【javafx 官方文档翻译 一】Getting Started with JavaFX
介绍
近期接到公司需求,需要做一个桌面系统,但由于自己java出身。前期做了可行性分析,可以用java1.8+javafx实现功能需求。但是在网上搜到的javafx相关文档较少。因此只能从官方文档下手。本人英文水平有限,特此将英文文档摘录下来,并用百度翻译逐步翻译。中间难免有些错误,还望理解。也欢迎大家一起讨论,共同进步。
官方目录
官方地址 Getting Started with JavaFX
- Title and Copyright Information
- Preface
- What's New
- Part I What Is JavaFX?
- 1 JavaFX Overview
- 2 Understanding the JavaFX Architecture
- Part II Getting Started with JavaFX Sample Applications
- 3 Hello World, JavaFX Style
- 4 Creating a Form in JavaFX
- 5 Fancy Forms with JavaFX CSS
- 6 Using FXML to Create a User Interface
- 7 Animation and Visual Effects in JavaFX
- A background.jpg
Title and Copyright Information
Getting Started with JavaFX
Release 8
E50607-02
August 2014
Get started with JavaFX by getting an overview of the available features, learning the architecture, and creating simple applications that introduce you to layouts, CSS, FXML, visual effects, and animation.
通过概述可用功能、学习架构和创建简单的应用程序来开始使用JavaFX,这些应用程序将向您介绍布局、CSS、FXML、视觉效果和动画。
JavaFX Getting Started with JavaFX, Release 8
E50607-02
Copyright © 2008, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Contributing Author: Jasper Potts, Nancy Hildebrandt, Joni Gordon, Cindy Castillo
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
本软件和相关文档根据包含使用和披露限制的许可协议提供,并受知识产权法保护。除非您的许可协议明确允许或法律允许,否则您不得以任何形式或通过任何方式使用、复制、转载、翻译、广播、修改、许可、传输、分发、展览、表演、发布或显示任何部分。除非法律要求互操作性,否则禁止对本软件进行逆向工程、反汇编或反编译。
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
本文所含信息如有更改,恕不另行通知,也不保证无误。如果您发现任何错误,请以书面形式向我们报告。
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
如果这是交付给美国政府或代表美国政府授权的任何人的软件或相关文档,则适用以下通知:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
美国政府最终用户:根据适用的《联邦采购条例》和特定机构的补充条例,交付给美国政府最终客户的Oracle程序,包括任何操作系统、集成软件、安装在硬件上的任何程序和/或文档,都是“商业计算机软件”。因此,程序的使用、复制、披露、修改和改编,包括任何操作系统、集成软件、安装在硬件上的任何程序和/或文档,均应遵守适用于程序的许可条款和许可限制。美国政府没有其他权利。
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate failsafe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
该软件或硬件是为各种信息管理应用程序中的通用而开发的。它不是为任何固有危险的应用而开发或打算使用的,包括可能造成人身伤害风险的应用。如果您在危险应用中使用此软件或硬件,则您有责任采取一切适当的故障保护、备份、冗余和其他措施,以确保其安全使用。Oracle Corporation及其附属公司对在危险应用中使用此软件或硬件造成的任何损害不承担任何责任。
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Oracle和Java是Oracle和/或其附属公司的注册商标。其他名称可能是其各自所有者的商标。
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Intel和Intel Xeon是英特尔公司的商标或注册商标。所有SPARC商标均经许可使用,是SPARC International,股份有限公司的商标或注册商标。AMD、Opteron、AMD徽标和AMD Opteron徽标是Advanced Micro Devices的商标或登记商标。UNIX是The Open Group的注册商标。
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information on content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.
此软件或硬件和文档可能提供对第三方内容、产品和服务的访问或信息。Oracle Corporation及其附属公司不对第三方内容、产品和服务的任何形式的保证负责,并明确表示不承担任何责任。Oracle Corporation及其附属公司不对因您访问或使用第三方内容、产品或服务而产生的任何损失、费用或损害负责。
Preface
This preface gives an overview about this tutorial and also describes the document accessibility features and conventions used in this tutorial - Getting Started with JavaFX
本前言概述了本教程,并描述了本教程中使用的文档可访问性功能和约定-JavaFX入门
About This Tutorial
This tutorial is a compilation of three documents that were previously delivered with the JavaFX 2.x documentation set: JavaFX Overview, JavaFX Architecture, and Getting Started with JavaFX. The combined content has been enhanced with updated information about the new JavaFX features included with the Java SE 8 release. This document contains the following parts:
本教程是之前随JavaFX 2.x文档集提供的三个文档的汇编:JavaFX概述、JavaFX架构和JavaFX入门。Java SE 8版本中包含的新JavaFX功能的更新信息增强了组合内容。本文件包含以下部分:
Each part contains chapters that introduce you to the JavaFX technology and gets you started in learning how to use it for your application development.
每一部分都包含向您介绍JavaFX技术的章节,并让您开始学习如何将其用于应用程序开发。
Audience
本文档面向JavaFX开发人员。
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
有关Oracle对可访问性的承诺的信息,请访问Oracle可访问性计划网站http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Access to Oracle Support
Oracle customers have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.
Oracle客户可以通过My Oracle support获得电子支持。有关信息,请访问http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info或访问http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs如果你听力受损。
Related Documents
For more information, see the rest of the JavaFX documentation set at http://docs.oracle.com/javase/javase-clienttechnologies.htm.
有关更多信息,请参阅JavaFX文档集的其余部分http://docs.oracle.com/javase/javase-clienttechnologies.htm.
Conventions
The following text conventions are used in this document:
本文档中使用了以下文本约定:
| Convention | Meaning |
|---|---|
| boldface | Boldface type indicates graphical user interface elements associated with an action, or terms defined in text or the glossary. 粗体类型表示与操作相关的图形用户界面元素,或文本或术语表中定义的术语 |
| italic | Italic type indicates book titles, emphasis, or placeholder variables for which you supply particular values. 斜体类型表示您为其提供特定值的书名、重音或占位符变量 |
| monospace | Monospace type indicates commands within a paragraph, URLs, code in examples, text that appears on the screen, or text that you enter. 单空格类型表示段落中的命令、URL、示例中的代码、屏幕上显示的文本或您输入的文本 |
What's New
This chapter summarizes the new features and significant product changes made in the JavaFX component of the Java SE 8 release.
本章总结了Java SE 8版本的JavaFX组件中的新功能和重大产品更改。
-
The new Modena theme is now the default theme for JavaFX applications. See the Modena theme section of Key Features.
新的Modena主题现在是JavaFX应用程序的默认主题。请参阅[主要功能]的Modena主题部分(https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/javafx/get-started-tutorial/jfx-overview.htm#A1131418).
-
Support for additional HTML5 features has been added. See Adding HTML Content to JavaFX Applications for more information.
添加了对其他HTML5功能的支持。请参阅向JavaFX应用程序添加HTML内容了解更多信息。
-
The new
SwingNodeclass improves the Swing interoperability feature. See Embedding Swing Content in JavaFX Applications.新的“SwingNode”类改进了Swing互操作性特性。请参阅在JavaFX中嵌入Swing内容应用程序。
-
New built-in UI controls,
DatePicker andTableView, are now available. See Using JavaFX UI Controls document for more information.新的内置UI控件“DatePicke”r和“TableView”现在可用。请参阅使用JavaFX UI控件文档以获取更多信息。
-
3D Graphics library has been enhanced with several new API classes. See 3D Graphics features section of Key Features and Getting Started with JavaFX 3D Graphics for more information.
三维图形库已通过几个新的API类进行了增强。请参阅[主要功能]的3D图形功能部分(https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/javafx/get-started-tutorial/jfx-overview.htm#A1131418)以及JavaFX 3D图形入门了解更多信息。
-
The
javafx.printpackage is now available and provides the public JavaFX printing APIs.“javafx.print”包现在可用,并提供公共javafx打印API。
-
Rich text support has been added.
已添加富文本支持。
-
Support for Hi-DPI displays have been made available.
已提供对高DPI显示器的支持。
-
CSS styleable classes became public APIs.
CSS样式类成为公共API。
-
Scheduled service class has been introduced.
已引入预定服务等级。
Part I What Is JavaFX?
1 JavaFX Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the types of applications you can build using JavaFX APIs, where to download the JavaFX libraries, and a high level information about the key JavaFX features being delivered.
本章概述了可以使用JavaFX API构建的应用程序类型、下载JavaFX库的位置,以及有关所提供的关键JavaFX功能的高级信息。
JavaFX is a set of graphics and media packages that enables developers to design, create, test, debug, and deploy rich client applications that operate consistently across diverse platforms.
JavaFX是一组图形和媒体包,使开发人员能够设计、创建、测试、调试和部署跨不同平台一致运行的富客户端应用程序。
- JavaFX Applications
- Availability
- Key Features
- What Can I Build with JavaFX?
- How Do I Run a Sample Application?
- How Do I Run a Sample in an IDE?
- How Do I Create a JavaFX Application?
- Resources
See the Understanding the JavaFX Architecture chapter to learn about the JavaFX platform architecture and to get a brief description of the JavaFX APIs for media streaming, web rendering, and user interface styling.
请参阅了解JavaFX架构第章了解JavaFX平台架构,并简要介绍用于媒体流、web渲染和用户界面样式的JavaFX API。
JavaFX Applications
Since the JavaFX library is written as a Java API, JavaFX application code can reference APIs from any Java library. For example, JavaFX applications can use Java API libraries to access native system capabilities and connect to server-based middleware applications.
由于JavaFX库是作为Java API编写的,因此JavaFX应用程序代码可以引用任何Java库中的API。例如,JavaFX应用程序可以使用Java API库访问本机系统功能并连接到基于服务器的中间件应用程序。
The look and feel of JavaFX applications can be customized. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) separate appearance and style from implementation so that developers can concentrate on coding. Graphic designers can easily customize the appearance and style of the application through the CSS. If you have a web design background, or if you would like to separate the user interface (UI) and the back-end logic, then you can develop the presentation aspects of the UI in the FXML scripting language and use Java code for the application logic. If you prefer to design UIs without writing code, then use JavaFX Scene Builder. As you design the UI, Scene Builder creates FXML markup that can be ported to an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) so that developers can add the business logic.
JavaFX应用程序的外观和感觉可以定制。级联样式表(CSS)将外观和样式与实现分开,以便开发人员可以专注于编码。图形设计师可以通过CSS轻松定制应用程序的外观和风格。如果你有网页设计背景,或者你想把用户界面(UI)和后端逻辑分开,那么你可以用FXML脚本语言开发UI的表示方面,并使用Java代码进行应用程序逻辑。如果你更喜欢在不编写代码的情况下设计UI,那么可以使用JavaFX场景生成器。在设计UI时,Scene Builder会创建可以移植到集成开发环境(IDE)的FXML标记,以便开发人员可以添加业务逻辑。
Availability
The JavaFX APIs are available as a fully integrated feature of the Java SE Runtime Environment (JRE) and the Java Development Kit (JDK ). Because the JDK is available for all major desktop platforms (Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux), JavaFX applications compiled to JDK 7 and later also run on all the major desktop platforms. Support for ARM platforms has also been made available with JavaFX 8. JDK for ARM includes the base, graphics and controls components of JavaFX.
JavaFX API是Java SE运行时环境(JRE)和Java开发工具包(JDK)的完全集成功能。由于JDK适用于所有主要的桌面平台(Windows、Mac OS X和Linux),因此编译为JDK 7及更高版本的JavaFX应用程序也可以在所有主要的台式机平台上运行。JavaFX 8也支持ARM平台。JDK for ARM包括JavaFX的基础、图形和控制组件。
The cross-platform compatibility enables a consistent runtime experience for JavaFX applications developers and users. Oracle ensures synchronized releases and updates on all platforms and offers an extensive support program for companies that run mission-critical applications.
跨平台兼容性为JavaFX应用程序开发人员和用户提供了一致的运行时体验。Oracle确保在所有平台上同步发布和更新,并提供广泛的支持计划适用于运行关键任务应用程序的公司。
On the JDK download page, you can get a zip file of JavaFX sample applications. The sample applications provide many code samples and snippets that show by example how to write JavaFX applications. See "How Do I Run a Sample Application?" for more information.
在JDK下载页面上,您可以获得JavaFX示例应用程序的zip文件。示例应用程序提供了许多代码示例和片段,通过示例展示了如何编写JavaFX应用程序。请参阅“如何运行示例应用程序?”了解更多信息。
Key Features
The following features are included in JavaFX 8 and later releases. Items that were introduced in JavaFX 8 release are indicated accordingly:
JavaFX 8及更高版本中包含以下功能。JavaFX 8版本中引入的项目相应地指出:
-
Java APIs. JavaFX is a Java library that consists of classes and interfaces that are written in Java code. The APIs are designed to be a friendly alternative to Java Virtual Machine (Java VM) languages, such as JRuby and Scala.
Java API。JavaFX是一个Java库,由用Java代码编写的类和接口组成。这些API旨在成为Java虚拟机(Java VM)语言(如JRuby和Scala)的友好替代品。
-
FXML and Scene Builder. FXML is an XML-based declarative markup language for constructing a JavaFX application user interface. A designer can code in FXML or use JavaFX Scene Builder to interactively design the graphical user interface (GUI). Scene Builder generates FXML markup that can be ported to an IDE where a developer can add the business logic.
FXML和场景生成器。FXML是一种基于XML的声明性标记语言,用于构建JavaFX应用程序用户界面。设计者可以在FXML中编码或使用JavaFX Scene Builder交互式设计图形用户界面(GUI)。场景生成器生成FXML标记,可以将其移植到IDE,开发人员可以在其中添加业务逻辑。
-
WebView. A web component that uses WebKitHTML technology to make it possible to embed web pages within a JavaFX application. JavaScript running in WebView can call Java APIs, and Java APIs can call JavaScript running in WebView. Support for additional HTML5 features, including Web Sockets, Web Workers, and Web Fonts, and printing capabilities have been added in JavaFX 8. See Adding HTML Content to JavaFX Applications.
