Android 时间计算工具 通用类TimeUtil
1.整体分析
1.1.源代码如下,可以直接Copy。

public class TimeUtil { private static final String TAG = "TimeUtil"; public static String computePastTime(String time) { // Log.v(TAG, "computePastTime: " + time); String result = "刚刚"; //2017-02-13T01:20:13.035+08:00 time = time.replace("T", " "); time = time.substring(0, 22); // Log.v(TAG, "computePastTime time: " + time); SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS", Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE); try { Date t = simpleDateFormat.parse(time); Date now = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); long diff = (now.getTime() - t.getTime()) / 1000; if (diff < 60) { result = "刚刚"; } else if ((diff /= 60) < 60) { result = diff + "分钟前"; } else if ((diff /= 60) < 24) { result = diff + "小时前"; } else if ((diff /= 24) < 30) { result = diff + "天前"; } else if ((diff /= 30) < 12) { result = diff + "月前"; } else { diff /= 12; result = diff + "年前"; } } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // Log.v(TAG, "computePastTime result: " + result); return result; } public static String formatTime(String time) { // Log.v(TAG, "formatTime: " + time); //2017-02-13T01:20:13.035+08:00 time = time.replace("T", " "); time = time.substring(0, 16); // Log.v(TAG, "formatTime result: " + time); return time; } }
1.2.主要方法
- computePastTime(String time)==>字符串转化为汉字的时间。
- formatTime(String time)==>格式化字符串时间
1.3.参考其他时间类。

public class MyTimeUtils { //获取时间戳 public static long getTime() { Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();// 获取当前日历对象 long unixTime = calendar.getTimeInMillis();// 获取当前时区下日期时间对应的时间戳 return unixTime; } public static String getTimeString() { return Long.toString(new Date().getTime()); } //获取标准时间 public static String getStandardTime() { SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat(BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.date_show_type_one)); Date curDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());// 获取当前时间 return formatter.format(curDate); } // 获取与现在时间的时间差(秒) public static int getDurationSecond(String time) { int durationSecond = 0; SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(<span style="font-family: SimHei;">"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"</span>); Date date; try { date = df.parse(time); MyLog.i("TimeUtils getDurationSecond Date=" + new Date().toString()); durationSecond = (int) ((new Date().getTime() - date.getTime()) / 1000); } catch (Exception e) { MyLog.e("TimeUtils getDurationSecond error=" + e); } return durationSecond; } // 获取时间差 public static String getDuration(String one, String two) { String duration = ""; SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(<span style="font-family: SimHei;">"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"</span><span style="font-family: SimHei;">);</span> Date date1; Date date2; try { date1 = df.parse(one); date2 = df.parse(two); int l = (int) ((date2.getTime() - date1.getTime()) / 1000 / 60); if (l > 60) { int hr = l / 60; int min = l % 60; duration = <span style="font-family: SimHei;">hr + "小时" + min + "分钟"</span>; } else { duration = <span style="font-family: SimHei;">l + "分钟";</span> } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return duration; } // 获取与当前时间差 public static String getcurDuration(String one) { String duration = ""; SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(<span style="font-family: SimHei;">"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"</span>); Date date1; Date date2; try { date1 = df.parse(one); date2 = new Date(); int l = (int) ((date2.getTime() - date1.getTime()) / 1000 / 60); if (l > 60) { int hr = l / 60; int min = l % 60; duration = <span style="font-family: SimHei;">hr + "小时" + min + "分钟"</span><span style="font-family: SimHei;">;</span> } else { duration =<span style="font-family: SimHei;"> l + "分钟";</span> } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return duration; } /** * @return格式化当前日期和时间为字符串 */ public static String mCurrentTime() { SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(<span style="font-family: SimHei;">"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"</span>); String currenttime = df.format(new Date()); return currenttime; } public static String parseBangTime(long time) { MyLog.out("time==>" + time); String timeTemp = ""; if (time < 60) { timeTemp = time + BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.seconds_before); } else if (time < (60 * 60)) { timeTemp = time / 60 + BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.minutes_before); } else if (time < (3600 * 24)) { timeTemp = time / 3600 + BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.hour_before); } else if (time < (60 * 60 * 24 * 30)) { timeTemp = time / (3600 * 24) + BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.today_before); } else { timeTemp = time / (3600 * 24 * 30) + BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.month_before); } return timeTemp; } public static String getTimeStamp() { SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.date_show_type_two)); String timeStamp = dateFormat.format(new Date()); MyLog.e("getTimeStamp=" + timeStamp); return timeStamp; } public static String getCurrentDate(){ SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(BaseApplication.getInstance().getString(R.string.date_show)); String currentDate = df.format(new Date()); return currentDate; } }
2.局部分析
2.1.字符串转化为汉字的时间
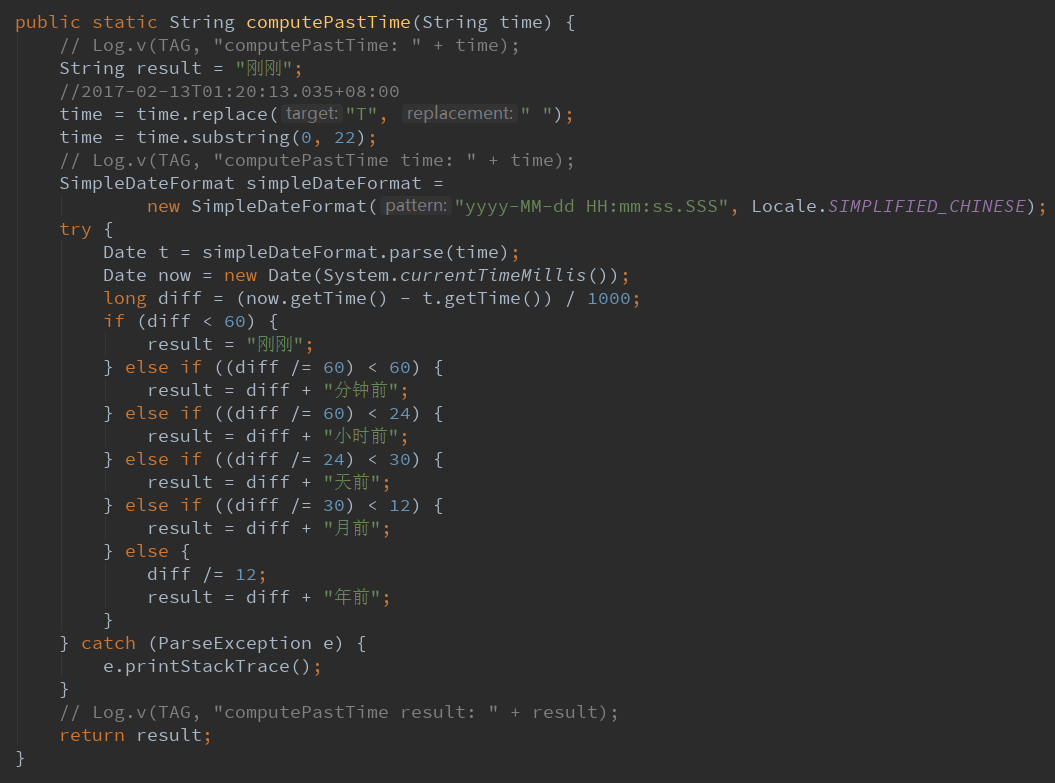
服务器返回的时间一般是一个字符串,如:2017-02-13T01:20:13.035+08:00
然后我要解析这段字符串,首先将T变成空格,然后截取前22个字符即可
然后利用SimpleDataFormat转化一下想要的格式
然后将字符串转化为Date
然后比较Dta和当前的时间差
从小到大排序:刚刚、分钟前、小时前、天前、月前、年前。
2.1.格式化字符串time
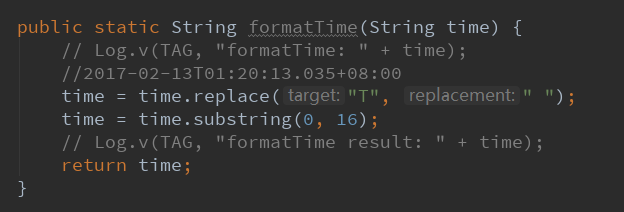
这个函数的作用也是解析一段字符串:2017-02-13T01:20:13.035+08:00
然后替换T为空格
然后截取前16个字符即可。
3.案例
3.1.写一个测试函数
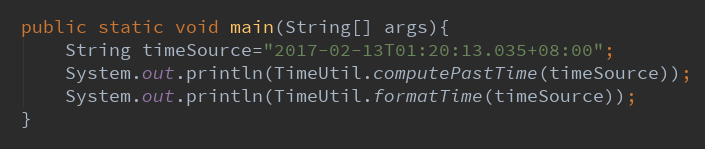
当前时间为:2017-11-28 16:15
3.2.执行结果
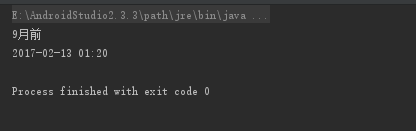
没问题,Over!
既然选择了,便不顾风雨兼程。Just follow yourself.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号