@Component
public class A {
@Transactional
public void addA() {
System.out.println("事务中的方法");
}
}
A类中有一个AddA方法,加了Spring事务标签,当调用这个方法时,会调用类CglibAopProxy中的内部类DynamicAdvisedInterceptor中的intercept()方法,其定义如下:intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy), 在这个方法中会调用下面的方法得到一个chain,对于addA()方法,只返回一个TransactionInterceptor : [org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor@ff89622],然后再new 一个CglibMethodInvocation对象,
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); ,
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed 方法: 一个个调用Intercepter
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// 事务会调这里:It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice 对象为 TransactionInterceptor@ff89622,所以会调它的invoke方法,invoke 方法,主要是调用:
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed); ---这个方法是在TransactionAspectSupport里定义的
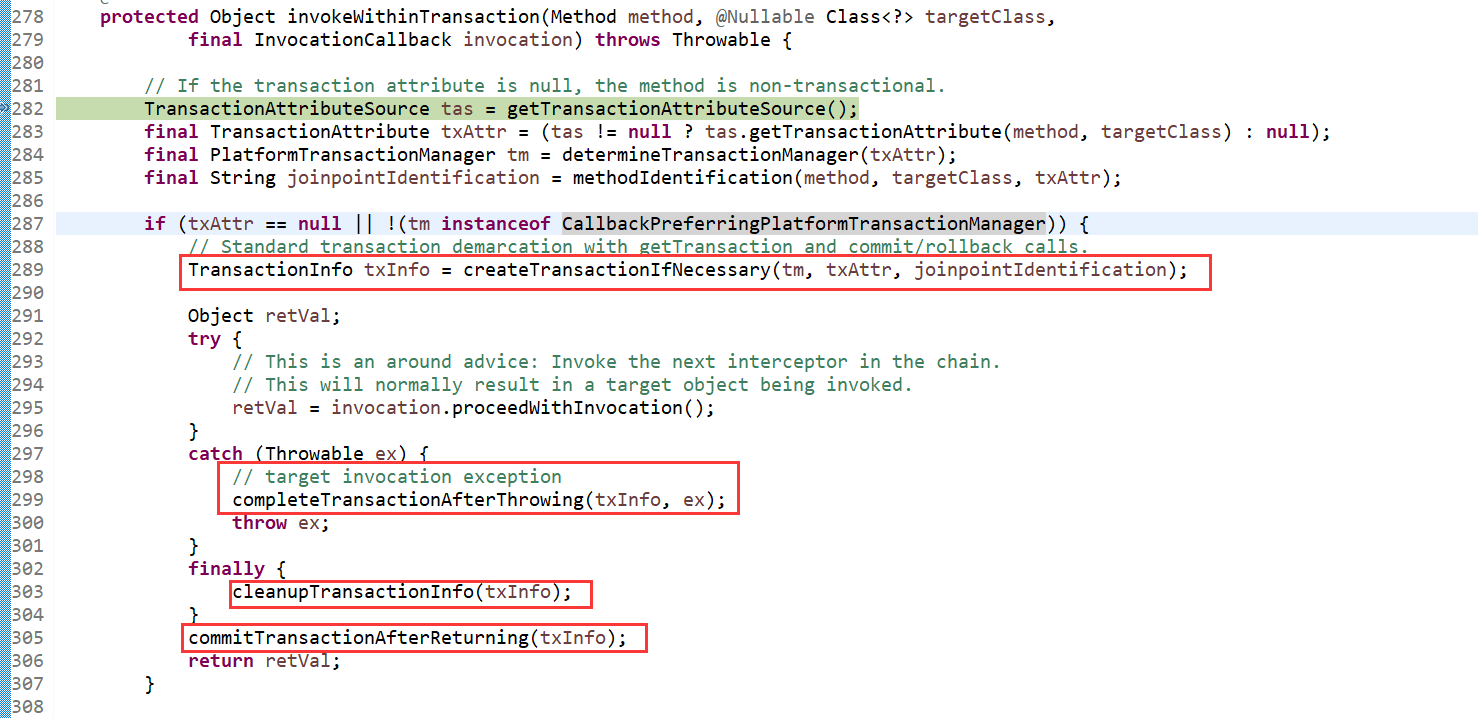
createTransactionIfNecessary方法中最主要是getTransaction(), 这个方法的注解:
Return a currently active transaction or create a new one, according to the specified propagation behavior.

getTransaction() 方法是属于类JPATransactionManager的,其调用的抽象类AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的实现,其代码如下:
/**
* This implementation handles propagation behavior. Delegates to
* {@code doGetTransaction}, {@code isExistingTransaction}
* and {@code doBegin}.