WebView。一种使用WebKitHTML技术将网页嵌入JavaFX应用程序的web组件。运行在WebView中的JavaScript可以调用Java API,Java API可以调用运行在WebView中的JavaScript。JavaFX 8中添加了对其他HTML5功能的支持,包括Web套接字、Web Workers和Web字体,以及打印功能。请参阅向JavaFX应用程序添加HTML内容.
-
Swing interoperability. Existing Swing applications can be updated with JavaFX features, such as rich graphics media playback and embedded Web content. The
SwingNodeclass, which enables you to embed Swing content into JavaFX applications, has been added in JavaFX 8. See the SwingNode API javadoc and Embedding Swing Content in JavaFX Applications for more information.Swing互操作性。现有的Swing应用程序可以使用JavaFX功能进行更新,例如丰富的图形媒体播放和嵌入式Web内容。JavaFX 8中添加了
SwingNode类,该类使您能够将Swing内容嵌入JavaFX应用程序中。请参阅SwingNode API javadoc以及在JavaFX应用程序中嵌入Swing内容了解更多信息。 -
Built-in UI controls and CSS. JavaFX provides all the major UI controls that are required to develop a full-featured application. Components can be skinned with standard Web technologies such as CSS. The DatePicker and TreeTableView UI controls are now available with the JavaFX 8 release. See Using JavaFX UI Controls for more information. Also, the CSS Styleable* classes have become public API, allowing objects to be styled by CSS.
内置UI控件和CSS。JavaFX提供了开发全功能应用程序所需的所有主要UI控件。组件可以使用CSS等标准Web技术进行蒙皮。DatePicker和TreeTableView UI控件现在可用于JavaFX 8版本。请参阅使用JavaFX UI控件了解更多信息。此外,CSS Styleable*类已经成为公共的API,允许使用CSS对对象进行样式设计。
-
Modena theme. The Modena theme replaces the Caspian theme as the default for JavaFX 8 applications. The Caspian theme is still available for your use by adding the
setUserAgentStylesheet(STYLESHEET_CASPIAN)line in your Application start() method. For more information, see the Modena blog at fxexperience.com摩德纳主题。Modena主题取代了Caspian主题,成为JavaFX 8应用程序的默认主题。通过在Application start()方法中添加
setUserAgentStylesheet(STYLESHET_Caspian)行,您仍然可以使用Caspian主题。有关更多信息,请参阅Modena博客在fxexperience.com -
3D Graphics Features. The new API classes for
Shape3D(Box, Cylinder, MeshView, and Spheresubclasses),SubScene, Material, PickResult, LightBase (AmbientLightandPointLightsubclasses), andSceneAntialiasinghave been added to the 3D Graphics library in JavaFX 8. TheCameraAPI class has also been updated in this release. For more information, see the Getting Started with JavaFX 3D Graphics document and the corresponding API javadoc forjavafx.scene.shape.Shape3D,javafx.scene.SubScene, javafx.scene.paint.Material, javafx.scene.input.PickResult, andjavafx.scene.SceneAntialiasing.3D图形功能。JavaFX 8中的3D图形库中添加了新的API类“Shape3D'”(“Box,Cylinder,MeshView,and Sphere”subclasses)、“SubScene,Material,PickResult,LightBase(AmbientLight”和“PointLight”子类)和“SceneAntialising”。“Camera”API类也在本版本中进行了更新。有关更多信息,请参阅JavaFX 3D图形入门文档和相应的API javadoc对于
javafx.scene.shape。Shape3D、javafx.scene。子场景,javafx.scene.paint。材料,javafx.scene.input。PickResult和javafx.scene。场景抗锯齿。 -
Canvas API. The Canvas API enables drawing directly within an area of the JavaFX scene that consists of one graphical element (node).
画布API。Canvas API允许直接在由一个图形元素(节点)组成的JavaFX场景区域内绘制。
-
Printing API. The
javafx.printpackage has been added in Java SE 8 release and provides the public classes for the JavaFX Printing API.打印API。Java SE 8版本中添加了
javafx.print包,并为javafx Printing API提供了公共类. -
Rich Text Support. JavaFX 8 brings enhanced text support to JavaFX, including bi-directional text and complex text scripts, such as Thai and Hindu in controls, and multi-line, multi-style text in text nodes.
富文本支持。JavaFX 8为JavaFX带来了增强的文本支持,包括双向文本和复杂的文本脚本,如控件中的泰语和印度语,以及文本节点中的多行、多样式文本。
-
Multitouch Support. JavaFX provides support for multitouch operations, based on the capabilities of the underlying platform.
多点触控支持。JavaFX基于底层平台的功能为多点触控操作提供支持。
-
Hi-DPI support. JavaFX 8 now supports Hi-DPI displays.
高DPI支持。JavaFX 8现在支持高DPI显示器。
-
Hardware-accelerated graphics pipeline. JavaFX graphics are based on the graphics rendering pipeline (Prism). JavaFX offers smooth graphics that render quickly through Prism when it is used with a supported graphics card or graphics processing unit (GPU). If a system does not feature one of the recommended GPUs supported by JavaFX, then Prism defaults to the software rendering stack.
硬件加速图形流水线。JavaFX图形基于图形渲染管道(Prism)。JavaFX提供平滑的图形,当与受支持的图形卡或图形处理单元(GPU)一起使用时,可以通过Prism快速渲染。如果系统没有JavaFX支持的推荐GPU之一,则Prism默认为软件渲染堆栈。
-
High-performance media engine. The media pipeline supports the playback of web multimedia content. It provides a stable, low-latency media framework that is based on the GStreamer multimedia framework.
高性能媒体引擎。媒体管道支持播放网络多媒体内容。它提供了一个基于GStreamer多媒体框架的稳定、低延迟的媒体框架。
-
Self-contained application deployment model. Self-contained application packages have all of the application resources and a private copy of the Java and JavaFX runtimes. They are distributed as native installable packages and provide the same installation and launch experience as native applications for that operating system.
自包含的应用程序部署模型。自包含的应用程序包包含所有应用程序资源以及Java和JavaFX运行时的私有副本。它们作为本机可安装包分发,并提供与该操作系统的本机应用程序相同的安装和启动体验。
What Can I Build with JavaFX?
With JavaFX, you can build many types of applications. Typically, they are network-aware applications that are deployed across multiple platforms and display information in a high-performance modern user interface that features audio, video, graphics, and animation.
使用JavaFX,您可以构建许多类型的应用程序。通常,它们是跨多个平台部署的网络感知应用程序,并在具有音频、视频、图形和动画功能的高性能现代用户界面中显示信息。
Table 1-1 shows images of a few of the sample JavaFX applications that are included with the JavaFX 8.n release.
表1-1显示了JavaFX 8.n版本中包含的几个示例JavaFX应用程序的图像。
Table 1-1 Sample JavaFX Applications
表1-1 JavaFX应用程序示例
| Sample Application | Description |
|---|---|
 Description of the illustration ensemble-small.gif Description of the illustration ensemble-small.gif |
JavaFX Ensemble8 Ensemble8 is a gallery of sample applications that demonstrate a large variety of JavaFX features, including animation, charts, and controls. You can view and interact with each running sample on ALL platforms, and read its descriptions. On the desktop platforms, you can copy each sample's source code, adjust the properties of the sample components used in several samples, and follow links to the relevant API documentation when you're connected to the Internet.Ensemble8 also runs with JavaFX for ARM. JavaFX集成8集成8是一个示例应用程序库,展示了各种JavaFX功能,包括动画、图表和控件。您可以在所有平台上查看和交互每个正在运行的示例,并阅读其描述。在桌面平台上,您可以复制每个示例的源代码,调整多个示例中使用的示例组件的属性,并在连接到Internet时遵循相关API文档的链接。Ensemble8还与ARM的JavaFX一起运行。 |
 Description of the illustration modena-sample.gif Description of the illustration modena-sample.gif |
Modena Modena is a sample application that demonstrates the look and feel of UI components using the Modena theme. It gives you the option to contrast Modena and Caspian themes, and explore various aspects of these themes. Modena Modena是一个示例应用程序,演示了使用Modena主题的UI组件的外观和感觉。它为您提供了对比摩德纳和里海主题的选项,并探索这些主题的各个方面。 |
 Description of the illustration sample-3dviewer.gif Description of the illustration sample-3dviewer.gif |
3D Viewer 3DViewer is a sample application that allows you to navigate and examine a 3D scene with a mouse or a trackpad. 3DViewer has importers for a subset of the features in OBJ and Maya files. The ability to import animation is also provided for Maya files. (Note that in the case of Maya files, construction history should be deleted on all the objects when saving as a Maya file.) 3DViewer also has the ability to export the contents of the scene as Java or FXML files. 3DViewer 3DViewer是一个示例应用程序,允许您使用鼠标或触控板导航和检查3D场景。3DViewer具有OBJ和Maya文件中部分特征的导入程序。Maya文件也提供了导入动画的功能。(请注意,对于Maya文件,在另存为Maya文件时,应删除所有对象的构造历史。)3DViewer还可以将场景内容导出为Java或FXML文件。 |
How Do I Run a Sample Application?
The steps in this section explain how to download and run the sample applications that are available as a separate download with the Java Platform (JDK 8).
本节中的步骤解释了如何下载和运行Java平台(JDK 8)中单独下载的示例应用程序。
Note:
Before you can run a sample JavaFX application, you need to have the JavaFX runtime libraries on your machine. Before you proceed with these steps, either install the latest version of the JDK 8 or the latest version of the JRE.
在运行示例JavaFX应用程序之前,您需要在计算机上安装JavaFX运行时库。在继续执行这些步骤之前,请安装最新版本的JDK 8或最新版本的JRE.
To download and run the sample applications:
要下载并运行示例应用程序,请执行以下操作:
-
Go to the Java SE Downloads page at
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/.转到Java SE下载页面
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/. -
Scroll down to locate the JDK 8 and JavaFX Demos and Samples section.
向下滚动以找到JDK 8和JavaFX演示和示例部分。
-
Click the Demos and Samples Download button to go to the downloads page.
单击演示和示例下载按钮转到下载页面。
-
On the Java SE Development Kit 8 Downloads page, scroll down to the JavaFX Demos and Samples Downloads section.
在Java SE Development Kit 8下载页面上,向下滚动到JavaFX演示和示例下载部分。
-
Download the zip file for the correct operating system and extract the files.
下载适用于正确操作系统的zip文件并解压缩文件。
The
javafx-samples-8.xdirectory is created and contains the files for the available samples. The NetBeans projects for the samples are in thejavafx-samples-8.x\srcdirectory.创建了
javafx-samples-8.x目录,其中包含可用示例的文件。示例的NetBeans项目位于javafx-samples-8.x\src目录中。 -
Double-click the executable file for a sample.
双击示例的可执行文件。
For example, to run the Ensemble8 pre-built sample application, double-click the
Ensemble8.jarfile.例如,要运行Ensemble8预构建的示例应用程序,请双击“Ensemble8.jar”文件。
How Do I Run a Sample in an IDE?
You can use several Java development IDEs to develop JavaFX applications. The following steps explain how to view and run the source code in the NetBeans IDE.
您可以使用多个Java开发IDE来开发JavaFX应用程序。以下步骤解释了如何在NetBeans IDE中查看和运行源代码。
To view and run the sample source code in NetBeans IDE:
要在NetBeans IDE中查看和运行示例源代码:
-
Download the samples, as described above, and extract the files.
如上所述下载示例并提取文件。
-
From a NetBeans 7.4 or later IDE, load the project for the sample you want to view.
从NetBeans 7.4或更高版本的IDE中,加载要查看的示例的项目。
-
From the File menu, select Open Project.
从“文件”菜单中,选择“打开项目”。
-
In the Open Project dialog box, navigate to the directory that lists the samples. The navigation path looks something like this:
在“打开项目”对话框中,导航到列出示例的目录。导航路径看起来像这样:
..\javafx_samples-8.x-<platform>\javafx-samples-8.x\src -
Select the sample you want to view.
选择要查看的样本。
-
Click the Open Project button.
单击“打开项目”按钮。
-
-
In the Projects window, right click the project you just opened and select Run.
在“项目”窗口中,右键单击刚刚打开的项目,然后选择“运行”。
Notice the Output window is updated and the sample project is run and deployed.
请注意,输出窗口已更新,示例项目已运行并部署。
How Do I Create a JavaFX Application?
Because JavaFX applications are written in the Java language, you can use your favorite editor or any integrated development environment (IDE) that supports the Java language (such as NetBeans, Eclipse, or IntelliJ IDEA) to create JavaFX applications.
因为JavaFX应用程序是用Java语言编写的,所以您可以使用您最喜欢的编辑器或任何支持Java语言的集成开发环境(IDE)(如NetBeans、Eclipse或IntelliJ IDEA)来创建JavaFX应用软件。
To create JavaFX applications:
要创建JavaFX应用程序:
-
Go to the Java SE Downloads page at
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/to download the Oracle® JDK 8 with JavaFX 8.n support. Links to the certified system configurations and release notes are also available on that page..转到Java SE下载页面
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/下载支持JavaFX 8.n的Oracle®JDK 8。该页面上还提供了认证系统配置和发行说明的链接。。 -
Use Getting Started with JavaFX Sample Applications to create simple applications that demonstrates how to work with layouts, style sheets, and visual effects.
使用JavaFX示例应用程序入门创建演示如何使用布局、样式表和视觉效果的简单应用程序。
-
Use JavaFX Scene Builder to design the UI for your JavaFX application without coding. You can drag and drop UI components to a work area, modify their properties, apply style sheets, and integrate the resulting code with their application logic.
使用JavaFX场景生成器为您的JavaFX应用程序设计UI,无需编码。您可以将UI组件拖放到工作区,修改它们的属性,应用样式表,并将生成的代码与其应用程序逻辑集成。
-
Download the JavaFX Scene Builder from the JavaFX Downloads page at
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/.从JavaFX下载页面下载JavaFX场景生成器,网址为
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/. -
Follow the Getting Started with JavaFX Scene Builder tutorial to learn more.
按照JavaFX场景生成器入门教程了解更多信息。
-
Resources
Use the following resources to learn more about the JavaFX technology.
