JAVA异常
异常
程序中的异常
程序在运行过程中,发生了非正常的事件,影响了程序的执行,叫做异常。
异常大的种类
1)不可控的异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
at com.sxt.day03.demo15.TestHeapJVM.main(TestHeapJVM.java:26)
凡是以Error结束的异常都是不可控,都是JVM级别的异常,必须认为介入,程序无法处理。
OutOfMemoryError简称OOM,什么情况会导致OOM?创建对象的速度大于垃圾收集的速度,从而导致分配的堆内存被全部占满
/**
* -Xms16m -Xms16m -XX:+PrintGCDetails
* -XX:+PrintGCDetails 打印GC的详细日志
* [GC (Allocation Failure) 分配内存失败,Young 进行年轻代的垃圾收集
* [PSYoungGen: 3151K->0K(4608K)] 8013K->4861K(15872K), 0.0002264 secs]
* GC之前年轻代总内存4608k 已经使用的内存3151k 垃圾收集之后0k
* 0.0002264 secs 执行一次垃圾收集所消耗的时间 万分之2秒
* 15872K 表示总的堆内存空间
* 8013K GC之前堆内存空间小号了8013k
* 4861K GC之后堆内存消耗减少到了4861
* 8013-4861的结果就是GC回收的内存
* [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
* at com.sxt.day03.demo15.TestHeapJVM.main(TestHeapJVM.java:23)
* OutOfMemoryError GC回收内存的速度赶不上内存分配的速度,导致16MB的内存使用完毕了
**/
public class TestHeapJVM {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while(true){
byte [] data = new byte[1024*1024*100];
}
}
}
StackOverflowError
public class StackError {
private static int index = 0;
/**
* 自己调用自己,没调用一次自己doSomething()方法就会被压入一次栈,此时只有入栈,没有出栈
* 当栈内存满了就会抛出Exception in thread "main" java.lang.StackOverflowError
*/
public void doSomething(){
System.out.println(++index);
doSomething();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new StackError().doSomething();
}
}
以上两种Error程序无法处理,是JVM级别的错误,不可控的
面试题:工作中你遇到过哪些Error
什么情况下会发生StackOverflowError和OutOfMemoryError?
异常的体系结构
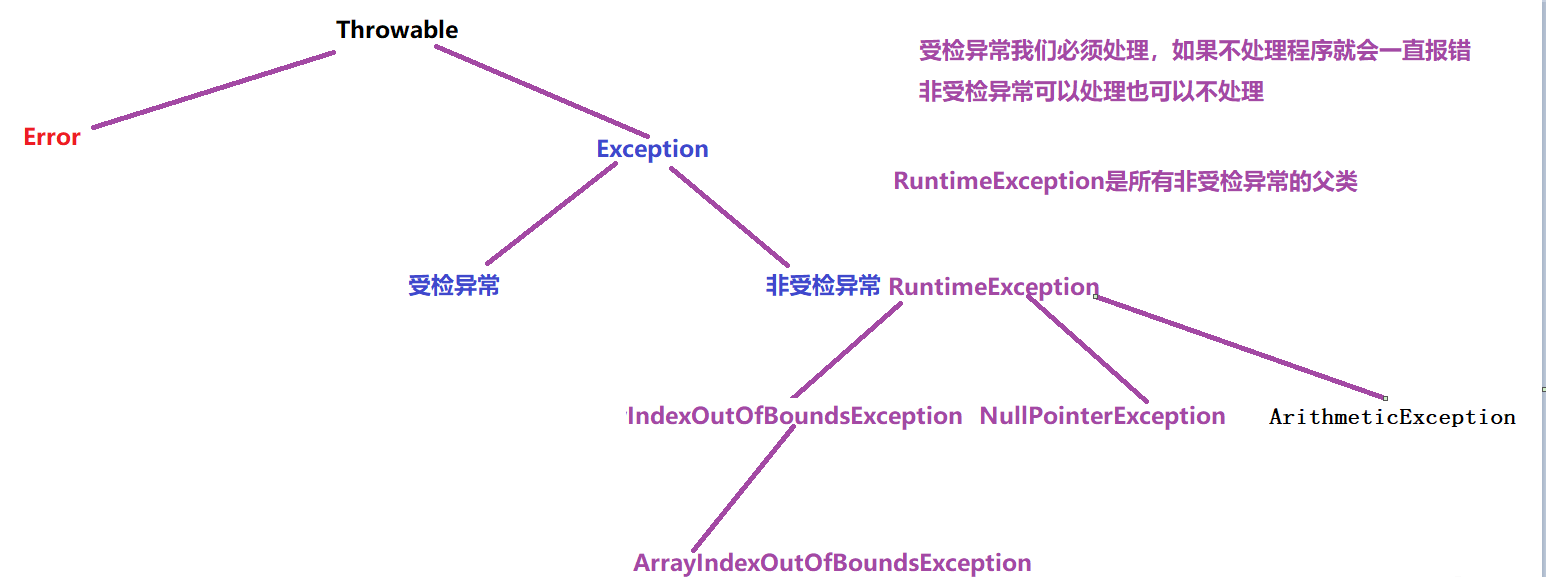
异常的关键字
try: 监控区 容易出现异常的代码必须写在try块中
catch
public class TestException2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num =10;
// 容易出现异常的代码放在try中,工作中要确保try块足够的小
