leetcode 深搜广搜

遍历整个grid数组,当发现有1的时候,就把和这个1连成片的1都置为0,并增加一个计数。最后返回这个计数。
广搜,但这个代码通不过测试,栈溢出。
class Solution {
public:
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid,int i,int j){
if(i<0||j<0||i>=grid.size()||j>=grid[0].size()) return;
if(grid[i][j]=='0') return;
//标记为以及记录过
grid[i][j]=='0';
bfs(grid,i+1,j);
bfs(grid,i-1,j);
bfs(grid,i,j+1);
bfs(grid,i,j-1);
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].size();j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='0') continue;
//当为”1“时
ans++;
bfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
解法2:
深搜(DFS) 。 这个题也是《挑战程序设计》的第一个深搜的题。
思路:与《挑战程序设计》相同。只不过这个题是要遍历上下左右四个方向,而《挑战程序设计》是8个方向。

class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid,int i,int j){
int nr = grid.size();
int nc = grid[0].size();
grid[i][j] = '0';
if(i-1>=0 && grid[i-1][j]=='1') dfs(grid,i-1,j);
if(i+1<nr && grid[i+1][j]=='1') dfs(grid,i+1,j);
if(j-1>=0 && grid[i][j-1]=='1') dfs(grid,i,j-1);
if(j+1<nc && grid[i][j+1]=='1') dfs(grid,i,j+1);
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int nr = grid.size();
if(!nr) return 0;
int nc = grid[0].size();
int isLand = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nr;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nc;j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
dfs(grid,i,j);
isLand++;
}
}
}
return isLand;
}
};


class Solution {
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].size();j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
res=max(res,helper(grid,i,j,0));
}
}
}
return res;
}
int helper(vector<vector<int>>& grid,int row,int col,int sum){
if(row<0||row>=grid.size()||col<0||col>=grid[0].size()||grid[row][col]!=1){
return 0;
}
grid[row][col]=0;
sum++;
sum+=helper(grid,row-1,col,0)
+helper(grid,row+1,col,0)
+helper(grid,row,col-1,0)
+helper(grid,row,col+1,0);
return sum;
}
};
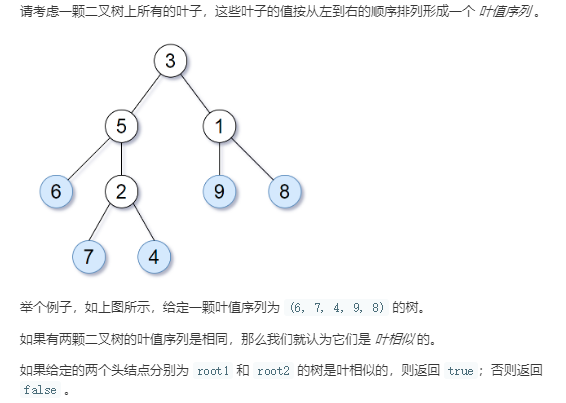
从这个题中,可以利用递归,把一个树的所有叶子节点按从左到右的顺序放入vector<int>型中。