使用以下资源了解有关JavaFX技术的更多信息。
-
Download the latest JDK 8 release and the JavaFX samples from the Java SE Downloads page at:
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/.从Java SE下载页面下载最新的JDK 8版本和JavaFX示例,网址为:
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/. -
Read Understanding the JavaFX Architecture.
阅读了解JavaFX架构.
-
Browse JavaFX tutorials and articles for developers.
浏览JavaFX教程和文章对于开发者来说。
2 Understanding the JavaFX Architecture
The chapter gives a high level description of the JavaFX architecture and ecosystem.
本章对JavaFX架构和生态系统进行了高层次的描述。
Figure 2-1 illustrates the architectural components of the JavaFX platform. The sections following the diagram describe each component and how the parts interconnect. Below the JavaFX public APIs lies the engine that runs your JavaFX code. It is composed of subcomponents that include a JavaFX high performance graphics engine, called Prism; a small and efficient windowing system, called Glass; a media engine, and a web engine. Although these components are not exposed publicly, their descriptions can help you to better understand what runs a JavaFX application.
图2-1展示了JavaFX平台的架构组件。下图后面的部分描述了每个组件以及这些部件是如何互连的。JavaFX公共API下面是运行JavaFX代码的引擎。它由子组件组成,其中包括一个名为Prism的JavaFX高性能图形引擎;一个名为Glass的小型高效窗口系统;媒体引擎和网络引擎。虽然这些组件没有公开,但它们的描述可以帮助您更好地理解运行JavaFX应用程序的内容。
- Scene Graph
- Java Public APIs for JavaFX Features
- Graphics System
- Glass Windowing Toolkit
- Media and Images
- Web Component
- CSS
- UI Controls
- Layout
- 2-D and 3-D Transformations
- Visual Effects
Figure 2-1 JavaFX Architecture Diagram
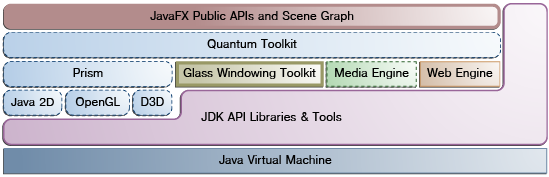
Description of "Figure 2-1 JavaFX Architecture Diagram"
Scene Graph
The JavaFX scene graph, shown as part of the top layer in Figure 2-1, is the starting point for constructing a JavaFX application. It is a hierarchical tree of nodes that represents all of the visual elements of the application's user interface. It can handle input and can be rendered.
JavaFX场景图,如图2-1中顶层的一部分所示,是构建JavaFX应用程序的起点。它是一个层次化的节点树,代表应用程序用户界面的所有视觉元素。它可以处理输入并可以呈现。
A single element in a scene graph is called a node. Each node has an ID, style class, and bounding volume. With the exception of the root node of a scene graph, each node in a scene graph has a single parent and zero or more children. It can also have the following:
场景图中的单个元素称为节点。每个节点都有一个ID、样式类和边界体积。除场景图的根节点外,场景图中的每个节点都有一个父节点和零个或多个子节点。它还可以具有以下功能:
-
Effects, such as blurs and shadows
效果,如模糊和阴影
-
Opacity
不透明度
-
Transforms
转型
-
Event handlers (such as mouse, key and input method)
事件处理程序(如鼠标、按键和输入法)
-
An application-specific state
特定于应用程序的状态
Unlike in Swing and Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT), the JavaFX scene graph also includes the graphics primitives, such as rectangles and text, in addition to having controls, layout containers, images and media.
与Swing和抽象窗口工具包(AWT)不同,JavaFX场景图除了包含控件、布局容器、图像和媒体外,还包括图形基元,如矩形和文本。
For most uses, the scene graph simplifies working with UIs, especially when rich UIs are used. Animating various graphics in the scene graph can be accomplished quickly using the javafx.animation APIs, and declarative methods, such as XML doc, also work well.
对于大多数用途,场景图简化了UI的使用,特别是在使用富UI时。使用javafx.animation APIs可以快速完成场景图中各种图形的动画制作,XML文档等声明性方法也很有效。
The javafx.scene API allows the creation and specification of several types of content, such as:
javafx.sceneAPI允许创建和指定几种类型的内容,例如:
-
Nodes: Shapes (2-D and 3-D), images, media, embedded web browser, text, UI controls, charts, groups, and containers
节点:形状(二维和三维)、图像、媒体、嵌入式web浏览器、文本、UI控件、图表、组和容器
-
State: Transforms (positioning and orientation of nodes), visual effects, and other visual state of the content
状态:转换(节点的定位和方向)、视觉效果和内容的其他视觉状态
-
Effects: Simple objects that change the appearance of scene graph nodes, such as blurs, shadows, and color adjustment
效果:更改场景图节点外观的简单对象,如模糊、阴影和颜色调整
For more information, see the Working with the JavaFX Scene Graph document.
有关更多信息,请参阅使用JavaFX场景图文件。
Java Public APIs for JavaFX Features
The top layer of the JavaFX architecture shown in Figure 2-1 provides a complete set of Java public APIs that support rich client application development. These APIs provide unparalleled freedom and flexibility to construct rich client applications. The JavaFX platform combines the best capabilities of the Java platform with comprehensive, immersive media functionality into an intuitive and comprehensive one-stop development environment. These Java APIs for JavaFX features:
JavaFX架构的顶层如图2-1所示提供了一套完整的Java公共API,支持富客户端应用程序开发。这些API为构建富客户端应用程序提供了无与伦比的自由度和灵活性。JavaFX平台将Java平台的最佳功能与全面、沉浸式的媒体功能相结合,形成了一个直观、全面的一站式开发环境。这些JavaFX功能的Java API:
-
Allow the use of powerful Java features, such as generics, annotations, multithreading, and Lamda Expressions (introduced in Java SE 8).
允许使用强大的Java特性,如泛型、注释、多线程和Lamda表达式(在Java SE 8中引入)。
-
Make it easier for Web developers to use JavaFX from other JVM-based dynamic languages, such as Groovy and JavaScript.
使Web开发人员更容易从其他基于JVM的动态语言(如Groovy和JavaScript)中使用JavaFX。
-
Allow Java developers to use other system languages, such as Groovy, for writing large or complex JavaFX applications.
允许Java开发人员使用其他系统语言(如Groovy)编写大型或复杂的JavaFX应用程序。
-
Allow the use of binding which includes support for the high performance lazy binding, binding expressions, bound sequence expressions, and partial bind reevaluation. Alternative languages (like Groovy) can use this binding library to introduce binding syntax similar to that of JavaFX Script.
允许使用绑定,其中包括对高性能延迟绑定、绑定表达式、绑定序列表达式和部分绑定重新计算的支持。其他语言(如Groovy)可以使用此绑定库引入类似于JavaFX Script的绑定语法。
-
Extend the Java collections library to include observable lists and maps, which allow applications to wire user interfaces to data models, observe changes in those data models, and update the corresponding UI control accordingly.
扩展Java集合库以包括可观察列表和映射,这允许应用程序将用户界面连接到数据模型,观察这些数据模型中的更改,并相应地更新相应的UI控件。
The JavaFX APIs and programming model are a continuation of the JavaFX 1.x product line. Most of the JavaFX APIs have been ported directly to Java. Some APIs, such as Layout and Media, along with many other details, have been improved and simplified based on feedback received from users of the JavaFX 1.x release. JavaFX relies more on web standards, such as CSS for styling controls and ARIA for accessibility specifications. The use of additional web standards is also under review.
JavaFX API和编程模型是JavaFX 1.x产品线的延续。大多数JavaFX API已经直接移植到Java。一些API,如布局和媒体,以及许多其他细节,已经根据JavaFX 1.x版本用户的反馈进行了改进和简化。JavaFX更多地依赖于web标准,例如用于样式控制的CSS和用于可访问性规范的ARIA。其他网络标准的使用也在审查中。
Graphics System
The JavaFX Graphics System, shown in blue in Figure 2-1, is an implementation detail beneath the JavaFX scene graph layer. It supports both 2-D and 3-D scene graphs. It provides software rendering when the graphics hardware on a system is insufficient to support hardware accelerated rendering.
JavaFX图形系统,如图2-1中蓝色所示,是JavaFX场景图层下的实现细节。它支持二维和三维场景图。当系统上的图形硬件不足以支持硬件加速渲染时,它提供软件渲染。
Two graphics accelerated pipelines are implemented on the JavaFX platform:
JavaFX平台上实现了两个图形加速管道:
-
Prism processes render jobs. It can run on both hardware and software renderers, including 3-D. It is responsible for rasterization and rendering of JavaFX scenes. The following multiple render paths are possible based on the device being used:
棱镜进程渲染作业。它可以在硬件和软件渲染器上运行,包括3D。它负责JavaFX场景的光栅化和渲染。根据所使用的设备,以下多种渲染路径是可能的:
-
DirectX 9 on Windows XP and Windows Vista
Windows XP和Windows Vista上的DirectX 9
-
DirectX 11 on Windows 7
Windows 7上的DirectX 11
-
OpenGL on Mac, Linux, Embedded
Mac、Linux、嵌入式OpenGL
-
Software rendering when hardware acceleration is not possible
硬件无法加速时的软件渲染
The fully hardware accelerated path is used when possible, but when it is not available, the software render path is used because the software render path is already distributed in all of the Java Runtime Environments (JREs). This is particularly important when handling 3-D scenes. However, performance is better when the hardware render paths are used.
尽可能使用完全硬件加速的路径,但当它不可用时,使用软件渲染路径,因为软件渲染路径已经分布在所有Java运行时环境(JRE)中。在处理3D场景时,这一点尤为重要。但是,使用硬件渲染路径时性能会更好。
-
-
Quantum Toolkit ties Prism and Glass Windowing Toolkit together and makes them available to the JavaFX layer above them in the stack. It also manages the threading rules related to rendering versus events handling.
Quantum Toolkit将Prism和Glass Windowing Toolkit连接在一起,并使它们在堆栈中的JavaFX层上可用。它还管理与渲染和事件处理相关的线程规则。
Glass Windowing Toolkit
The Glass Windowing Toolkit, shown in beige in the middle portion of Figure 2-1, is the lowest level in the JavaFX graphics stack. Its main responsibility is to provide native operating services, such as managing the windows, timers, and surfaces. It serves as the platform-dependent layer that connects the JavaFX platform to the native operating system.
玻璃窗口工具包,以米黄色显示在图2-1的中间部分,是JavaFX图形堆栈中的最低级别。它的主要职责是提供本机操作服务,如管理窗口、计时器和表面。它作为平台依赖层,将JavaFX平台连接到本机操作系统。
The Glass toolkit is also responsible for managing the event queue. Unlike the Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT), which manages its own event queue, the Glass toolkit uses the native operating system's event queue functionality to schedule thread usage. Also unlike AWT, the Glass toolkit runs on the same thread as the JavaFX application. In AWT, the native half of AWT runs on one thread and the Java level runs on another thread. This introduces a lot of issues, many of which are resolved in JavaFX by using the single JavaFX application thread approach.
Glass工具包还负责管理事件队列。与管理自己的事件队列的抽象窗口工具包(AWT)不同,Glass工具包使用本机操作系统的事件队列功能来调度线程使用。与AWT不同,Glass工具包与JavaFX应用程序在同一线程上运行。在AWT中,AWT的本机部分在一个线程上运行,Java级别在另一个线程中运行。这引入了许多问题,其中许多问题在JavaFX中通过使用单JavaFX应用程序线程方法得到了解决。
Threads
The system runs two or more of the following threads at any given time.
系统在任何给定时间运行以下两个或多个线程。
-
JavaFX application thread: This is the primary thread used by JavaFX application developers. Any ”live” scene, which is a scene that is part of a window, must be accessed from this thread. A scene graph can be created and manipulated in a background thread, but when its root node is attached to any live object in the scene, that scene graph must be accessed from the JavaFX application thread. This enables developers to create complex scene graphs on a background thread while keeping animations on 'live' scenes smooth and fast. The JavaFX application thread is a different thread from the Swing and AWT Event Dispatch Thread (EDT), so care must be taken when embedding JavaFX code into Swing applications.
JavaFX应用线程:这是JavaFX应用程序开发人员使用的主要线程。任何“实时”场景,即窗口的一部分,都必须从该线程访问。场景图可以在后台线程中创建和操作,但当其根节点附加到场景中的任何活动对象时,必须从JavaFX应用程序线程访问该场景图。这使开发人员能够在后台线程上创建复杂的场景图,同时保持“实时”场景上的动画流畅快速。JavaFX应用程序线程与Swing和AWT事件调度线程(EDT)是不同的线程,因此在将JavaFX代码嵌入Swing应用程序时必须小心。
-
Prism render thread: This thread handles the rendering separately from the event dispatcher. It allows frame N to be rendered while frame N +1 is being processed. This ability to perform concurrent processing is a big advantage, especially on modern systems that have multiple processors. The Prism render thread may also have multiple rasterization threads that help off-load work that needs to be done in rendering.
Prism渲染线程:此线程与事件调度器分开处理渲染。它允许在处理帧N+1的同时渲染帧N。这种执行并发处理的能力是一个很大的优势,特别是在具有多个处理器的现代系统上。Prism渲染线程也可能有多个光栅化线程,有助于减轻渲染中需要完成的工作。
-
Media thread: This thread runs in the background and synchronizes the latest frames through the scene graph by using the JavaFX application thread.
媒体线程:此线程在后台运行,并使用JavaFX应用程序线程通过场景图同步最新帧。
Pulse
A pulse is an event that indicates to the JavaFX scene graph that it is time to synchronize the state of the elements on the scene graph with Prism. A pulse is throttled at 60 frames per second (fps) maximum and is fired whenever animations are running on the scene graph. Even when animation is not running, a pulse is scheduled when something in the scene graph is changed. For example, if a position of a button is changed, a pulse is scheduled.
