Spring MVC 控制器接收各类请求参数
Spring MVC控制器接收各类请求参数
使用控制器接收参数往往是Spring MVC开发业务逻辑的第一步。Spring提供了诸多的注解来解析参数,目的在于把控制器从复杂的Servlet API中剥离,这样就可以在非web容器环境中重用控制器,也方便测试人员对其进行有效测试。
接收普通请求参数
Spring MVC比较智能,如果传递过来的参数名称和Http的请求参数名保持一致,那么无须任何注解就可以获取参数。
ParameterController.java
package com.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class ParameterController {
/**
* spring mvc 控制器接收普通参数
* Spring MVC比较智能,如果传递过来的参数名称和Http的请求参数名保持一致,那么无须任何注解就可以获取参数。
* request.getParameter("username")
* @param username username参数
* @param age age参数
* @param married married参数
* @param model 模型对象
* @return 视图名称
*/
@RequestMapping("/mvc/normal.do")
public String normal(String username, Integer age, boolean married, Model model) {
// 绑定模型数据
model.addAttribute("username", username);
model.addAttribute("age", age);
model.addAttribute("married", married);
// request.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/views/param.jsp").forward(request,response);
return "param"; // /WEB-INF/views/param.jsp
}
}
param.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: Jing61
Date: 2025/12/23
Time: 10:31
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
普通请求参数:<br/>
username:${username} <br/>
age:${age} <br/>
married:${married} <br/>
</body>
</html>
注意事项
通过参数名称和HTTP请求参数的名称保持一致来获取参数,如果不一致是没法获取到的,这样的方式允许参数为空。spring mvc消息处理机制是通过反射获取方法参数名称。需要在构建脚本build.gradle中添加构建参数-parameters。新的编译参数会自动生效。此时,通过反射获取方法参数名称时,就能正确获取到参数名,而不会出现 “参数名称未指定” 的错误。
tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {
options.compilerArgs.add("-parameters")
}
使用@RequestParam注解获取参数
有些时候传入参数与方法参数名不一致时,可以使用@RequestParam注解进行映射。
注解属性说明
value/name:http请求参数名称,默认值是参数名称required:是否必须,默认值是true,表示必须传递该参数defaultValue:默认值,如果请求中没有该参数,则使用默认值
代码示例
/**
* @RequestParam 注解: 映射请求参数
* value/name:http请求参数名称,默认值是参数名称
* required:是否必须,默认值是true,表示必须传递该参数
* defaultValue:默认值,如果请求中没有该参数,则使用默认值
* @param pageIndex pageIndex参数
* @param pageSize pageSize参数
* @param model 模型对象
* @return 视图名称
*/
@RequestMapping("/mvc/request.do")
public String requestParam(@RequestParam(name = "index") Integer pageIndex,
@RequestParam(name = "size") Integer pageSize, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("pageIndex", pageIndex);
model.addAttribute("pageSize", pageSize);
return "param";
}
类上添加统一请求路径前缀
可以在控制器类上添加@RequestMapping注解指定统一的请求路径前缀,简化方法上的请求路径配置。
ParameterController.java(优化后)
package com.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mvc") // 统一请求路径前缀
public class ParameterController {
/**
* spring mvc 控制器接收普通参数
* Spring MVC比较智能,如果传递过来的参数名称和Http的请求参数名保持一致,那么无须任何注解就可以获取参数。
* request.getParameter("username")
* @param username username参数
* @param age age参数
* @param married married参数
* @param model 模型对象
* @return 视图名称
*/
@RequestMapping("/normal.do") // 完整路径:/mvc/normal.do
