异或线性基学习笔记
模拟赛考到了,还是板子,但不会,我有抑郁症。
1 基本定义及性质
对于一个集合 \(S\),异或线性基是一个最小的集合 \(S'\),满足:
- 定义 \(f(S)\) 为 \(S\) 的任意非空的子集异或和的所有可能值所形成的集合,则 \(f(S) = f(S')\)。
\(S'\) 满足以下性质:
- 原序列的任意一个数都可以由线性基内部的一些数异或得到。
- 线性基内部的任意数异或起来都不能得到 \(0\)。
- 线性基内部的数个数唯一,且在保持性质一的前提下,数的个数是最少的。
证明就不讲了,可以去看洛谷日报。
下面的部分涉及后面的内容。
对于线性基还有一个神秘结论:对于任意两个个数 \(x, y\) 和一个线性基 \(S\),记 \(h(S)\) 为 \(S\) 中所有数的异或和,\(\oplus\) 为异或操作,\(g(x)\) 为 \(\max_{S' \in S}\{h(S') \oplus x\}\),\(g'(x)\) 为 \(\min_{S' \in S}\{h(S') \oplus x\}\),则 \(g(x \oplus y) = g(x) \oplus g'(y)\)。
证明:考虑每一个线性基 \(S\) 都可以通过类似高斯消元的方法,使其变成一个等价的线性基 \(S'\),满足:
- \(S'\) 每一个数的最高位,在其它数中对应位是 \(0\)。
这样对于初始的数,异或每一个数,都不会对其它数是否被异或没有影响,可以将每个数视作是独立的。
再考虑插入数的过程,对于某一位,若 \(S'\) 中没有一个数使得其最高位是它,则答案不受它影响,我们只考虑其它位。
设两个数的当前位为 \(x', y'\),\(S'\) 中最高位为这一位的数为 \(b\),分类讨论:
- \(x' = y' = 0\),则 \(x' \oplus y' = 0\),则在计算的时候 \(g(x \oplus y), g(x)\) 都会异或 \(b\),对应 \(b = b \oplus 0\);
- \(x' = 0, y' = 1\),则 \(x' \oplus y' = 1\),则在计算的时候 \(g(x), g'(y)\) 都会异或 \(b\),对应 \(0 = b \oplus b\);
- \(x' = 1, y' = 0\),则 \(x' \oplus y' = 1\),则在计算的时候三个函数都不会异或 \(b\),对应 \(0 = 0 \oplus 0\);
- \(x' = y' = 1\),则 \(x' \oplus y' = 0\),则在计算的时候 \(g(x \oplus y), g'(y)\) 都会异或 \(b\),对应 \(b = 0 \oplus b\)。
注意到对于任意的 \(x', y'\),\(g(x \oplus y)\) 会异或 \((\lnot(x' \oplus y')) \cdot b\),\(g(x)\) 会异或 \((\lnot x') \cdot b\),\(g(y)\) 会异或 \(y' \cdot b\)。而:
\[(\lnot(x' \oplus y')) \cdot b = ((\lnot x') \cdot b) \oplus (y' \cdot b) \]在 \(b \not = 0\) 时当且仅当:
\[\lnot(x' \oplus y') = (\lnot x') \oplus y' \]上式显然成立,所以原命题成立。
2 基本操作
异或线性基的最高位互不相同,所以可以有以下的操作。
2.1 插入
考虑从高位向低位插入,如果这个位置上没有数,就插入,否则强制让这一位置零(就是异或 \(d_i\),以保证插入后线性基性质),再向更低一位尝试。
若无法插入,说明线性基内已有子集的异或和为当前插入的数,说明插入后线性基内有子集元素异或和为 \(0\),标记即可。
void Add(ll x) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1ll) {
if(!d[i]) {
d[i] = x;
return ;
}
x ^= d[i];
}
}
p0 = true;
}
2.2 查询异或最大值
从高位向低位贪心即可。
ll Query_Max() {
ll res = 0, i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((res ^ d[i]) > res) {
res ^= d[i];
}
}
return res;
}
对于初值为 \(x\) 的异或最大值,只需将 res 的初值设置为 \(x\) 即可。
2.3 查询异或最小值
考虑线性基内最小的 \(d_i\),它与其他元素异或的值一定大于它本身,证明显然。
所以只需判断能否产生 \(0\) 即可。
ll Query_Min() {
ll i;
if(p0) {
return 0;
}
for(i = 0; i <= 62; i++) {
if(d[i]) {
return d[i];
}
}
}
2.4 查询是否在线性基内
因为线性基的最高位互不相同,充分理解后就可以轻松得到以下代码。
bool Count(ll x) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1) {
x ^= d[i];
}
}
return x == 0;
}
2.5 合并线性基
暴力合并即可。
friend Base operator +(Base x, Base y) {
int i;
Base res = x;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if(y.d[i]) {
res.Add(y.d[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
2.6 查询第 \(K\) 小
根据线性基的性质,含有线性基内最高位为 \(2^k\) 的数(设这个数为 \(x\))的集合中,集合异或和小于 \(2^{k + 1}\) 且不为 \(0\) 的数恰有 \(2^{k + 1} - 1\) 个(此时线性基内小于等于 \(x\) 的数恰有 \(k + 1\) 个,其非空子集恰有 \(2^{k + 1} - 1\) 个)。
可以从高位到低位枚举,注意特判 \(0\) 的情况,具体见代码。
ll Query_kth(ll x) {
if(p0) {
x--;
}
