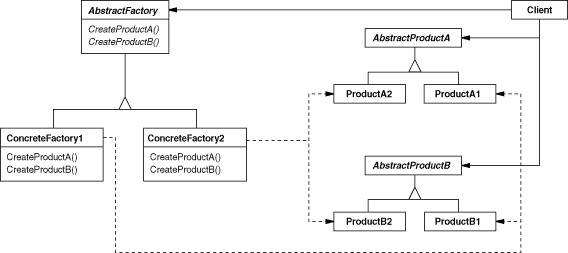
Abstract Factory:提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。
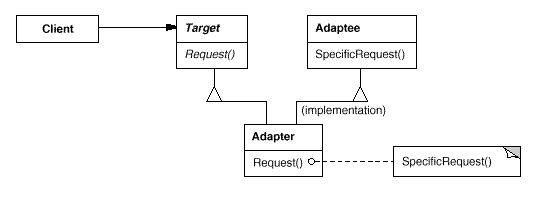
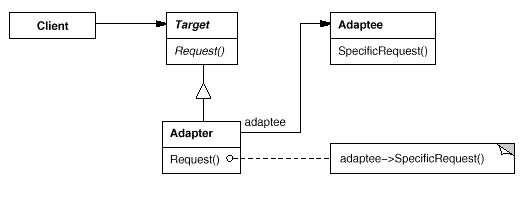
Adapter:将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口。Adapter模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。
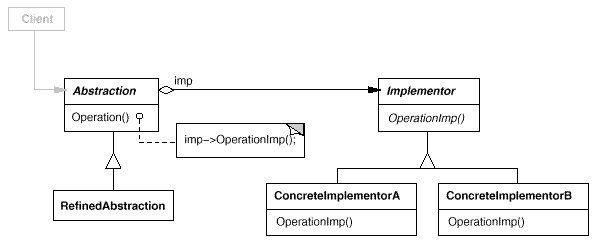
Bridge:将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。
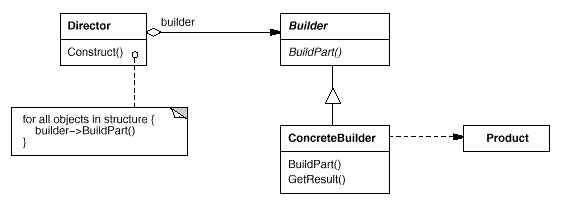
Builder:将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
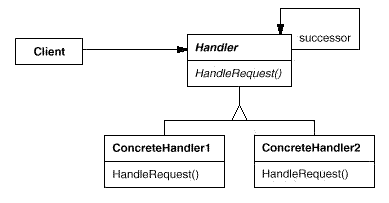
Chain of Responsibility:为解除请求的发送者和接收者之间耦合,而使多个对象都有机会处理这个请求。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象
处理它。
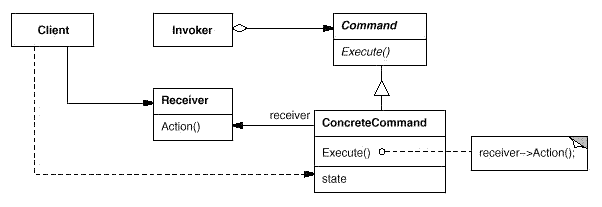
Command:将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可取消的操作。
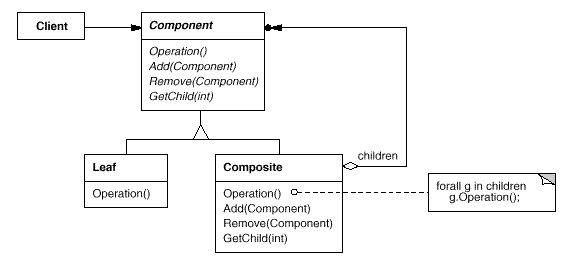
Composite:将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分 -整体”的层次结构。Composite使得客户对单个对象和复合对象的使用具有一致性。
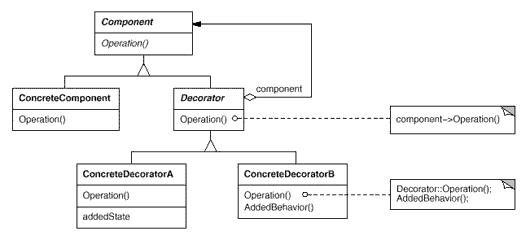
Decorator:动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就扩展功能而言,Decorator模式比生成子类方式更为灵活。
Facade:为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,Facade模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
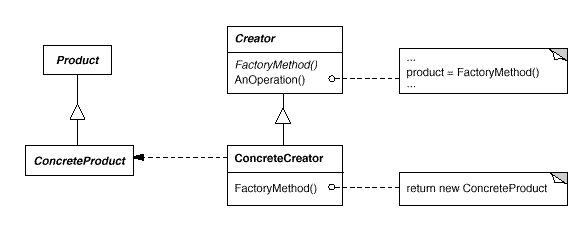
Factory Method:定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定将哪一个类实例化。Factory Method使一个类的实例化延迟到其子类。
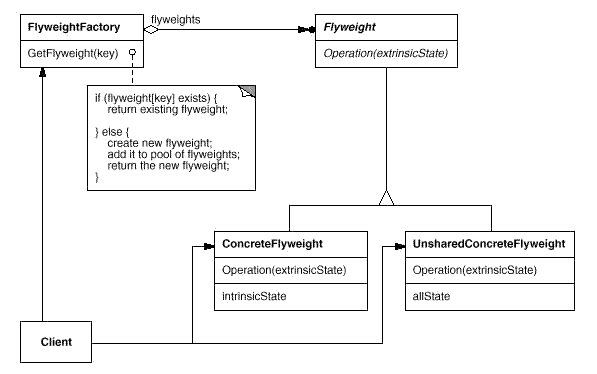
Flyweight:运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
Interpreter:给定一个语言, 定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,该解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
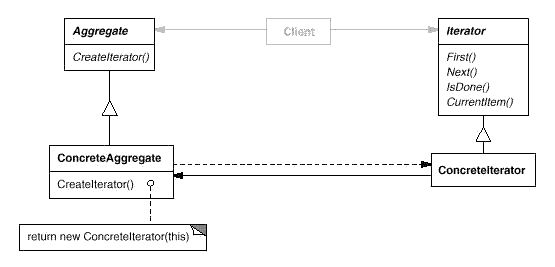
Iterator:提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素 , 而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
Mediator:用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互。中介者使各对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使其耦合松散,而且可以独立地改变它们之间的交互。
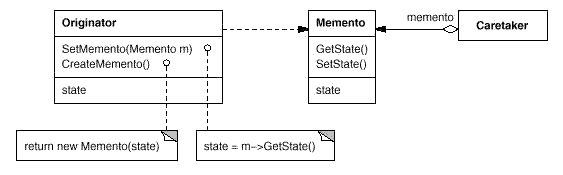
Memento:在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可将该对象恢复到保存的状态。
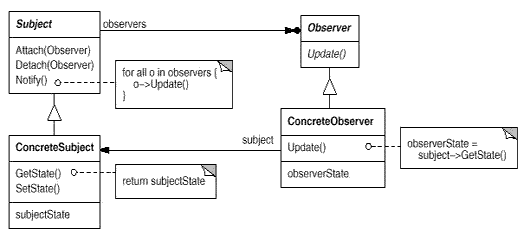
Observer:定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,以便当一个对象的状态发生改变时,
所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并自动刷新。
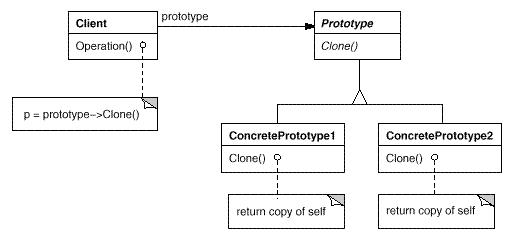
Prototype:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这个原型来创建新的对象。
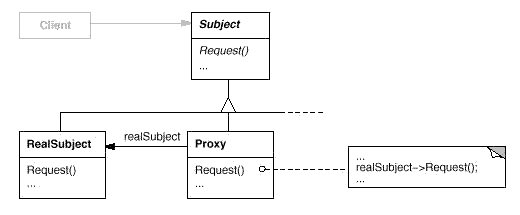
Proxy:为其他对象提供一个代理以控制对这个对象的访问。
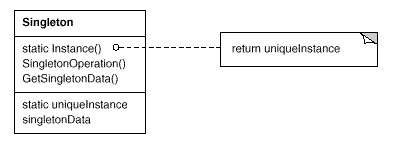
Singleton:保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点。
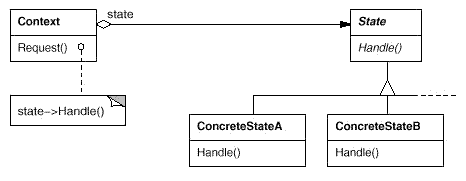
State:允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。对象看起来似乎修改了它所属的类。
Strategy:定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来, 并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法的变化可独立于使用它的客户。
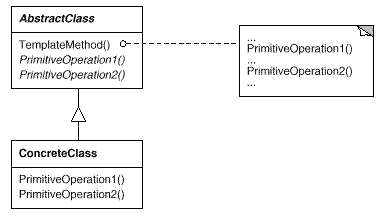
Template Method:定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。Template Method使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