public String normal(String username, Integer age, boolean married, Model model) {
// 绑定模型数据
model.addAttribute("username", username);
model.addAttribute("age", age);
model.addAttribute("married", married);
// request.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/views/param.jsp").forward(request,response);
return "param"; // /WEB-INF/views/param.jsp
}
/**
* @RequestParam 注解: 映射请求参数
* value/name:http请求参数名称,默认值是参数名称
* required:是否必须,默认值是true,表示必须传递该参数
* defaultValue:默认值,如果请求中没有该参数,则使用默认值
* @param pageIndex pageIndex参数
* @param pageSize pageSize参数
* @param model 模型对象
* @return 视图名称
*/
@RequestMapping("/request.do") // 完整路径:/mvc/request.do
public String requestParam(@RequestParam(name = "index") Integer pageIndex,
@RequestParam(name = "size") Integer pageSize, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("pageIndex", pageIndex);
model.addAttribute("pageSize", pageSize);
return "param";
}
}
param.jsp(优化后)
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: Jing61
Date: 2025/12/23
Time: 10:31
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
普通请求参数:<br/>
username:${username} <br/>
age:${age} <br/>
married:${married} <br/>
@RequestParam注解参数:<br/>
pageIndex:${pageIndex} <br/>
pageSize:${pageSize} <br/>
</body>
</html>
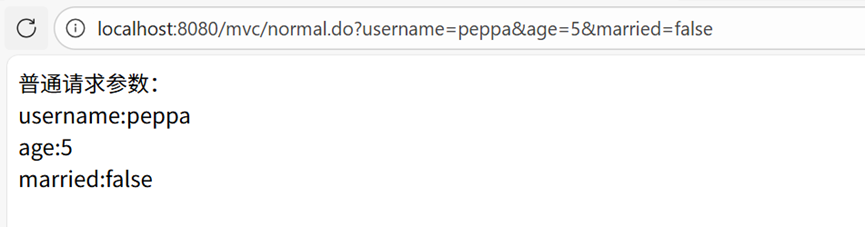
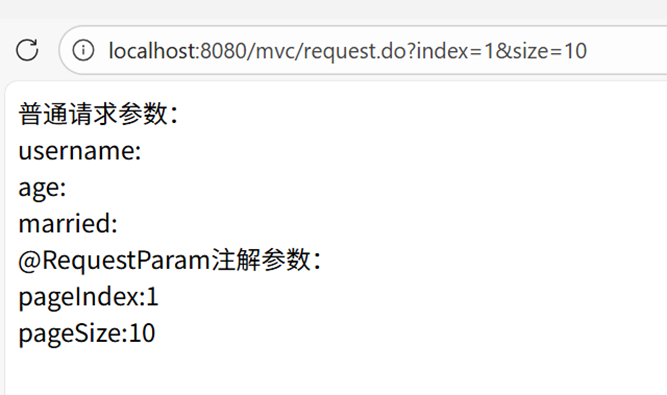
访问示例
请求地址:localhost:8080/mvc/request.do?index=1&size=10
页面输出:
普通请求参数:
username:
age:
married:
@RequestParam注解参数:
pageIndex:1
pageSize:10
传递一个对象参数
在参数很多的情况下(如新增用户需要十几个字段),可以使用POJO来管理这些参数,Spring MVC会自动将请求参数映射到POJO的属性中。
步骤1:创建图书POJO类
package com.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
@Data // 自动生成getter、setter、toString等方法
@Accessors(chain = true) // 支持链式调用
public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String author;
private String press;
private Double price;
private String intro;
}
步骤2:创建表单页面(book_save.html)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/mvc/book/save.do" method="post" >
<div>
<label>title:</label>
<input type="text" name="title"/> <!-- 名称与Book类属性一致 -->
</div>
<div>
<label>author:</label>
<input type="text" name="author"/> <!-- 名称与Book类属性一致 -->
</div>
<div>
<label>price:</label>
<input type="text" name="price"/> <!-- 名称与Book类属性一致 -->
</div>
<div>
<label>press:</label>
<input type="text" name="press"/> <!-- 名称与Book类属性一致 -->
</div>
<div>
<label>intro:</label>
<textarea cols="40" rows="5" name="intro"></textarea> <!-- 名称与Book类属性一致 -->
</div>
<input type="submit" value="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
步骤3:更新param.jsp(添加POJO参数展示)
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: Jing61
Date: 2025/12/23
Time: 10:31
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
普通请求参数:<br/>