脉冲是一种事件,它向JavaFX场景图指示是时候将场景图上元素的状态与Prism同步了。脉冲被限制在每秒60帧(fps)的最大值,并在场景图上运行动画时触发。即使动画没有运行,当场景图中的某些内容发生变化时,也会安排一个脉冲。例如,如果按钮的位置发生了变化,则会安排一个脉冲。
When a pulse is fired, the state of the elements on the scene graph is synchronized down to the rendering layer. A pulse enables application developers a way to handle events asynchronously. This important feature allows the system to batch and execute events on the pulse.
当触发脉冲时,场景图上元素的状态会同步到渲染层。脉冲使应用程序开发人员能够异步处理事件。这一重要功能允许系统对脉冲进行批处理和执行事件。
Layout and CSS are also tied to pulse events. Numerous changes in the scene graph could lead to multiple layout or CSS updates, which could seriously degrade performance. The system automatically performs a CSS and layout pass once per pulse to avoid performance degradation. Application developers can also manually trigger layout passes as needed to take measurements prior to a pulse.
布局和CSS也与脉冲事件相关联。场景图中的许多更改可能会导致多次布局或CSS更新,这可能会严重降低性能。系统每脉冲自动执行一次CSS和布局传递,以避免性能下降。应用程序开发人员还可以根据需要手动触发布局过程,以便在脉冲之前进行测量。
The Glass Windowing Toolkit is responsible for executing the pulse events. It uses the high-resolution native timers to make the execution.
玻璃窗口工具包负责执行脉冲事件。它使用高分辨率的本地计时器来执行
Media and Images
JavaFX media functionality is available through the javafx.scene.media APIs. JavaFX supports both visual and audio media. Support is provided for MP3, AIFF, and WAV audio files and FLV video files. JavaFX media functionality is provided as three separate components: the Media object represents a media file, the MediaPlayer plays a media file, and a MediaView is a node that displays the media.
JavaFX媒体功能可通过JavaFX.scene.media API获得。JavaFX支持视觉和音频媒体。支持MP3、AIFF和WAV音频文件以及FLV视频文件。JavaFX媒体功能由三个单独的组件提供:media对象表示媒体文件,MediaPlayer播放媒体文件,而MediaView是显示媒体的节点。
The Media Engine component, shown in green in Figure 2-1, has been designed with performance and stability in mind and provides consistent behavior across platforms. For more information, read the Incorporating Media Assets into JavaFX Applications document.
媒体引擎组件,如图2-1中绿色所示,在设计时考虑了性能和稳定性,并提供了跨平台的一致行为。有关更多信息,请阅读将媒体资源合并到JavaFX应用程序中文件。
Web Component
The Web component is a JavaFX UI control, based on Webkit, that provides a Web viewer and full browsing functionality through its API. This Web Engine component, shown in orange in Figure 2-1, is based on WebKit, which is an open source web browser engine that supports HTML5, CSS, JavaScript, DOM, and SVG. It enables developers to implement the following features in their Java applications:
Web组件是一个基于Webkit的JavaFX UI控件,通过其API提供Web查看器和完整的浏览功能。此Web引擎组件在图2-1中以橙色显示,基于WebKit,这是一个支持HTML5、CSS、JavaScript、DOM和SVG的开源web浏览器引擎。它使开发人员能够在他们的Java应用程序中实现以下功能:
-
Render HTML content from local or remote URL
从本地或远程URL呈现HTML内容
-
Support history and provide Back and Forward navigation
支持历史记录并提供前后导航
-
Reload the content
重新加载内容
-
Apply effects to the web component
将效果应用于web组件
-
Edit the HTML content
编辑HTML内容
-
Execute JavaScript commands
执行JavaScript命令
-
Handle events
处理事件
This embedded browser component is composed of the following classes:
此嵌入式浏览器组件由以下类组成:
-
WebEngineprovides basic web page browsing capability.WebEngine提供基本的网页浏览功能。 -
WebViewencapsulates a WebEngine object, incorporates HTML content into an application's scene, and provides fields and methods to apply effects and transformations. It is an extension of aNodeclass.WebView封装了WebEngine对象,将HTML内容合并到应用程序的场景中,并提供了应用效果和转换的字段和方法。它是Node类的扩展。
In addition, Java calls can be controlled through JavaScript and vice versa to allow developers to make the best of both environments. For more detailed overview of the JavaFX embedded browser, see the Adding HTML Content to JavaFX Applications document.
此外,Java调用可以通过JavaScript进行控制,反之亦然,以使开发人员能够充分利用这两种环境。有关JavaFX嵌入式浏览器的更多详细概述,请参阅向JavaFX应用程序添加HTML内容文件。
CSS
JavaFX Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) provides the ability to apply customized styling to the user interface of a JavaFX application without changing any of that application's source code. CSS can be applied to any node in the JavaFX scene graph and are applied to the nodes asynchronously. JavaFX CSS styles can also be easily assigned to the scene at runtime, allowing an application's appearance to dynamically change.
JavaFX级联样式表(CSS)提供了将自定义样式应用于JavaFX应用程序的用户界面的能力,而无需更改该应用程序的任何源代码。CSS可以应用于JavaFX场景图中的任何节点,并且可以异步应用于节点。JavaFX CSS样式也可以在运行时轻松分配给场景,允许应用程序的外观动态更改。
Figure 2-2 demonstrates the application of two different CSS styles to the same set of UI controls.
图2-2演示了将两种不同的CSS样式应用于同一组UI控件。
Figure 2-2 CSS Style Sheet Sample
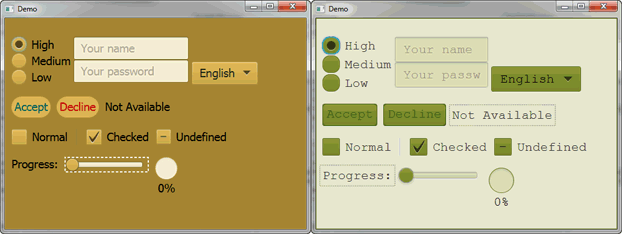
Description of "Figure 2-2 CSS Style Sheet Sample"
JavaFX CSS is based on the W3C CSS version 2.1 specifications, with some additions from current work on version 3. The JavaFX CSS support and extensions have been designed to allow JavaFX CSS style sheets to be parsed cleanly by any compliant CSS parser, even one that does not support JavaFX extensions. This enables the mixing of CSS styles for JavaFX and for other purposes (such as for HTML pages) into a single style sheet. All JavaFX property names are prefixed with a vendor extension of ”-fx-”, including those that might seem to be compatible with standard HTML CSS, because some JavaFX values have slightly different semantics.
JavaFX CSS基于W3C CSS 2.1版本规范,并在当前版本3的工作中添加了一些内容。JavaFX CSS支持和扩展旨在允许任何兼容的CSS解析器(即使是不支持JavaFX扩展的解析器)清晰地解析JavaFX CSS样式表。这使得JavaFX和其他用途(如HTML页面)的CSS样式可以混合到一个样式表中。所有JavaFX属性名的前缀都是供应商扩展名“-fx-”,包括那些似乎与标准HTML CSS兼容的属性名,因为一些JavaFX值的语义略有不同。
For more detailed information about JavaFX CSS, see the Skinning JavaFX Applications with CSS document.
关JavaFX CSS的更多详细信息,请参阅使用CSS对JavaFX应用程序进行蒙皮文件。
UI Controls
The JavaFX UI controls available through the JavaFX API are built by using nodes in the scene graph. They can take full advantage of the visually rich features of the JavaFX platform and are portable across different platforms. JavaFX CSS allows for theming and skinning of the UI controls.
通过JavaFX API可用的JavaFX UI控件是通过使用场景图中的节点构建的。它们可以充分利用JavaFX平台丰富的视觉特性,并可在不同平台上移植。JavaFX CSS允许对UI控件进行主题化和蒙皮。
Figure 2-3 shows some of the UI controls that are currently supported. These controls reside in the javafx.scene.control package.
图2-3显示了当前支持的一些UI控件。这些控件位于javafx.scene.control包中。
Figure 2-3 JavaFX UI Controls Sample
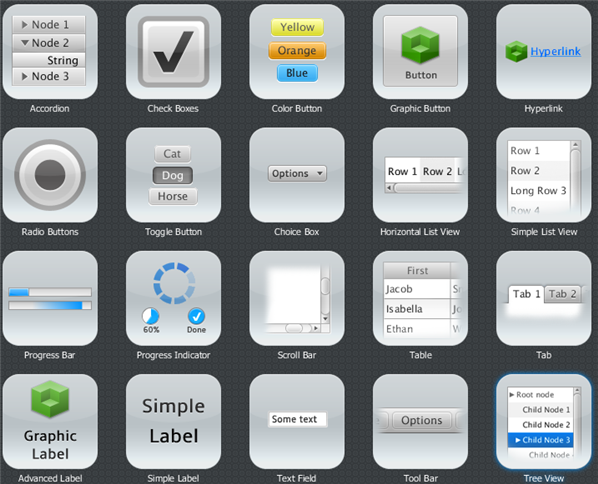
Description of "Figure 2-3 JavaFX UI Controls Sample"
For more detailed information about all the available JavaFX UI controls, see the Using JavaFX UI Controls and the API documentation for the javafx.scene.control package.
有关所有可用JavaFX UI控件的更多详细信息,请参阅使用JavaFX UI控制和API文件对于javafx.scene.control包。
Layout
Layout containers or panes can be used to allow for flexible and dynamic arrangements of the UI controls within a scene graph of a JavaFX application. The JavaFX Layout API includes the following container classes that automate common layout models:
布局容器或窗格可用于在JavaFX应用程序的场景图中灵活动态地排列UI控件。JavaFX布局API包括以下容器类,这些类可自动实现常见布局模型:
-
The
BorderPaneclass lays out its content nodes in the top, bottom, right, left, or center region.BorderPane类将其内容节点布置在顶部、底部、右侧、左侧或中心区域。 -
The
HBoxclass arranges its content nodes horizontally in a single row.HBox类将其内容节点水平排列在一行中。 -
The
VBoxclass arranges its content nodes vertically in a single column.VBox类将其内容节点垂直排列在一列中。 -
The
StackPaneclass places its content nodes in a back-to-front single stack.StackPane类将其内容节点放置在从后到前的单个堆栈中。 -
The
GridPaneclass enables the developer to create a flexible grid of rows and columns in which to lay out content nodes.GridPane类使开发人员能够创建灵活的行和列网格,在其中布局内容节点。 -
The
FlowPaneclass arranges its content nodes in either a horizontal or vertical ”flow,” wrapping at the specified width (for horizontal) or height (for vertical) boundaries.FlowPane类将其内容节点排列成水平或垂直的“流”,以指定的宽度(用于水平)或高度(用于垂直)边界包裹。 -
The
TilePaneclass places its content nodes in uniformly sized layout cells or tilesTilePane类将其内容节点放置在大小均匀的布局单元格或图块中 -
The
AnchorPaneclass enables developers to create anchor nodes to the top, bottom, left side, or center of the layout.AnchorPane类使开发人员能够在布局的顶部、底部、左侧或中心创建锚节点。
To achieve a desired layout structure, different containers can be nested within a JavaFX application.
为了实现所需的布局结构,可以在JavaFX应用程序中嵌套不同的容器。
To learn more about how to work with layouts, see the Working with Layouts in JavaFX article. For more information about the JavaFX layout API, see the API documentation for the javafx.scene.layout package.
要了解有关如何使用布局的更多信息,请参阅在JavaFX中使用布局文章。有关JavaFX布局API的更多信息,请参阅JavaFX.secene.layout包的API文档。
2-D and 3-D Transformations
Each node in the JavaFX scene graph can be transformed in the x-y coordinate using the following javafx.scene.tranform classes:
JavaFX场景图中的每个节点都可以使用以下JavaFX.scene.transform类在x-y坐标系中进行转换:
-
translate– Move a node from one place to another along the x, y, z planes relative to its initial position.“平移”-将节点相对于其初始位置沿x、y、z平面从一个位置移动到另一个位置。
-
scale– Resize a node to appear either larger or smaller in the x, y, z planes, depending on the scaling factor.“缩放”-根据缩放因子,调整节点的大小,使其在x、y、z平面上显示得更大或更小。
-
shear– Rotate one axis so that the x-axis and y-axis are no longer perpendicular. The coordinates of the node are shifted by the specified multipliers.“剪切”-旋转一个轴,使x轴和y轴不再垂直。节点的坐标会根据指定的乘数进行偏移。
-
rotate– Rotate a node about a specified pivot point of the scene.“rotate”–围绕场景的指定枢轴点旋转节点。
-
affine– Perform a linear mapping from 2-D/3-D coordinates to other 2-D/3-D coordinates while preserving the 'straight' and 'parallel' properties of the lines. This class should be used withTranslate,Scale,Rotate, orSheartransform classes instead of being used directly.“仿射”-执行从2D/3D坐标到其他2D/3D座标的线性映射,同时保持直线的“直线”和“平行”特性。此类应与“Translate”、“Scale”、“Rotate”或“Shear”变换类一起使用,而不是直接使用。
To learn more about working with transformations, see the Applying Transformations in JavaFX document. For more information about the javafx.scene.transform API classes, see the API documentation.
要了解有关使用转换的更多信息,请参阅在JavaFX中应用转换文件。有关javafx.secene.transformneneneba API类的更多信息,请参阅API文档.
Visual Effects
The development of rich client interfaces in the JavaFX scene graph involves the use of Visual Effects or Effects to enhance the look of JavaFX applications in real time. The JavaFX Effects are primarily image pixel-based and, hence, they take the set of nodes that are in the scene graph, render it as an image, and apply the specified effects to it.
在JavaFX场景图中开发富客户端界面涉及使用视觉效果或特效来实时增强JavaFX应用程序的外观。JavaFX效果主要基于图像像素,因此,它们采用场景图中的节点集,将其渲染为图像,并对其应用指定的效果。
Some of the visual effects available in JavaFX include the use of the following classes:
JavaFX中可用的一些视觉效果包括使用以下类:
-
Drop Shadow– Renders a shadow of a given content behind the content to which the effect is applied.“Drop Shadow”–在应用效果的内容后面渲染给定内容的阴影。
-
Reflection– Renders a reflected version of the content below the actual content.“反射”-在实际内容下方呈现内容的反射版本。
-
Lighting– Simulates a light source shining on a given content and can give a flat object a more realistic, three-dimensional appearance.“照明”-模拟光源照射在给定内容上,可以为平面对象提供更逼真的三维外观。
For examples on how to use some of the available visual effects, see the Creating Visual Effects document. For more information about all the available visual effects classes, see the API documentation for the javafx.scene.effect package.