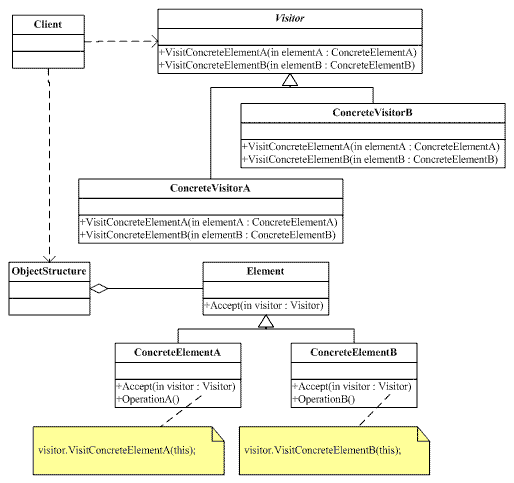
Visitor:表示一个作用于某对象结构中的各元素的操作。它使你可以在不改变各元素的类的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新操作。
/* factory method
/* note: concrete factory A can only create concrete product A
/************************************************************************/
#include "stdio.h"
/************************************************************************/
/* abstract product
/************************************************************************/
class Product
{
};
/************************************************************************/
/* series of concrete products
/************************************************************************/
class ConcreateProductA : public Product
{
};
class ConcreateProductB : public Product
{
};
class ConcreateProductC : public Product
{
};
/************************************************************************/
/* abstract factory
/************************************************************************/
class Factory
{
public:
virtual Product *CreateProduct() = 0;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* series of concrete factories - creating corresponding series of concrete products
/************************************************************************/
class ConcreateFactoryA : public Factory
{
virtual Product *CreateProduct() { return new ConcreateProductA(); }
};
class ConcreateFactoryB : public Factory
{
virtual Product *CreateProduct() { return new ConcreateProductB(); }
};
class ConcreateFactoryC : public Factory
{
virtual Product *CreateProduct() { return new ConcreateProductC(); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
Factory *pA = new ConcreateFactoryA();
pA->CreateProduct();
Factory *pB = new ConcreateFactoryB();
pB->CreateProduct();
Factory *pC = new ConcreateFactoryC();
pC->CreateProduct();
}
/* factory method
/* note: concrete factory A can only create concrete product A
/************************************************************************/
#include "stdio.h"
/************************************************************************/
/* abstract product
/************************************************************************/
class Product
{
};
/************************************************************************/
/* series of concrete products
/************************************************************************/
class ConcreateProductA : public Product
{
};
class ConcreateProductB : public Product
{
};
class ConcreateProductC : public Product
{
};
/************************************************************************/
/* abstract factory
/************************************************************************/
class Factory
{
public:
void Operation() { Product *p = CreateProduct(); }
protected:
virtual Product *CreateProduct() = 0;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* series of concrete factories - creating corresponding series of concrete products
/************************************************************************/
class ConcreateFactoryA : public Factory
{
protected:
virtual Product *CreateProduct() { return new ConcreateProductA(); }
};
class ConcreateFactoryB : public Factory
{
protected:
virtual Product *CreateProduct() { return new ConcreateProductB(); }
};
class ConcreateFactoryC : public Factory
{
protected:
virtual Product *CreateProduct() { return new ConcreateProductC(); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
Factory *pA = new ConcreateFactoryA();
pA->Operation();
Factory *pB = new ConcreateFactoryB();
pB->Operation();
Factory *pC = new ConcreateFactoryC();
pC->Operation();
}
/************************************************************************/
/* Singleton */
/************************************************************************/
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton* Instance()
{
if (NULL == m_pInstance)
{
m_pInstance = new Singleton();
}
return m_pInstance;
}
protected:
Singleton() {};
private:
static Singleton* m_pInstance;
};
Singleton* Singleton::m_pInstance = NULL;
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
Singleton *p1 = Singleton::Instance();
Singleton *p2 = Singleton::Instance();
if (p1 == p2)
{
printf("same instance %p\n", p1);
}
}
/* abstract factory
/* note: concrete factory1 can create concrete product1 for all product families
/************************************************************************/
#include "stdio.h"
/************************************************************************/
/* product families
/************************************************************************/
class ProductA /* family A */
{
};
class ProductB /* family B */
{
};
class ProductC /* family C */
{
};
/************************************************************************/
/* series of concrete products
/************************************************************************/
class ConcreateProductA1 : public ProductA { };
class ConcreateProductA2 : public ProductA { };
class ConcreateProductB1 : public ProductB { };
class ConcreateProductB2 : public ProductB { };
class ConcreateProductC1 : public ProductC { };
class ConcreateProductC2 : public ProductC { };
/************************************************************************/
/* abstract factory
/************************************************************************/
class Factory
{
public:
virtual ProductA *CreateProductA() = 0;
virtual ProductB *CreateProductB() = 0;
virtual ProductC *CreateProductC() = 0;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* series of concrete factories - creating corresponding series of concrete products
/* # of concrete factory equal to # of one of a kind of product family.