username:${requestScope.username} <br/>
age:${requestScope.age} <br/>
married:${requestScope.married} <br/>
@RequestParam注解参数:<br/>
pageIndex:${requestScope.pageIndex} <br/>
pageSize:${requestScope.pageSize} <br/>
<hr/>
pojo参数:<br/>
title:${requestScope.book.title} <br/>
<!-- 不写requestScope,会从最小作用域中查找,顺序为:pageContext,request,session,application -->
author:${book.author} <br/>
press:${book.press} <br/>
price:${book.price} <br/>
intro:${book.intro} <br/>
</body>
</html>
步骤4:添加控制器方法
/**
* 接收POJO类型参数
* @param book book参数(Spring MVC自动映射请求参数到POJO属性)
* @param model 模型对象
* @return 视图名称
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/book/save.do", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String pojo(Book book, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("book", book); // 将POJO对象存入模型
return "param";
}
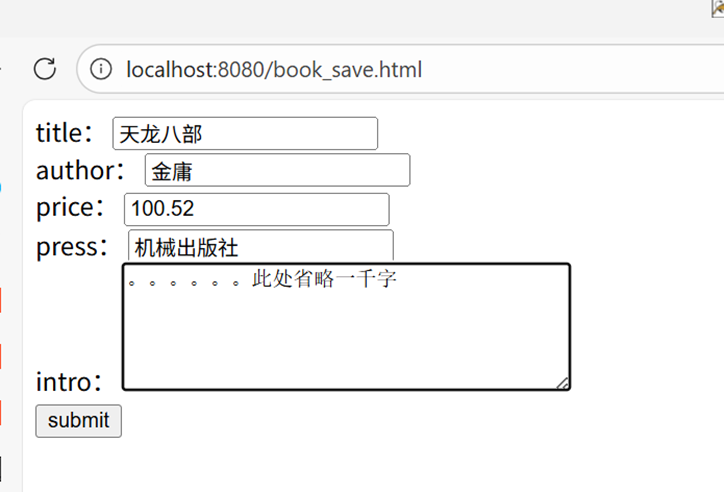
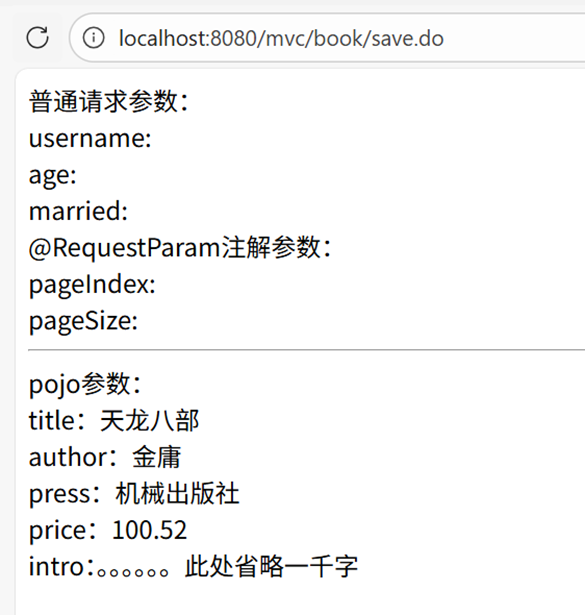
访问示例
- 访问表单页面:
localhost:8080/book_save.html - 输入表单数据:
- title:天龙八部
- author:金庸
- price:100.52
- press:机械出版社
- intro:[省略内容]
- 点击提交,跳转至
localhost:8080/mvc/book/save.do
页面输出:
使用URL传递参数(RESTful风格)
一些网站使用URL的形式传递参数,符合RESTful风格(如获取图书信息:/book/1,其中1是图书编号)。Spring MVC通过@PathVariable注解支持从URL中获取参数。
相关参考
步骤1:创建响应结果类(ResponseResult)
package com.response;
/**
* 统一响应结果类(使用record简化代码,JDK16+支持)
* @param <T> 响应数据类型
*/
public record ResponseResult<T> (int code, T data, String message) {
// 成功响应(无数据)
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> ok() {
return new ResponseResult<>(200, null, "success");
}
// 成功响应(带数据)
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> ok(T data) {
return new ResponseResult<>(200, data, "success");
}
// 成功响应(带数据和自定义消息)
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> ok(T data, String message) {
return new ResponseResult<>(200, data, message);
}
// 失败响应(无数据)
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> fail() {
return new ResponseResult<>(500, null, "fail");
}
// 失败响应(带自定义消息)
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> fail(String message) {
return new ResponseResult<>(500, null, message);
}
// 失败响应(带数据和自定义消息)
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> fail(T data, String message) {
return new ResponseResult<>(500, data, message);
}
}
步骤2:控制器方法(获取图书信息)
import com.pojo.Book;
import com.response.ResponseResult;
import com.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* RESTful风格接口示例
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class BookApiController {
@Resource
private BookService bookService; // Service层对象,需自行实现
/**
* 通过URL路径参数获取图书信息
* @param id 图书编号(从URL中获取)
* @return 响应结果(JSON格式)
*/
@GetMapping("/books/{id}") // 等价于 @RequestMapping(value = "/books/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody // 将返回结果直接序列化为JSON响应到客户端