class Solution {
public:
bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
vector<int> res1,res2;
vert(root1,res1);
vert(root2,res2);
if(res1==res2) return true;
return false;
}
void vert(TreeNode* root,vector<int>& res){
//递归终止条件
if(!root) return;
//本层要做的事:先找到左边的叶子节点,把val放入res中,再对右叶子做同样操作
vert(root->left,res);
//判断叶子节点的条件
if(!root->left&&!root->right) res.push_back(root->val);
vert(root->right,res);
}
};
从这个题中学到了用map,实现映射,其实也算hash。以便某些题目需要的时候避免了反复用循环来查询。但map需要初始化。
map 的实现是红黑树,unordered_map的实现是hash。
借鉴评论(此代码超时)用stack存储:
这其实也是广度优先搜索,但是效率没有下面的高。
class Solution {
public:
int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {
stack<int> e;
int count=0;
e.push(id);
while(!e.empty()){
int node=e.top();
vector<int> vec;
e.pop();
for(int i=0;i<employees.size();i++){
if(employees[i]->id==id){
count += employees[i]->importance;
vec=employees[i]->subordinates;
for(int j=0;j<vec.size();j++){
e.push(vec[j]);
}
break;
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
用map 存储
深搜(递归):
class Solution {
public:
int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {
map<int,Employee*> m;
for(auto e:employees){//初始化map
m[e->id]=e;
}
int res=dfs(id,m);
return res;
}
int dfs(int id,map<int,Employee*> map){
if(map[id]->subordinates.size()==0) return map[id]->importance;
int imp=map[id]->importance;
for(auto tmp:map[id]->subordinates){
imp += dfs(tmp,map);
}
return imp;
}
};
来自巨佬的代码:
广度优先搜索:
先介绍unordered_map:
https://www.cnblogs.com/tp-16b/p/9156810.html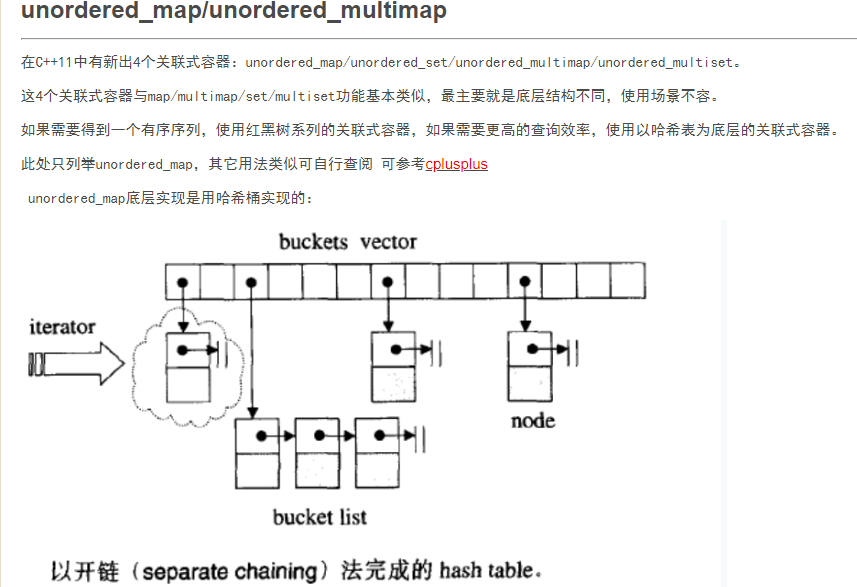

class Solution {
public:
int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {
int sumImportance=0;
unordered_map<int,Employee*> hashMap;
//初始化
for(auto employee:employees){
hashMap[employee->id]=employee;
}
queue<int> myQue;//广度优先搜索队列
myQue.push(id);
//开始搜索
while(!myQue.empty()){
id=myQue.front();
myQue.pop();
sumImportance += hashMap[id]->importance;
for(auto subordinate:hashMap[id]->subordinates){
myQue.push(subordinate);
}
}
return sumImportance;
}
};
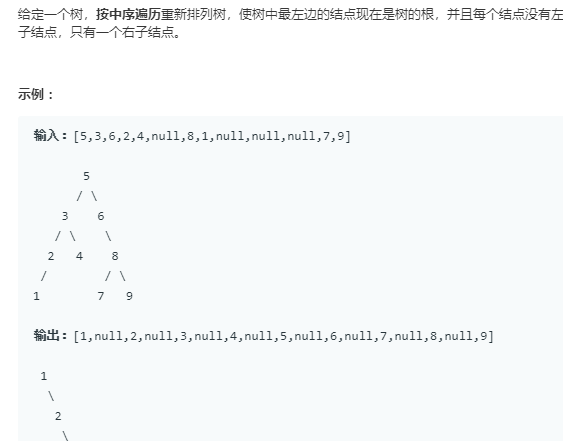


