JAVA第四,五,六次PTA作业总结
一、前言
第二阶段的JAVA大作业与第一阶段的作业相比,其难度大大提高,知识点也更加贴合面向对象的使用。在本阶段,将会更加深入学习面向对象的思想,用更加合理的方式完成相应的功能。此阶段也是极具挑战性的一个阶段,相比于上一阶段这一阶段实属有些磕磕绊绊,但是也同时学到不少新的东西,对面向对象也有了更深刻的了解。
二、作业概况
第四次作业
第四次作业的题目分别是:
-
- 7-1 水文数据校验及处理
- 7-2 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
- 7-3 图形继承
运用知识点:
-
- 正则表达式的运用
- 正则表达式对输入数据进行合法性校验
- Java中类的聚合关系的使用方法
- 类的继承与封装
- 构造父类和子类,并使用this及super等关键字
题目难度:
第五次作业总共分为三道题题,第一题是水文数据校验及处理,对于这道题也是这次作业中最难的题,开始看这道题的时候内心复杂,因为这道题的题目又是一个文件,这文件中写的全是这道题的要求还有过程。这是我学Java以来接触的最长的题目。看了很久才知道大概过程,然后花了很久的时间才渐渐写出了大概过程,但是当时我还是不怎么会正则表达式,而且题目过程太复杂中间一些没考虑好的地方也很多,所以最后,还是没做出来;后面两题分别是类的聚合和图形继承也就父类子类的运用,除了聚合相对多花点时间调试做出来还是十分顺利的。
第五次作业
第五次作业的题目分别是:
-
- 7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
- 7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数
- 7-2 合并两个有序数组为新的有序数组
- 7-3 对整型数据排序
运用知识点:
-
- 类的聚合的运用但是使Year、Month、Day与DateUtil的聚合关系发生变化。
- 用数组存储月份天数。
- 使用Set和List或Map等接口
- 正则表达式判断数据
- 简单的数组排序输出
题目难度:
第一题和上一次作业类的聚合类似但是Year、Month、Day与DateUtil的聚合关系发生变化,之前的求前n天和后n天的函数进行了修改,个人感觉有点繁琐;第二题难度较高而且还运用了正则表达式以及map等接口的运用,十分复 杂,处理学习和同学讨论了许久才解决;后面两题为简单的数组排序题,很好解决。
第六次作业
第六次作业的题目分别是:
-
- 7-1 正则表达式训练-QQ号校验
- 7-2 字符串训练-字符排序
- 7-3 正则表达式训练-验证码校验
- 7-4 正则表达式训练-学号校验
- 7-5 图形继承与多态
- 7-6 实现图形接口及多态性
运用知识点:
-
- 正则表达式的使用
- 字符转义成ASCII的形式再进行排序
- 图形继承多态,collections类中的sort方法还有Arrayslist<>类中的等方法的运用
- 较为简单的接口使用,类的封装性、继承性和多态性。
题目难度:
前四题都是对简单正则表达式训练,其难度并不大,其中,6-7-2的排序问题采用了将字符转义成ASCII的形式再进行排序,为字符的排序增添了一种新的方法;题五图形继承与多态要求掌握类的继承和多态,感觉相对来说有点繁琐复杂,本次作业以抽象类定义实体类构建,而两个方法分别是方法重载和方法重写。并且使用了ArrayList类型的列表,对 list 中的图形对象在 list 中进行升序排序,多种类的设计;题六实现图形接口及多态性涉及了实现类的封装性、继承性和多态性。
三、作业分析(包括设计分析,踩坑心得和改进建议)
题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-5)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
第四次题目集:7-2:日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
1、 设计与分析
(1)设计:
源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int x=in.nextInt();
if(x==1) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil z=new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(z.check()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
z.getnextday(n);
z.show();
}
}
if(x==2) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil z=new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(z.check()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
z.before(n);
z.show();
}
}
if(x==3) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int year2=in.nextInt();
int month2=in.nextInt();
int day2=in.nextInt();
DateUtil z=new DateUtil(day,month,year);
DateUtil z2=new DateUtil(day2,month2,year2);
if(z.check()==false||z2.check()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
if(year==year2&&month==month2&day==day2) {
System.out.println(0);
}
else {
System.out.println(z.getnumber(z2));
}
}
else if(x>3&&x<1){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");}
}
}
class Year{
private int value;
Year(){
}
Year(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {
if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 !=0 )||(value % 400 == 0)) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value<1900||value>2050) {
return false;
}
else
return true;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value=value+1;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value=value-1;
}
}
class Month{
private int value;
private Year year;
Month(){
}
Month(int yearvalue,int monthvalue){
this.value=monthvalue;
this.year=new Year(yearvalue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value>12||value<1) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
public int monthget(){
int x;
if(value==1||value==3||value==5||value==7||value==8||value==10||value==12) {
x=31;
return x;
}
else if(value==4||value==6||value==9||value==11) {
x=30;
return x;
}
else if(value==2) {
if(year.isLeapYear()==true) {
x=29;
return 29;
}
else {
x=28;
return x;
}
}
return 0;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
if(value<12) {
value++;
}
else {
value=1;
year.yearIncrement();
}
}
public void monthReduction() {
if(value>1) {
value--;
}
else {
value=12;
year.yearReduction();
}
}
}
class Day {
private int value;
private Month month;
int []monmaxnum= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
Day(){
}
Day(int yearvalue,int monthvalue,int dayvalue){
this.value=dayvalue;
this.month=new Month(yearvalue,monthvalue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
int i;
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==true) {
monmaxnum[1]=29;
}
else {
monmaxnum[1]=28;
}
value=monmaxnum[month.getValue()-1];
}
public boolean validate() {
if(month.getValue()==1||month.getValue()==3||month.getValue()==5||month.getValue()==7||month.getValue()==8||month.getValue()==10||month.getValue()==12){
if(value<1||value>31) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
if(month.getValue()==4||month.getValue()==6||month.getValue()==9||month.getValue()==11) {
if(value<1||value>30) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==true) {
if(value<1||value>29) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
else if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==false) {
if(value<1||value>28) {
return false;
}
}
else {
return true;
}
return true;
}
public void DayIncrement() {
int days=month.monthget();
if(value<days) {
value++;
}
else {
value=1;