/************************************************************************/
class ConcreateFactory1 : public Factory
{
public:
virtual ProductA *CreateProductA() { printf("factory 1 produces product A1\n"); return new ConcreateProductA1(); }
virtual ProductB *CreateProductB() { printf("factory 1 produces product B1\n"); return new ConcreateProductB1(); }
virtual ProductC *CreateProductC() { printf("factory 1 produces product C1\n"); return new ConcreateProductC1(); }
};
class ConcreateFactory2 : public Factory
{
public:
virtual ProductA *CreateProductA() { printf("factory 2 produces product A2\n"); return new ConcreateProductA2(); }
virtual ProductB *CreateProductB() { printf("factory 2 produces product B2\n"); return new ConcreateProductB2(); }
virtual ProductC *CreateProductC() { printf("factory 2 produces product C2\n"); return new ConcreateProductC2(); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
ProductA *pA = NULL;
ProductB *pB = NULL;
ProductC *pC = NULL;
Factory *pFactory1 = NULL;
Factory *pFactory2 = NULL;
pFactory1 = new ConcreateFactory1(); pA = pFactory1->CreateProductA(); /* factory 1 to produce product A1*/
pFactory2 = new ConcreateFactory2(); pA = pFactory2->CreateProductA(); /* factory 2 to produce product A2*/
pFactory1 = new ConcreateFactory1(); pB = pFactory1->CreateProductB(); /* factory 1 to produce product B1*/
pFactory2 = new ConcreateFactory2(); pB = pFactory2->CreateProductB(); /* factory 2 to produce product B2*/
pFactory1 = new ConcreateFactory1(); pC = pFactory1->CreateProductC(); /* factory 1 to produce product C1*/
pFactory2 = new ConcreateFactory2(); pC = pFactory2->CreateProductC(); /* factory 2 to produce product C2*/
}
/* Adaper pattern be used when interfaces differ in parameters,
/* but similar in function. Study this by comparing with Proxy pattern.
/************************************************************************/
#include "stdio.h"
/************************************************************************/
/* Target - contain interfaces for applications */
/************************************************************************/
class Compute
{
public:
virtual int Add(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual int Sub(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual int Mul(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual int Div(int x, int y) = 0;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Adaptee - contain interfaces which are functionally similar
/* to those in Target, but parameters are inconsistent
/************************************************************************/
class ExistedCompute
{
public:
int Add(int x, int y, int *p) { if(NULL == p) return x + y; else return 0;}
int Sub(int x, int y, int *p) { if(NULL == p) return x - y; else return 0;}
int Mul(int x, int y, int *p) { if(NULL == p) return x * y; else return 0;}
int Div(int x, int y, int *p) { if(NULL == p) return x / y; else return 0;}
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Adapter */
/************************************************************************/
class DerivedCompute : public Compute
{
public:
int Add(int x, int y) { return m_pExistedCompute->Add(x, y, NULL); }
int Sub(int x, int y) { return m_pExistedCompute->Sub(x, y, NULL); }
int Mul(int x, int y) { return m_pExistedCompute->Mul(x, y, NULL); }
int Div(int x, int y) { return m_pExistedCompute->Div(x, y, NULL); }
/* this func adapter to Target */ /* this func adapter to Adaptee */
public:
DerivedCompute(ExistedCompute *pExistedCompute) { m_pExistedCompute = pExistedCompute; }
private:
ExistedCompute *m_pExistedCompute;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
Compute *pCompute = new DerivedCompute(new ExistedCompute());
printf("Add(%d + %d) = %d\n", 10, 20, pCompute->Add(10, 20));
printf("Sub(%d - %d) = %d\n", 10, 20, pCompute->Sub(10, 20));
printf("Mul(%d * %d) = %d\n", 10, 20, pCompute->Mul(10, 20));
printf("Div(%d / %d) = %d\n", 30, 20, pCompute->Div(30, 20));
}
/************************************************************************/
/* ICompute - real & proxy class's common interface class, pure virtual
/* functions to sure that both class get consistent interfaces
/************************************************************************/
class ICompute
{
public:
virtual int Add(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual int Sub(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual int Mul(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual int Div(int x, int y) = 0;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* RealCompute - remote */
/************************************************************************/
class RealCompute : public ICompute
{
public:
int Add(int x, int y) { printf("computing...\n"); return x + y; }