思路:利用中序遍历得到vector,之后就好办了!
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* increasingBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return NULL;
vector<int> v=inorderTraversal(root);
TreeNode* temp=new TreeNode(v[0]);
TreeNode* p=temp;
temp->left=NULL;
for(int i=1;i<=v.size()-1;i++){
TreeNode* node=new TreeNode(v[i]);
temp->right=node;
temp=node;
}
return p;
}
//中序遍历
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
vector<int> vec;
while(root!=NULL||!stk.empty()){
if(root!=NULL){//根节点进栈,遍历左子树
stk.push(root);
root=root->left;
}
else{//根节点退栈,访问根节点,遍历右子树
root=stk.top(); stk.pop();
vec.push_back(root->val);
root=root->right;
}
}
return vec;
}
};
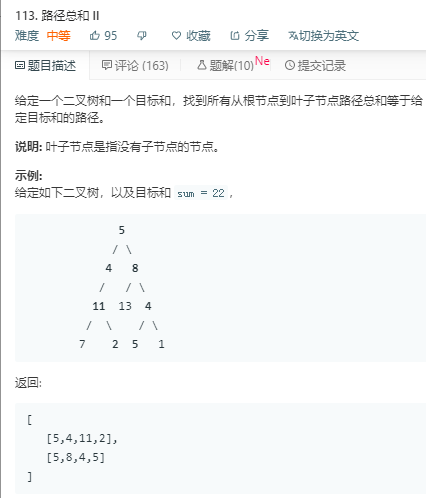
解法1:
思路:借鉴评论区的代码。深搜。但是效率不高。自己没想起来怎么写。

class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> res;//要在这里声明全局变量
vector<int> result;
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
path(root,sum,result);
return res;
}
void path(TreeNode* root,int sum,vector<int> p){ //注意这里没加引用。可能是因为全局变量
if(!root){//递归终止条件
return;
}
p.push_back(root->val);
if(!(root->left)&&!(root->right)&&sum==root->val)//一直往下找,直到找到路径总和为sum的元素
res.push_back(p);
path(root->left,sum - root->val,p);
path(root->right,sum - root->val,p);
}
};
解法2:
思路:比上一个解法多了一个回溯。效率增加了很多。代码借鉴的题解

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> res;//要在这里声明全局变量
vector<int> result;
path(root,sum,res,result);
return res;
}
void path(TreeNode* root,int sum,vector<vector<int>> &res,vector<int> &result){ //注意这里加了引用。可能是局部变量,所以要加引用
if(!root){//递归终止条件
return;
}
sum=sum-root->val;
result.push_back(root->val);
if(sum==0&&root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL){
res.push_back(result);
}
if(root->left){
path(root->left,sum,res,result);
result.pop_back();//回溯
}
if(root->right){
path(root->right,sum,res,result);
result.pop_back();//回溯
}
}
};
回溯和递归的区别:(非常重要!):总的来说,回溯算法和递归算法不能以类别的形式进行比较。在很多情况下,二者是一起使用的。
区别与联系
- 递归是一种算法结构。
- 回溯是一种算法思想,可以用递归实现。
https://blog.csdn.net/lym940928/article/details/89679157