有关如何使用某些可用视觉效果的示例,请参阅创建视觉效果文件。有关所有可用视觉效果类的更多信息,请参阅API文档对于javafx.scene.effect包。
Part II Getting Started with JavaFX Sample Applications
3 Hello World, JavaFX Style
The best way to teach you what it is like to create and build a JavaFX application is with a ”Hello World” application. An added benefit of this tutorial is that it enables you to test that your JavaFX technology is properly installed.
教你创建和构建JavaFX应用程序的最佳方式是使用“Hello World”应用程序。本教程的另一个好处是,它使您能够测试JavaFX技术是否已正确安装。
The tool used in this tutorial is NetBeans IDE 7.4. Before you begin, ensure that the version of NetBeans IDE that you are using supports JavaFX 8. See the Certified System Configurations section of the Java SE 8 downloads page for details.
本教程中使用的工具是NetBeans IDE 7.4。在开始之前,请确保您使用的NetBeans IDE版本支持JavaFX 8。请参阅认证系统配置有关详细信息,请参阅Java SE 8下载页面的部分。
Construct the Application
-
From the File menu, choose New Project.
从“文件”菜单中,选择“新建项目”。
-
In the JavaFX application category, choose JavaFX Application. Click Next.
在JavaFX应用类别中,选择JavaFX应用程序。单击下一步。
-
Name the project HelloWorld and click Finish.
将项目命名为HelloWorld,然后单击Finish。
NetBeans opens the
HelloWorld.javafile and populates it with the code for a basic Hello World application, as shown in Example 3-1.NetBeans打开“HelloWorld.java”文件,并用基本Hello World应用程序的代码填充它,如示例3-1所示.
Example 3-1 Hello World
package helloworld; import javafx.application.Application; import javafx.event.ActionEvent; import javafx.event.EventHandler; import javafx.scene.Scene; import javafx.scene.control.Button; import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane; import javafx.stage.Stage; public class HelloWorld extends Application { @Override public void start(Stage primaryStage) { Button btn = new Button(); btn.setText("Say 'Hello World'"); btn.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() { @Override public void handle(ActionEvent event) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); } }); StackPane root = new StackPane(); root.getChildren().add(btn); Scene scene = new Scene(root, 300, 250); primaryStage.setTitle("Hello World!"); primaryStage.setScene(scene); primaryStage.show(); } public static void main(String[] args) { launch(args); } }
Here are the important things to know about the basic structure of a JavaFX application:
以下是关于JavaFX应用程序基本结构的重要信息:
-
The main class for a JavaFX application extends the
javafx.application.Applicationclass. Thestart()method is the main entry point for all JavaFX applications.JavaFX应用程序的主类扩展了
javafx.application.Application类。start()方法是所有JavaFX应用程序的主要入口点。 -
A JavaFX application defines the user interface container by means of a stage and a scene. The JavaFX
Stageclass is the top-level JavaFX container. The JavaFXSceneclass is the container for all content. Example 3-1 creates the stage and scene and makes the scene visible in a given pixel size.JavaFX应用程序通过舞台和场景定义用户界面容器。JavaFX“Stage”类是顶级JavaFX容器。JavaFX的“Scene”类是所有内容的容器。示例3-1创建舞台和场景,并使场景以给定的像素大小可见。
-
In JavaFX, the content of the scene is represented as a hierarchical scene graph of nodes. In this example, the root node is a
StackPaneobject, which is a resizable layout node. This means that the root node's size tracks the scene's size and changes when the stage is resized by a user.在JavaFX中,场景的内容表示为节点的分层场景图。在这个例子中,根节点是一个“StackPane”对象,它是一个可调整大小的布局节点。这意味着根节点的大小会跟踪场景的大小,并在用户调整舞台大小时发生变化。
-
The root node contains one child node, a button control with text, plus an event handler to print a message when the button is pressed.
根节点包含一个子节点、一个带文本的按钮控件,以及一个事件处理程序,用于在按下按钮时打印消息。
-
The
main()method is not required for JavaFX applications when the JAR file for the application is created with the JavaFX Packager tool, which embeds the JavaFX Launcher in the JAR file. However, it is useful to include themain()method so you can run JAR files that were created without the JavaFX Launcher, such as when using an IDE in which the JavaFX tools are not fully integrated. Also, Swing applications that embed JavaFX code require themain()method.当使用JavaFX Packager工具创建应用程序的JAR文件时,JavaFX应用程序不需要
main()方法,该工具将JavaFX Launcher嵌入JAR文件中。但是,包含main()方法是有用的,这样您就可以运行在没有JavaFX Launcher的情况下创建的JAR文件,例如在使用未完全集成JavaFX工具的IDE时。此外,嵌入JavaFX代码的Swing应用程序需要main()方法。
Figure 3-1 shows the scene graph for the Hello World application. For more information on scene graphs see Working with the JavaFX Scene Graph.
图3-1显示了Hello World应用程序的场景图。有关场景图的更多信息,请参阅使用JavaFX场景图.
Figure 3-1 Hello World Scene Graph
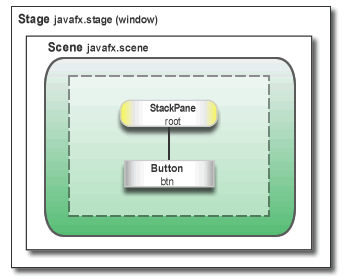
Description of "Figure 3-1 Hello World Scene Graph"
Run the Application
-
In the Projects window, right-click the HelloWorld project node and choose Run.
在“项目”窗口中,右键单击HelloWorld项目节点并选择“运行”。
-
Click the Say Hello World button.
单击“向世界问好”按钮。
-
Verify that the text ”Hello World!” is printed to the NetBeans output window.
验证文本“Hello World!”打印到NetBeans输出窗口。
Figure 3-2 shows the Hello World application, JavaFX style.
图3-2显示了JavaFX风格的Hello World应用程序。
Figure 3-2 Hello World, JavaFX style
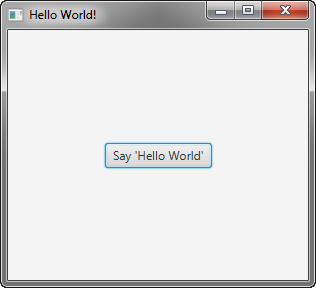
Description of "Figure 3-2 Hello World, JavaFX style"
Where to Go Next
This concludes the basic Hello World tutorial, but continue reading for more lessons on developing JavaFX applications:
Hello World基本教程到此结束,但请继续阅读有关开发JavaFX应用程序的更多课程:
-
Creating a Form in JavaFX teaches the basics of screen layout, how to add controls to a layout, and how to create input events.
在JavaFX中创建表单教授屏幕布局的基础知识,如何向布局中添加控件,以及如何创建输入事件。
-
Fancy Forms with JavaFX CSS provides simple style tricks for enhancing your application, including adding a background image and styling buttons and text.
使用JavaFX CSS的花式表单提供了增强应用程序的简单样式技巧,包括添加背景图像、设置按钮和文本的样式。
-
Using FXML to Create a User Interface shows an alternate method for creating the login user interface. FXML is an XML-based language that provides the structure for building a user interface separate from the application logic of your code.
使用FXML创建用户界面显示了创建登录用户界面的另一种方法。FXML是一种基于XML的语言,它为构建与代码的应用程序逻辑分离的用户界面提供了结构。
-
Animation and Visual Effects in JavaFX shows how to bring an application to life by adding timeline animation and blend effects.
JavaFX中的动画和视觉效果展示了如何通过添加时间线动画和混合效果来使应用程序栩栩如生。
4 Creating a Form in JavaFX
Creating a form is a common activity when developing an application. This tutorial teaches you the basics of screen layout, how to add controls to a layout pane, and how to create input events.
在开发应用程序时,创建表单是一项常见的活动。本教程将教您屏幕布局的基础知识,如何向布局窗格添加控件,以及如何创建输入事件。
In this tutorial, you will use JavaFX to build the login form shown in Figure 4-1.
在本教程中,您将使用JavaFX构建如图4-1所示的登录表单.
Figure 4-1 Login Form
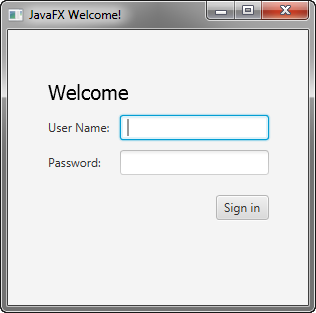
Description of "Figure 4-1 Login Form"
The tool used in this Getting Started tutorial is NetBeans IDE. Before you begin, ensure that the version of NetBeans IDE that you are using supports JavaFX 8. See the Certified System Configurations page of the Java SE Downloads page for details.
本入门教程中使用的工具是NetBeans IDE。在开始之前,请确保您使用的NetBeans IDE版本支持JavaFX 8。请参阅Java SE下载页面的认证系统配置页面了解详情。
Create the Project
Your first task is to create a JavaFX project in NetBeans IDE and name it Login:
您的第一个任务是在NetBeans IDE中创建一个JavaFX项目,并将其命名为Login:
-
From the File menu, choose New Project.
从“文件”菜单中,选择“新建项目”。
-
In the JavaFX application category, choose JavaFX Application. Click Next.
在JavaFX应用类别中,选择JavaFX应用程序。单击下一步。
-
Name the project Login and click Finish.
将项目命名为登录,然后单击完成。
When you create a JavaFX project, NetBeans IDE provides a Hello World application as a starting point, which you have already seen if you followed the Hello World tutorial.
当你创建一个JavaFX项目时,NetBeans IDE提供了一个Hello World应用程序作为起点,如果你遵循Holo World,你已经看到了教程。
-
Remove the
start()method that NetBeans IDE generated and replace it with the code in Example 4-1.删除NetBeans IDE生成的
start()方法,并将其替换为示例4-1中的代码.Example 4-1 Application Stage
@Override public void start(Stage primaryStage) { primaryStage.setTitle("JavaFX Welcome"); primaryStage.show(); }
Tip: After you add sample code into a NetBeans project, press Ctrl (or Cmd) + Shift + I to import the required packages. When there is a choice of import statements, choose the one that starts with javafx.
提示:将示例代码添加到NetBeans项目中后,按Ctrl(或Cmd)+Shift+I导入所需的包。当有导入语句可供选择时,请选择以“javafx”开头的语句。
Create a GridPane Layout
For the login form, use a GridPane layout because it enables you to create a flexible grid of rows and columns in which to lay out controls. You can place controls in any cell in the grid, and you can make controls span cells as needed.
对于登录表单,使用“GridPane”布局,因为它使您能够创建灵活的行和列网格来布局控件。您可以将控件放置在网格中的任何单元格中,也可以根据需要使控件跨越单元格。
The code to create the GridPane layout is in Example 4-2. Add the code before the line primaryStage.show();
创建“GridPane”布局的代码在示例4-2中. 在primaryStage.show()行之前添加代码
Example 4-2 GridPane with Gap and Padding Properties
GridPane grid = new GridPane();
grid.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
grid.setHgap(10);
grid.setVgap(10);
grid.setPadding(new Insets(25, 25, 25, 25));
Scene scene = new Scene(grid, 300, 275);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
Example 4-2 creates a GridPane object and assigns it to the variable named grid. The alignment property changes the default position of the grid from the top left of the scene to the center. The gap properties manage the spacing between the rows and columns, while the padding property manages the space around the edges of the grid pane. The insets are in the order of top, right, bottom, and left. In this example, there are 25 pixels of padding on each side.
示例4-2创建一个“GridPane”对象并将其分配给名为“grid”的变量。对齐特性将栅格的默认位置从场景的左上角更改为中心。间隙属性管理行和列之间的间距,而填充属性管理网格窗格边缘周围的空间。插图按顶部、右侧、底部和左侧的顺序排列。在这个例子中,每侧有“25”个像素的填充。
The scene is created with the grid pane as the root node, which is a common practice when working with layout containers. Thus, as the window is resized, the nodes within the grid pane are resized according to their layout constraints. In this example, the grid pane remains in the center when you grow or shrink the window. The padding properties ensure there is a padding around the grid pane when you make the window smaller.
场景是以网格窗格作为根节点创建的,这是使用布局容器时的常见做法。因此,当调整窗口大小时,网格窗格中的节点会根据其布局约束调整大小。在本例中,当您增大或缩小窗口时,网格窗格仍位于中心。padding属性可确保在缩小窗口时,网格窗格周围有一个填充。
This code sets the scene width and height to 300 by 275. If you do not set the scene dimensions, the scene defaults to the minimum size needed to display its contents.
此代码将场景宽度和高度设置为300乘275。如果不设置场景尺寸,则场景默认为显示其内容所需的最小大小。
Add Text, Labels, and Text Fields
Looking at Figure 4-1, you can see that the form requires the title ”Welcome ”and text and password fields for gathering information from the user. The code for creating these controls is in Example 4-3. Add this code after the line that sets the grid padding property.
查看图4-1,您可以看到,该表单需要标题“Welcome”以及文本和密码字段来从用户那里收集信息。创建这些控件的代码在示例4-3中. 在设置网格填充属性的行之后添加此代码。
Example 4-3 Controls
Text scenetitle = new Text("Welcome");
scenetitle.setFont(Font.font("Tahoma", FontWeight.NORMAL, 20));
grid.add(scenetitle, 0, 0, 2, 1);
Label userName = new Label("User Name:");
grid.add(userName, 0, 1);
TextField userTextField = new TextField();
grid.add(userTextField, 1, 1);
Label pw = new Label("Password:");
grid.add(pw, 0, 2);
PasswordField pwBox = new PasswordField();
grid.add(pwBox, 1, 2);
The first line creates a Text object that cannot be edited, sets the text to Welcome, and assigns it to a variable named scenetitle. The next line uses the setFont() method to set the font family, weight, and size of the scenetitle variable. Using an inline style is appropriate where the style is bound to a variable, but a better technique for styling the elements of your user interface is by using a style sheet. In the next tutorial, Fancy Forms with JavaFX CSS, you will replace the inline style with a style sheet.
