ryu控制器与mininet连接的简单使用(2021.6.16)
进入ryu/ryu/app目录,然后启动相应模块:
sudo ryu-manager --verbose simple_switch_13.py ofctl_rest.py rest_topology.py
simple_switch_13.py模块是一个简单的交换机,是openflow1.3的交换机。后面的两个文件是为了进行restapi的调用加载的,方便直接用浏览器查看。
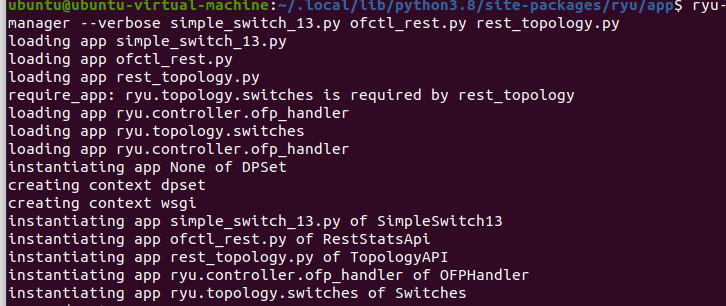
再启动mininet,远程连接ryu控制器(ip地址:192.168.231.131,如果是在一台虚拟机里,则为本地ip:127.0.0.1):
sudo mn --controller=remote,ip=192.168.231.131,port=6653 --switch=ovsk,protocols=OpenFlow13
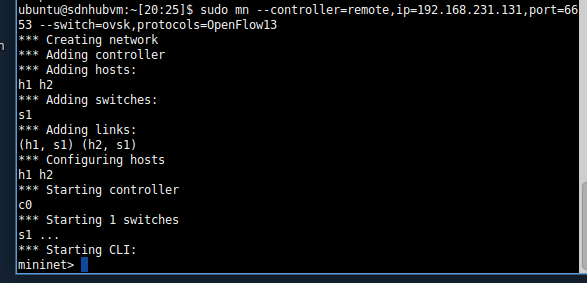
相应的,ryu控制器打开的终端输出信息:
mininet常用交互命令:
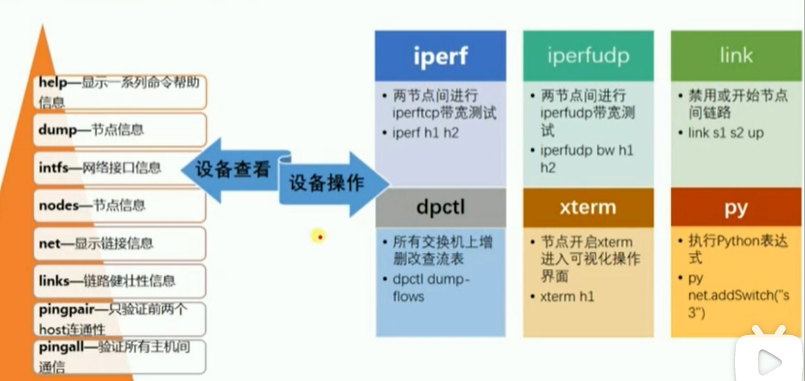
py经常用于扩展网络,py的应用:添加h3:h3节点,s1-h3链路,s1-eth3接口,h3-eth0 ip,链路发现h1 ping h3
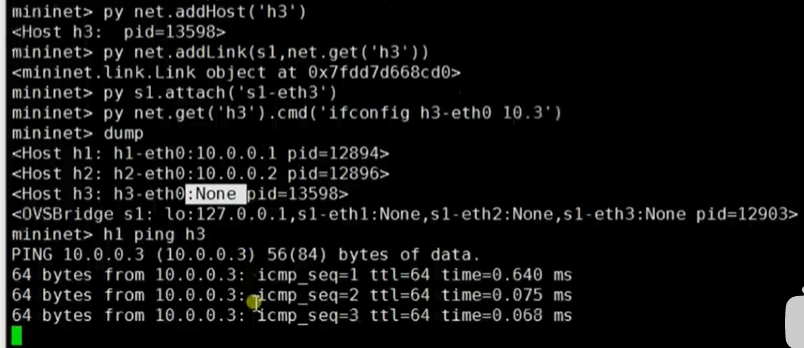
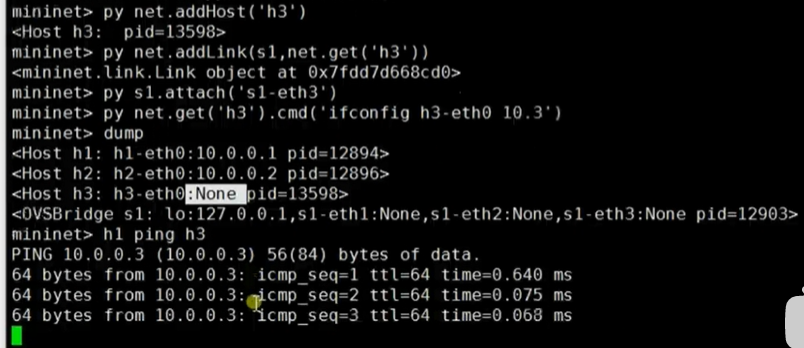
相关py命令可以使用py help(s1)类似的命令查看。
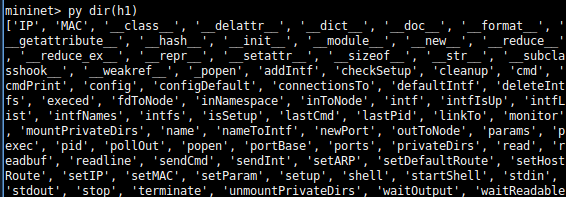
也可以使用更简短的py dir(h1)命令查看。
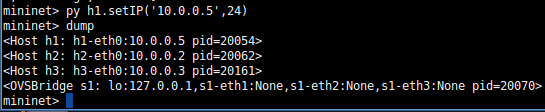
若设置h1的ip。
下面参考https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34415266/article/details/92795959
在浏览器中调用ryu的api
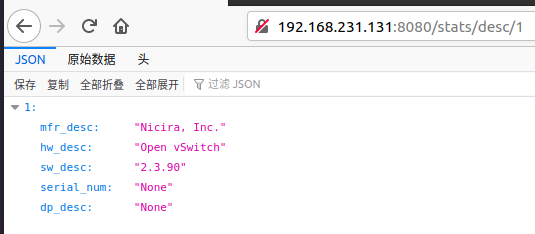
①得到某台交换机的状态信息:http://192.168.231.131(这里是控制器ip地址):8080/stats/desc/1
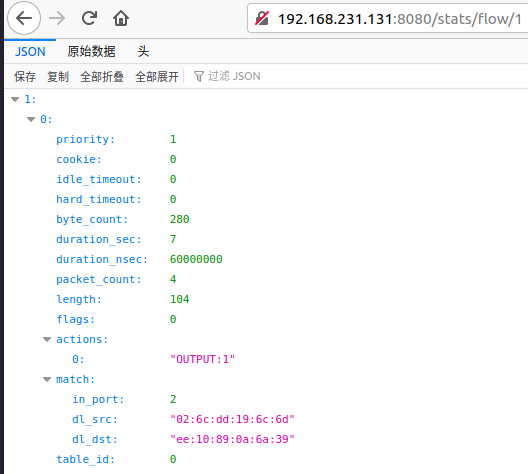
②查看交换机当前的流表:http://192.168.231.131(这里是控制器ip地址):8080/stats/flow/1

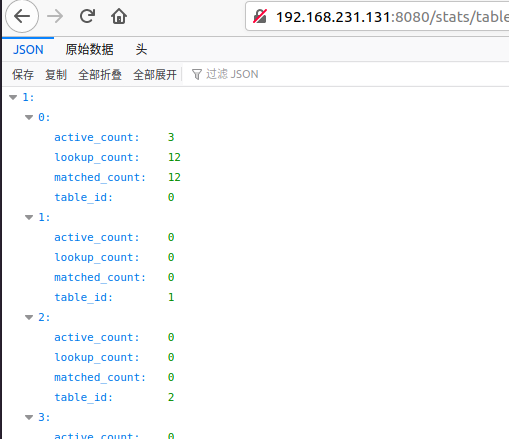
查询指定交换机上所有流表的统计信息:http://192.168.231.131(这里是控制器ip地址):8080/stats/table/1
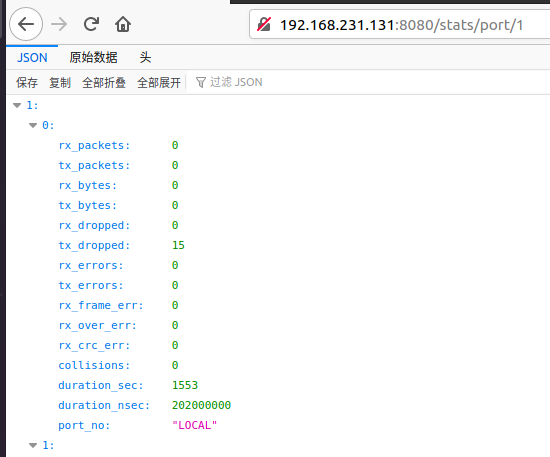
得到端口的统计信息:http://192.168.231.131(这里是控制器ip地址):8080/stats/port/1
得到端口配置信息:http://192.168.231.131(这里是控制器ip地址):8080/stats/portdesc/1
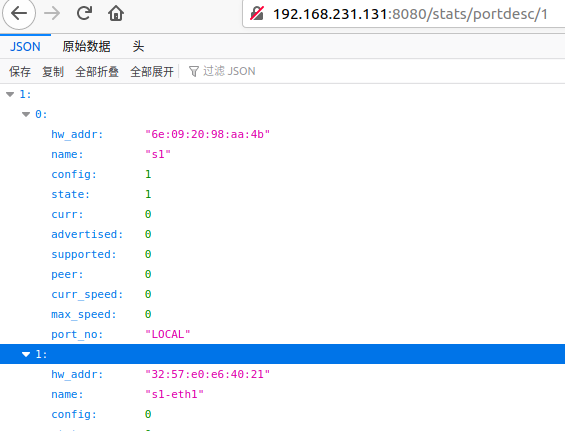
在浏览器中除了可以查询流表信息外,还可以对流表进行操作,但需要支持构造post、delete等请求的浏览器插件,如httprequester、restclient等。
我这里使用的是火狐的restclient。
安装restclient:附件组件-扩展-restclient-安装
点击 该插件进行使用。
该插件进行使用。
例如,查看交换机1的状态信息:
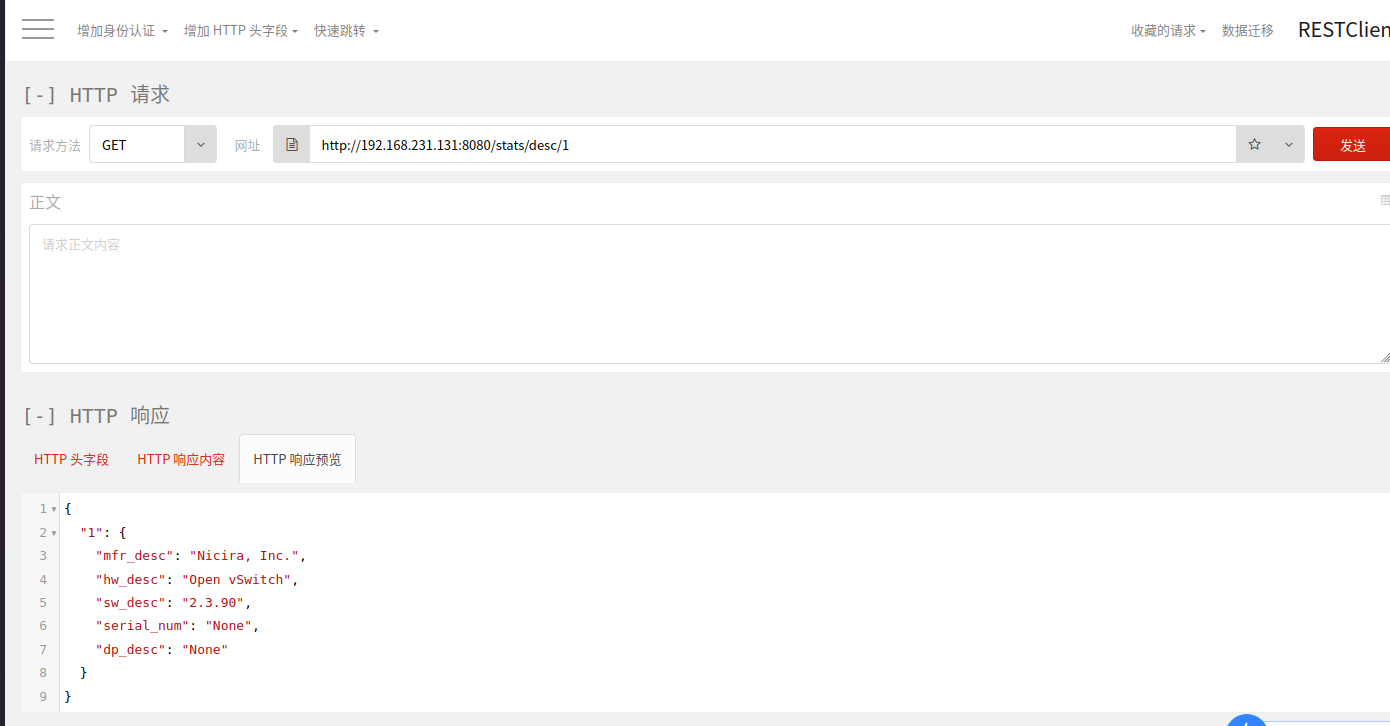
其他例如:获取交换机流表
# 获取交换机列表
GET /stats/switches
# 获取某台交换机的设备信息
GET /stats/desc/<dpid>
# get flows desc stats of the switch
GET /stats/flowdesc/<dpid>
# get flows desc stats of the switch filtered by the fields
POST /stats/flowdesc/<dpid>
# 得到指定交换机的所有flow的状态信息
GET /stats/flow/<dpid>
# 有条件地查询某台交换机的流表
POST /stats/flow/<dpid>
# 查询指定交换机的全局统计流表的字段
GET /stats/aggregateflow/<dpid>
# 有条件的查询指定交换机的全局统计流表的字段
POST /stats/aggregateflow/<dpid>
# 查询指定交换机上所有流表的统计信息
GET /stats/table/<dpid>
# get table features stats of the switch
GET /stats/tablefeatures/<dpid>
# 得到端口的统计信息
GET /stats/port/<dpid>[/<port>]
# Note: Specification of port number is optional
# get queues stats of the switch
GET /stats/queue/<dpid>[/<port>[/<queue_id>]]
# Note: Specification of port number and queue id are optional
# If you want to omitting the port number and setting the queue id,
# please specify the keyword "ALL" to the port number
# e.g. GET /stats/queue/1/ALL/1
# get queues config stats of the switch
GET /stats/queueconfig/<dpid>[/<port>]
# Note: Specification of port number is optional
# get queues desc stats of the switch
GET /stats/queuedesc/<dpid>[/<port>[/<queue_id>]]
# Note: Specification of port number and queue id are optional
# If you want to omitting the port number and setting the queue id,
# please specify the keyword "ALL" to the port number
# e.g. GET /stats/queuedesc/1/ALL/1
# get meter features stats of the switch
GET /stats/meterfeatures/<dpid>
# get meter config stats of the switch
GET /stats/meterconfig/<dpid>[/<meter_id>]
# Note: Specification of meter id is optional
# get meter desc stats of the switch
GET /stats/meterdesc/<dpid>[/<meter_id>]