month.monthIncrement();
}
}
public void DayReduction() {
int days=month.monthget();
if(value>=2) {
value--;
}
else {
month.monthReduction();
value=month.monthget();
}
}
}
class DateUtil{
private Day day;
DateUtil(){
}
DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){
this.day=new Day(y,m,d);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean check() {
if(day.getMonth().getYear().validate()==false||day.getMonth().validate()==false||day.validate()==false) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
public boolean comparedate(DateUtil date) {
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()<day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return false;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()>day.getMonth().getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()<day.getMonth().getValue()) {
return false;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()>day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()<day.getValue()) {
return false;
}
return false;
}
public boolean same(DateUtil date) {
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()==day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue());
}
public DateUtil getnextday(int n) {
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
day.DayIncrement();
}
return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
}
public DateUtil before(int n) {
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
day.DayReduction();
}
return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
}
public int getnumber(DateUtil date) {
int c=0;
if(comparedate(date)==true) {
while(comparedate(date)==true) {
day.DayIncrement();
c++;
}
return c;
}
if(comparedate(date)==false) {
while(comparedate(date)==false) {
date.day.DayIncrement();
c++;
if(same(date)==true) {
break;
}
}
return c;
}
else
return 0;
}
}
实验要求:设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31]。分别实现求下n天、前n天、以及两个日期相差的天数。此题的所要实现的功能是结合了前一阶段的opp作业日期类题目进行的汇总。
首先用三个if选出一种功能进行实现。接着,分别将剩下四个类的框架以及其中所含有的变量写好。代码在主函数里通过DateUtil dateutil=new DateUtil(year,month,day)将年月日三个值传入DateUtil类中,并用来接收三值;在此,同时创建Day类,同时将三值传入Day中,实现两类之间的连接,从而以此类推完成全部的连接。
在计算前n天和下n天的时候采用逐天递减的方法,有些小偷懒所以也为聚合二求n天的方法进行修改埋下伏笔。
在计算天数差时采用的是比较的方法,输入一个参数对天数进行存储然后通过使小的的日期通过不断递增运用comparedate方法进行比较,不断使参数自增而得到最后的结果。
public int getnumber(DateUtil date) { int c=0; if(comparedate(date)==true) { while(comparedate(date)==true) { day.DayIncrement(); c++; } return c; } if(comparedate(date)==false) { while(comparedate(date)==false) { date.day.DayIncrement(); c++; if(same(date)==true) { break; } } return c; } else return 0; }
(2)分析:
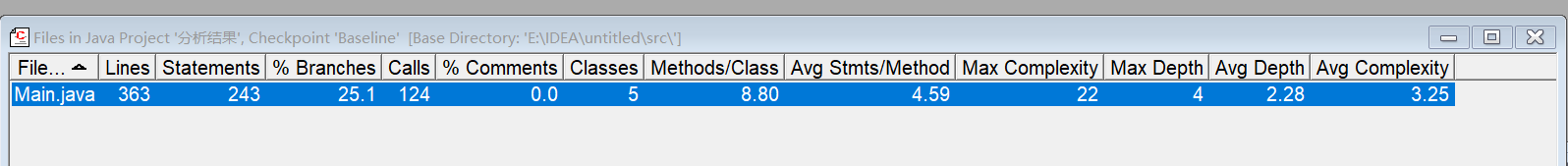
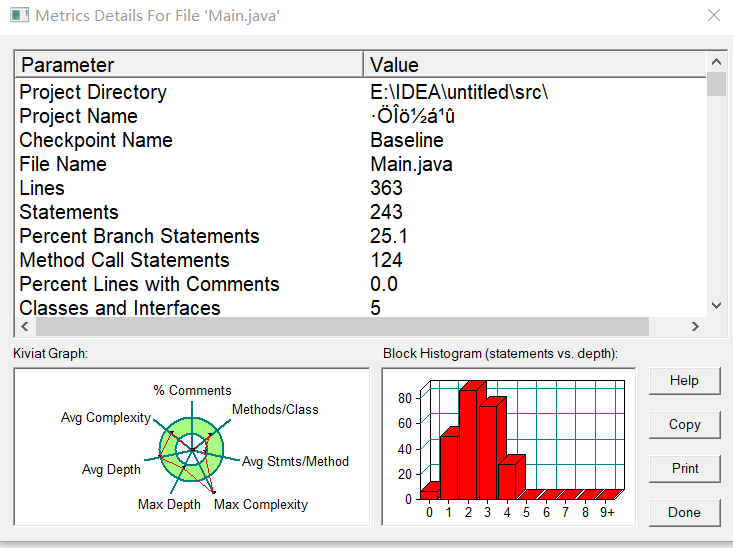
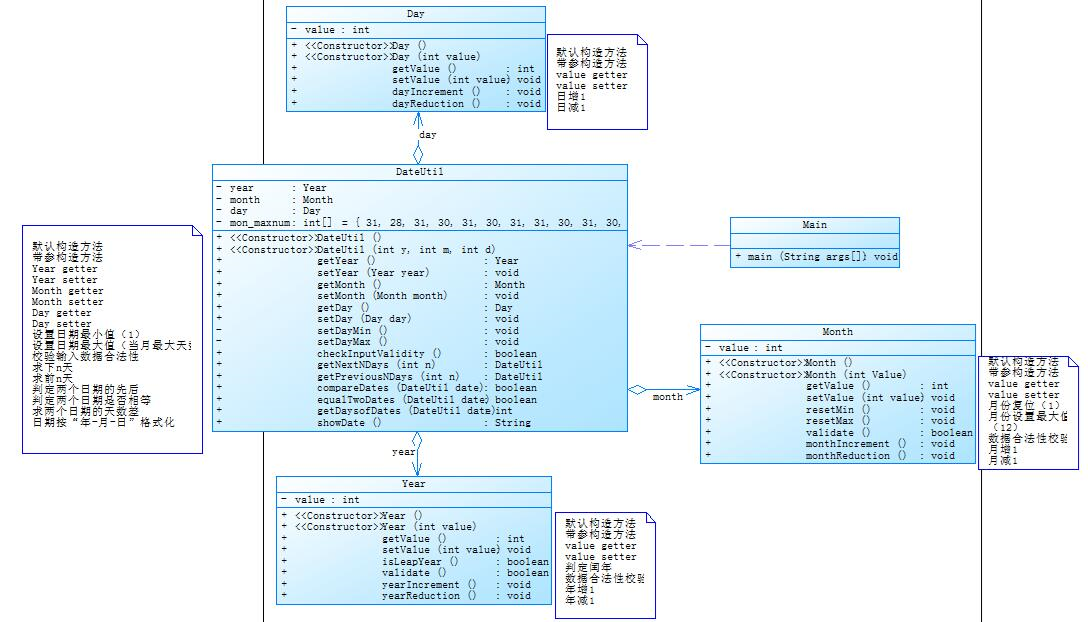
根据PowerDesigner的类图显示,该题采用的是聚合的关系。根据题目所给类图可知,Year聚合Month,Month聚合Day,Day聚合DateUtil类。该四个类环环相扣,每个环节都不能出现问题。

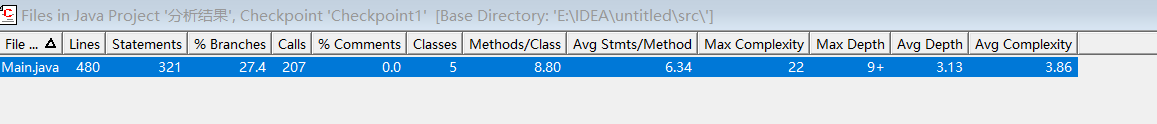
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
2、踩坑心得:
(1)if语句可以用switch语句代替,求前n天和后n天的方法可以按年减少再按月份减少,按天减少的话如果数据过大运行时间容易超时。
(2)由于一开始对这种聚合关系的掌握还不是特别深刻,在不同类中获取相应年月日的值成了问题所在,但是通过查找资料学习了解之后,学会了用day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()、(day.getMonth().getValue()和 day.getValue()得到三者的值。此类有关问题便迎刃而解。
(3)年月日合法性的判断一开始有点疏忽,导致判断出现纰漏。
3、改进建议:求前n天和后n天可以一次减去一整年的天数再是一个月的天数,最后再是一天天的加减计算,否则容易运行超时。
第五次题目集:7-5:日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
1、 设计与分析
(1)设计:
源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int x=in.nextInt();
if(x>3||x<1){
System.out.print("Wrong Format");}
if(x==1) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil z=new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(z.check()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
z.getnextday(n);
System.out.print(year+"-"+month+"-"+day+ " next "+ n +" days is:");
z.show();
}
}
if(x==2) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil z=new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(z.check()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
z.before(n);
System.out.print(year+"-"+month+"-"+day+ " previous "+ n +" days is:");
z.show();
}
}
if(x==3) {
int year1=in.nextInt();
int month1=in.nextInt();
int day1=in.nextInt();
int year2=in.nextInt();
int month2=in.nextInt();
int day2=in.nextInt();
DateUtil z=new DateUtil(day1,month1,year1);
DateUtil z2=new DateUtil(day2,month2,year2);
if(z.check()==false||z2.check()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
if(year1==year2&&month1==month2&day1==day2) {
System.out.println(0);
}
else {
System.out.println("The days between "+year1+"-"+month1+"-"+day1+" and "+year2+"-"+month2+"-"+day2+" are:"+z.getnumber(z2));
}
}
}
}
class Year{
private int value;
Year(){
}
Year(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {
if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 !=0 )||(value % 400 == 0)) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value<1820||value>2020) {
return false;
}
else
return true;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value=value+1;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value=value-1;
}
}
class Month{
private int value;
private Year year;
Month(){
}
Month(int yearvalue,int monthvalue){
this.value=monthvalue;
this.year=new Year(yearvalue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value>12||value<1) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
