JavaDay12(上)
Java learning_Day12(上)
本人学习视频用的是马士兵的,也在这里献上
<链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1qKNGJNh0GgvlJnitTJGqgA>
提取码:fobs
内容
- AWT
-
布局管理器
AWT
-
AWT(Abstarct Window Toolkit)包括了很多类和接口,用于 Java Application 的 GUI(Graphics User Interface 用户图形界面)编程。
-
GUI 的各种元素(如:窗口,按钮,文本框等)由 Java 类实现。
-
使用 AWT 所涉及的类一般在 java.awt 包及其子包中。
-
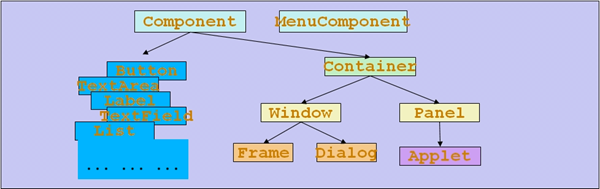
Container 和 Component 是 AWT 中的两个核心类。
![PotPlayerMini64_EJHVvWnM3u.png]()
Component&Container
- Java 的图形用户界面的最基本组成部分是 Component,Component 类及其子类的对象用来描述以图形化的方式显示在屏幕上并能与用户进行交互的 GUI 元素,例如,一个按钮,一个标签等。
- 一般的 Component 对象不能独立地显示出来,必须将“放在”某一的 Container 对象中才可以显示出来。
- Container 是 Component 子类,Container 子类对象可以“容纳”别的 Component 对象。
- Container 对象可使用方法 add(...) 向其中添加其他 Component 对象。
- Container 是 Component 的子类,因此 Container 对象也可以被当作 Component 对象添加到其他 Container 对象中。
- 有两种常用的 Container:
- Window:其对象表示自由停泊的顶级窗口
- Panel:其对象可作为容纳其它 Component 对象,但不能独立存在,必须被添加到其它 Container 中(如 Windows 或 Applet)
Frame
- Frame 是 Window 的子类,由 Frame 或其子类创建的对象为一个窗体。
- Frame 的常用构造方法:
-
Frame()
-
Frame(String s)创建标题栏为字符串s的窗口。
![PotPlayerMini64_WtXGfu0XKE.png]()
-
TestFrame.java
import java.awt.*;
public class TestFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("My first frame");
frame.setSize(200, 100); //设置大小,数字代表像素
frame.setLocation(300, 300);
frame.setBackground(Color.blue);
frame.setResizable(false); //不可调大小
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
TestMultiFrame.java
import java.awt.*;
public class TestMultiFrame {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyFrame f1 =
new MyFrame(100,100,200,200,Color.BLUE);
MyFrame f2 =
new MyFrame(300,100,200,200,Color.YELLOW);
MyFrame f3 =
new MyFrame(100,300,200,200,Color.GREEN);
MyFrame f4 =
new MyFrame(300,300,200,200,Color.MAGENTA);
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
static int id = 0;
MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color){
super("MyFrame " + (++id));
setBackground(color);
setLayout(null);
setBounds(x,y,w,h);
setVisible(true);
}
}
Panel
- Panel 对象可以看成可以容纳 Component 的空间
- Panel 对象可以拥有自己的布局管理器
- Panel 类拥有其从父类继承来的
- setBounds(int x, int y, int width, int height)
- setSize(int width, int height)
- setLocation(int x, int y)
- setBackground(Color c)
- setLayout(LayouManager mgr)等方法
- Panel 的构造方法为:
- Panel() 使用默认的 FlowLayout 类布局管理器初始化。
- Panel(LayoutManager layout)使用指定的布局管理器初始化。
示例1
import java.awt.*;
public class TestPanel {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Frame f =
new Frame("Java Frame with Panel");
Panel p = new Panel(null);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setBounds(300,300,500,500);
f.setBackground(new Color(0,0,102));
p.setBounds(50,50,400,400);
p.setBackground(new Color(204,204,255));
f.add(p);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
示例2
import java.awt.*;
public class TestMultiPanel {
public static void main(String args[]) {
new MyFrame2("MyFrameWithPanel",300,300,400,300);
}
}
class MyFrame2 extends Frame{
private Panel p1,p2,p3,p4;
MyFrame2(String s,int x,int y,int w,int h){
super(s);
setLayout(null);
p1 = new Panel(null); p2 = new Panel(null);
p3 = new Panel(null); p4 = new Panel(null);
p1.setBounds(0,0,w/2,h/2);
p2.setBounds(0,h/2,w/2,h/2);
p3.setBounds(w/2,0,w/2,h/2);
p4.setBounds(w/2,h/2,w/2,h/2);
p1.setBackground(Color.BLUE);
p2.setBackground(Color.GREEN);
p3.setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
p4.setBackground(Color.MAGENTA);
add(p1);add(p2);add(p3);add(p4);
setBounds(x,y,w,h);
setVisible(true);
}
}