第一行创建了一个不可编辑的“Text”对象,将文本设置为“Welcome”,并将其分配给一个名为“scenetitle”的变量。下一行使用setFont()方法设置scenetitle变量的字体族、权重和大小。当样式绑定到变量时,使用内联样式是合适的,但更好的用户界面元素样式设置技术是使用样式表。在下一个教程中,使用JavaFX CSS的花式表单,您将用样式表替换内联样式。
The grid.add() method adds the scenetitle variable to the layout grid. The numbering for columns and rows in the grid starts at zero, and scenetitle is added in column 0, row 0. The last two arguments of the grid.add``() method set the column span to 2 and the row span to 1.
grid.add()方法将scenetitle变量添加到布局grid 中。网格中的列和行的编号从零开始,“scenetitle”添加在列0的第0行。grid.add()`方法的最后两个参数将列跨度设置为2,行跨度设置为1。
The next lines create a Label object with text User Name at column 0, row 1 and a Text Field object that can be edited. The text field is added to the grid pane at column 1, row 1. A password field and label are created and added to the grid pane in a similar fashion.
接下来的几行在第0列第1行创建了一个带有文本“用户名”的“标签”对象和一个可编辑的“文本字段”对象。文本字段将添加到网格窗格的第1列第1行。密码字段和标签以类似的方式创建并添加到网格窗格中。
When working with a grid pane, you can display the grid lines, which is useful for debugging purposes. In this case, you can add grid.setGridLinesVisible(true) after the line that adds the password field. Then, when you run the application, you see the lines for the grid columns and rows as well as the gap properties, as shown in Figure 4-2.
使用网格窗格时,可以显示网格线,这对调试非常有用。在这种情况下,您可以在添加密码字段的行后添加grid.setGridLinesVisible(true)。然后,当您运行应用程序时,您会看到网格列和行的行以及间隙属性,如图4-2所示.
Figure 4-2 Login Form with Grid Lines
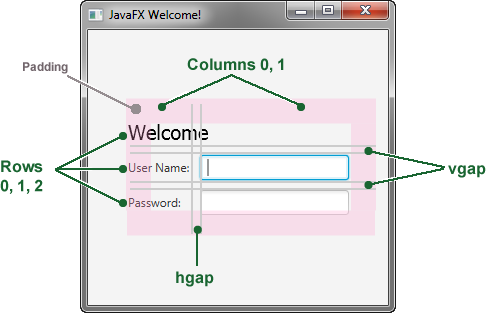
Description of "Figure 4-2 Login Form with Grid Lines"
Add a Button and Text
The final two controls required for the application are a Button control for submitting the data and a Text control for displaying a message when the user presses the button.
应用程序所需的最后两个控件是用于提交数据的“按钮”控件和用于在用户按下按钮时显示消息的“文本”控件。
First, create the button and position it on the bottom right, which is a common placement for buttons that perform an action affecting the entire form. The code is in Example 4-4. Add this code before the code for the scene.
首先,创建按钮并将其放置在右下角,这是执行影响整个表单的操作的按钮的常见位置。代码在示例4-4中. 在场景代码之前添加此代码。
Example 4-4 Button
Button btn = new Button("Sign in");
HBox hbBtn = new HBox(10);
hbBtn.setAlignment(Pos.BOTTOM_RIGHT);
hbBtn.getChildren().add(btn);
grid.add(hbBtn, 1, 4);
The first line creates a button named btn with the label Sign in, and the second line creates an HBox layout pane named hbBtn with spacing of 10 pixels. The HBox pane sets an alignment for the button that is different from the alignment applied to the other controls in the grid pane. The alignment property has a value of Pos.BOTTOM_RIGHT, which positions a node at the bottom of the space vertically and at the right edge of the space horizontally. The button is added as a child of the HBox pane, and the HBox pane is added to the grid in column 1, row 4.
第一行创建了一个名为“btn”的按钮,标签为“登录”,第二行创建了名为“hbBtn”的“HBox”布局窗格,间距为“10”像素。“HBox”窗格为按钮设置的对齐方式不同于应用于网格窗格中其他控件的对齐方式。“alignment”属性的值为“Pos.BOTTOM_RIGHT”,它将节点垂直定位在空间底部,水平定位在空间右边缘。该按钮被添加为“HBox”窗格的子级,“HBox“窗格被添加到第1列第4行的网格中。
Now, add a Text control for displaying the message, as shown in Example 4-5. Add this code before the code for the scene.
现在,添加一个“文本”控件来显示消息,如示例4-5所示. 在场景代码之前添加此代码。
Example 4-5 Text
final Text actiontarget = new Text();
grid.add(actiontarget, 1, 6);
Figure 4-3 shows the form now. You will not see the text message until you work through the next section of the tutorial, Add Code to Handle an Event.
图4-3现在显示表单。在完成本教程的下一节添加代码以处理事件之前,您将看不到文本消息.
Figure 4-3 Login Form with Button

Description of "Figure 4-3 Login Form with Button"
Add Code to Handle an Event
Finally, make the button display the text message when the user presses it. Add the code in Example 4-6 before the code for the scene.
最后,让按钮在用户按下时显示文本消息。添加示例4-6中的代码在场景代码之前。
Example 4-6 Button Event
btn.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent e) {
actiontarget.setFill(Color.FIREBRICK);
actiontarget.setText("Sign in button pressed");
}
});
The setOnAction() method is used to register an event handler that sets the actiontarget object to Sign in button pressed when the user presses the button. The color of the actiontarget object is set to firebrick red.
setOnAction()方法用于注册一个事件处理程序,当用户按下按钮时,该处理程序将actiontarget对象设置为Sign-in button pressed 。“actiontarget”对象的颜色设置为耐火砖红色。
Run the Application
Right-click the Login project node in the Projects window, choose Run, and then click the Sign in button. Figure 4-4 shows the results. If you run into problems, then take a look at the code in the Login.java file that is included in the downloadable Login.zip file.
右键单击“项目”窗口中的“登录”项目节点,选择“运行”,然后单击“登录”按钮。图4-4显示了结果。如果您遇到问题,请查看可下载的Login.zip中包含的Login.java文件中的代码文件。
Figure 4-4 Final Login Form
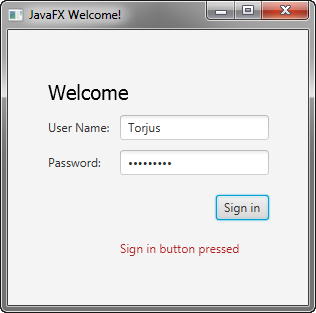
Description of "Figure 4-4 Final Login Form"
Where to Go from Here
This concludes the basic form tutorial, but you can continue reading the following tutorials on developing JavaFX applications.
基本表单教程到此结束,但您可以继续阅读以下关于开发JavaFX应用程序的教程。
-
Fancy Forms with JavaFX CSS provides tips on how to add a background image and radically change the style of the text, label, and button in the login form.
使用JavaFX CSS的花式表单提供了如何添加背景图像以及从根本上更改登录表单中的文本、标签和按钮样式的提示。
-
Using FXML to Create a User Interface shows an alternate method for creating the login user interface. FXML is an XML-based language that provides the structure for building a user interface separate from the application logic of your code.
使用FXML创建用户界面显示了创建登录用户界面的另一种方法。FXML是一种基于XML的语言,它为构建与代码的应用程序逻辑分离的用户界面提供了结构。
-
Working With Layouts in JavaFX explains the built-in JavaFX layout panes, and tips and tricks for using them.
在JavaFX中使用布局解释了内置的JavaFX布局窗格,以及使用它们的提示和技巧。
Also try out the JavaFX samples, which you can download from the JDK Demos and Samples section of the Java SE Downloads page at https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/. The Ensemble sample contains examples of layouts and their source code.
还可以尝试JavaFX示例,您可以从Java SE下载页面的JDK演示和示例部分下载,网址为https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/. Ensemble示例包含布局及其源代码的示例。
5 Fancy Forms with JavaFX CSS
This tutorial is about making your JavaFX application look attractive by adding a Cascading Style Sheet (CSS). You develop a design, create a .css file, and apply the new styles.
本教程是关于通过添加级联样式表(CSS)使JavaFX应用程序看起来更有吸引力。您开发一个设计,创建一个.css文件,并应用新样式。
In this tutorial, you will take a Login form that uses default styles for labels, buttons, and background color, and, with a few simple CSS modifications, turn it into a stylized application, as shown in Figure 5-1.
在本教程中,您将使用一个登录表单,该表单使用标签、按钮和背景颜色的默认样式,并通过一些简单的CSS修改将其转换为风格化的应用程序,如图5-1所示.
Figure 5-1 Login Form With and Without CSS
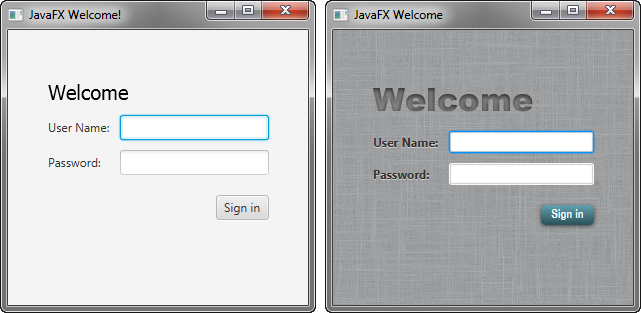
Description of "Figure 5-1 Login Form With and Without CSS"
The tool used in this Getting Started tutorial is NetBeans IDE. Before you begin, ensure that the version of NetBeans IDE that you are using supports JavaFX 8. See the Certified System Configurations page of the Java SE Downloads page for details.
本入门教程中使用的工具是NetBeans IDE。在开始之前,请确保您使用的NetBeans IDE版本支持JavaFX 8。请参阅Java SE下载页面的认证系统配置页面了解详情。
Create the Project
If you followed the Getting Started guide from the start, then you already created the Login project required for this tutorial. If not, download the Login project by right-clicking Login.zip and saving it to your file system. Extract the files from the zip file, and then open the project in NetBeans IDE.
如果您从一开始就遵循了《入门指南》,那么您已经创建了本教程所需的登录项目。如果没有,请右键单击Login.zip下载Login项目并将其保存到您的文件系统。从zip文件中提取文件,然后在NetBeans IDE中打开项目。
Create the CSS File
Your first task is to create a new CSS file and save it in the same directory as the main class of your application. After that, you must make the JavaFX application aware of the newly added Cascading Style Sheet.
您的第一个任务是创建一个新的CSS文件,并将其保存在与应用程序的主类相同的目录中。之后,您必须使JavaFX应用程序知道新添加的级联样式表。
-
In the NetBeans IDE Projects window, expand the Login project node and then the Source Packages directory node.
在NetBeans IDE项目窗口中,展开登录项目节点,然后展开源代码包目录节点。
-
Right-click the login folder under the Source Packages directory and choose New, then Other.
右键单击Source Packages目录下的登录文件夹,选择New,然后选择Other。
-
In the New File dialog box, choose Other, then Cascading Style Sheet, and click Next.
在“新建文件”对话框中,选择“其他”,然后选择“层叠样式表”,然后单击“下一步”。
-
Enter Login for the File Name text field and ensure the Folder text field value is
src\login.在“文件名”文本字段中输入“登录”,并确保“文件夹”文本字段值为“src\Login”。
-
Click Finish.
单击“完成”。
-
In the
Login.javafile, initialize thestyle sheetsvariable of theSceneclass to point to the Cascading Style Sheet by including the line of code shown in bold below so that it appears as shown in Example 5-1.在“Login.java”文件中,初始化“Scene”类的“stylesheets”变量,通过包含下面粗体显示的代码行来指向级联样式表,使其显示如示例5-1所示.
Example 5-1 Initialize the stylesheets Variable
Scene scene = new Scene(grid, 300, 275); primaryStage.setScene(scene); scene.getStylesheets().add (Login.class.getResource("Login.css").toExternalForm()); primaryStage.show();This code looks for the style sheet in the
src\logindirectory in the NetBeans project.此代码在NetBeans项目的
src\login目录中查找样式表。
Add a Background Image
A background image helps make your form more attractive. For this tutorial, you add a gray background with a linen-like texture.
背景图像有助于使您的表单更具吸引力。在本教程中,您将添加一个具有亚麻纹理的灰色背景。
First, download the background image by right-clicking the background.jpg image and saving it into the src\login folder in the Login NetBeans project.
首先,右键单击background.jpg下载背景图像图像并将其保存到login NetBeans项目中的src\login文件夹中。
Now, add the code for the background-image property to the CSS file. Remember that the path is relative to the style sheet. So, in the code in Example 5-2, the background.jpg image is in the same directory as the Login.css file.
现在,将“background image”属性的代码添加到CSS文件中。请记住,路径是相对于样式表的。因此,在示例5-2中的代码中,“background.jpg”图像与“Login.css”文件位于同一目录中。
Example 5-2 Background Image
.root {
-fx-background-image: url("background.jpg");
}
The background image is applied to the .root style, which means it is applied to the root node of the Scene instance. The style definition consists of the name of the property (-fx-background-image) and the value for the property (url(”background.jpg”)).
背景图像应用于“.root”样式,这意味着它应用于“Scene”实例的根节点。样式定义由属性的名称(-fx background image)和属性的值(url(“background.jpg”))组成。
Figure 5-2 shows the login form with the new gray background.
图5-2显示了带有新灰色背景的登录表单。
Figure 5-2 Gray Linen Background
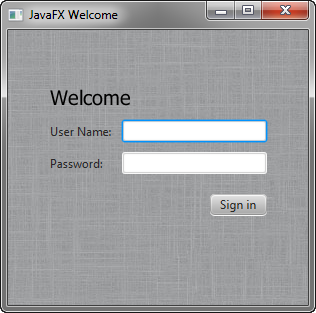
Description of "Figure 5-2 Gray Linen Background"
Style the Labels
The next controls to enhance are the labels. You will use the .label style class, which means the styles will affect all labels in the form. The code is in Example 5-3.