ll i, res = 0;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1) {
res ^= d[i];
}
}
return res;
}
2.7 完整代码
综上所述,我们可以得到以下代码:
struct Base {
ll d[65];
bool p0;
void Add(ll x) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1ll) {
if(!d[i]) {
d[i] = x;
return ;
}
x ^= d[i];
}
}
p0 = true;
}
ll Query_Max() {
ll res = 0, i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((res ^ d[i]) > res) {
res ^= d[i];
}
}
return res;
}
ll Query_Min() {
ll i;
if(p0) {
return 0;
}
for(i = 0; i <= 62; i++) {
if(d[i]) {
return d[i];
}
}
}
bool Count(ll x) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1) {
x ^= d[i];
}
}
return x == 0;
}
friend Base operator +(Base x, Base y) {
int i;
Base res = x;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if(y.d[i]) {
res.Add(y.d[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
ll Query_kth(ll x) {
if(p0) {
x--;
}
ll i, res = 0;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1) {
res ^= d[i];
}
}
return res;
}
};
3 进阶版——带删除线性基
不会在线的,只能讲讲离线的。
3.1 原理
其实很简单,对于每个线性基内的数,记录一个被删除时间 \(t\) 即可。
3.2 插入
增加参数 \(t'\),表示插入元素的被删除时间,当查找到当前位时,贪心的考虑,若 \(t' > t\),那么保留原来的元素一定是不优的,因为插入的更晚删去,将已经在线性基内的元素作为待插入的元素,插入的元素成为新线性基内的元素之一,并更新被删去的时间。
void Add(ll x, int tim) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1ll) {
if(t[i] < tim) {
swap(t[i], tim), swap(x, d[i]);
}
if(!t[i]) {
return ;
}
x ^= d[i];
}
}
p0 = true;
}
3.3 查询最大值
增加参数 \(t'\),然后对 \(t \le t'\) 的情况特判。
ll Query_Max(int tim) {
ll res = 0, i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if(tim < t[i] && (res ^ d[i]) > res) {
res ^= d[i];
}
}
return res;
}
4 例题
4.1 就是模拟赛那道题
给定一个序列,长度为 \(N\),有权值 \(\{t_i\}\) 与价值 \(\{p_i\}\),要求选出一个连续子序列,满足价值和小于一个给定的数 \(K\),再在子序列中取出任意个元素(个数不为 \(0\)),最大化权值的异或和。
可令每个元素的删除时间为其下标,查询时以满足条件的最左端点的下标为 \(t'\) 进行查询,然后相当于板子,直接套即可。
可使用双指针维护左端点,复杂度 \(O(N \log V)\),\(V\) 为值域大小。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll Read() {
int sig = 1;
ll num = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) {
if(c == '-') {
sig = -1;
}
c = getchar();
}
while(isdigit(c)) {
num = (num << 3) + (num << 1) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return num * sig;
}
void Write(ll x) {
if(x < 0) {
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x >= 10) {
Write(x / 10);
}
putchar((x % 10) ^ 48);
}
struct Base {
int t[65];
ll d[65];
bool p0;
void Add(ll x, int tim) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1ll) {
if(t[i] < tim) {
swap(t[i], tim), swap(x, d[i]);
}
if(!t[i]) {
return ;
}
x ^= d[i];
}
}
p0 = true;
}
ll Query_Max(int tim) {
ll res = 0, i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if(tim <= t[i] && (res ^ d[i]) > res) {
res ^= d[i];
}
}
return res;
}
}b;
const int N = 100005;
struct tNode {
ll p, t;
}a[N];
int main() {
int i, j, n = Read();
ll k = Read();
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i].t = Read(), a[i].p = Read();
