管道陷入阻塞,无法退出
管道分写和读端,当写端全部close(),读端read时,会返回0,这样读端就可以此退出循环
while(read(fds[0], &val, sizeof(int)) != 0){}
但是管道如果没有正确的关闭,就会陷入阻塞
例
int p[2];
int main() {
pipe(p);
int pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { // child thread
int val;
while (read(p[0], &val, sizeof(int))) {
printf("%d\n", val);
}
close(p[1]), close(p[0]);
exit(0);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
write(p[1], "hello", 5);
close(p[0]), close(p[1]);
wait(0);
}
}
运行后会发现read陷入阻塞,明明主线程已经close了写端口,为什么会这样?是因为管道没有正确关闭
管道使用的是引用计数法,当调用pipe时,会对所有资源进行复制,因此此时父子进程都持有读端和写端的引用
运行时是这样:
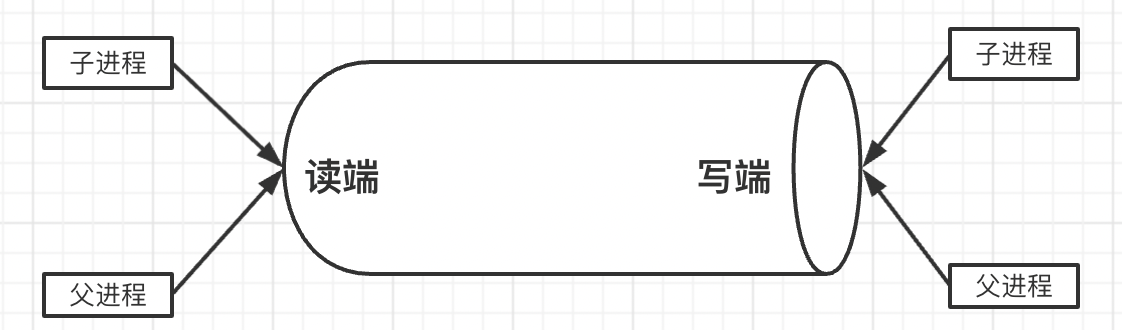
因此当父进程close两个端后,管道的引用状态是这样

可以看出,pipe的读端并没有被完全关闭,因此陷入阻塞
启发
不需要的使用的端口一定要尽早关闭,只需要读的端,一开始就把写端关闭,
上述代码可以改成这样
int p[2];
int main() {
pipe(p);
int pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { // child thread
// 子进程只读不写,一开始就关闭写端
close(p[1]);
int val;
while (read(p[0], buf, 5)) {
buf[5] = 0;
printf("%s.\n", buf);
}
close(p[0]);
exit(0);
} else {
// 父进程只写不读,一开始就关闭读端
close(p[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
write(p[1], "hello", 5);
close(p[1]);
wait(0);
}
}
这样就可以正常退出了



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号