接下来要增强的控件是标签。您将使用.label样式类,这意味着样式将影响表单中的所有标签。代码在示例5-3中.
Example 5-3 Font Size, Fill, Weight, and Effect on Labels
.label {
-fx-font-size: 12px;
-fx-font-weight: bold;
-fx-text-fill: #333333;
-fx-effect: dropshadow( gaussian , rgba(255,255,255,0.5) , 0,0,0,1 );
}
This example increases the font size and weight and applies a drop shadow of a gray color (#333333). The purpose of the drop shadow is to add contrast between the dark gray text and the light gray background. See the section on effects in the JavaFX CSS Reference Guide for details on the parameters of the drop shadow property.
此示例增加字体大小和权重,并应用灰色阴影(#333333)。阴影的目的是增加深灰色文本和浅灰色背景之间的对比度。请参阅JavaFX CSS参考指南中的效果部分有关阴影属性参数的详细信息。
The enhanced User Name and Password labels are shown in Figure 5-3.
增强的用户名和密码标签如图5-3所示.
Figure 5-3 Bigger, Bolder Labels with Drop Shadow
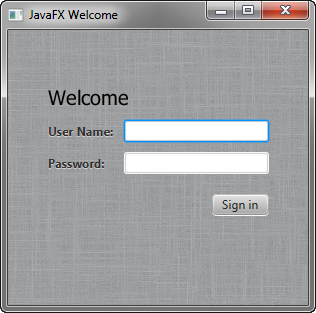
Description of "Figure 5-3 Bigger, Bolder Labels with Drop Shadow"
Style Text
Now, create some special effects on the two Text objects in the form: scenetitle, which includes the text Welcome, and actiontarget, which is the text that is returned when the user presses the Sign in button. You can apply different styles to Text objects used in such diverse ways.
现在,在表单中的两个“Text”对象上创建一些特殊效果:“scenetitle”,其中包括文本“Welcome”,以及“actiontarget”,这是用户按下登录按钮时返回的文本。您可以对以不同方式使用的“文本”对象应用不同的样式。
-
In the
Login.javafile, remove the following lines of code that define the inline styles currently set for the text objects:在
Login.java文件中,删除以下定义当前为文本对象设置的内联样式的代码行:scenetitle.setFont(Font.font(”Tahoma”, FontWeight.NORMAL, 20));actiontarget.setFill(Color.FIREBRICK);By switching to CSS over inline styles, you separate the design from the content. This approach makes it easier for a designer to have control over the style without having to modify content.
通过切换到CSS而不是内联样式,您可以将设计与内容分开。这种方法使设计者更容易控制样式,而无需修改内容。
-
Create an ID for each text node by using the
setID()method of the Node class: Add the following lines in bold so that they appear as shown in Example 5-4.使用node类的
setID()方法为每个文本节点创建一个ID:添加以下粗体行,使其显示如示例5-4所示.Example 5-4 Create ID for Text Nodes
... Text scenetitle = new Text("Welcome"); scenetitle.setId("welcome-text"); ... ... grid.add(actiontarget, 1, 6); actiontarget.setId("actiontarget"); .. -
In the
Login.cssfile, define the style properties for thewelcome-textandactiontargetIDs. For the style name, use the ID preceded by a number sign (#), as shown in Example 5-5.在“Login.css”文件中,定义“欢迎文本”和“actiontarget”ID的样式属性。对于样式名称,使用前面有数字符号(#)的ID,如示例5-5所示.
Example 5-5 Text Effect
#welcome-text { -fx-font-size: 32px; -fx-font-family: "Arial Black"; -fx-fill: #818181; -fx-effect: innershadow( three-pass-box , rgba(0,0,0,0.7) , 6, 0.0 , 0 , 2 ); } #actiontarget { -fx-fill: FIREBRICK; -fx-font-weight: bold; -fx-effect: dropshadow( gaussian , rgba(255,255,255,0.5) , 0,0,0,1 ); }
The size of the Welcome text is increased to 32 points and the font is changed to Arial Black. The text fill color is set to a dark gray color (#818181) and an inner shadow effect is applied, creating an embossing effect. You can apply an inner shadow to any color by changing the text fill color to be a darker version of the background. See the section on effects in the JavaFX CSS Reference Guide for details about the parameters of inner shadow property.
欢迎文本的大小增加到32点,字体更改为Arial Black。文本填充颜色设置为深灰色(#818181),并应用内部阴影效果,从而产生压花效果。通过将文本填充颜色更改为背景的较暗版本,可以将内部阴影应用于任何颜色。请参阅JavaFX CSS参考指南中的效果部分有关内部阴影属性参数的详细信息。
The style definition for actiontarget is similar to what you have seen before.
“actiontarget”的样式定义与您之前看到的类似。
Figure 5-4 shows the font changes and shadow effects on the two Text objects.
图5-4显示了两个“文本”对象的字体变化和阴影效果。
Figure 5-4 Text with Shadow Effects
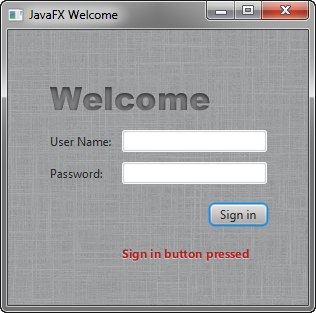
Description of "Figure 5-4 Text with Shadow Effects"
Style the Button
The next step is to style the button, making it change style when the user hovers the mouse over it. This change will give users an indication that the button is interactive, a standard design practice.
下一步是设置按钮的样式,当用户将鼠标悬停在按钮上时,使其更改样式。此更改将向用户指示按钮是交互式的,这是一种标准的设计实践。
First, create the style for the initial state of the button by adding the code in Example 5-6. This code uses the .button style class selector, such that if you add a button to the form at a later date, then the new button will also use this style.
首先,通过添加示例5-6中的代码,为按钮的初始状态创建样式. 这段代码使用“.button”样式的类选择器,这样如果你以后在表单中添加一个按钮,那么新按钮也会使用这种样式。
Example 5-6 Drop Shadow for Button
.button {
-fx-text-fill: white;
-fx-font-family: "Arial Narrow";
-fx-font-weight: bold;
-fx-background-color: linear-gradient(#61a2b1, #2A5058);
-fx-effect: dropshadow( three-pass-box , rgba(0,0,0,0.6) , 5, 0.0 , 0 , 1 );
}
Now, create a slightly different look for when the user hovers the mouse over the button. You do this with the hover pseudo-class. A pseudo-class includes the selector for the class and the name for the state separated by a colon (😃, as shown in Example 5-7.
现在,当用户将鼠标悬停在按钮上时,创建一个稍微不同的外观。您可以使用hover伪类来完成此操作。伪类包括类的选择器和状态的名称,用冒号(:)分隔,如示例5-7所示.
Example 5-7 Button Hover Style
.button:hover {
-fx-background-color: linear-gradient(#2A5058, #61a2b1);
}
Figure 5-5 shows the initial and hover states of the button with its new blue-gray background and white bold text.
图5-5显示了按钮的初始和悬停状态及其新的蓝灰色背景和白色粗体文本。
Figure 5-5 Initial and Hover Button States

Description of "Figure 5-5 Initial and Hover Button States"
Figure 5-6 shows the final application.
图5-6显示了最终的应用程序。
Figure 5-6 Final Stylized Application
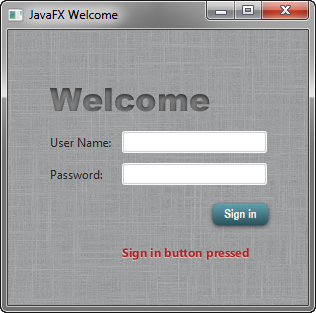
Description of "Figure 5-6 Final Stylized Application"
Where to Go from Here
Here are some things for you to try next:
以下是一些你接下来要尝试的事情:
-
See what you can create using CSS. Some documents that can help you are Skinning JavaFX Applications with CSS, Styling Charts with CSS, and the JavaFX CSS Reference Guide. The Skinning with CSS and the CSS Analyzer section of the JavaFX Scene Builder User Guide also provides information on how you can use the JavaFX Scene Builder tool to skin your JavaFX FXML layout.
看看你可以用CSS创建什么。一些可以帮助你的文档是使用CSS对JavaFX应用程序进行蒙皮使用CSS设置图表样式,以及JavaFX CSS参考指南。JavaFX场景生成器用户指南的CSS蒙皮和CSS分析器部分还提供了如何使用JavaFX场景构建器工具对JavaFX FXML布局进行蒙皮的信息。
-
See Styling FX Buttons with CSS for examples of how to create common button styles using CSS.
请参阅使用CSS设置FX按钮的样式例如如何使用CSS创建常见按钮样式。
6 Using FXML to Create a User Interface
This tutorial shows the benefits of using JavaFX FXML, which is an XML-based language that provides the structure for building a user interface separate from the application logic of your code.
本教程展示了使用JavaFX FXML的好处,这是一种基于XML的语言,为构建与代码的应用程序逻辑分离的用户界面提供了结构。
If you started this document from the beginning, then you have seen how to create a login application using just JavaFX. Here, you use FXML to create the same login user interface, separating the application design from the application logic, thereby making the code easier to maintain. The login user interface you build in this tutorial is shown in Figure 6-1.
如果您从头开始阅读本文档,那么您已经了解了如何仅使用JavaFX创建登录应用程序。在这里,您可以使用FXML创建相同的登录用户界面,将应用程序设计与应用程序逻辑分离,从而使代码更易于维护。您在本教程中构建的登录用户界面如图6-1所示.
Figure 6-1 Login User Interface
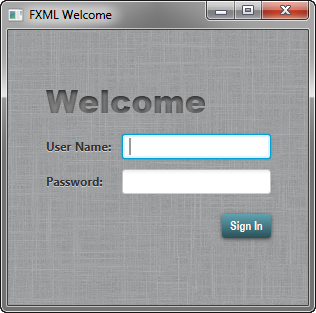
Description of "Figure 6-1 Login User Interface"
This tutorial uses NetBeans IDE. Ensure that the version of NetBeans IDE that you are using supports JavaFX 8. See the Certified System Configurations section of the Java SE Downloads page for details.
本教程使用NetBeans IDE。确保您使用的NetBeans IDE版本支持JavaFX 8。请参阅Java SE下载页面的认证系统配置部分了解详情。
Set Up the Project
Your first task is to set up a JavaFX FXML project in NetBeans IDE:
您的第一个任务是在NetBeans IDE中设置JavaFX FXML项目:
-
From the File menu, choose New Project.
从“文件”菜单中,选择“新建项目”。
-
In the JavaFX application category, choose JavaFX FXML Application. Click Next.
在JavaFX应用程序类别中,选择JavaFX FXML应用程序。单击下一步。
-
Name the project FXMLExample and click Finish.
将项目命名为FXMLExample,然后单击Finish。
NetBeans IDE opens an FXML project that includes the code for a basic Hello World application. The application includes three files:
NetBeans IDE打开一个FXML项目,其中包含基本Hello World应用程序的代码。该应用程序包括三个文件:
-
FXMLExample.java.This file takes care of the standard Java code required for an FXML application.FXMLExample.java。此文件负责FXML应用程序所需的标准Java代码。 -
FXMLDocument.fxml.This is the FXML source file in which you define the user interface.FXMLDocument.fxml.这是FXML源文件,您可以在其中定义用户界面。 -
FXMLDocumentController.java.This is the controller file for handling the mouse and keyboard input.FXMLDocumentController.java。这是用于处理鼠标和键盘输入的控制器文件。
-
-
Rename
FXMLDocumentController.javato FXMLExampleController.javaso that the name is more meaningful for this application.将
FXMLDocumentController.java重命名为FXMLExampleController.java,以便该名称对此应用程序更有意义。-
In the Projects window, right-click FXMLDocumentController.java and choose Refactor then Rename.
在“项目”窗口中,右键单击FXMLDocumentController.java,选择“重构”,然后选择“重命名”。
-
Enter FXMLExampleController, and click Refactor.
输入FXMLExampleController,然后单击重构。
-
-
Rename
FXMLDocument.fxmltofxml_example.fxml.将“FXMLDocument.fxml”重命名为“fxml_example.xml”`
-
Right-click FXMLDocument.fxml and choose Rename.
右键单击FXMLDocument.fxml并选择重命名。
-
Enter fxml_example and click OK.
输入fxml_example并单击“确定”。
-
Load the FXML Source File
The first file you edit is the FXMLExample.java file. This file includes the code for setting up the application main class and for defining the stage and scene. More specific to FXML, the file uses the FXMLLoader class, which is responsible for loading the FXML source file and returning the resulting object graph.
您编辑的第一个文件是FXMLExample.java文件。此文件包括用于设置应用程序主类和定义阶段和场景的代码。更具体地说,该文件使用“FXMLLoader”类,该类负责加载FXML源文件并返回结果对象图。
Make the changes shown in bold in Example 6-1.
进行示例6-1中粗体显示的更改.
Example 6-1 FXMLExample.java
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) throws Exception {
Parent root = FXMLLoader.load(getClass().getResource("fxml_example.fxml"));
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 300, 275);
stage.setTitle("FXML Welcome");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
A good practice is to set the height and width of the scene when you create it, in this case 300 by 275; otherwise the scene defaults to the minimum size needed to display its contents.
一个好的做法是在创建场景时设置场景的高度和宽度,在本例中为300乘275;否则,场景默认为显示其内容所需的最小大小。
Modify the Import Statements
Next, edit the fxml_example.fxml file. This file specifies the user interface that is displayed when the application starts. The first task is to modify the import statements so your code looks like Example 6-2.
接下来,编辑fxml_example.fxml文件。此文件指定应用程序启动时显示的用户界面。第一个任务是修改导入语句,使代码看起来像示例6-2.
