Java 并行编程
Java 并行编程
核心思想
当前计算机多为多CPU、多核架构,为充分发挥硬件性能,可将一个大任务拆分成多个独立小任务。这些小任务在不同处理器核心上并行执行,执行完成后合并结果,最终得到大任务的解决方案。
Fork/Join 框架介绍
JDK7 引入 Fork/Join 框架,专为并行编程设计,是分而治之思想的并行实现。
核心组件
- ForkJoinPool:ExecutorService 的实现类,属于特殊线程池,负责执行 ForkJoinTask 任务,通过少量核心线程管理大量任务。
- ForkJoinTask:任务抽象基类,类似线程但更轻量级,支持通过 fork() 异步拆分任务、join() 等待任务完成。
- 核心子类
- RecursiveAction:用于定义无返回值的并行任务。
- RecursiveTask:用于定义有返回值的并行任务,需指定返回值类型。
- 要定义具体的任务类根据情况继承上面两个子类,自己的任务重写
compute()方法来指定任务是如何执行的。
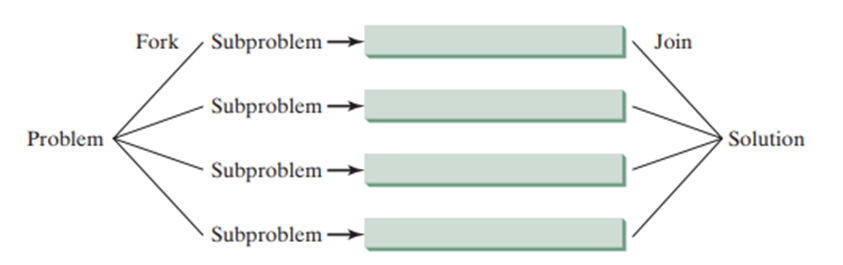
工作流程
- 拆分(Fork):大任务递归拆分为多个不重叠的子任务,直到子任务达到阈值(无需再拆分)。
- 执行:子任务在 ForkJoinPool 中并行执行。
- 合并(Join):收集所有子任务的执行结果,合并为大任务的最终结果。
![image]()
示例一:归并排序对比(无返回值)
普通(单线程)归并排序
package com.forkjoin;
/**
* 递归实现归并排序
* @author Jing61
*/
public class MergeSort {
public static void sort(int[] list) {
if (list.length <= 1) return;
int middle = list.length / 2;
int[] firstHalf = new int[middle];
System.arraycopy(list, 0, firstHalf, 0, firstHalf.length);
sort(firstHalf);
int[] secondHalf = new int[list.length - middle];
System.arraycopy(list, middle, secondHalf, 0, secondHalf.length);
sort(secondHalf);
merge(firstHalf, secondHalf, list);
}
public static void merge(int[] firstHalf, int[] secondHalf, int[] list) {
int firstIndex = 0;
int secondIndex = 0;
int listIndex = 0;
while (firstIndex < firstHalf.length && secondIndex < secondHalf.length) {
if (firstHalf[firstIndex] < secondHalf[secondIndex]) list[listIndex++] = firstHalf[firstIndex++];
else list[listIndex++] = secondHalf[secondIndex++];
}
while (firstIndex < firstHalf.length) list[listIndex++] = firstHalf[firstIndex++];
while (secondIndex < secondHalf.length) list[listIndex++] = secondHalf[secondIndex++];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] list = new int[]{5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
sort(list);
for (int i : list) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
并行归并排序(基于 Fork/Join 框架)与普通方法对比
package com.forkjoin;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction;
/**
* Fork/Join框架高效地自动执行和协调所有任务
* @author Jing61
*/
public class ParallelMergeSort {
// 5000000条数据
public static final int SIZE = 50000000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 用于普通归并排序
int[] list1 = new int[SIZE];
// 用于并行归并排序
int[] list2 = new int[SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) list1[i] = list2[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100000000);
// 普通归并排序
var begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
MergeSort.sort(list1);
var end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("普通(单线程)归并排序耗时:" + (end - begin) + "ms");
// 并行归并排序
begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
sort(list2);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("并行归并排序耗时:" + (end - begin) + "ms");
}
public static void sort(int[] list) {
var pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.invoke(new SortTask(list));
}
/**
* 创建一个任务
* RecursiveAction:定义不返回值的任务
* RecursiveTask:定义返回值的任务
*/
public static class SortTask extends RecursiveAction {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final int THRESHOLD = 500;
private int[] list;
public SortTask(int[] list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
protected void compute() {
if (list.length <= THRESHOLD) { // 数据量小于500时,使用普通排序算法
Arrays.sort(list);
return;
} // 递归终止条件
int middle = list.length / 2;
int[] firstHalf = new int[middle];
System.arraycopy(list, 0, firstHalf, 0, firstHalf.length);
int[] secondHalf = new int[list.length - middle];
System.arraycopy(list, middle, secondHalf, 0, secondHalf.length);
// fork/join
invokeAll(new SortTask(firstHalf), new SortTask(secondHalf));
// 合并数组
MergeSort.merge(firstHalf, secondHalf, list);
}
}
}
执行结果对比
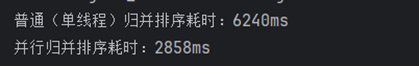
并行排序通过多线程并行处理子任务,耗时显著低于单线程排序。
示例二:线性表查找最大数(有返回值)
普通(单线程)查找方法与并行查找方法对比
package com.forkjoin;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
/**
* @author Jing61
*/
public class ParalleMax {
private static final int SIZE = 50000000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] list = new Integer[SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) list[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 1000000000);
// 普通方法获取最大值
var begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer max = list[0];
for (int i = 1; i < SIZE; i++) max = Math.max(list[i], max);
var end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("普通方法获取最大值为:" + max + "耗时:" + (end - begin) + "ms");
// 并行方法获取最大值
begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
max = max(list);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("并行方法获取最大值为:" + max + "耗时:" + (end - begin) + "ms");
}
public static Integer max(Integer[] list) {
var pool = new ForkJoinPool();
return pool.invoke(new MaxTask(list, 0, list.length - 1));
}
/**
* RecursiveTask:定义返回值的任务
* <>里面填写返回值类型
*/
static class MaxTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final int THRESHOLD = 500;
private Integer[] list;
private int low;
private int high;
public MaxTask(Integer[] list, int low, int high) {
this.list = list;
this.low = low;
this.high = high;
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
// 数组小于等于阈值时,使用普通算法更加高效
if(high - low + 1 <= THRESHOLD) {
Integer max = list[low];
for(int i = low + 1; i <= high; i++) if(list[i] > max) max = list[i];
return max;
} else {
int middle = low + (high - low) / 2;
// invokeAll(new MaxTask(list, low, middle), new MaxTask(list, middle + 1, high));
var left = new MaxTask(list, low, middle);
var right = new MaxTask(list, middle + 1, high);
left.fork();
right.fork();
return Math.max(left.join(), right.join());
}
}
}
}
执行结果对比
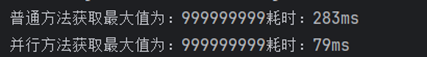
并行查找通过拆分任务并行处理,大幅提升查找效率。
补充说明
- 阈值设置原则:阈值过小会导致任务拆分过多,增加线程调度开销;阈值过大则无法充分利用并行优势,需根据任务类型和数据量合理调整。
- 适用场景:Fork/Join 框架适合处理可拆分、无依赖的任务,如排序、查找、数据统计等,不适合处理有状态或依赖外部资源的任务。
- 性能优势:通过多线程并行利用多核CPU资源,减少整体任务执行时间,数据量越大,并行优势越明显。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号