}
ll sum = 0, ans = 0;
for(i = 1, j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
sum += a[j].p;
b.Add(a[j].t, j);
while(sum > k) {
sum -= a[i++].p;
}
ans = max(ans, b.Query_Max(i));
}
Write(ans);
return 0;
}
4.2 [WC2011] 最大 XOR 和路径
题目链接
考虑结点 \(1\) 到结点 \(N\) 的路径唯一,且图无环的情况:
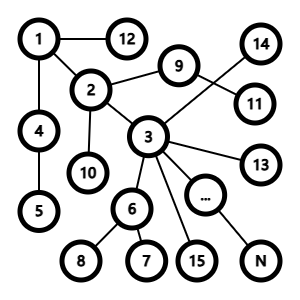
此时答案显然。
考虑添加一些环,与路径不交(如红边所示):
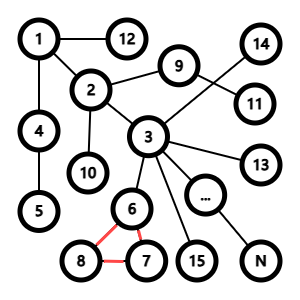
考虑这个环怎么贡献到答案内,只需经过两次绿边,按箭头所示走即可,此时绿边不会统计到答案内。
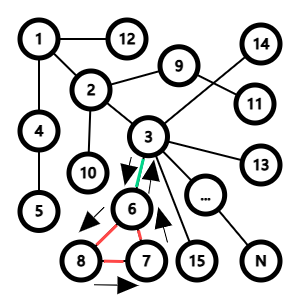
考虑当环与原路径相交时,即结点 \(1\) 到结点 \(N\) 的路径不唯一时怎么做:
遍历整个图,当遇到已遍历的结点时将这个环统计进答案,可以证明每个环的异或和都可以由若干个这样的环异或和再异或得到。
答案即为链的路径异或和与若干个环异或和异或的最大值,使用线性基即可。
原路径可以为任意路径,具体见代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll Read() {
int sig = 1;
ll num = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) {
if(c == '-') {
sig = -1;
}
c = getchar();
}
while(isdigit(c)) {
num = (num << 3) + (num << 1) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return num * sig;
}
void Write(ll x) {
if(x < 0) {
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x >= 10) {
Write(x / 10);
}
putchar((x % 10) ^ 48);
}
const int N = 100005;
struct Edge {
int to, nxt;
ll w;
}e[N << 1];
int n, head[N], cntedge;
void Add_Edge(int u, int v, ll w) {
e[++cntedge] = {v, head[u], w};
head[u] = cntedge;
}
bool vis[N];
struct Base {
ll d[65];
bool p0;
void Add(ll x) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1ll) {
if(!d[i]) {
d[i] = x;
return ;
}
x ^= d[i];
}
}
p0 = true;
}
ll Query_Max(ll x) {
ll res = x, i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((res ^ d[i]) > res) {
res ^= d[i];
}
}
return res;
}
ll Query_Min() {
ll i;
if(p0) {
return 0;
}
for(i = 0; i <= 62; i++) {
if(d[i]) {
return d[i];
}
}
}
bool Count(ll x) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1) {
x ^= d[i];
}
}
return x == 0;
}
friend Base operator +(Base x, Base y) {
int i;
Base res = x;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if(y.d[i]) {
res.Add(y.d[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
}b;
ll xorsum[N];
void Dfs(int u, ll cur) {
xorsum[u] = cur, vis[u] = true;
int i;
for(i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt) {
int v = e[i].to;
ll w = e[i].w;
if(vis[v]) {
b.Add(cur ^ w ^ xorsum[v]);
}
else {
Dfs(v, cur ^ w);
}
}
}
int main() {
int m;
n = Read(), m = Read();
while(m--) {
int u = Read(), v = Read();
ll w = Read();
Add_Edge(u, v, w), Add_Edge(v, u, w);
}
Dfs(1, 0);
Write(b.Query_Max(xorsum[n]));
return 0;
}
4.2.1 [WC2011] 最大 XOR 和路径加强版
令原问题起点为 \(s\),终点为 \(t\) 的答案为 \(f(s, t)\),给定 \(l, r\),求 \(\sum_{l \le x < y \le r} f(x, y)\)。
考虑上面的结论,然后可以预处理 \(1\) 号点到 \(i\) 号点的任意一个路径的异或和 \(xs_i\),然后将 \(g(xs_i)\) 与 \(g'(xs_i)\) 记为 \(a_i\) 与 \(b_i\),拆位考虑然后用前缀和随便搞一下就行了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
inline ll Read() {
int sig = 1;