public int monthget(){
int x;
if(value==1||value==3||value==5||value==7||value==8||value==10||value==12) {
x=31;
return x;
}
else if(value==4||value==6||value==9||value==11) {
x=30;
return x;
}
else if(value==2) {
if(year.isLeapYear()==true) {
x=29;
return 29;
}
else {
x=28;
return x;
}
}
return 0;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
if(value<12) {
value++;
}
else {
value=1;
year.yearIncrement();
}
}
public void monthReduction() {
if(value>1) {
value--;
}
else {
value=12;
year.yearReduction();
}
}
}
class Day {
private int value;
private Month month;
int []monmaxnum= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
Day(){
}
Day(int yearvalue,int monthvalue,int dayvalue){
this.value=dayvalue;
this.month=new Month(yearvalue,monthvalue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
int i;
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==true) {
monmaxnum[1]=29;
}
else {
monmaxnum[1]=28;
}
value=monmaxnum[month.getValue()-1];
}
public boolean validate() {
if(month.getValue()==1||month.getValue()==3||month.getValue()==5||month.getValue()==7||month.getValue()==8||month.getValue()==10||month.getValue()==12){
if(value<1||value>31) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
if(month.getValue()==4||month.getValue()==6||month.getValue()==9||month.getValue()==11) {
if(value<1||value>30) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==true) {
if(value<1||value>29) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
else if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==false) {
if(value<1||value>28) {
return false;
}
}
else {
return true;
}
return true;
}
public void DayIncrement() {
int days=month.monthget();
if(value<days) {
value++;
}
else {
value=1;
month.monthIncrement();
}
}
public void DayReduction() {
int days=month.monthget();
if(value>=2) {
value--;
}
else {
month.monthReduction();
value=month.monthget();
}
}
}
class DateUtil{
private Day day;
int []monmaxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
DateUtil(){
}
DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){
this.day=new Day(y,m,d);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean check() {
if(day.getMonth().getYear().validate()==false||day.getMonth().validate()==false||day.validate()==false) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
public boolean comparedate(DateUtil date) {
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()<day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return false;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()>day.getMonth().getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()<day.getMonth().getValue()) {
return false;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()>day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()<day.getValue()) {
return false;
}
return false;
}
public boolean same(DateUtil date) {
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()==day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public void show() {
System.out.print(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue());
}
public DateUtil getnextday(int n) {
while (n > 0) {
if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
monmaxnum[2]=29;
if (n >= 366) {
day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
n = n - 366;
if(day.getMonth().getValue()>2){
day.DayIncrement();
if(day.getValue()>monmaxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]) {
day.getMonth().monthIncrement();
day.resetMin();
if(day.getMonth().getValue()==13){
day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
day.getMonth().resetMin();
day.resetMin();
}
}
}
} else {
day.DayIncrement();
if(day.getValue()>monmaxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]){
day.getMonth().monthIncrement();
day.resetMin();
if(day.getMonth().getValue()==13){
day.getMonth().resetMin();
day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
day.resetMin();
}
}
n--;
}
}
else if(!day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){
monmaxnum[2]=28;
if (n >= 365) {
day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
n = n - 365;
if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
if (day.getMonth().getValue() > 2) {
day.DayReduction();
if (day.getValue() == 0) {
day.getMonth().monthReduction();
day.resetMax();
if (day.getMonth().getValue() == 0) {
day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
day.getMonth().resetMax();
day.resetMax();
}
}
}
}
}else {
day.DayIncrement();
if(day.getValue()>monmaxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]){
day.getMonth().monthIncrement();
day.resetMin();
if(day.getMonth().getValue()==13){
day.getMonth().resetMin();
day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
day.resetMin();
}
}
n--;
}
}
}
return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
}
public DateUtil before(int n) {
while (n > 0) {
if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
monmaxnum[2]=29;
if (n >= 366) {
day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
n = n - 366;
} else {
day.DayReduction();
if(day.getValue()==0){
day.getMonth().monthReduction();
day.resetMax();
if(day.getMonth().getValue()==0){