int Sub(int x, int y) { printf("computing...\n"); return x - y; }
int Mul(int x, int y) { printf("computing...\n"); return x * y; }
int Div(int x, int y) { printf("computing...\n"); return x / y; }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* ProxyCompute - local */
/************************************************************************/
class ProxyCompute : public ICompute
{
public:
int Add(int x, int y) { ConnectServer(); return m_pRealCompute->Add(x, y); }
int Sub(int x, int y) { ConnectServer(); return m_pRealCompute->Sub(x, y); }
int Mul(int x, int y) { ConnectServer(); return m_pRealCompute->Mul(x, y); }
int Div(int x, int y) { ConnectServer(); return m_pRealCompute->Div(x, y); }
public:
ProxyCompute(RealCompute *pRealCompute) { m_pRealCompute = pRealCompute; }
private:
RealCompute *m_pRealCompute;
void ConnectServer() { printf("connecting server...\n"); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
ProxyCompute proxyCompute(new RealCompute());
printf("Add(%d + %d) = %d\n", 10, 20, proxyCompute.Add(10, 20));
printf("Sub(%d - %d) = %d\n", 10, 20, proxyCompute.Sub(10, 20));
printf("Mul(%d * %d) = %d\n", 10, 20, proxyCompute.Mul(10, 20));
printf("Div(%d / %d) = %d\n", 30, 20, proxyCompute.Div(30, 20));
}
/************************************************************************/
/* Base */
/************************************************************************/
class Base
{
public:
void toCompute() //某种算法, 封装在基类中
{
this->step1();
this->step2();
this->step3();
}
private:
virtual void step1() = 0;
virtual void step2() = 0;
virtual void step3() = 0;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Derived1 */
/************************************************************************/
class Derived1 : public Base
{
private:
void step1() { printf("Derived1::step1()\n"); }
void step2() { printf("Derived1::step2()\n"); }
void step3() { printf("Derived1::step3()\n"); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Derived2 */
/************************************************************************/
class Derived2 : public Base
{
private:
void step1() { printf("Derived2::step1()\n"); }
void step2() { printf("Derived2::step2()\n"); }
void step3() { printf("Derived2::step3()\n"); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Derived3 */
/************************************************************************/
class Derived3 : public Base
{
private:
void step1() { printf("Derived3::step1()\n"); }
void step2() { printf("Derived3::step2()\n"); }
void step3() { printf("Derived3::step3()\n"); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
Base *pBase[3] = { new Derived1(), new Derived2(), new Derived3() };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
pBase[i]->toCompute();
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/* Base */
/************************************************************************/
class Base
{
public:
virtual void step1() = 0;
virtual void step2() = 0;
virtual void step3() = 0;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Derived1 */
/************************************************************************/
class Derived1 : public Base
{
public:
void step1() { printf("Derived1::step1()\n"); }
void step2() { printf("Derived1::step2()\n"); }
void step3() { printf("Derived1::step3()\n"); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Derived2 */
/************************************************************************/
class Derived2 : public Base
{
public:
void step1() { printf("Derived2::step1()\n"); }
void step2() { printf("Derived2::step2()\n"); }
void step3() { printf("Derived2::step3()\n"); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Derived3 */
/************************************************************************/
class Derived3 : public Base
{
public:
void step1() { printf("Derived3::step1()\n"); }
void step2() { printf("Derived3::step2()\n"); }
void step3() { printf("Derived3::step3()\n"); }
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Context */
/************************************************************************/
class Context
{
public:
Context(Base *pBase) : m_pBase(pBase) { }
~Context() { if (m_pBase) delete m_pBase; }
void toCompute() //某种算法, 封装在另一个类中
{
m_pBase->step1();
m_pBase->step2();
m_pBase->step3();
}
protected:
private:
Base *m_pBase;
};
/************************************************************************/
/* Client */
/************************************************************************/
void main()
{
Base *pBase[3] = { new Derived1(), new Derived2(), new Derived3() };
Context *pContext[3] = { new Context(pBase[0]), new Context(pBase[1]), new Context(pBase[2]) };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
pContext[i]->toCompute();
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号