ll num = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) { if(c == '-') sig = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(isdigit(c)) num = (num << 3) + (num << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar();
return num * sig;
}
void Write(__int128 x) {
if(x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;
if(x >= 10) Write(x / 10);
putchar((x % 10) ^ 48);
}
const int N = 100005;
int n, m;
bool vis[N];
vector<pair<int, ll> > e[N];
ll xs[N], as[62][N], bs[62][N], ans[62][N];
struct Base {
ll b[62];
void Insert(ll x) {
for(int i = 61; i >= 0; i--) if((x >> i) & 1) {
if(!b[i]) { b[i] = x; return ; }
else x ^= b[i];
}
}
ll Query_Max(ll x) { for(int i = 61; i >= 0; i--) if((x ^ b[i]) > x) x ^= b[i]; return x; }
ll Query_Min(ll x) { for(int i = 61; i >= 0; i--) if((x ^ b[i]) < x) x ^= b[i]; return x; }
}base;
void Dfs(int u, ll cxs) {
xs[u] = cxs, vis[u] = true;
for(auto p : e[u]) {
int v = p.first; ll w = p.second;
if(vis[v]) base.Insert(w ^ cxs ^ xs[v]);
else Dfs(v, cxs ^ w);
}
}
int main() {
int i, j, q; n = Read(), m = Read(), q = Read();
for(i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int u = Read(), v = Read(); ll w = Read(); e[u].emplace_back(v, w), e[v].emplace_back(u, w); }
Dfs(1, 0);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ll a = base.Query_Max(xs[i]), b = base.Query_Min(xs[i]);
for(j = 60; j >= 0; j--) as[j][i] = (a >> j) & 1, bs[j][i] = (b >> j) & 1;
}
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(j = 0; j <= 60; j++) {
ans[j][i] += ans[j][i - 1] + (as[j][i] ? (i - 1 - bs[j][i - 1]) : bs[j][i - 1]);
as[j][i] += as[j][i - 1], bs[j][i] += bs[j][i - 1];
}
while(q--) {
int l = Read(), r = Read();
__int128 res = 0;
for(i = 0; i <= 60; i++) res += ((__int128)(1ll << i)) * ((__int128)(ans[i][r] - ans[i][l - 1] - (as[i][r] - as[i][l - 1]) * (l - 1 - bs[i][l - 1]) - (r - l + 1 - as[i][r] + as[i][l - 1]) * bs[i][l - 1]));
Write(res), putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
4.3 DZY Loves Chinese II
题目链接
正常做很难,考虑人类智慧。
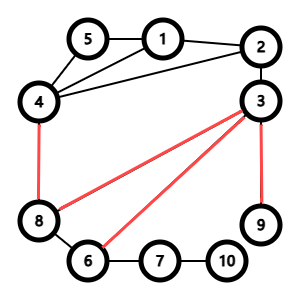
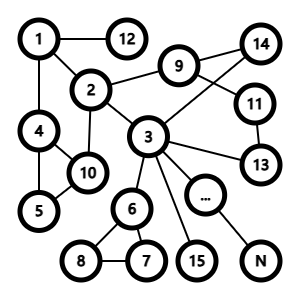
如图,如果想要把 \(S_1 = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}\) 和 \(S_2 = \{6, 7, 8, 9, 10\}\) 分开,就一定要把全部的红色边割掉,令这个边集为 \(E'(S_1, S_2)\),则给出的边集 \(C = \{c_1, c_2, \dots, c_k\}\) 要满足割掉后图不连通,则需满足,存在非空集 \(S \subset V\),使得 \(C \subseteq E'(S, V - S)\),其中 \(V\) 为原图点集。
若我们能给每个 \(E'\) 中的边赋一个边权,使得对于任意的非空集合 \(S \subset V\),设 \(E'(S, V - S)\) 的边权异或和为 \(f(S)\),则 \(f(S) = 0\)。
考虑如下构造:
- 对原图 \(G\) 随机一个生成树 \(T = \{V_T, E_T\}\)。
- 对所有的 \(e \not \in E_T\),\(w_e\) 为一随机权值。
- 遍历整棵树,对于 \(e \in E_T\),设 \(e = \{u, v\}\),且 \(u\) 是 \(v\) 的父亲,\(w_e\) 为端点为 \(v\) 的其它边的边权的异或和。
对于 \(|S| = 1\) 的情况,显然 \(f(S) = 0\)。
假设对于 \(|S| = k\) 有 \(f(S) = 0\),考虑加入一个新的点 \(v\),\(f(S \cup \{v\}) = f(S) \operatorname{xor} f(\{v\}) = 0\)(相当于 \(S\) 中所有与 \(v\) 的连边的边权被异或了两次,然后被抵消了)。