day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
day.getMonth().resetMax();
day.resetMax();
}
}
n--;
}
}
else if(!day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){
monmaxnum[2]=28;
if (n >= 365) {
day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
n = n - 365;
}else {
day.DayReduction();
if(day.getValue()==0){
day.getMonth().monthReduction();
day.resetMax();
if(day.getMonth().getValue()==0){
day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
day.getMonth().resetMax();
day.resetMax();
}
}
n--;
}
}
}
return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
}
public int getnumber(DateUtil date) {
int c=0;
if(comparedate(date)==true) {
while(comparedate(date)==true) {
day.DayIncrement();
c++;
}
return c;
}
if(comparedate(date)==false) {
while(comparedate(date)==false) {
date.day.DayIncrement();
c++;
if(same(date)==true) {
break;
}
}
return c;
}
else
return 0;
}
}
实验要求设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] 。本题所要实现的功能及方法和4-7-2中的几乎一致,只不过使用的是Year、Month、Day分别与DateUtil形成的聚合关系。
同时,由于年月日三个类是独立出来的,故此在DateUtil中获取三者的值直接采用year.getValue()、month.getValue()和day.getValue()即可。
但是测试的数据相比上一次要大一些,所以求前n天和后n天采用之前一天一天的计算方法已经不行了,会产生以下错误
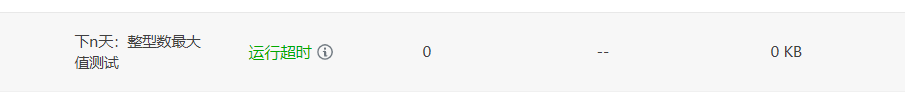
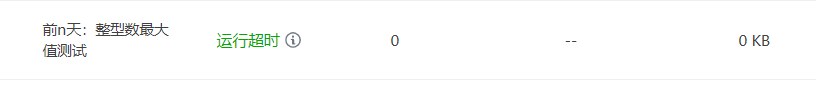
因此需要重写求前n天和下n天的函数,用年去减,但是要考虑整年减的日期越界情况
public DateUtil getnextday(int n) { while (n > 0) { if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { monmaxnum[2]=29; if (n >= 366) { day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); n = n - 366; if(day.getMonth().getValue()>2){ day.DayIncrement(); if(day.getValue()>monmaxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]) { day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); day.resetMin(); if(day.getMonth().getValue()==13){ day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); day.getMonth().resetMin(); day.resetMin(); } } } } else { day.DayIncrement(); if(day.getValue()>monmaxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]){ day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); day.resetMin(); if(day.getMonth().getValue()==13){ day.getMonth().resetMin(); day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); day.resetMin(); } } n--; } } else if(!day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ monmaxnum[2]=28; if (n >= 365) { day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); n = n - 365; if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { if (day.getMonth().getValue() > 2) { day.DayReduction(); if (day.getValue() == 0) { day.getMonth().monthReduction(); day.resetMax(); if (day.getMonth().getValue() == 0) { day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); day.getMonth().resetMax(); day.resetMax(); } } } } }else { day.DayIncrement(); if(day.getValue()>monmaxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]){ day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); day.resetMin(); if(day.getMonth().getValue()==13){ day.getMonth().resetMin(); day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); day.resetMin(); } } n--; } } } return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); } public DateUtil before(int n) { while (n > 0) { if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { monmaxnum[2]=29; if (n >= 366) { day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); n = n - 366; } else { day.DayReduction(); if(day.getValue()==0){ day.getMonth().monthReduction(); day.resetMax(); if(day.getMonth().getValue()==0){ day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); day.getMonth().resetMax(); day.resetMax(); } } n--; } } else if(!day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ monmaxnum[2]=28; if (n >= 365) { day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); n = n - 365; }else { day.DayReduction(); if(day.getValue()==0){ day.getMonth().monthReduction(); day.resetMax(); if(day.getMonth().getValue()==0){ day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); day.getMonth().resetMax(); day.resetMax(); } } n--; } } } return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); }
(2)分析:
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
2、踩坑心得:闰年特殊月份的特殊情况没有想到,判定要多思考情况,整年减少去出现bug,比如闰年的2月29号减少一年变成平年依然是29号,但是应该是平年的28号,容易判断失误,所以应该在前面再加一个对年份的判断,在日期加一天或者减少一天。
3、改进建议:我觉得日期的增减如果逻辑思维够强,可以先用年去加减再用月份加减判断,例如让它先加一个数值到下一个月的一号然后利用数组整月加减。
优劣比较
题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计
分析完以上两题后让我们开进行对这两道相似的题目进行比较:
- 根据PowerDesigner图可以发现,对于题目集4-2,year类作为month类的部分、month类作为day类的部分、day类作为dateuial类的一部分,这四者之间是层层调用的关系,在具体应用的过程中,如求n天后,题目集4-2需要通过this.getday().getmonth().getyear().getvalue()操作才能获取到年份的数值,对年份的操作需要通过day牵扯到month再牵扯到yuar。而在题目集5-1中,year、month、day三个类是平等被dateuial类调用的,对年份数值的查看只需要this.getyear().getvalue()即可;所以第一种的类出现问题时,后面类的结果也会受其影响,而第二种则是许多环套在同一个大环中,其中一个出现问题,另外的类是不会出现问题的,问题排查性也能大大提高。
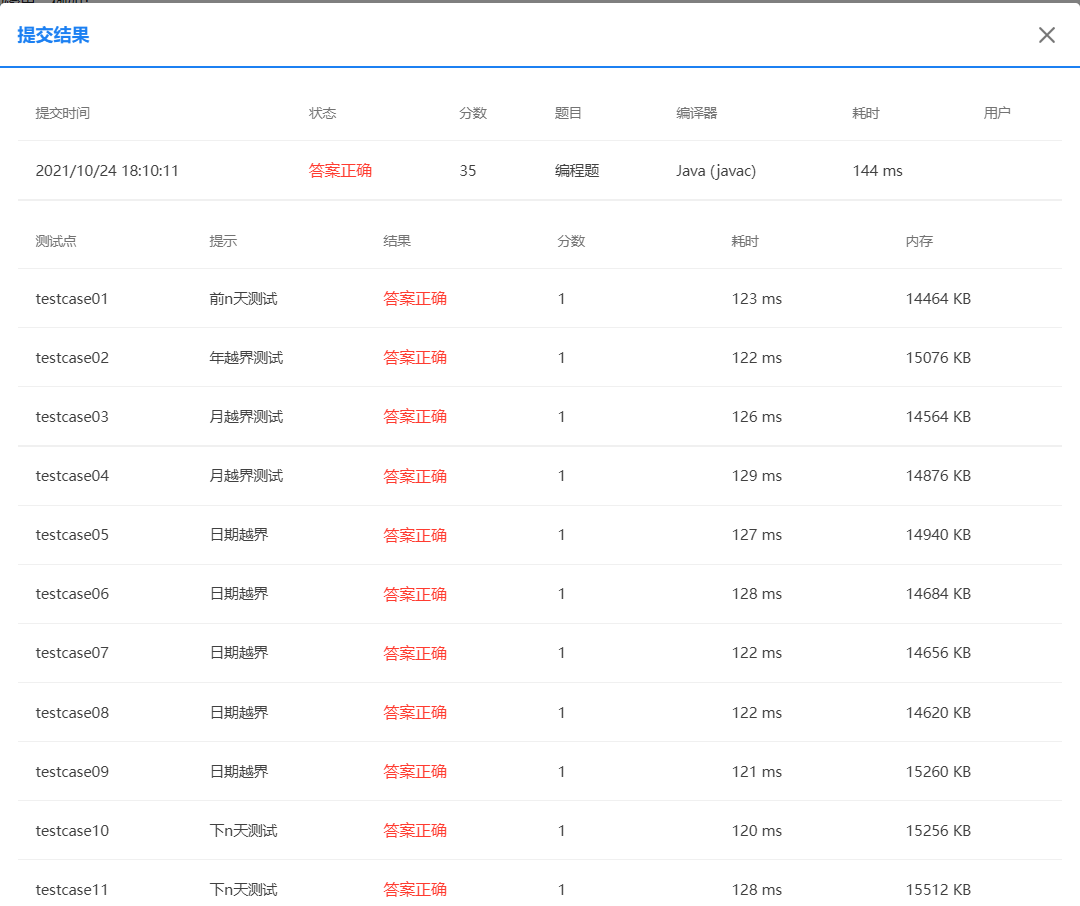
- 但是经过两次测试的截图可知,第二种日期类前后n天整数型最大值测试点的运行时间相比第一种要长出很多,说明第二种的代码运行效率较低,因为题目集4-2,由于三个类组合在一起构成的时间概念,因此很大一部分组合判断已经完成,减轻了dateuial类的负担,所以处理的效率肯定会更好一些。
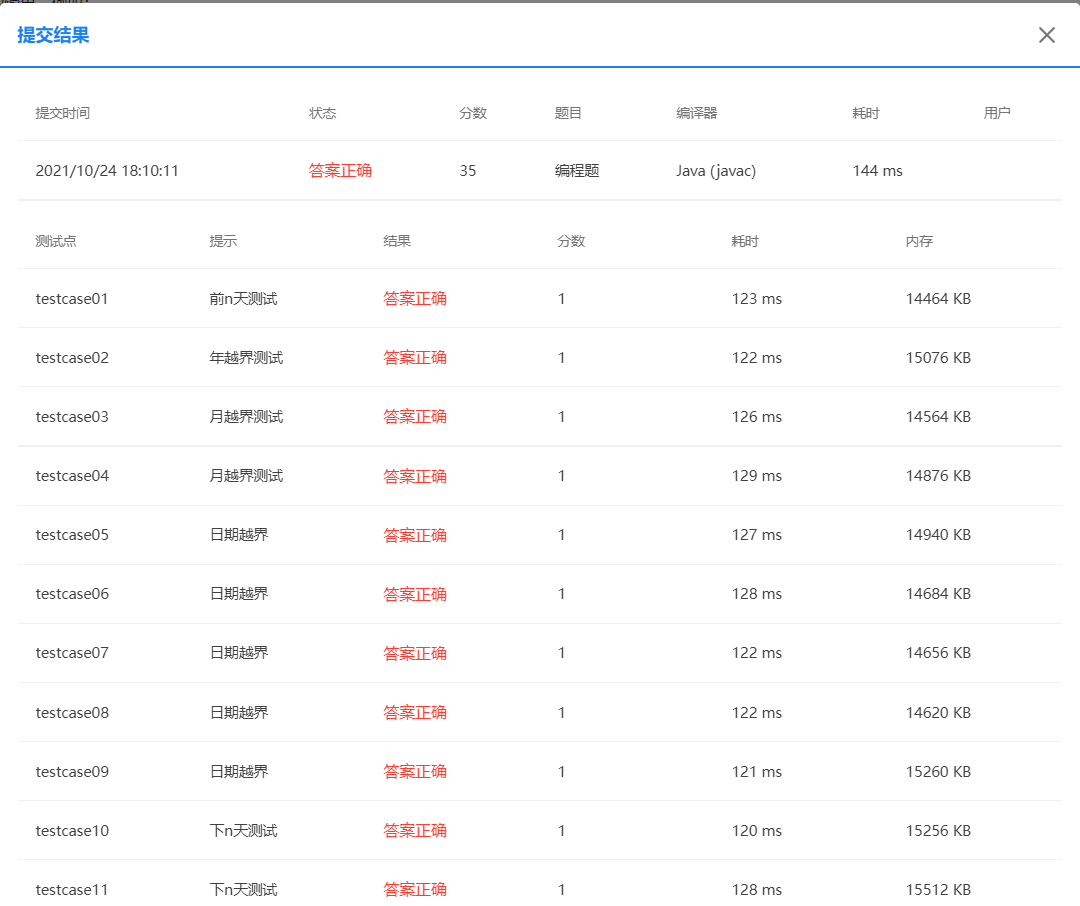
题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
第四次题目集:7-3: 图形继承
1、 设计与分析
(1)设计:
源代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int n; n = input.nextInt(); if(n==1){ double radius=input.nextDouble(); if(radius<=0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else { Circle a=new Circle(); a.setRadius(radius); System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",a.getArea()); System.exit(0); } } if(n==2){ double width=input.nextDouble(); double length=input.nextDouble(); if(width<=0||length<=0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else{ Rectangle b=new Rectangle(); b.setWidth(width); b.setLength(length); System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f",b.getArea()); System.exit(0); } } if(n==3){ double radius=input.nextDouble(); if(radius<=0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else { Ball c=new Ball(); c.setRadius(radius); System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",c.getArea()); System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f",c.getVolume()); System.exit(0); } } if(n==4){ double width=input.nextDouble(); double length=input.nextDouble(); double height=input.nextDouble(); if(width<=0||length<=0||height<=0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else { Box d=new Box(); d.setHeight(height); d.setLength(length); d.setWidth(width); System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",d.getArea()); System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f",d.getVolume()); } } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } class Shape { Shape() { System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); } public double getArea() { return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape{ protected double radius; Circle(){ System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); } /*public double getRadius() { return radius; }*/ public void setRadius(double newRadius) { this.radius=newRadius; } public double getArea() { super.getArea(); return radius*radius*Math.PI; } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ protected double width; protected double length; Rectangle(){ System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); } /*public double getWidth(){ return width; }*/ public void setWidth(double newWidth){ this.width=newWidth; } /*public double getLength(){ return length; }*/ public void setLength(double newLength){ this.length=newLength; } public double getArea() { super.getArea(); return width*length; } } class Ball extends Circle{ Ball(){ System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); } /*public double getRadius(){ return radius; }*/ public void setRadius(double newRadius){ this.radius=newRadius; } public double getArea() { super.getArea(); return 4*Math.PI*radius*radius; } public double getVolume() {//求球体积 return (4*Math.PI*radius*radius*radius)/3; } } class Box extends Rectangle{ protected double height; Box(){ System.out.println("Constructing Box"); } /*public double getHeight() { return height; }*/ public void setHeight(double newHeight) { height=newHeight; } public double getArea() { super.getArea(); return 2*((width*length)+(width*height)+(length*height)); } public double getVolume() { return width*length*height; } }
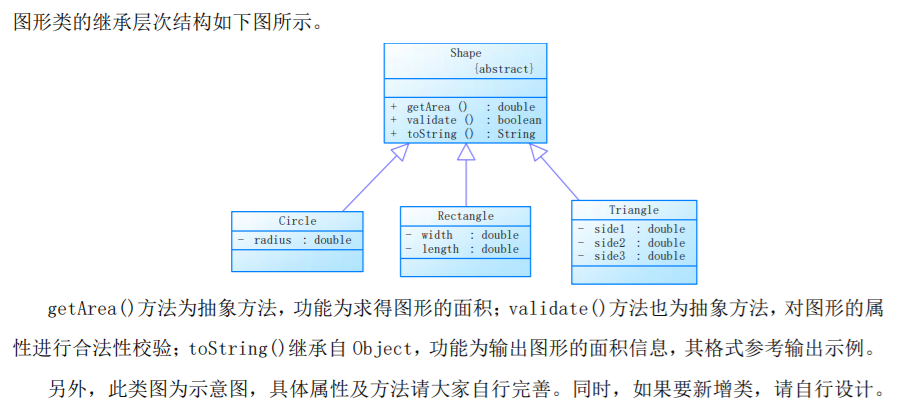
本题要求编写程序,实现图形类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。
- 类Shape,无属性,有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法
public double getArea();//求图形面积 - 类Circle,继承自Shape,有一个私有实型的属性radius(半径),重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求圆的面积
- 类Rectangle,继承自Shape,有两个私有实型属性width和length,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求矩形的面积
- 类Ball,继承自Circle,其属性从父类继承,重写父类求面积方法,求球表面积,此外,定义一求球体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求球体积 - 类Box,继承自Rectangle,除从父类继承的属性外,再定义一个属性height,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求立方体表面积,此外,定义一求立方体体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求立方体体积
由此可知首先通过if或者switch进行功能的选择,用double radius=input.nextDouble();和circle.setRadius(radius);实现数据的输入。
其次,写出父类Shape,其次,用Circle和Rectangle进行父类的继承(class Circle extends Shape)、(class Rectangle extends Shape)接着用Ball和Box分别继承Circle(class Ball extends Circle)和Rectangle(class Box extends Rectangle),以上是整体继承的大致结构。
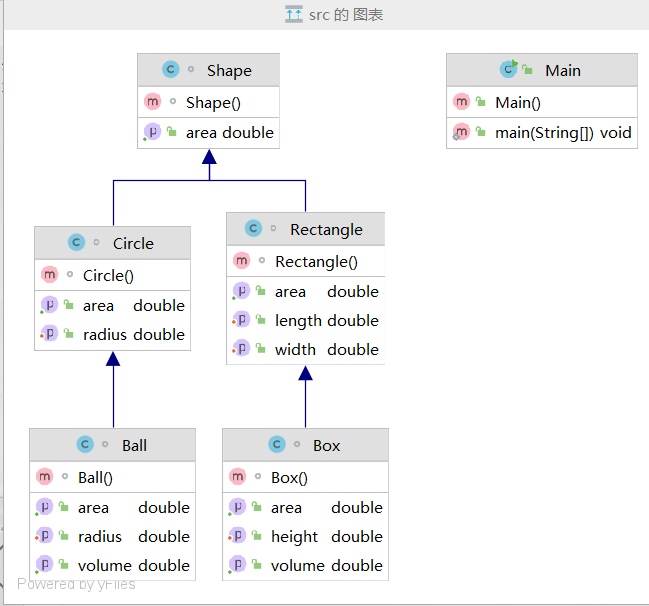
(2)分析:
根据PowerDesigner的类图显示,该题只有六个类,一个main类,shape作为circle和rectangle的父类,而circle和rectangle分别作为ball和box的父类:
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
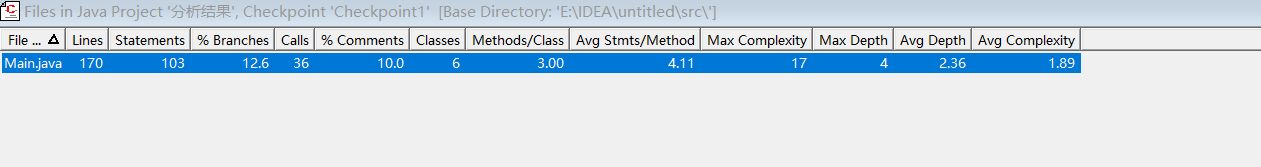
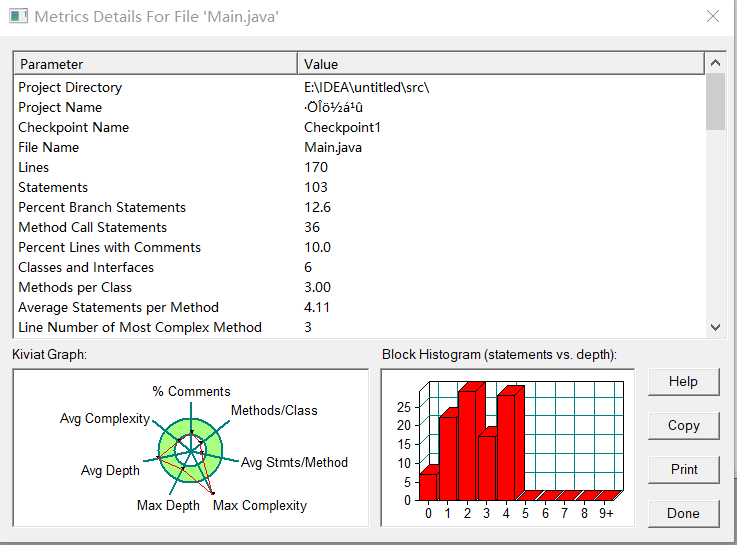
2、踩坑心得:
本题中值得注意的是,在算圆的面积的时候,应该使用Math.PI。
由于第一次做父类继承的题,一开始在方法重写时,不知如何使用,后经过学习了解了 super()和this的区别和用法。
3、改进建议:主函数还可以稍微修改的简洁一点或者用set方法传入图形数据。
第六次题目集:7-5: 图形继承与多态
1、 设计与分析
(1)设计:
源代码