// 下面的代码会发生异常,但是程序运行期间没有打印结果也没有处理异常是一个空白的,这种做法叫做压制异常
// 工作中不能这样
try {
int [] arrays = null;
// 一旦try块中出现了异常,try后面的代码不会被执行,而是直接跳转到catch块中
System.out.println(arrays[0]);
System.out.println("......");
//工作中异常可以嵌套,但是层次不要超过3层(<=2)
// try{}catch(Exception ee){}
// System.out.println(1/0);
// 一个try后面可以跟多个catch,一旦try发生异常只能处理一次异常,此时第一个catch块处理异常
// 处理完毕会跳过第二个catch块
}catch(NullPointerException npe){
// 打印异常栈信息 给开发人员定位问题用的,告诉开发人员哪一行出现了异常,出现异常的种类
// 工作中关于异常最大的两个忌讳:
// 1 catch啥都不写,叫做压制异常 2 打印一句话了事printStackTrace(),只是打印了异常信息,并没有处理异常
// 工作中catch块要么处理异常要么继续抛出异常
npe.printStackTrace();
// 处理异常
System.err.println("数组不能为空 NPE....");
}
catch (Exception e){ // catch块用来抓住try块中出现的异常,处理异常
// 此时catch块的参数是异常的父类Exception,程序运行期有可能出现各种各样的异常,在处理过程中
// 为了达到正确的处理,所以需要使用instanceof判断运行期的具体异常
if(e instanceof ArithmeticException){
System.err.println("除数不能为0");
}
if(e instanceof NullPointerException){
System.err.println("数组不能为空");
}
// catch块处理异常完毕,退出main方法,try后面的代码不会被执行
// return ;
}
// Java中子类异常只能定义在父类异常的前面
// catch (NullPointerException npe){
// System.out.println("aaa");
// }
System.out.println("try后面的逻辑代码");
}
}
一个catch参数可以定义多个异常
public class TestException3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("aaa");
// 一个catch参数可以定义多个异常 多个异常之间使用 | 分隔
// Since JDK6
}catch (NullPointerException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
finally: 用来在异常处理过程中完成清理的动作,如论是否发生异常都会执行。可以跟在try后面也可以跟在catch后面,但是不能单独存在。
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
场景:从控制台输入两个整数进行求商,有可能除数为0,一旦除数为0 就会处理异常,一旦程序执行完毕,我们需要使用finally块来释放new Scanner所占用的内存。
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Scanner输入整数,计算商
*
