LeetCode148. 排序链表
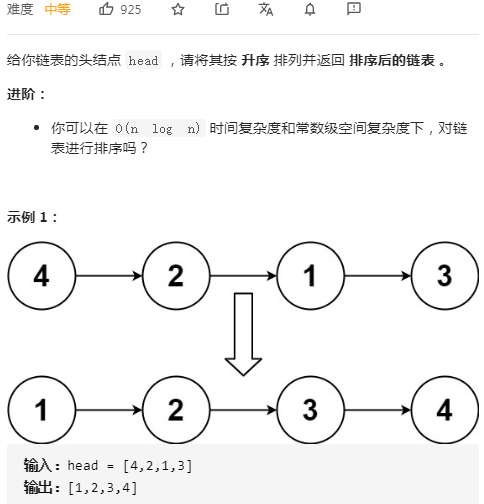
链表的归并操作不需要额外空间,因而使用归并排序符合本题常数级空间复杂度的要求。最适合单链表的排序算法是归并排序。
☆☆☆思路1:自顶向下的归并排序(递归) 时间复杂度O(nlogn), 空间复杂度O(logn),其中空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间。
主要考察:1)归并排序思想;2)寻找链表中间节点;3)合并两个有序链表
☆☆☆☆思路2:自底向上的归并排序(迭代) 时间复杂度O(nlogn), 空间复杂度O(1)
☆☆☆☆思路3:单链表的快排实现(面试常考)
代码1:(归并 递归)
class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } ListNode right = slow.next; slow.next = null; ListNode l1 = sortList(head); ListNode l2 = sortList(right); return merge(l1, l2); } // 合并两个有序链表 public ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); ListNode cur = dummyHead; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val < l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; }else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } if (l1 != null) cur.next = l1; if (l2 != null) cur.next = l2; return dummyHead.next; } }
代码2:(归并 非递归)
class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; int len = getLength(head); ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); dummyHead.next = head; for (int step = 1; step < len; step *= 2) { //依次将链表分成1块,2块,4块... //每次变换步长,pre指针和cur指针都初始化在链表头 ListNode pre = dummyHead, cur = dummyHead.next; while (cur != null) { ListNode head1 = cur; //第一部分头(第二次循环之后,cur为剩余部分头, ListNode head2 = split(head1, step); //第二部分头 cur = split(head2, step); //剩余部分的头 ListNode temp = merge(head1, head2); pre.next = temp; while (pre.next != null) { pre = pre.next; //把pre指针移动到排序好的部分的末尾 } } } return dummyHead.next; } // 断链操作 返回第二部分链表头 public ListNode split(ListNode head,int step){ if (head == null) return head; ListNode cur = head; for (int i = 1; i < step && cur.next != null; i++) { // 注意 i 从1开始 cur = cur.next; } ListNode right = cur.next; cur.next = null; return right; } // 获取链表长度 public int getLength(ListNode head) { int len = 1; while (head.next != null) { head = head.next; len ++; } return len; } // 合并两个有序链表 public ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); ListNode cur = dummyHead; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val <= l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; }else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } if (l1 != null) cur.next = l1; if (l2 != null) cur.next = l2; return dummyHead.next; } }
代码3:(快排)
具体过程如下:
1. 将原链表中所有节点依次划分成三个链表,分别为small代表左部分,equal代表中间部分,big代表有部分。
2. 将small、equal和big三个链表重新串起来即可。
3. 整个过程需要特别注意对null节点的判断和处理。
class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { return quickSort(head)[0]; } private ListNode[] quickSort(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return new ListNode[]{head, head}; ListNode[][] parAns = listPartition(head); ListNode[] left = quickSort(parAns[0][0]); ListNode[] right = quickSort(parAns[2][0]); // 小的和相等的重新连接 if (left[1] != null) { left[1].next = parAns[1][0]; parAns[1][1] = parAns[1][1] != null ? parAns[1][1] : left[1]; } // 所有的重新连接 if (parAns[1][1] != null) { parAns[1][1].next = right[0]; } // 返回的数组中第一个是头节点,第二个是尾节点 return new ListNode[]{left[0] != null ? left[0] : (parAns[1][0] != null ? parAns[1][0] : right[0]), right[1] != null ? right[1] : (parAns[1][1] != null ? parAns[1][1] : left[1])}; } private ListNode[][] listPartition(ListNode head) { ListNode sH = null; // 小的头 ListNode sT = null; // 小的尾 ListNode eH = null; // 相等的头 ListNode eT = null; // 相等的尾 ListNode bH = null; // 大的头 ListNode bT = null; // 大的尾 ListNode next = null; // 保存下一个节点 int pivot = head.val; while (head != null) { next = head.next; head.next = null; // 删除可以AC,否则会超时 if (head.val < pivot) { if (sH == null) { sH = head; sT = head; }else { sT.next = head; sT = head; } }else if (head.val == pivot) { if (eH == null) { eH = head; eT = head; }else{ eT.next = head; eT = head; } }else { // head.val > pivot if (bH == null) { bH = head; bT = head; }else { bT.next = head; bT = head; } } head = next; } if (sT != null) sT.next = null; if (eT != null) eT.next = null; if (bT != null) bT.next = null; return new ListNode[][]{{sH,sT},{eH,eT},{bH,bT}}; } }
单链表快排参考:
左神书P55


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号