public ResponseResult<Book> findById(@PathVariable Integer id) { // @PathVariable从URL中获取参数
Book book = bookService.findById(id);
return book == null ? ResponseResult.fail() : ResponseResult.ok(book);
}
}
说明
@PathVariable:用于从URL路径中获取参数,{id}对应URL中的路径片段@ResponseBody:将方法返回值直接响应到客户端,对象会自动序列化为JSON格式@GetMapping:简化的请求映射注解,等价于@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)@PathVariable允许对应的参数为空
访问示例
请求地址:localhost:8080/api/books/1
成功响应(JSON格式):
{
"code": 200,
"data": {
"id": 1,
"title": "天龙八部",
"author": "金庸",
"press": "机械出版社",
"price": 100.52,
"intro": "[省略内容]"
},
"message": "success"
}
失败响应(JSON格式):
{
"code": 500,
"data": null,
"message": "fail"
}
传递JSON参数
当需要传递多个复杂参数(如多条件查询+分页)时,可以将参数封装到POJO中,客户端以JSON格式传递,后台通过@RequestBody注解接收。
步骤1:创建参数封装类(BookParams)
package com.wise.tiger.pojo;
/**
* 图书查询参数封装类(多条件查询+分页)
*/
public class BookParams {
private String title; // 图书标题
private String author; // 作者
private String publisher; // 出版社
private float price; // 价格
private int pageIndex; // 页码
private int pageSize; // 每页条数
// getter和setter方法(必须提供,Spring MVC通过反射注入参数)
public String getTitle() { return title; }
public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; }
public String getAuthor() { return author; }
public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; }
public String getPublisher() { return publisher; }
public void setPublisher(String publisher) { this.publisher = publisher; }
public float getPrice() { return price; }
public void setPrice(float price) { this.price = price; }
public int getPageIndex() { return pageIndex; }
public void setPageIndex(int pageIndex) { this.pageIndex = pageIndex; }
public int getPageSize() { return pageSize; }
public void setPageSize(int pageSize) { this.pageSize = pageSize; }
}
步骤2:客户端JavaScript(模拟JSON参数传递)
在表单页面(如book_save.html)中添加JavaScript代码,使用jQuery发送JSON格式请求:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>图书查询</title>
<!-- 引入jQuery -->
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
// JSON参数(与BookParams类属性一一对应)
var data = {
title: '天龙八部',
author: '金庸',
price: 500,
publisher: '三联出版社',
pageIndex: 1,
pageSize: 20
};
// 发送POST请求(JSON格式参数)
$.post({
url: '/book/findBooks',
contentType: 'application/json', // 必须指定参数类型为JSON
data: JSON.stringify(data), // 将JSON对象转为字符串传递
success: function(result){
console.log("查询结果:", result);
}
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
步骤3:后台控制器方法(接收JSON参数)
import com.wise.tiger.pojo.BookParams;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@RestController // 等价于 @Controller + @ResponseBody(所有方法返回值自动转为JSON)
@RequestMapping("/book")
public class BookQueryController {
@Resource
private BookService bookService; // Service层对象,需自行实现
/**
* 接收JSON格式参数,进行多条件查询