**/
public class TestException5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = null;
try {
input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个整数");
int num1 = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个整数");
int num2 = input.nextInt();
int result = num1 / num2;
System.out.println(result);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
if(e instanceof ArithmeticException){
System.err.println("除数不能为0");
}
}finally { // 无论是否发生异常finally都会执行,主要释放对象占用的内存,清理的操作
if(null != input){
input.close();
input = null;
}
}
}
}
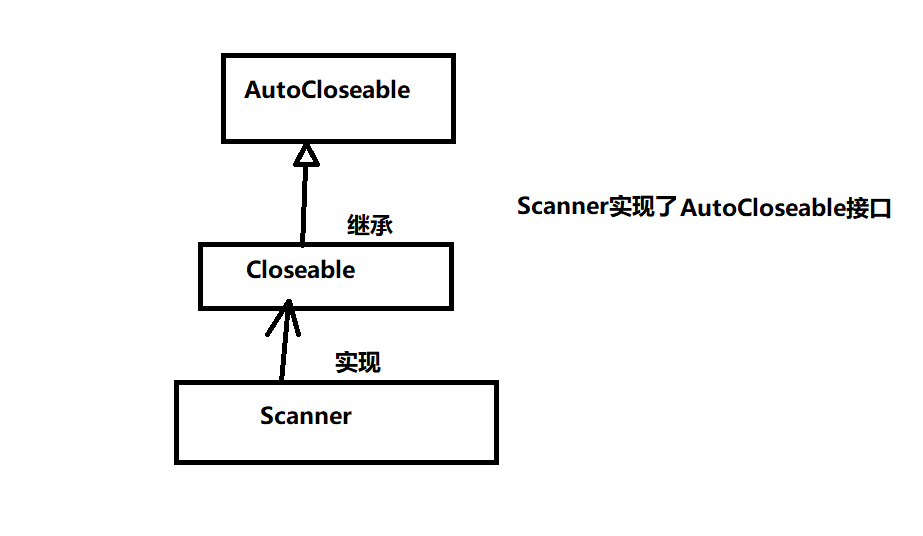
JDK7只有的新特性:try with resource
自动关闭对象占用的内存资源,由JVM在运行的时候帮我自动关闭,我只需要告诉JVM要关闭哪些资源。
好处:代码更简洁,忽略了finally
throw 抛出一个异常,不会处理异常。如果某个方法使用了throw抛出异常,那么调用这个方法必须处理这个异常或者继续往上抛出异常
throws 只能在方法签名中声明一个异常
// eat()方法有可能会发生异常,此时不会处理异常,交给调用这个方法的调用者去处理
public void eat() throws Exception{}
public class TestException8 {
/**
* 计算两个参数的商
* throws Exception 为doCalc方法声明一个异常,该方法可能会抛出异常,也可能不抛出异常
*
* @param first
* @param second
* @return first/second
* @throws Exception
*/
public static int doCalc(int first,int second)throws Exception{
// 条件成立:表示除数为0,使用throw关键字创建一个异常对象(抛出一个异常对象)
if(second ==0 ){
throw new ArithmeticException("除数不能为0");
}
return first/second;
}
/**
* java.lang.ArithmeticException: 除数不能为0
* at com.sxt.day04.demo04.TestException8.doCalc(TestException8.java:22)
* at com.sxt.day04.demo04.TestException8.main(TestException8.java:31)
* "异常能够告诉你足够多的信息":
* ArithmeticException 异常的类型
* doCalc(TestException8.java:22) 异常的第一线程,由于22行抛出的异常导致了异常事件的发生
* main(TestException8.java:31) 31行调用了22行
* 小结:异常栈由栈顶向栈底抛出(由上而下)
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Unhandled exception: java.lang.Exception
