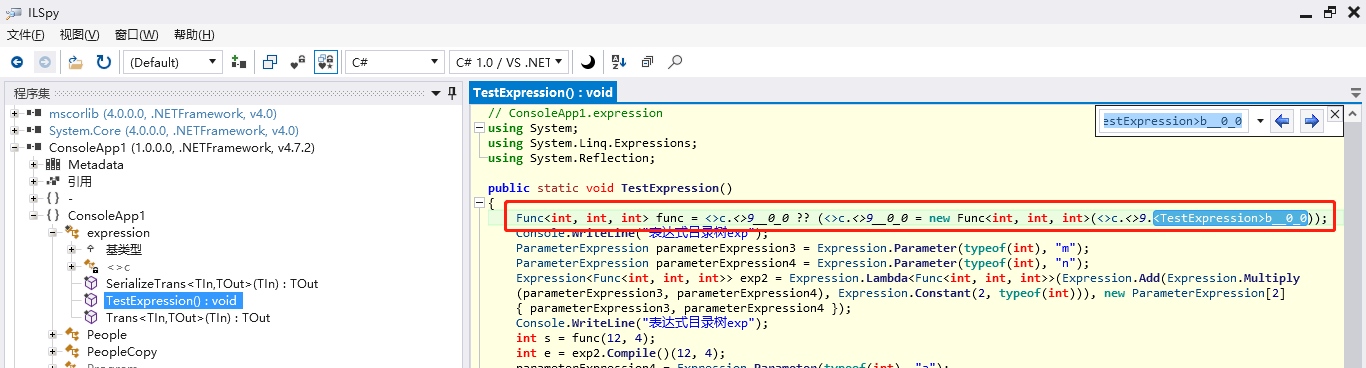
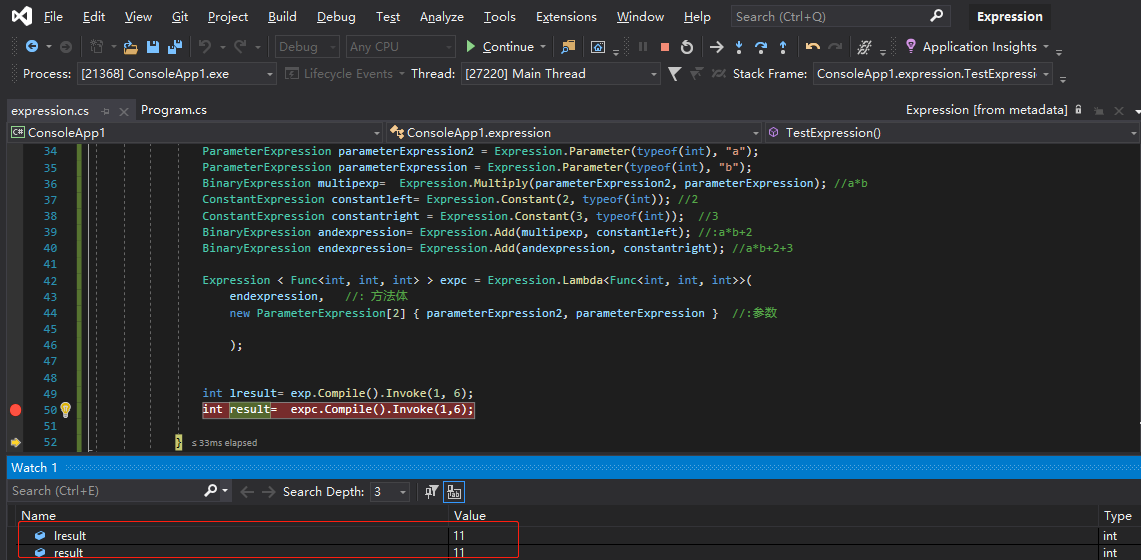
1 //:手动拼装表达式目录树 2 { 3 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (a, b) => a * b + 2+3; //:lambda表达式声明方式 4 5 //:手动拼接实现 6 ParameterExpression parameterExpression2 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "a"); 7 ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "b"); 8 BinaryExpression multipexp= Expression.Multiply(parameterExpression2, parameterExpression); //a*b 9 ConstantExpression constantleft= Expression.Constant(2, typeof(int)); //2 10 ConstantExpression constantright = Expression.Constant(3, typeof(int)); //3 11 BinaryExpression andexpression= Expression.Add(multipexp, constantleft); //:a*b+2 12 BinaryExpression endexpression= Expression.Add(andexpression, constantright); //a*b+2+3 13 14 Expression < Func<int, int, int> > expc = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>( 15 endexpression, //:方法体 16 new ParameterExpression[2] { parameterExpression2, parameterExpression } //:参数 17 18 ); 19 20 21 int lresult= exp.Compile().Invoke(1, 6); 22 int result= expc.Compile().Invoke(1,6); 23 24 }
2.1 调试可以看到,lambda表达式声明和手动拼接执行结果相同:
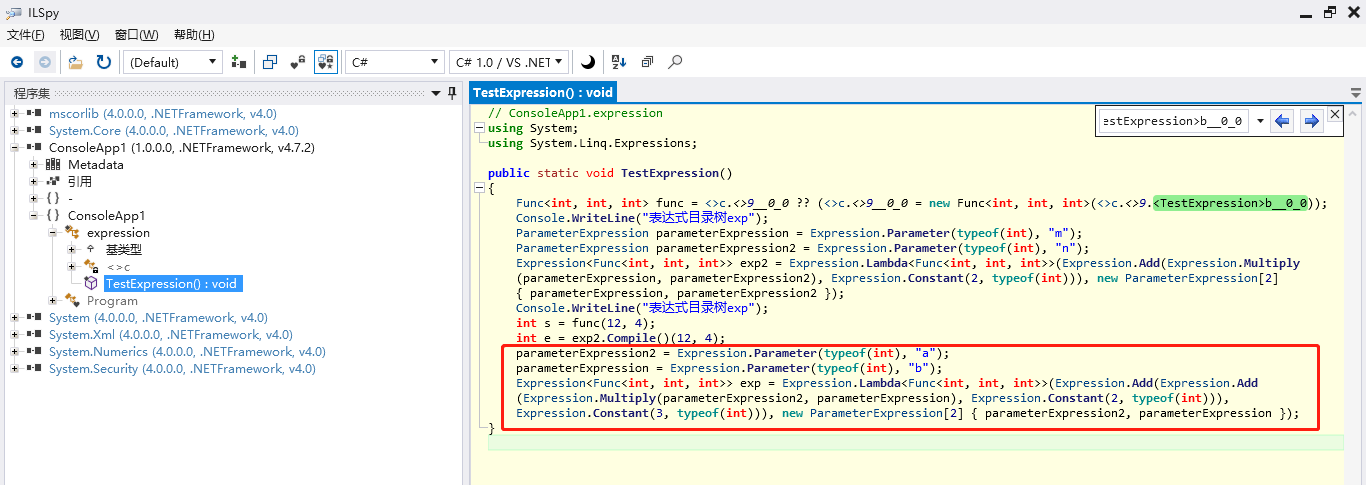
2.2 如果不熟悉或者记不住语法,如何手动拼接Expression表达式目录树【反编译】,以下以 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (a, b) => a * b + 2+3; 为例
可以先用lambda表达式声明一个需要的Expression表达式目录树,然后用反编译工具ILSpy查看反编译后的Code,Copy对应的Code。
3、表达式目录树使用场景分析
// 开发过程中我们一般会遇到将不同对象的相同名字的属性映射,比如将People映射到PeopleCopy
People people = new People() { Id = 11, Name = "Nigle", Age = 31 };
1 、如下代码,直接映射,硬编码 //:优点:效率最高 //:缺点:代码写死了,如果代码中有很多个需要转换的类或者一个类中含有很多个字段需要匹配,则不适用
PeopleCopy peopleCopy = new PeopleCopy() { Id = people.Id, Name = people.Name, Age = people.Age };
2、利用反射映射 优点:利用反射可以适用于多个实体转换 缺点:性能不高,后面会做对比
PeopleCopy RefpeopleCopy = Trans<People, PeopleCopy>(people); //:调用 public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { TOut tOut = Activator.CreateInstance<TOut>(); foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetProperties()) { foreach (var itemIn in tIn.GetType().GetProperties()) { if (itemOut.Name.Equals(itemIn.Name)) { itemOut.SetValue(tOut, itemIn.GetValue(tIn)); break; } } } foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetFields()) { foreach (var itemIn in tIn.GetType().GetFields()) { if (itemOut.Name.Equals(itemIn.Name)) { itemOut.SetValue(tOut, itemIn.GetValue(tIn)); break; } } } return tOut; }
3、 序列化再反序列化
PeopleCopy SerializepeopleCopy = SerializeTrans<People, PeopleCopy>(people); /// <summary>序列化反序列化方式/summary> public static TOut SerializeTrans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TOut>(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(tIn)); }