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); Export export = new Export(); int a = input.nextInt(); int b = input.nextInt(); int c = input.nextInt(); if (a < 0 || b < 0 || c < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else { for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) { double radius = input.nextDouble(); Shape circle = new Circle(radius); if(circle.validate() == false) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } export.add(new Circle(radius)); } for (int j = 0; j < b; j++) { double width = input.nextDouble(); double length = input.nextDouble(); Shape rectangle = new Rectangle(width,length); if(rectangle.validate() == false) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } export.add(new Rectangle(width, length)); } for (int k = 0; k < c; k++) { double side1 = input.nextDouble(); double side2 = input.nextDouble(); double side3 = input.nextDouble(); Shape triangle = new Triangle(side1,side2,side3); if(triangle.validate() == false) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } export.add(new Triangle(side1, side2, side3)); } export.Printall(); export.Sum(); export.sort(); export.Sum(); } } } /*(1)ArrayList 应用 要求创建的各个图形对象均存储在 ArrayList<Shape>类型的列表中,可能会用到的方法如下(仅 作提示): add()、addAll()、toArray(),此外,还可能用到 Arrays 类或者 Collections 类。 (2)排序要求 根据图形的面积大小进行升序排序,要求必须对 list 中的图形对象在 list 中进行排序,而不 是对求得的面积进行排序,排序后再次求出各图形的面积并输出。 此处建议大家考虑该排序方法以及求得所有图形面积总和的方法应该设计在哪个类中? ➢ 各个图形的面积; ➢ 所有图形的面积总和; ➢ 排序后的各个图形面积; ➢ 再次输出所有图形的面积总和 输入示例 : 0 2 2 2.3 2.5 56.4 86.5 64.3 85.6 74.6544 3.2 6.1 4.5 输出示例 : Original area: 5.75 4878.60 2325.19 7.00 Sum of area:7216.54 Sorted area: 5.75 7.00 2325.19 4878.60 Sum of area:7216.54 */ class Export { ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>(); Export(){} public void add(Shape shape) { list.add(shape); } public void Printall() { System.out.println("Original area:"); for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i).toString() + " "); } } public void Sum() { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { sum=sum+list.get(i).getArea(); } System.out.println("\n" + "Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sum)); } public void sort() { System.out.println("Sorted area:"); int i, j; Shape temp; for (i = 1;i < list.size();i++){ temp = list.get(i); for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && list.get(j).getArea() > temp.getArea(); j--){ list.set(j + 1, list.get(j)); } list.set(j + 1, temp); } for(i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i).toString() + " "); } } } abstract class Shape { public Shape() { } public abstract double getArea(); public abstract boolean validate(); public abstract String toString(); } class Circle extends Shape { private double radius; public Circle() { } public Circle(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getArea() { return radius * radius * Math.PI; } @Override public boolean validate() { boolean validate = false; if (radius > 0) { validate = true; getArea(); } else { validate = false; } return validate; } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("%.2f", this.getArea()); } } class Rectangle extends Shape { private double width; private double length; public Rectangle() { } public Rectangle(double width, double length) { this.width = width; this.length = length; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getArea() { return length * width; } @Override public boolean validate() { boolean validate = false; if (length >= 0 && width >= 0) { validate = true; getArea(); } else { validate = false; } return validate; } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("%.2f", this.getArea()); } } class Triangle extends Shape { private double side1; private double side2; private double side3; public Triangle() { } public Triangle(double side1, double side2, double side3) { this.side1 = side1; this.side2 = side2; this.side3 = side3; } public double getSide1() { return side1; } public void setSide1(double side1) { this.side1 = side1; } public double getSide2() { return side2; } public void setSide2(double side2) { this.side2 = side2; } public double getSide3() { return side3; } public void setSide3(double side3) { this.side3 = side3; } public double getArea() { double num = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2; return Math.sqrt(num * (num - side1) * (num - side2) * (num - side3)); } @Override public boolean validate() { if(side1 < 0 || side2 < 0 || side3 < 0 || (side1 + side2 <= side3) || (side2 + side3 <= side1) || (side1 + side3 <= side2)) return false; else return true; } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("%.2f", this.getArea()); } }
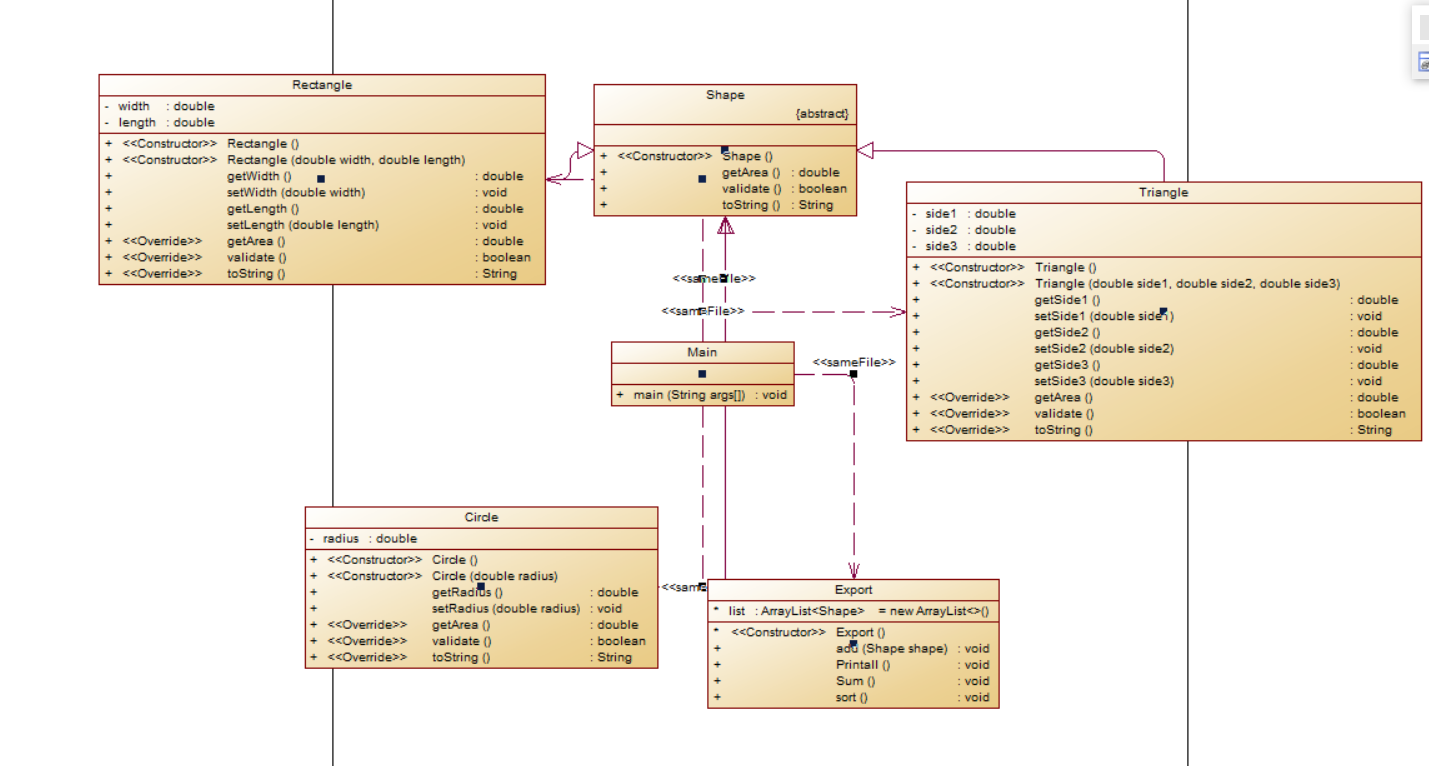
实验要求设计如下:从键盘首先输入三个整型值(例如a b c),分别代表想要创建的Circle、Rectangle及Triangle对象的数量,然后根据图形数量继续输入各对象的属性值(均为实型数)进而实现以下四个功能(必须使用面向对象的封装性、继承性及多态性以及ArrayList)。
本题为类的多态的运用,本身难度不高但是多了以下的要求:

首先根据输入要求创建不同数量的Circle、Rectangle及Triangle对象,这里采用for循环的方法进行。同时,想到最终的所有数据(shape)要存入ArrayList数组中进行判断和处理ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>();,我创建了一个Export类来存储和输出图形的面积:
class Export { ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>(); Export(){} public void add(Shape shape) { list.add(shape); } public void Printall() { System.out.println("Original area:"); for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i).toString() + " "); } } public void Sum() { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { sum=sum+list.get(i).getArea(); } System.out.println("\n" + "Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sum)); } public void sort() { System.out.println("Sorted area:"); int i, j; Shape temp; for (i = 1;i < list.size();i++){ temp = list.get(i); for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && list.get(j).getArea() > temp.getArea(); j--){ list.set(j + 1, list.get(j)); } list.set(j + 1, temp); } for(i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i).toString() + " "); } } }
然后本题的父类为抽象类,皆为空的方法,子类需要完全重写