解法1:递归就完事了

class Solution {
public:
int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) {
return helper(root,0);
}
int helper(TreeNode* root,int sum){
if(!root){
return 0;
}
else if(!root->left&&!root->right){
return 10*sum+root->val;
}
return helper(root->left,10*sum+root->val)+helper(root->right,10*sum+root->val);
}
};
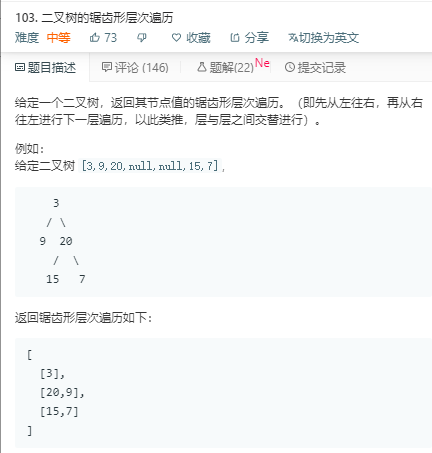
解法1:
思路:(借鉴评论)双栈。一个栈存储奇数行的结点。一个栈存储偶数行的结点
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root)
return res;
stack<TreeNode*> sta1;//遍历中使用的临时栈1,存放奇数层节点
stack<TreeNode*> sta2;//遍历中使用的临时栈2,存放偶数层节点
sta2.push(root);
int index=0;//用于保存当前的层数
while(sta1.size()||sta2.size()){
vector<int> tempres;//本层遍历的结果
if(index%2==0){
while(sta2.size()){
//从栈2中出栈
TreeNode* temp=sta2.top();
sta2.pop();
//输出结点
tempres.push_back(temp->val);
//将子节点入栈1,偶数行先左后右
if(temp->left)
sta1.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right)
sta1.push(temp->right);
}
}
else{
while(sta1.size()){
//从栈1中出栈
TreeNode* temp=sta1.top();
sta1.pop();
//输出结点
tempres.push_back(temp->val);
//将子节点入栈2,奇数行先右后左
if(temp->right)
sta2.push(temp->right);
if(temp->left)
sta2.push(temp->left);
}
}
//将本层的结点输出加入结果中,更新层数
index += 1;
res.push_back(tempres);
}
return res;
}
};
解法2:
思路:(评论区) 双端队列
解法1:
思路:利用BFS,队列,判断是否为同一层和同一父节点。若是同一层且父节点不同,则说明为堂兄弟
class Solution {
public:
bool isCousins(TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {//判断是否为同一父节点和同一层
if(x==y)//当两个结点为指向同一个结点时
return true;
queue<TreeNode*> record;
record.push(root);
int count=1;
while(!record.empty()){
int flag_x=0,flag_y=0;
while(count--){//每层的元素个数
TreeNode* temp=record.front();
record.pop();
if(temp->left&&temp->right&&((temp->left->val==x&&temp->right->val==y)||(temp->left->val==y&&temp->right->val==x)))
return false;
if(temp->val==x)
flag_x=1;
if(temp->val==y)
flag_y=1;
if(flag_x&&flag_y)
return true;
if(temp->left)
record.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right)
record.push(temp->right);
}
count=record.size();
}
return false;
}
};

解法1:思路:大佬的DFS。
利用了C++中的resize()函数


class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root,0);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int depth){
if(!root){
return;
}
if(depth>=res.size()){
res.resize(depth+1,INT_MIN);
}
res[depth] = max(res[depth],root->val);
dfs(root->left,depth+1);
dfs(root->right,depth+1);
}
private:
vector<int> res;
};
解法2:
BFS广度搜索
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(!root) return res;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int sz = q.size();
int max = INT_MIN;
for(int i=0; i<sz; ++i){
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
if(t->val > max) max = t->val;
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
res.push_back(max);
}
return res;
}
};
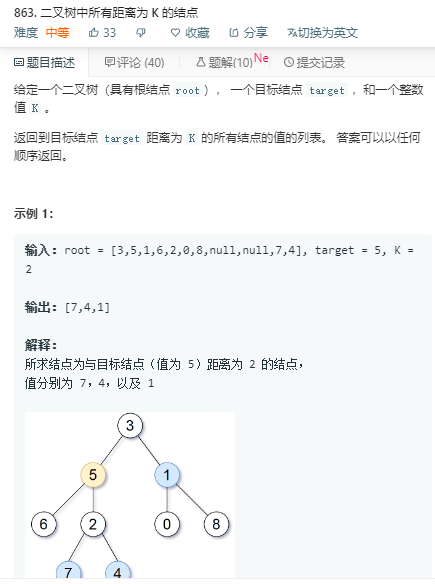
解法1:
思路:把树转为图,就成了距离该节点为K的节点了。