这样问题就转化为对于每个 \(C\),是否存在非空子集 \(C' \subseteq C\),使得 \(C'\) 中边权异或和为 \(0\),使用线性基即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
using namespace std;
ll Read() {
int sig = 1;
ll num = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) {
if(c == '-') {
sig = -1;
}
c = getchar();
}
while(isdigit(c)) {
num = (num << 3) + (num << 1) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return num * sig;
}
void Write(ll x) {
if(x < 0) {
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x >= 10) {
Write(x / 10);
}
putchar((x % 10) ^ 48);
}
const int N = 100005, M = 500005;
struct Base {
ull d[65];
bool p0;
void Init() {
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));
p0 = false;
}
void Add(ull x) {
ll i;
for(i = 63; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1ll) {
if(!d[i]) {
d[i] = x;
return ;
}
x ^= d[i];
}
}
p0 = true;
}
}b;
struct Edge {
int to, nxt;
bool is_tree;
ull w;
}e[M << 1];
int n, head[N], cntedge = 1;
void Add_Edge(int u, int v) {
e[++cntedge] = {v, head[u], 0ll, 0ll};
head[u] = cntedge;
}
bool vis[N];
void Dfs(int u) {
vis[u] = true;
int i;
for(i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt) {
int v = e[i].to;
if(vis[v]) {
continue;
}
e[i].is_tree = e[i ^ 1].is_tree = true;
Dfs(v);
}
}
ull xorw[N];
void Dfs2(int u) {
vis[u] = true;
int i;
for(i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt) {
int v = e[i].to;
if(vis[v] || !e[i].is_tree) {
continue;
}
Dfs2(v);
e[i].w = e[i ^ 1].w = xorw[v];
xorw[u] ^= xorw[v], xorw[v] = 0;
}
}
mt19937_64 rnd;
int main() {
rnd.seed(time(0));
int i, j, m;
n = Read(), m = Read();
for(i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int u = Read(), v = Read();
Add_Edge(u, v), Add_Edge(v, u);
}
Dfs(1);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(j = head[i]; j; j = e[j].nxt) {
if(!e[j].is_tree) {
e[j].w = e[j ^ 1].w = rnd();
}
}
}
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(j = head[i]; j; j = e[j].nxt) {
xorw[i] ^= e[j].w;
}
}
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
Dfs2(1);
int q = Read(), cnt = 0;
while(q--) {
int k = Read();
b.Init();
while(k--) {
int x = Read() ^ cnt;
b.Add(e[x * 2].w);
}
if(b.p0) {
printf("Disconnected\n");
}
else {
printf("Connected\n"), cnt++;
}
}
return 0;
}
4.4 玛里苟斯
题目链接
考虑对不同 \(k\) 分开处理。
- \(k = 1\)
考虑每一位对答案的贡献,可以证明对于二进制下的每一位,若一个数在该位的值为 \(0\),其对答案没有影响。
所以设 \(a\) 个数在该位的值为 \(1\),因为可以证明异或得到的数该位为 \(1\) 的方案数为:\[2^{n-a} \cdot\sum_{i=0}^{\lfloor\frac{a - 1}{2}\rfloor} \binom{a}{2 \times i + 1} = 2^{a-1} \cdot 2^{n-a} = 2^{n-1}. \]所以异或得到的数该位为 \(1\) 的概率为 \(\frac{2^{n - 1}}{2^n} = \frac{1}{2}\),因此若 \(a > 0\),该位是从低位往高位数第 \(x\) 位,则其对答案的贡献为 \(\frac{2^{x - 1}}{2} = 2^{x - 2}\)。
暴力统计即可。
- \(k = 2\)