* @param bookParams JSON参数封装对象(@RequestBody自动将JSON转为POJO)
* @return 查询结果(自动转为JSON)
*/
@RequestMapping("/findBooks")
public List<Book> findBooks(@RequestBody BookParams bookParams){
return bookService.findBooks(bookParams); // Service层查询逻辑,需自行实现
}
}
说明
@RequestBody:用于接收HTTP请求体中的JSON数据,并自动转换为对应的POJO对象contentType: 'application/json':客户端必须指定该请求头,否则Spring MVC无法正确解析JSON参数JSON.stringify(data):将JSON对象转为字符串传递(HTTP请求体中只能传输字符串)@RestController:组合注解,等价于@Controller + @ResponseBody,适用于纯API接口控制器
接收列表数据和表单序列化
接收列表/数组数据(如批量删除)
客户端JavaScript
$(document).ready(function(){
// 批量删除的图书ID数组
var ids = [1, 3, 5, 10];
// 发送JSON数组参数
$.post({
url: '/book/removeBooks',
contentType: 'application/json', // 必须指定参数类型为JSON
data: JSON.stringify(ids), // 将数组转为JSON字符串
success: function(result){
console.log("删除结果:", result);
}
});
});
后台控制器方法
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/book")
public class BookBatchController {
@Resource
private BookService bookService;
/**
* 批量删除图书(接收JSON数组参数)
* @param ids 图书ID数组(@RequestBody自动将JSON数组转为Java数组)
* @return 操作结果
*/
@RequestMapping("/removeBooks")
public String removeBooks(@RequestBody Integer[] ids){ // 也可使用 List<Integer> ids
bookService.removeBooks(ids); // 批量删除逻辑,需自行实现
return "删除成功";
}
}
表单序列化传递参数
对于普通表单(或需要动态计算的隐藏表单),可以使用serialize()方法将表单数据序列化为title=xxx&author=ooo格式传递,后台直接通过POJO接收。
客户端JavaScript
$(document).ready(function(){
// 表单序列化提交
$.post({
url: '/book/commonParam',
data: $('form').serialize(), // 将表单数据序列化为键值对字符串
success: function(result){
console.log("提交结果:", result);
}
});
});
后台控制器方法
import com.pojo.Book;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/book")
public class BookFormController {
@Resource
private BookService bookService;
/**
* 接收表单序列化参数(自动映射到POJO)
* @param book 图书对象(表单字段名与POJO属性名一致)
* @return 操作结果
*/
@RequestMapping("/commonParam")
public String commonParam(Book book){
bookService.saveOrUpdate(book); // 保存或更新逻辑,需自行实现
return "提交成功";
}
}
不推荐的方式:通过原生HttpServletRequest获取参数
虽然Spring MVC支持直接注入HttpServletRequest对象获取参数,但这种方式与Servlet API耦合,不利于控制器重用和测试,不推荐使用。
代码示例
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/book")
public class BookOriginalController {
/**
* 通过原生HttpServletRequest获取参数(不推荐)
* @param request HttpServletRequest对象(Spring MVC自动注入)
* @param model 模型对象
* @return 视图名称
*/
@RequestMapping("/original")
public String commonParam(HttpServletRequest request, Model model) {
// 与Servlet获取参数方式一致
String title = request.getParameter("title");
String author = request.getParameter("author");
model.addAttribute("title", title);
model.addAttribute("author", author);
return "param";
}
}
松耦合替代方案(获取Web上下文对象)
如果确实需要使用HttpServletRequest等对象,可通过RequestContextHolder获取,避免直接注入:
// 在方法内部获取
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号