# Note: Specification of meter id is optional
# get meters stats of the switch
GET /stats/meter/<dpid>[/<meter_id>]
# Note: Specification of meter id is optional
# get group features stats of the switch
GET /stats/groupfeatures/<dpid>
# get groups desc stats of the switch
GET /stats/groupdesc/<dpid>[/<group_id>]
# Note: Specification of group id is optional (OpenFlow 1.5 or later)
# get groups stats of the switch
GET /stats/group/<dpid>[/<group_id>]
# Note: Specification of group id is optional
# get ports description of the switch
GET /stats/portdesc/<dpid>[/<port_no>]
# Note: Specification of port number is optional (OpenFlow 1.5 or later)
再比如更新交换机流表项
# 添加流表项
POST /stats/flowentry/add
# 修改所有匹配的流表项
POST /stats/flowentry/modify
# modify flow entry strictly matching wildcards and priority
POST /stats/flowentry/modify_strict
# delete all matching flow entries
POST /stats/flowentry/delete
# delete flow entry strictly matching wildcards and priority
POST /stats/flowentry/delete_strict
# delete all flow entries of the switch
DELETE /stats/flowentry/clear/<dpid>
# add a meter entry
POST /stats/meterentry/add
# modify a meter entry
POST /stats/meterentry/modify
# delete a meter entry
POST /stats/meterentry/delete
# add a group entry
POST /stats/groupentry/add
# modify a group entry
POST /stats/groupentry/modify
# delete a group entry
POST /stats/groupentry/delete
# modify behavior of the physical port
POST /stats/portdesc/modify
# modify role of controller
POST /stats/role
# send a experimeter message
POST /stats/experimenter/<dpid>
注意!:先用sudo mn -c去清除配置信息。
下面是自定义拓扑文件。
1.py拓扑代码如下:
__author__ = 'jmh081701' from mininet.topo import Topo class MyTopo(Topo): def __init__(self): Topo.__init__(self) left=[] left.append(self.addHost("h1")) left.append(self.addHost("h2")) right=[] right.append(self.addHost("h3")) right.append(self.addHost("h4")) switchs=[] switchs.append(self.addSwitch("s1")) switchs.append(self.addSwitch("s2")) self.addLink(left[0],switchs[0]) self.addLink(left[1],switchs[0]) self.addLink(right[0],switchs[1]) self.addLink(right[1],switchs[1]) self.addLink(switchs[0],switchs[1]) topos={'mytopo':(lambda : MyTopo())}
注意!:mininet/custom/ 目录用来存放自定义的拓扑文件,所以把1.py文件放在custom/目录下。
启动mininet
sudo mn --controller=remote,ip=192.168.1.197,port=6653 --custom 1.py --topo mytopo --mac
其中 1.py是刚刚定义的拓扑python文件, mytopo是 topos={'mytopo':(lambda : MyTopo())} 中指定的拓扑名,--mac使mac地址可读性提高有规律
注意!:加载自定义拓扑文件时 是使用 --custom .py 格式,而不是--custom=.py 格式 --topo 也是类似。
Get方法 http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/switches
得到一个json list,里面有两个元素:1和2,表示共有两台交换机。
这是他们的DPID,datapath id
URL: http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/flow/
方法:GET
如得到交换机1的所有流表项:

{ "1": [ { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:3" ],(动作,转发到3 号端口) "idle_timeout": 0,(空闲后存活时间) "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 2,(包计数) "hard_timeout": 0,(存活时间) "byte_count": 140,(比特计数) "duration_nsec": 111000000, "priority": 32768,(优先级) "duration_sec": 985,(已经存活时间) "table_id": 0,(在流表1) "match": (匹配字段) { "dl_dst": "02:28:7c:93:27:af",(过滤目的地址为02:28:7c:93:27:af的包,就是去主机3的包) "in_port": 2(从2号口子来的) } (作用:从2号口子来的,要到h3的报文都从3号口子出去哈) }, { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:2" ], "idle_timeout": 0, "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 7, "hard_timeout": 0, "byte_count": 518, "duration_nsec": 113000000, "priority": 32768, "duration_sec": 