class Solution {
public:
vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int K) {
vector<int> res;
map<TreeNode*, vector<TreeNode*>> conn;
dfs(root,conn);//建立邻接矩阵
queue<TreeNode*> q;
set<TreeNode*> visited;
q.push(target);
visited.insert(target);
int step = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
if(step == K){
while(!q.empty()){
res.push_back(q.front()->val);
q.pop();
}
return res;//一定在这里返回
}
int size = q.size();
for(int i=0; i<size;i++){
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j =0;j<conn[curr].size();j++){
TreeNode* next = conn[curr][j];
if(visited.find(next)!= visited.end()) continue;//如果被访问过,则继续循环
visited.insert(next);
q.push(next);
}
}
step++;
}
return res;//不会在这里返回
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, map<TreeNode*,vector<TreeNode*>>& conn){//DFS建立邻接矩阵
if(!root) return;
if(root->left){
conn[root].push_back(root->left);
conn[root->left].push_back(root);
dfs(root->left,conn);
}
if(root->right){
conn[root].push_back(root->right);
conn[root->right].push_back(root);
dfs(root->right,conn);
}
}
};
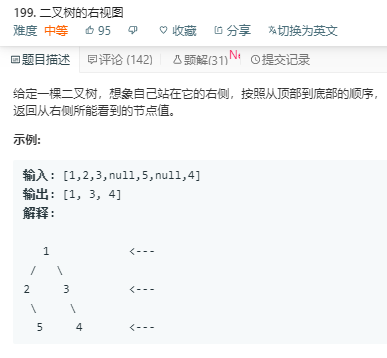
广搜,入队列
解法1:思路:使用层序遍历,并只保留每层最后一个节点的值

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(!root) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
res.push_back(q.front()->val);
while(size--){
TreeNode* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(temp->right) q.push(temp->right);//一定要最右节点先入队
if(temp->left) q.push(temp->left);
}
}
return res;
}
};

先贴上代码,慢慢看。
自己在深搜广搜,图的应用还是不熟练。
class Solution {
public:
int minKnightMoves(int x, int y) {
if ( x==0 && y==0 ) return 0;
x += 300;
y += 300;
int dir[8][2] = { {1,2},{2,1},{1,-2},{2,-1},{-1,2},{-2,1},{-1,-2},{-2,-1} };
int level = 0;
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
q.push({300,300});
int vis[1000][1000]={0};
vis[300][300] = 1 ;
while( !q.empty() ){
for ( int t=q.size()-1; t>=0; --t ){
pair<int,int> cor = q.front(); q.pop();
for ( int k=0; k<8; ++k ){
int ny = cor.first + dir[k][0];
int nx = cor.second + dir[k][1];
if ( ny==y && nx==x ) return level +1 ;
if ( nx>=0 && ny>=0 && nx<=603 && ny<=603 && vis[ny][nx]==0 ){
q.push({ny,nx});
vis[ny][nx]=1;
}
}
}
++level;
}
return -1;
}
};

参考题解:
https://leetcode.com/problems/word-ladder/discuss/40707/C%2B%2B-BFS
注意:判断有一个字母不同,其他字母都相同的代码是如何写的。
解法1:
2019-10-09(第一次)
BFS
注意:判断有一个字母不同,其他字母都相同的代码是如何写的。

class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> dict(wordList.begin(),wordList.end());
int Lader = 1;
queue<string> q;
q.push(beginWord);
while(!q.empty()){
int n = q.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
string word = q.front();
q.pop();
if(word == endWord){
return Lader;
}
dict.erase(word);
for(int j=0;j<word.size();++j){
char c= word[j];
for(int k=0;k<26;++k){//判断有一个字母不同,其他字母都相同的代码是如何写的
word[j] = 'a' + k;
if(dict.find(word)!=dict.end()){
q.push(word);
}
}
word[j] = c;
}
}
Lader++;
}
return 0;
}
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号