布局管理器
- Java 语言中,提供了布局管理器类的对象可以管理
- 管理 Component 在 Container 中的布局,不必直接设置每个 Component 位置和大小。
- 每个 Container 都有一个布局管理器对象,当容器需要对某个组件进行定位或判断其大小尺寸时,就会调用其对应的布局管理器,调用 Container 的 setLayout 方法改变其布局管理器对象。
- AWT 提供了5种布局管理器类:
- FlowLayout
- BorderLayout
- GridLayout
- CardLayout
- GridBagLayout
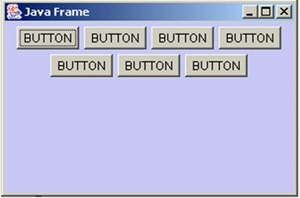
FlowLayout 布局管理器
-
FlowLayout 是 Panel 类的默认布局管理器。
- FlowLayout 布局管理器对组件逐行定位,行内从左到右,一行排满后换行。
- 不改变组件的大小,按组件原有尺寸显示组件,可设置不同的组件间距、行距以及对齐方式。
-
FlowLayout 布局管理器默认的对齐方式是居中。
![PotPlayerMini64_YiUfqNbyLa.png]()
import java.awt.*;
public class TestFlowLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("FlowLayout");
Button b1 = new Button("These");
Button b2 = new Button("are");
Button b3 = new Button("buttons");
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); //默认居中对齐
frame.add(b1);
frame.add(b2);
frame.add(b3);
frame.setSize(100, 100);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
控制按钮间距
import java.awt.*;
public class TestFlowLayout2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("Flow Layout");
FlowLayout f = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 20, 40); //水平间距20,垂直间距40
frame.setLayout(f);
frame.setLocation(200, 200);
frame.setSize(100, 100);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
frame.add(new Button("Button"));
}
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
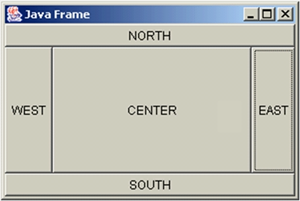
BorderLayout 布局管理器
-
BorderLayout 是 Frame 类的默认布局管理器。
-
BorderLayout 将整个容器的布局划分成五个区域,组件只能被添加到指定的区域。
- 东(EAST)
- 西(WEST)
- 南(SOUTH)
- 北(NORTH)
- 中(CENTER)
-
如不指定组件的加入部位,则默认加入到CENTER区。
-
每个区域只能加入一个组件,如加入多个,则先前加入的会被覆盖。
-
BorderLayout 型布局容器尺寸缩放原则:
-
北、南两个区域在水平方向缩放。
-
东、西两个区域在垂直方向缩放。
-
中部可在两个方向上缩放。
![PotPlayerMini64_k8TAmRfJLY.png]()
-
示例
import java.awt.*;
public class TestBorderLayout {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Frame f;
f = new Frame("Border Layout");
Button bn = new Button("BN");
Button bs = new Button("BS");
Button bw = new Button("BW");
Button be = new Button("BE");
Button bc = new Button("BC");
f.add(bn, "North");
f.add(bs, "South");
f.add(bw, "West");
f.add(be, "East");
f.add(bc, "Center");
// 也可使用下述语句
/*
f.add(bn, BorderLayout.NORTH);
f.add(bs, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
f.add(bw, BorderLayout.WEST);
f.add(be, BorderLayout.EAST);
f.add(bc, BorderLayout.CENTER);
*/
f.setSize(200,200);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
GridLayout 布局管理器
- GridLayout 型布局管理器将空间划分成规则的矩形网络,每个单元格区域大小相等。组件被添加到每个单元格中,先从左到右填满一行后换行,再从上到下。
- 在 GridLayout 构造方法中指定分割的行数和列数:如 GridLayout(3, 4)
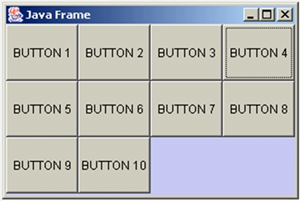
示例
import java.awt.*;
public class TestGridLayout {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Frame f = new Frame("GridLayout Example");
Button b1 = new Button("b1");
Button b2 = new Button("b2");
Button b3 = new Button("b3");
Button b4 = new Button("b4");
Button b5 = new Button("b5");
Button b6 = new Button("b6");
f.setLayout (new GridLayout(3,2));
f.add(b1);
f.add(b2);
f.add(b3);
f.add(b4);
f.add(b5);
f.add(b6);
f.pack(); //是窗口大小刚好显示所有按钮
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
布局管理器总结
- Frame 是一个顶级窗口,Frame 的缺省布局管理器为 BorderLayout
- Panel 无法单独显示,必须添加到某个容器中。
- Panel 的缺省布局管理器为 FlowLayout。
- 当把 Panel 作为一个组件添加到某个容器中后,该 Panel 仍然可以拥有自己的布局管理器。
- 使用布局管理器时,布局管理器负责各个组件的大小和位置,因此用户无法在这种情况下设置组件大小和位置属性,如果试图使用 Java 语言提供的 setLocation(), setSize(), setBounds() 等方法,则都会被布局管理器覆盖。
- 如果用户确实需要亲自设置组件大小或位置,则应取消该容器的布局管理器,方法为:setLayout(null)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号