令 \(f(x, i) = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{if }x\text{'s }i\text{-th digit (in binary) is }1 \\ 0 & \text{otherwise.} \end{cases}\),\(g(x, i) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{if }x\text{'s }i\text{-th digit (in binary) is }1 \\ 1 & \text{otherwise.} \end{cases}\)。
考虑二进制拆位后再平方,考虑从低位往高位数第 \(i\) 位与第 \(j\) 位的贡献,根据 \(k = 1\) 的结论有(下文的贡献系数指,若对答案的实际贡献为 \(x \cdot 2^{i + j - 1}\),其贡献系数为 \(x\)):
- 若 \(i = j\),且有数 \(x\) 满足 \(f(x, i) = 1\),则其对答案的贡献系数是 \(\frac{1}{2}\)。
- 若 \(i \not = j\),则:
- 若有两个数,使得有数 \(x\) 满足 \(f(x, i) \land f(x, j) = 1\):
- 若有数 \(y\) 满足 \((f(y, i) \land g(y, j)) \lor (f(y, j) \land g(y, i)) = 1\),\(x\) 与 \(y\) 异或后会有 \(\frac{1}{2}\) 的贡献系数;
- 否则会有 \(1\) 的贡献系数。
- 否则,若有两个数 \(x, y\) 使得 \((f(x, i) \land g(x, j)) \land (f(y, j) \land g(y, i)) = 1\),两数异或后会有 \(\frac{1}{2}\) 的贡献系数。
- 否则贡献系数为 \(0\)。
分类讨论即可。
- \(k \ge 3\)
注意到若有数 \(x\),则答案至少有 \(x^k\)。
因此由答案小于 \(2^{63}\),可得每个数小于 \(\sqrt[k]{2^{63}}\)。
当 \(k \ge 3\) 时,可得每个数小于 \(2^{21}\)。
将数插入线性基,暴搜即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll __int128
using namespace std;
ll Read() {
int sig = 1;
ll num = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) {
if(c == '-') {
sig = -1;
}
c = getchar();
}
while(isdigit(c)) {
num = (num << 3) + (num << 1) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return num * sig;
}
void Write(ll x) {
if(x < 0) {
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x >= 10) {
Write(x / 10);
}
putchar((x % 10) ^ 48);
}
struct Base {
ll d[65];
int cnt = 0;
void Add(ll x) {
ll i;
for(i = 62; i >= 0; i--) {
if((x >> i) & 1ll) {
if(!d[i]) {
d[i] = x;
cnt++;
return ;
}
x ^= d[i];
}
}
}
ll Dfs(int u, ll res, ll k) {
if(u < 0) {
return (k == 3) ? res * res * res : ((k == 4) ? res * res * res * res : res * res * res * res * res);
}
return d[u] ? (Dfs(u - 1, res, k) + Dfs(u - 1, res ^ d[u], k)) : Dfs(u - 1, res, k);
}
}b;
int n, k;
bool cnt[2][65][65], cnts[65];
int main() {
n = Read(), k = Read();
if(k == 1) {
ll ans = 0;
while(n--) {
ll a = Read();
ans |= a;
}
Write(ans / 2);
if(ans & 1) {
printf(".5");
}
return 0;
}
else if(k == 2) {
ll ans = 0, i, j;
while(n--) {
ll a = Read();
for(i = 0; i <= 63; i++) {
if((a >> i) & 1ll) {
for(j = 0; j <= 63; j++) {
cnt[(a >> j) & 1ll][i][j] = true;
}
cnts[i] = true;
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i <= 63; i++) {
for(j = i + 1; j <= 63; j++) {
ll w = 0;
if(cnt[1][i][j]) {
if(cnt[0][i][j] || cnt[0][j][i]) {
w = 1;
}
else {
w = 2;
}
}
if(cnt[0][i][j] && cnt[0][j][i]) {
w = 1;
}
ans += w * (1ll << (i + j));
}
if(cnts[i]) {
ans += (1ll << (2ll * i));
}
}
Write(ans / 2);
if(ans & 1) {
printf(".5");
}
return 0;
}
else {
while(n--) {
ll a = Read();
b.Add(a);
}
ll x = b.Dfs(22, 0, k);
Write(x / (1ll << b.cnt));
if((x / (1ll << (b.cnt - 1))) & 1) {
printf(".5");
}
return 0;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号