985, "table_id": 0, "match": { "dl_dst": "d2:3e:55:89:f3:a1", "in_port": 3 } (作用:从3号口子来的,发往h2的包都从2号口子出去哈) }, { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:3" ], "idle_timeout": 0, "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 2, "hard_timeout": 0, "byte_count": 140, "duration_nsec": 155000000, "priority": 32768, "duration_sec": 985, "table_id": 0, "match": { "dl_dst": "02:28:7c:93:27:af", "in_port": 1 } (作用:从1号口子来的,发往h3的的包都从3号口子出去哈 }, { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:1" ], "idle_timeout": 0, "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 3, "hard_timeout": 0, "byte_count": 238, "duration_nsec": 171000000, "priority": 32768, "duration_sec": 985, "table_id": 0, "match": { "dl_dst": "fe:3b:25:cc:04:97", "in_port": 2 } (作用:从2号口子来的,发往h1的包都从1号口子出去哈) }, { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:2" ], "idle_timeout": 0, "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 2, "hard_timeout": 0, "byte_count": 140, "duration_nsec": 169000000, "priority": 32768, "duration_sec": 985, "table_id": 0, "match": { "dl_dst": "d2:3e:55:89:f3:a1", "in_port": 1 } (从1号口子来的,发给h2的包都从2号口子出去哈 }, { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:3" ], "idle_timeout": 0, "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 2, "hard_timeout": 0, "byte_count": 140, "duration_nsec": 137000000, "priority": 32768, "duration_sec": 985, "table_id": 0, "match": { "dl_dst": "ba:94:88:a1:55:63", "in_port": 1 } (从1号口子来的,发往h4的,从3号口子出去哈) }, { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:1" ], "idle_timeout": 0, "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 7, "hard_timeout": 0, "byte_count": 518, "duration_nsec": 