4、AutoMapper 此处不做详细讲解
5、 泛型+字典缓存+表达式树
GenericExpression<People, PeopleCopy>(people); private static Dictionary<string, object> _Dictionary = new Dictionary<string, object>(); //:字典缓存 private static Tout GenericExpression<Tin,Tout>(Tin t) { string key = string.Format($"func_{typeof(Tin).FullName}_{typeof(Tout).FullName}"); if (!_Dictionary.ContainsKey(key)) { ParameterExpression GenericExpression3 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Tin), "p"); List<MemberBinding> Genericmemberbinglst = new List<MemberBinding>(); foreach (var item in typeof(Tout).GetProperties()) { MemberExpression Property = Expression.Property(GenericExpression3, typeof(Tin).GetProperty(item.Name)); MemberBinding PmemberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, Property); Genericmemberbinglst.Add(PmemberBinding); } foreach (var item in typeof(Tout).GetFields()) { MemberExpression FieldProperty = Expression.Field(GenericExpression3, typeof(Tin).GetField(item.Name)); MemberBinding FmemberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, FieldProperty); Genericmemberbinglst.Add(FmemberBinding); } NewExpression newGenericExpression = Expression.New(typeof(Tout)); Expression genericexpression1 = Expression.MemberInit( newGenericExpression, Genericmemberbinglst); Expression<Func<Tin, Tout>> genericexpression2 = Expression.Lambda<Func<Tin, Tout>>( genericexpression1 //:方法体 , new ParameterExpression[1] { GenericExpression3 }); //:参数列表 _Dictionary[key] = genericexpression2.Compile(); } return ((Func<Tin, Tout>)_Dictionary[key]).Invoke(t); }
6、泛型+泛型缓存+表达式
GenericCacheExpressionClass<People, PeopleCopy>.GenericCacheExpression(people); //:调用
public class GenericCacheExpressionClass<Tin,Tout> //:泛型类 { private static Func<Tin, Tout> _Func = null; //: static GenericCacheExpressionClass() //:静态构造函数 { ParameterExpression GenericExpression3 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Tin), "p"); List<MemberBinding> Genericmemberbinglst = new List<MemberBinding>(); foreach (var item in typeof(Tout).GetProperties()) { MemberExpression Property = Expression.Property(GenericExpression3, typeof(Tin).GetProperty(item.Name)); MemberBinding PmemberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, Property); Genericmemberbinglst.Add(PmemberBinding); } foreach (var item in typeof(Tout).GetFields()) { MemberExpression FieldProperty = Expression.Field(GenericExpression3, typeof(Tin).GetField(item.Name)); MemberBinding FmemberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, FieldProperty); Genericmemberbinglst.Add(FmemberBinding); } NewExpression newGenericExpression = Expression.New(typeof(Tout)); Expression genericexpression1 = Expression.MemberInit( newGenericExpression, Genericmemberbinglst); Expression<Func<Tin, Tout>> genericexpression2 = Expression.Lambda<Func<Tin, Tout>>( genericexpression1 //:方法体 , new ParameterExpression[1] { GenericExpression3 }); //:参数列表 _Func = genericexpression2.Compile(); } public static Tout GenericCacheExpression(Tin t) //:对外提供一个方法调用 { return _Func(t); } }
4、性能对比
{
// 开发过程中我们一般会遇到将不同对象的相同名字的属性映射,比如将People映射到PeopleCopy
// 1、直接映射,硬编码
//:优点:效率最高
//:缺点:代码写死了,如果代码中有很多个需要转换的类,则不适用
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
PeopleCopy peopleCopy = new PeopleCopy()
{
Id = people.Id,
Name = people.Name,
Age = people.Age
};
}
watch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"直接映射耗时:{ watch.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
Stopwatch fwatch = new Stopwatch();
fwatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
//2、利用反射映射
PeopleCopy RefpeopleCopy = Trans<People, PeopleCopy>(people);
}
fwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"利用反射映射耗时:{ fwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
Stopwatch swatch = new Stopwatch();
swatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
//3、序列化再反序列化
PeopleCopy SerializepeopleCopy = SerializeTrans<People, PeopleCopy>(people);
}
swatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"序列化再反序列化映射耗时:{ swatch.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
//4、AutoMapper
Stopwatch fcswatch = new Stopwatch();
fcswatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
//5、泛型+字典缓存+表达式树
//Expression<Func<People, PeopleCopy>> expression = p =>
//new PeopleCopy()
//{
// Id = p.Id,
// Name = p.Name,
// Age = p.Age
//};
GenericExpression<People, PeopleCopy>(people);
}
fcswatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"泛型+字典缓存+表达式树映射耗时:{ fcswatch.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
Stopwatch fcsswatch = new Stopwatch();
fcsswatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
//6、泛型+泛型缓存+表达式
GenericCacheExpressionClass<People, PeopleCopy>.GenericCacheExpression(people);
}
fcsswatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"泛型+泛型缓存+表达式映射耗时:{ fcsswatch.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
}
执行1000000次赋值,相应耗时如下:
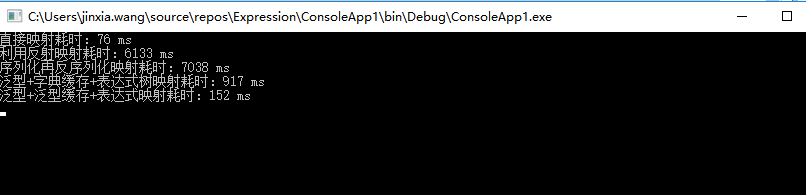
5、总结
1、直接按照类映射的形式效率最高,但是不适用于一个类的字段很多或者存在多个实体转换的业务场景
2、序列化和反序列化耗时最高
3、利用泛型缓存比字典缓存效率高



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号