* @see #doGetTransaction
* @see #isExistingTransaction
* @see #doBegin
*/
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
// 1. 先解释第一个方法 doGetTransaction,调用了JpaTransactionManager的doGetTransaction() ,从ThreadLocal 得到两个变量,一个是EntityManagerHolder ,
//另一个是ConnectionHolder
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
}
//2. 如果这个事务是存在,则需要处理
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
// --handleExistingTransaction方法在AbstractPlatformTransactionManager 这个类中
return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled); } // Check definition settings for new transaction. if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout()); } // No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
//如果是事务必须存在于一个已经在的事务中,则抛出异常, 因为如果存在事务,会在上面的代码返回
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
//如果是第一次进来,挂起返回Null
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition);
}
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
//创建事务状态对象,其实就是封装了事务对象的一些信息,记录事务状态的
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
//这个方法会开启一个事务
doBegin(transaction, definition);
//开启事务后,改变事务状态
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + definition);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
a. 先解释第一个方法 doGetTransaction,调用了JpaTransactionManager的doGetTransaction() ,从ThreadLocal 得到两个变量,一个是EntityManagerHolder , 另一个是ConnectionHolder 。
protected Object doGetTransaction() { JpaTransactionObject txObject = new JpaTransactionObject(); txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed()); EntityManagerHolder emHolder = (EntityManagerHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainEntityManagerFactory()); if (emHolder != null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Found thread-bound EntityManager [" + emHolder.getEntityManager() + "] for JPA transaction"); } txObject.setEntityManagerHolder(emHolder, false); } if (getDataSource() != null) { ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(getDataSource()); txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder); } return txObject; }
在 TransactionSynchronizationManager类中TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource方法,可以看到ConnectionHolder 是从ThreadLocal里获取的,也就是当前线程;但是仔细思考下我们是第一次进来,所以这里肯定获取不到的,反之,要从这里获取到值,那必然是同一个线程第二次及以后进入到这里
Key: org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean@45a1915d
Value: org.springframework.orm.jpa.EntityManagerHolder@2a4715b-- getResource 返回的结果
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources = new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
继续往后,创建完transaction对象后,会调用isExistingTransaction判断是否已经存在一个事务,如果存在就会调用handleExistingTransaction方法,这个方法就是处理事务传播的核心方法,因为我们是第一次进来,肯定不存在事务,所以先跳过。
b.hasTransaction 是用entityManagerHolder的isTransactionActive()方法来判断的,如果不前事务开启了,就会把isTransactionActive设置为true
public boolean hasTransaction() {
return (this.entityManagerHolder != null && this.entityManagerHolder.isTransactionActive());
}
c. 处理已经存在的事务
/** * Create a TransactionStatus for an existing transaction. */ private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction( TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled) throws TransactionException { //1. never: 直接Throw 异常 if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) { throw new IllegalTransactionStateException( "Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'"); } //2. not-spport, 需要挂起当前的事务,返回一个prepareTransactionStatus if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Suspending current transaction"); } Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction); boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS); return prepareTransactionStatus( definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); } //3.require_new if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]"); } SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction); try { boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); doBegin(transaction, definition); prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) { resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx); throw beginEx; } } //4. nested if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) { if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) { throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException( "Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " + "specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'"); } if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]"); } if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) { // Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction, // through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus. // Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization. DefaultTransactionStatus status = prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null); status.createAndHoldSavepoint(); return status; } else { // Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls. // Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here // in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction. boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null); doBegin(transaction, definition); prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } } // Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED. if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction"); } if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) { if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) { Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(); if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) { Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants; throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" + definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " + (currentIsolationLevel != null ? isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) : "(unknown)")); } } if (!definition.isReadOnly()) { if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) { throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" + definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is"); } } } boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null); }
e. doBegin方法--JpaTransactionManager类
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
JpaTransactionObject txObject = (JpaTransactionObject) transaction;
if (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && !txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Pre-bound JDBC Connection found! JpaTransactionManager does not support " +
"running within DataSourceTransactionManager if told to manage the DataSource itself. " +
"It is recommended to use a single JpaTransactionManager for all transactions " +
"on a single DataSource, no matter whether JPA or JDBC access.");
}
try {
if (!txObject.hasEntityManagerHolder() ||
txObject.getEntityManagerHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
EntityManager newEm = createEntityManagerForTransaction();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Opened new EntityManager [" + newEm + "] for JPA transaction");
}
txObject.setEntityManagerHolder(new EntityManagerHolder(newEm), true);
}
EntityManager em = txObject.getEntityManagerHolder().getEntityManager();
// Delegate to JpaDialect for actual transaction begin.
final int timeoutToUse = determineTimeout(definition);
Object transactionData = getJpaDialect().beginTransaction(em,
new JpaTransactionDefinition(definition, timeoutToUse, txObject.isNewEntityManagerHolder()));
txObject.setTransactionData(transactionData);
// Register transaction timeout.
if (timeoutToUse != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getEntityManagerHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeoutToUse);
}
// Register the JPA EntityManager's JDBC Connection for the DataSource, if set.
if (getDataSource() != null) {
ConnectionHandle conHandle = getJpaDialect().getJdbcConnection(em, definition.isReadOnly());
if (conHandle != null) {
ConnectionHolder conHolder = new ConnectionHolder(conHandle);
if (timeoutToUse != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
conHolder.setTimeoutInSeconds(timeoutToUse);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Exposing JPA transaction as JDBC [" + conHandle + "]");
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getDataSource(), conHolder);
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Not exposing JPA transaction [" + em + "] as JDBC transaction because " +
"JpaDialect [" + getJpaDialect() + "] does not support JDBC Connection retrieval");
}
}
}
// Bind the entity manager holder to the thread.
if (txObject.isNewEntityManagerHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(
obtainEntityManagerFactory(), txObject.getEntityManagerHolder());
}
txObject.getEntityManagerHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
closeEntityManagerAfterFailedBegin(txObject);
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
closeEntityManagerAfterFailedBegin(txObject);
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JPA EntityManager for transaction", ex);
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号