157000000, "priority": 32768, "duration_sec": 985, "table_id": 0, "match": { "dl_dst": "fe:3b:25:cc:04:97", "in_port": 3 } (作用:从3号口子来的,发给h1的包都从1号口子出去哈) }, { "actions": [ "OUTPUT:3" ], "idle_timeout": 0, "cookie": 0, "packet_count": 2, "hard_timeout": 0, "byte_count": 140, "duration_nsec": 92000000, "priority": 32768, "duration_sec": 985, "table_id": 0, "match": { "dl_dst": "ba:94:88:a1:55:63", "in_port": 2 } (从2号口子来的,发给h4的都从3号口子出去哈) } ] }
我们可以分析出:
第一个交换机一个有3个端口
端口1与h1直连
端口2与h2直连
端口3负责与另外一个交换机直连
另一个交换机也是类似的作法
有条件地查询某台交换机的流表
URL: http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/flow/
方法:POST
其实就是通过POST一些过滤条件来返回结果,类似于SQL里面的where语句
支持的过滤字段有:
table_id:流表ID
out_port:出端口号
out_group:出组号
cookie:
cookie_mask:
match:匹配字段
prority:优先级
举个栗子:
我们想获取所以目的地为h1的流表项:只要过滤那些匹配域中目的为h1即可:
在BODY里面填:
{
"match":
{ "dl_dst": "fe:3b:25:cc:04:97" } }
结果:
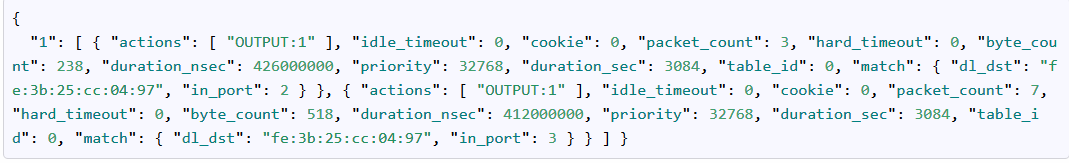
把所有发给h1的流表项都过滤出来了
查询指定交换机的全局统计流表的字段
URL: http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/aggregateflow/
方式:get
查交换机1的:
{
"1": [ { "packet_count": 27, "byte_count": 1974, "flow_count": 8 } ] }
可以看出是交换机所有流表项的全局性统计
有条件的查询指定交换机的全局统计流表的字段
与上面方法类似,也是通过POST方法来过滤掉一些结果
过滤字段一样
查询指定交换机上所有流表的统计信息
URL: http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/table/
方法:GET
比如查交换机1的流表相关信息

得到端口的统计信息
URL: http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/port//[/]
方法:GET
得到指定交换机下的某端口统计信息(如果没有指定端口则获取所有端口)
如得到交换机1下端口1的:
http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/port/1/1
结果: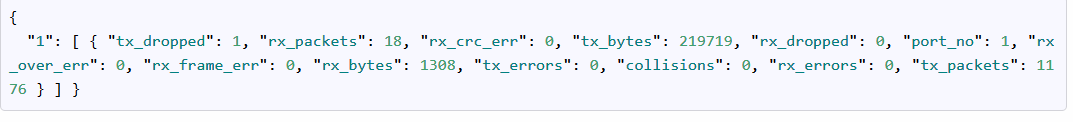
得到端口配置信息:
URL: http://192.168.1.197:8080/stats/portdesc/1
方法:GET
得到交换机1的结果:
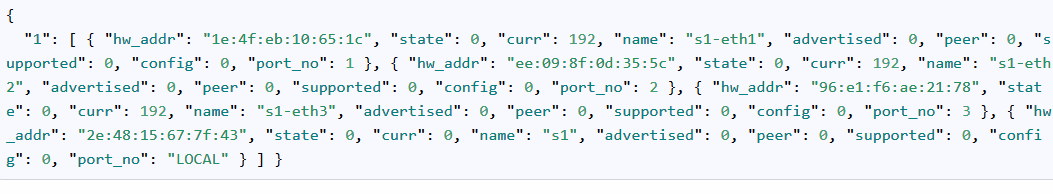



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号