abstract class Shape { public Shape() { } public abstract double getArea(); public abstract boolean validate(); public abstract String toString(); }
(2)分析:
根据PowerDesigner的类图显示,直观地看出明显的继承和重写方法:
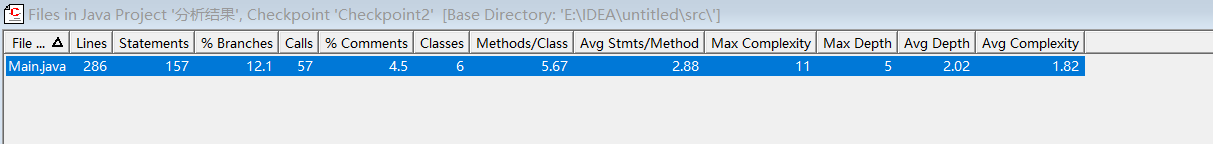
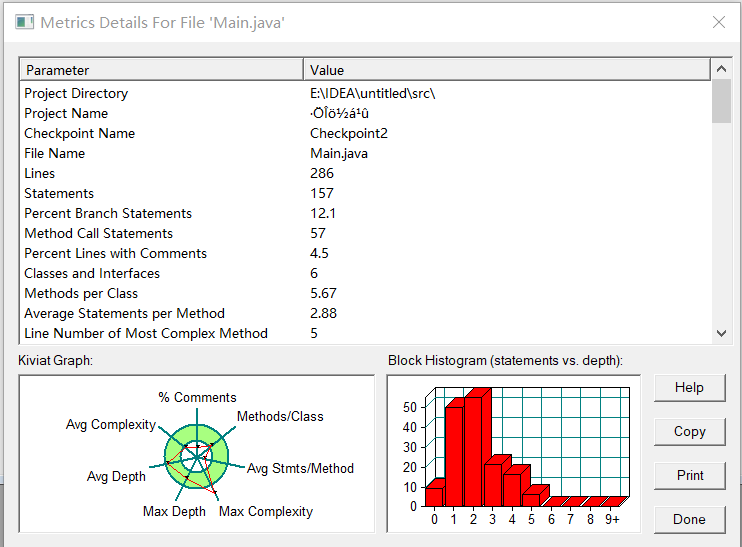
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
2、踩坑心得:此题应该注意的是在在 ArrayList内部似乎不可以对存储的list使用Arrays 类或者 Collections 类进行内部排序,也可能是我的软件或者代码的问题,它显示了相冲突我也不晓得怎么解决,只能内部重写了一个排序解决;
同时由于第一次运用ArrayList进行数据的获取和传入,有关知识点还不熟,于是通过查阅书上的有关材料以及菜鸟教程里面的有关信息了解到了相关用法list.get(i).getArea()和list.set(j, list.get(j-1))。
3、改进建议:main类中还是有不少繁琐的操作,还是可以用别的类去执行的,排序可以用Arrays 类或者 Collections 类进行内部排序,然后用ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>()存储的掌握还是不够尤其是对get,set的使用。
第六次题目集:7-6:实现图形接口及多态性
1、 设计与分析
(1)设计:
源代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); double a=in.nextDouble(); double b=in.nextDouble(); double c=in.nextDouble(); if(a<=0||b<=0||c<=0) { System.out.print("Wrong Format"); } else { Circle x=new Circle(a); x.geprint(); Rectangle y=new Rectangle(b,c); y.geprint(); } } } interface getarea{ public double getarea(); } class Circle implements getarea{ private double radius; Circle(){ } Circle(double a){ radius=a; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getarea() { return Math.PI*radius*radius; } public void geprint() { System.out.printf("%.2f\n",getarea()); } } class Rectangle implements getarea{ private double width; private double length; Rectangle(){ } Rectangle(double width,double length){ this.width=width; this.length=length; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getarea() { return width*length; } public void geprint() { System.out.printf("%.2f\n",getarea()); } }
- GetArea为一个接口,无属性,只有一个GetArea(求面积)的抽象方法;
- Circle及Rectangle分别为圆类及矩形类,分别实现GetArea接口
- 要求:在Main类的主方法中分别定义一个圆类对象及矩形类对象(其属性值由键盘输入),使用接口的引用分别调用圆类对象及矩形类对象的求面积的方法,直接输出两个图形的面积值。
首先本题第一次引入了接口的概念,且接口中有一个抽象方法,通过查阅相关资料后了解了接口的大致用法,同时要求使用到类的封装性、继承性和多态性,故此在Circle及Rectangle类中分别创建get与set方法,同时重写getArea方法。
interface getarea{
public double getarea();
}
(2)分析:
根据PowerDesigner的类图显示,能明显的看出Circle及Rectangle类继承接口GetArea,同时调用了接口中getArea的方法:
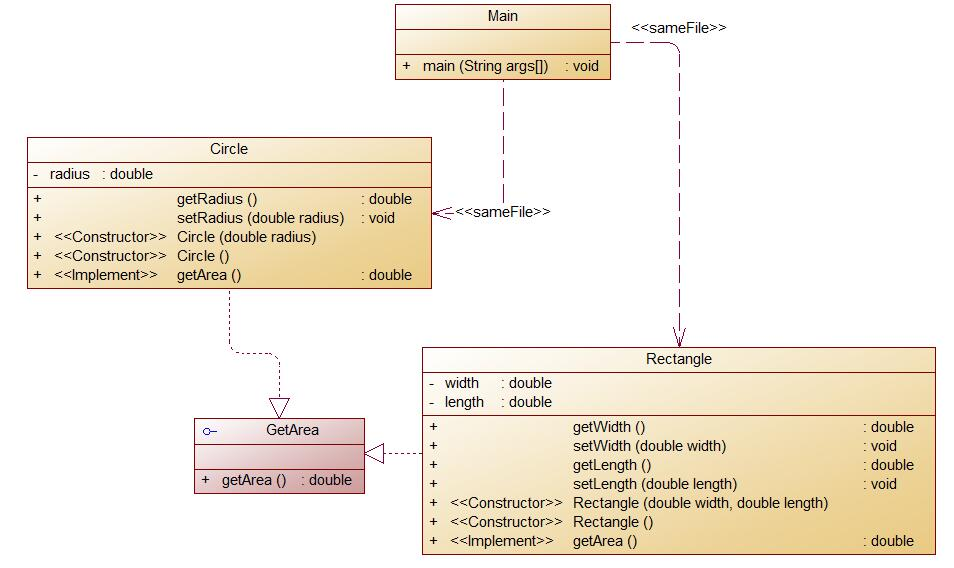
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
2、踩坑心得:本题第一次接触接口,导致刚开始写时连基本的书写格式都不清楚,但了解了interface和implements GetArea的用法后,这题还是相对容易很多的。
3、改进建议:暂无。
对三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路
- 对于题目集4-3,它在设计只用到了封装和继承。其中Rectangle, Circle继承自Shape类,Box继承自Rectangle,Ball继承自Circle。关于shape类在整体上并没有用到多态的特性,都是Ball借用Circle的半径和面积,Box借用Rectangle的长宽和面积,二者又多了更多自己的独自的体积求法,的确合理的用到了继承,提高了复用性。
- 对于题目集6-5中,才是典型的多态应用,抽象类Shape为父类同时构建图形类列表,将不同的形状类批量化装在Shape列表中;其定义的area也同样为Rectangle, Circle,Triangle三者共需的基础属性,而方法getArea()、validate()、suanArea(),在子类中重写后方便多态的使用,可以说多态的应用极大的提高了代码的复用性。
- 对于题目集6-6用接口来求面积的操作,同样实现了多态。虽然都是对图形面积求解输出,但是不同题目的设计有很大的多样性,我们可以通过封装隐藏具体的实现,用继承提高代码复用性,用多态使代码更灵活。
对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
第六次题目集:7-1:正则表达式训练-QQ号校验
- 要求必须是 5-15 位;
- 0 不能开头;
- 必须都是数字;
boolean s=a.matches("[1-9][0-9]{4,14}");
[0-9]表示全部为数字;
{数字,数字}表示位数(若为{0,}则表示无限数字);
第六次题目集:7-3:正则表达式训练-验证码校验
要求:验证码是由四位数字或者字母(包含大小写)组成的字符串。
String b="(^[A-Za-z0-9]+$){4}";
boolean c=a.matches(b);
这里[A-Za-z0-9]表示全体大小写字母或数字都能匹配
^和$分别表示开头和结尾的标志;
(?!+数字)表示不能以该数字为开头;
第六次题目集:7-4:正则表达式训练-学号校验
对软件学院2020级同学学号进行校验,学号共八位,规则如下:
- 1、2位:入学年份后两位,例如20年
- 3、4位:学院代码,软件学院代码为20
- 5位:方向代码,例如1为软件工程,7为物联网
- 6位:班级序号
- 7、8位:学号(序号)
要求如下:
- 只针对2020级
- 其中软件工程专业班级分别为:202011~17、61,物联网工程专业班级为202071~202073,数据科学与大数据专业班级为202081~82
- 每个班级学号后两位为01~40
String b="[2][0][2][0]([1][1-7]|[6][1]|[7][1-3]|[8][1-2])([0][1-9]|[1-3][1-9]|[4][0])";
boolean c=a.matches(b);
在正则中用()进行匹配区间的划分,提取匹配的字符串,用“|”表示或;
(a[b-c])表示以数字a为十位数,以b到c之间包括本身的数字为个位数;
第五次题目集:7-4 :统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数
本题在匹配完之后用空格进行代替,从而达到删去的目的。
//去除注释 空格 换行符 Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile("//.+");// '.'表示任何字符 Matcher matcher1 = pattern1.matcher(sb); sb = matcher1.replaceAll("");//去除单行注释,将匹配到的单行注释全都换成“ ” Pattern pattern2 = Pattern.compile("/\\*.*?\\*/",Pattern.DOTALL); //Pattern.DoTALL这个字段的意思是:可以匹配任何字符,包括行结束符 Matcher matcher2 = pattern2.matcher(sb);//去除多行注释 sb = matcher2.replaceAll(" "); //去除换行符 Pattern pattern3 = Pattern.compile("\\n"); Matcher matcher3 = pattern3.matcher(sb);//创建匹配器 sb = matcher3.replaceAll(" ");//去除换行符 Pattern pattern4 = Pattern.compile("\\t"); Matcher matcher4 = pattern4.matcher(sb);//创建匹配器 sb = matcher4.replaceAll(" ");//去除制表符 //sb=sb.replace("=","a"); addKeywords();//把关键字加入到Map中 sb=sb.replaceAll("/\\*(.*?)\\*/", " "); sb=sb.replaceAll("\"(.*?)\"", " "); sb=sb.replace("["," "); sb=sb.replace("]"," "); sb=sb.replace("=","WOSHISHABNI"); sb=sb.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]"," "); String[] strs = sb.split("[ .,;:!?(){}]");//将sb切割开来,分成每个单词
第四次题目集:7-1 :水文数据校验及处理
假定分水口门的数据上报时是采用人工输入的方式,每一行代表一个整点时刻的分水数据,各数据之间采用“|”符号进行分隔,每次可以输入多条数据,直到遇到用户输入“exit”为止,每一行输入数据共包含五部分:测量时间、目标水位、实际水位、开度(包含目标开度和实际开度,以“/”分隔)、流量。 各数据格式要求如下:
- 测量时间:格式为“年/月/日 时:分”,其中年份取值范围为[1,9999],“月”与“日”为一位数时之前不加“0”,日期与时间之间有一个空格,“时”与“分”之间采用冒号分隔(英文半角),“时”为一位数时之前不加“0”,“分”始终保持两位,且始终为“00”。注意:“时”数必须是24小时进制中的偶数值。
- 目标水位、实际水位、流量:均为实型数,取值范围为[1,1000), 小数点后保留1-3位小数或无小数(也无小数点)
- 目标开度、实际开度:实型数,取值范围为[1,10),必须保留2位小数,两个开度之间用“/”分隔
Pattern p1 = Pattern.compile("((?<!\\d)[1-9][0-9]{0,3})/([0-9]|[1][0-2])/(([1-2][0-9]|[3][01])|[1-9]) (([02468])|([1][02468])|([2][024])):([0][0])");