// 调用者要么处理异常,要么继续向上抛出异常
int result = 0;
try {
result = doCalc(1,0);
System.out.println("result = "+result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 处理异常
if(e instanceof ArithmeticException){
System.err.println("除数不能为0");
}
}
}
}
最好在最前沿(此时的最前沿是main方法)处理异常,不要在中间层(此时的中间层是doCalc方法)处理异常,中间层最好只声明异常、抛出异常
注意:工作中不要在最前沿throws Exception

自定义异常
自己定义异常,需要使用的时候使用 throw new XXXXXException
注意:可以参考RuntimeException源码
public class J0622Exception extends Exception {
public J0622Exception(){
super();
}
/**
* @param message 出现异常的信息
*/
public J0622Exception(String message) {
super(message);
}
/**
*
* @param message 异常的根
* @param cause
*/
public J0622Exception(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public J0622Exception(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
使用自定义异常:
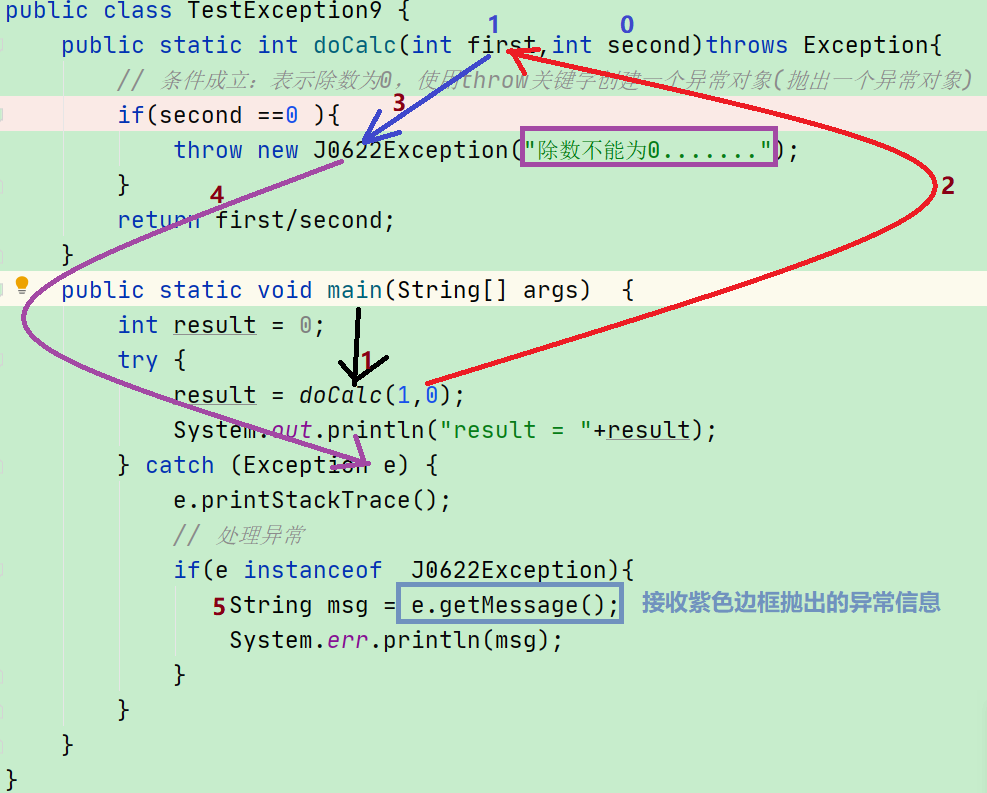
public class TestException9 {
public static int doCalc(int first,int second)throws Exception{
// 条件成立:表示除数为0,使用throw关键字创建一个异常对象(抛出一个异常对象)
if(second ==0 ){
throw new J0622Exception("除数不能为0.......");
}
return first/second;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = 0;
try {
result = doCalc(1,0);
System.out.println("result = "+result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 处理异常
if(e instanceof J0622Exception){
String msg = e.getMessage();
System.err.println(msg);
}
}
}
}
异常面试题:
public interface AAAAA {
public void doSomething()throws Exception;
}
class BBBBB implements AAAAA{
/**
* 实现类的异常级别可以跟接口平级、可以比接口低,但是不能比接口高
* @throws ArithmeticException
*/
@Override
public void doSomething() throws ArithmeticException {
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号