Pattern p2 = Pattern.compile("((?<!\\.)[1-9][0-9]{0,3}\\.[0-9]{1,3}(?!\\w))|(?<!(\\.|\\d))([1-9][0-9]{0,3})(?!((\\.)|\\d))");
Pattern p3 = Pattern.compile("(([1][0]\\.[0][0])|(?<!\\d)([\\d]\\.[\\d][\\d]))");
第五次题目集:7-4: 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数
1、 设计与分析
(1)设计:
源代码
import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeMap; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static Map<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); String sb1 = new String(); sb1 = input.nextLine();//数据的输入 int a = 0; while(sb1.compareTo("exit") != 0) {//当遇到"exit"时停下来 str.append(sb1); str.append("\n"); sb1 = input.nextLine(); a++; } if(a == 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } String sb = str.toString(); //System.out.println(sb); //去除注释 空格 换行符 Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile("//.+");// '.'表示任何字符 Matcher matcher1 = pattern1.matcher(sb); sb = matcher1.replaceAll("");//去除单行注释,将匹配到的单行注释全都换成“ ” Pattern pattern2 = Pattern.compile("/\\*.*?\\*/",Pattern.DOTALL); //Pattern.DoTALL这个字段的意思是:可以匹配任何字符,包括行结束符 Matcher matcher2 = pattern2.matcher(sb);//去除多行注释 sb = matcher2.replaceAll(" "); //去除换行符 Pattern pattern3 = Pattern.compile("\\n"); Matcher matcher3 = pattern3.matcher(sb);//创建匹配器 sb = matcher3.replaceAll(" ");//去除换行符 Pattern pattern4 = Pattern.compile("\\t"); Matcher matcher4 = pattern4.matcher(sb);//创建匹配器 sb = matcher4.replaceAll(" ");//去除制表符 //sb=sb.replace("=","a"); addKeywords();//把关键字加入到Map中 sb=sb.replaceAll("/\\*(.*?)\\*/", " "); sb=sb.replaceAll("\"(.*?)\"", " "); sb=sb.replace("["," "); sb=sb.replace("]"," "); sb=sb.replace("=","WOSHISHABNI"); sb=sb.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]"," "); String[] strs = sb.split("[ .,;:!?(){}]");//将sb切割开来,分成每个单词 //System.out.println(sb); //遍历每个单词 如果是关键字就++ for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) { if(map.containsKey(strs[i])) { int value = map.get(strs[i]) + 1; map.put(strs[i], value);//将对应的关键字数量加入 } } //遍历一下map 如果value>0 就output Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet(); //然后用foreach遍历 for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : set) { if(entry.getValue() > 0) { System.out.println(entry.getValue() + "\t" + entry.getKey()); } } } public static void addKeywords(){//将53个关键字输入进一个字符数组 String[] keywordString = {"abstract", "assert", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char", "class", "const", "continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extends", "for", "final", "finally", "float", "goto", "if", "implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", "native", "new", "package", "private", "protected", "public", "return", "short", "static", "strictfp", "super", "switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw", "throws", "transient", "try", "void", "volatile", "while", "true", "false", "null"}; for(int i = 0; i < keywordString.length; i++) { map.put(keywordString[i], 0); } } }
实验要求设计如下:编写程序统计一个输入的Java源码中关键字(区分大小写)出现的次数。
- 注释中出现的关键字不用统计
- 字符串中出现的关键字不用统计
- 统计出的关键字及数量按照关键字升序进行排序输出
- 未输入源码则认为输入非法
输入Java源码字符串,可以一行或多行,以exit行作为结束标志且必须使用List、Set或Map中一种或多种
首先将百度搜索的53个关键词放入一个字符串数组中,接着实现“以exit行作为结束标志”的要求,这里最好使用StringBuilder输入较多的字符串,并用append的方法将每行字符串相连,代码如下:
public static void addKeywords(){//将53个关键字输入进一个字符数组 String[] keywordString = {"abstract", "assert", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char", "class", "const", "continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extends", "for", "final", "finally", "float", "goto", "if", "implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", "native", "new", "package", "private", "protected", "public", "return", "short", "static", "strictfp", "super", "switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw", "throws", "transient", "try", "void", "volatile", "while", "true", "false", "null"}; for(int i = 0; i < keywordString.length; i++) { map.put(keywordString[i], 0); } }
把全部的字符串用keywordString[i]存储然后map映射输出。
(2)分析:
根据PowerDesigner的类图显示,该题只有一个main类以及一个map接口:
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析


2、踩坑心得:正则表达式符号的判断还是有一大部分纰漏,得全部列出来多多思考,并且map映射的使用还是不是很好,还是得多训练。
3、改进建议:本题有一个测试点是卡bug强行过的,代码sb=sb.replace("=","WOSHISHABNI");,把等于号替换成任意一个字符串就行。
在用正则进行符号代替时,最好不要使用\\p{Punct},该正则可能会忽略一些符号,推荐采用str=str.replace("[", " ");的格式进行书写。
四、PTA其他题目的踩坑心得和改进建议
关于其他的题目的话,其实上面的典型且有难度的题目已经涵盖了我大部分的心得和感受,其他题目的改进建议也和上面大同小异,所以我便不再赘述。
五、总结
本次作业相比较于上一次难度提升了很多,我也对面向对象的思想有了更多的理解:
1.对于面向对象的三大特性理解:
(1)封装 对于类中的属性,我们可以用private对属性进行封装,不仅仅如此我们可以让使用者可以看到我们想让他们看到的,同样的也可以让他们看不到一些内容。
(2)继承 继承的好处有很多,子类可以继承父类的一些属性同样的也可以继承父类的一些方法。这大大提高了类的可复用性,例如图形可以分为园,矩形,三角形等。通过第五次作业的第三题我们可以体会到继承的方便。
(3)多态是通过继承以及方法重写来实现这样就可以方便解决很多问题,例如每个图形都有面积,但他们的就面积方法都不同,这个时候通过继承以及方法重写来实现求面积的方法。
2.面向对象设计的基本原则理解:
单一职责原则就是每个类中都有自己功能和作用,不需要一个类来同时做很多工作。
开闭原则就是一个程序在修改或添加其他程序时可以直接在不修改源码的情况下添加。
这个阶段对类的封装、继承、多态性体现的淋漓尽致。经过多次练习,我已清楚的了解到运用类的继承和多态其中的方法和一些代码的书写方式,这可以大大提高代码的复用性,使代码量大大减少,同时方法的重写也更加符合现实中的逻辑思维。同时,接口的使用也再次拓宽了我们的知识面,了解了如何利用Map、List、Set等接口进行一些数据处理的优化。
3.面向的对象的编程思维的理解
面向对象思维必须弄清楚的是我们所写的程序是面向对象而不是面向过程,对象各自都有自己的作用和功能,在使用时分工明确,而不是仅仅只是一个过程。
面向对象中类的设计是个有趣的过程,通过分析这个对象并将他的功能属性一一写出来,每一个类都有他们自己的职权,主管一部分功能。
总的来说,虽然难度上升的比较突然,但是这又同时刺激提高了我们在短时间内学习不同知识点的能力。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号