Example 6-2 XML Declaration and Import Statements
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?import java.net.*?>
<?import javafx.geometry.*?>
<?import javafx.scene.control.*?>
<?import javafx.scene.layout.*?>
<?import javafx.scene.text.*?>
As in Java, class names can be fully qualified (including the package name), or they can be imported using the import statement, as shown in Example 6-2. If you prefer, you can use specific import statements that refer to classes.
与Java一样,类名可以是完全限定的(包括包名),也可以使用import语句导入,如示例6-2所示. 如果愿意,可以使用引用类的特定导入语句。
Create a GridPane Layout
The Hello World application generated by NetBeans uses an AnchorPane layout. For the login form, you will use a GridPane layout because it enables you to create a flexible grid of rows and columns in which to lay out controls.
NetBeans生成的Hello World应用程序使用“AnchorPane”布局。对于登录表单,您将使用“GridPane”布局,因为它使您能够创建灵活的行和列网格来布局控件。
Remove the AnchorPane layout and its children and replace it with the GridPane layout in Example 6-3.
删除“AnchorPane”布局及其子布局,并将其替换为示例6-3中的“GridPane”版面.
Example 6-3 GridPane Layout
<GridPane fx:controller="fxmlexample.FXMLExampleController"
xmlns:fx="http://javafx.com/fxml" alignment="center" hgap="10" vgap="10">
<padding><Insets top="25" right="25" bottom="10" left="25"/></padding>
</GridPane>
In this application, the GridPane layout is the root element of the FXML document and as such has two attributes. The fx:controller attribute is required when you specify controller-based event handlers in your markup. The xmlns:fx attribute is always required and specifies the fx namespace.
在这个应用程序中,GridPane布局是FXML文档的根元素,因此有两个属性。在标记中指定基于控制器的事件处理程序时,需要fx:controller属性。xmlns:fx属性始终是必需的,并指定了fx命名空间。
The remainder of the code controls the alignment and spacing of the grid pane. The alignment property changes the default position of the grid from the top left of the scene to the center. The gap properties manage the spacing between the rows and columns, while the padding property manages the space around the edges of the grid pane.
代码的其余部分控制网格窗格的对齐和间距。对齐特性将栅格的默认位置从场景的左上角更改为中心。“gap”属性管理行和列之间的间距,而“padding”属性管理网格窗格边缘周围的空间。
As the window is resized, the nodes within the grid pane are resized according to their layout constraints. In this example, the grid remains in the center when you grow or shrink the window. The padding properties ensure there is a padding around the grid when you make the window smaller.
当调整窗口大小时,网格窗格中的节点会根据其布局约束调整大小。在本例中,当您增大或缩小窗口时,网格仍位于中心。padding属性可确保在缩小窗口时网格周围有一个填充。
Add Text and Password Fields
Looking back at Figure 6-1, you can see that the login form requires the title ”Welcome” and text and password fields for gathering information from the user. The code in Example 6-4 is part of the GridPane layout and must be placed above the </GridPane> statement.
回顾图6-1,您可以看到登录表单需要标题“Welcome”以及文本和密码字段来从用户那里收集信息。示例6-4中的代码是“GridPane”布局的一部分,必须放置在</GridPane>语句上方。
Example 6-4 Text, Label, TextField, and Password Field Controls
<Text text="Welcome"
GridPane.columnIndex="0" GridPane.rowIndex="0"
GridPane.columnSpan="2"/>
<Label text="User Name:"
GridPane.columnIndex="0" GridPane.rowIndex="1"/>
<TextField
GridPane.columnIndex="1" GridPane.rowIndex="1"/>
<Label text="Password:"
GridPane.columnIndex="0" GridPane.rowIndex="2"/>
<PasswordField fx:id="passwordField"
GridPane.columnIndex="1" GridPane.rowIndex="2"/>
The first line creates a Text object and sets its text value to Welcome. The GridPane.columnIndex and GridPane.rowIndex attributes correspond to the placement of the Text control in the grid. The numbering for rows and columns in the grid starts at zero, and the location of the Text control is set to (0,0), meaning it is in the first column of the first row. The GridPane.columnSpan attribute is set to 2, making the Welcome title span two columns in the grid. You will need this extra width later in the tutorial when you add a style sheet to increase the font size of the text to 32 points.
第一行创建一个“Text”对象,并将其文本值设置为“Welcome”。“GridPane.columnIndex”和“GridPane.rowIndex”属性对应于“Text”控件在网格中的位置。网格中行和列的编号从零开始,“Text”控制器的位置设置为(0,0),这意味着它位于第一行的第一列。“GridPane.columnSpan”属性设置为2,使欢迎标题在网格中跨两列。在本教程稍后添加样式表以将文本字体大小增加到32点时,您将需要此额外宽度。
The next lines create a Label object with text User Name at column 0, row 1 and a TextField object to the right of it at column 1, row 1. Another Label and PasswordField object are created and added to the grid in a similar fashion.
接下来的几行在第0列第1行创建了一个带有文本“用户名”的“标签”对象,在其右侧的第1列第1行将创建一个“文本字段”对象。以类似的方式创建另一个“标签”和“密码字段”对象并将其添加到网格中。
When working with a grid layout, you can display the grid lines, which is useful for debugging purposes. In this case, set the gridLinesVisible property to true by adding the statement <gridLinesVisible>true</gridLinesVisible> right after the <padding></padding> statement. Then, when you run the application, you see the lines for the grid columns and rows as well as the gap properties, as shown in Figure 6-2.
使用网格布局时,可以显示网格线,这对调试非常有用。在这种情况下,通过在“
Figure 6-2 Login Form with Grid Lines
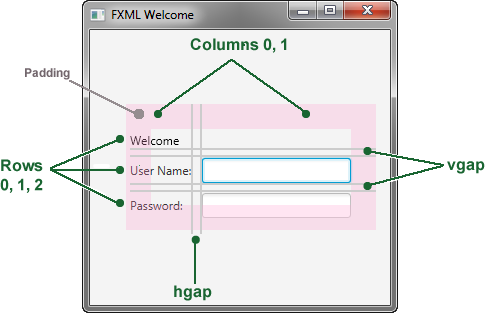
Description of "Figure 6-2 Login Form with Grid Lines"
Add a Button and Text
The final two controls required for the application are a Button control for submitting the data and a Text control for displaying a message when the user presses the button. The code is in Example 6-5. Add this code before </GridPane>.
应用程序所需的最后两个控件是用于提交数据的“按钮”控件和用于在用户按下按钮时显示消息的“文本”控件。代码在示例6-5中. 在“”之前添加此代码。
Example 6-5 HBox, Button, and Text
<HBox spacing="10" alignment="bottom_right"
GridPane.columnIndex="1" GridPane.rowIndex="4">
<Button text="Sign In"
onAction="#handleSubmitButtonAction"/>
</HBox>
<Text fx:id="actiontarget"
GridPane.columnIndex="0" GridPane.columnSpan="2"
GridPane.halignment="RIGHT" GridPane.rowIndex="6"/>
An HBox pane is needed to set an alignment for the button that is different from the default alignment applied to the other controls in the GridPane layout. The alignment property is set to bottom_right, which positions a node at the bottom of the space vertically and at the right edge of the space horizontally. The HBox pane is added to the grid in column 1, row 4.
需要一个“HBox”窗格来设置按钮的对齐方式,该对齐方式不同于应用于“GridPane”布局中其他控件的默认对齐方式。“alignment”属性设置为“bottom_right”,它将节点垂直定位在空间底部,水平定位在空间右边缘。“HBox”窗格被添加到第1列第4行的网格中。
The HBox pane has one child, a Button with text property set to Sign in and an onAction property set to handleSubmitButtonAction(). While FXML is a convenient way to define the structure of an application's user interface, it does not provide a way to implement an application's behavior. You implement the behavior for the handleSubmitButtonAction() method in Java code in the next section of this tutorial, Add Code to Handle an Event.
“HBox”面板有一个子面板,一个“Button”,其中“text”属性设置为“Sign-in”,“onAction”属性设置成“handleSubmitButtonAction()”。虽然FXML是定义应用程序用户界面结构的一种方便方法,但它并没有提供实现应用程序行为的方法。在本教程的下一节添加代码以处理事件中,您将在Java代码中实现handleSubmitButtonAction()方法的行为.
Assigning an fx:id value to an element, as shown in the code for the Text control, creates a variable in the document's namespace, which you can refer to from elsewhere in the code. While not required, defining a controller field helps clarify how the controller and markup are associated.
如“Text”控件的代码所示,为元素分配一个“fx:id”值,会在文档的命名空间中创建一个变量,您可以从代码的其他地方引用该变量。虽然不是必需的,但定义控制器字段有助于阐明控制器和标记是如何关联的。
Add Code to Handle an Event
Now make the Text control display a message when the user presses the button. You do this in the FXMLExampleController.java file. Delete the code that NetBeans IDE generated and replace it with the code in Example 6-6.
现在,当用户按下按钮时,让“文本”控件显示一条消息。您可以在FXMLExampleController.java文件中执行此操作。删除NetBeans IDE生成的代码,并将其替换为示例6-6中的代码.
Example 6-6 FXMLExampleController.java
package fxmlexample;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.fxml.FXML;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class FXMLExampleController {
@FXML
private Text actiontarget;
@FXML
protected void handleSubmitButtonAction(ActionEvent event) {
actiontarget.setText("Sign in button pressed");
}
}
The @FXML annotation is used to tag nonpublic controller member fields and handler methods for use by FXML markup. The handleSubmtButtonAction method sets the actiontarget variable to Sign in button pressed when the user presses the button.
“@FXML”注释用于标记非公共控制器成员字段和处理程序方法,以供FXML标记使用。当用户按下按钮时,handleSubmtButtonAction方法将actiontarget变量设置为Sign-in button pressed 。
You can run the application now to see the complete user interface. Figure 6-3 shows the results when you type text in the two fields and click the Sign in button. If you have any problems, then you can compare your code against the FXMLLogin example.
您现在可以运行应用程序以查看完整的用户界面。图6-3显示在两个字段中键入文本并单击“登录”按钮时的结果。如果您有任何问题,可以将您的代码与FXMLLogin示例进行比较。
Figure 6-3 FXML Login Window
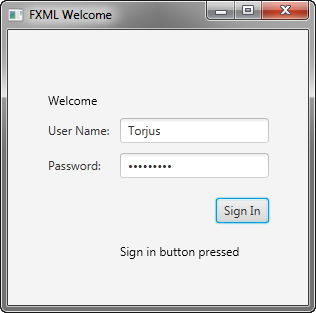
Description of "Figure 6-3 FXML Login Window"
Use a Scripting Language to Handle Events
As an alternative to using Java code to create an event handler, you can create the handler with any language that provides a JSR 223-compatible scripting engine. Such languages include JavaScript, Groovy, Jython, and Clojure.
作为使用Java代码创建事件处理程序的替代方法,您可以使用任何提供JSR 223兼容脚本引擎的语言创建处理程序。这些语言包括JavaScript、Groovy、Jython和Clojure。
Optionally, you can try using JavaScript now.
您现在可以尝试使用JavaScript。
-
In the file
fxml_example.fxml, add the JavaScript declaration after the XML doctype declaration.在文件
fxml_example.fxml中,在XML doctype声明后添加JavaScript声明。<?language javascript?> -
In the
Buttonmarkup, change the name of the function so the call looks as follows:在“Button”标记中,更改函数的名称,使调用如下:
onAction="handleSubmitButtonAction(event);" -
Remove the
fx:controllerattribute from theGridPanemarkup and add the JavaScript function in a<script>tag directly under it, as shown in Example 6-7.从“GridPane”标记中删除“fx:controller”属性,并在其正下方的
<script>标签中添加JavaScript函数,如示例6-7所示.Example 6-7 JavaScript in FXML
<GridPane xmlns:fx="http://javafx.com/fxml" alignment="center" hgap="10" vgap="10"> <fx:script> function handleSubmitButtonAction() { actiontarget.setText("Calling the JavaScript"); } </fx:script>Alternatively, you can put the JavaScript functions in an external file (such as
fxml_example.js) and include the script like this:或者,您可以将JavaScript函数放在外部文件(如
fxml_example.js)中,并包含如下脚本:<fx:script source="fxml_example.js"/>
The result is in Figure 6-4.
Figure 6-4 Login Application Using JavaScript
Description of "Figure 6-4 Login Application Using JavaScript"
If you are considering using a scripting language with FXML, then note that an IDE might not support stepping through script code during debugging.
如果您正在考虑在FXML中使用脚本语言,请注意,IDE可能不支持在调试期间逐步执行脚本代码。
Style the Application with CSS
The final task is to make the login application look attractive by adding a Cascading Style Sheet (CSS).
最后一个任务是通过添加级联样式表(CSS)使登录应用程序看起来更有吸引力。
-
Create a style sheet.
创建样式表。
-
In the Project window, right-click the fxmlexample folder under Source Packages and choose New, then Other.
在“项目”窗口中,右键单击“源包”下的fxmlexample文件夹,选择“新建”,然后选择“其他”。
-
In the New File dialog box, choose Other, then Cascading Style Sheet and click Next.
在“新建文件”对话框中,选择“其他”,然后选择“层叠样式表”,然后单击“下一步”。
-
Enter Login and click Finish.
输入Login并单击Finish。
-
Copy the contents of the
Login.cssfile into your CSS file. TheLogin.cssfile is included in the downloadable LoginCSS.zip file. For a description of the classes in the CSS file, see Fancy Forms with JavaFX CSS.将
Login.css文件的内容复制到css文件中。“Login.css”文件包含在可下载的LoginCSS.zip中文件。有关CSS文件中类的描述,请参阅使用JavaFX CSS的花式表单.
-
-
Download the gray, linen-like image for the background by right-clicking the background.jpg file and saving it to the
fxmlexamplefolder.右键单击background.jpg下载灰色亚麻布状图像作为背景文件并将其保存到“fxmlexample”文件夹中。
-
Open the
fxml_example.fxmlfile and add a stylesheets element before the end of the markup for theGridPanelayout as shown in Example 6-8.打开
fxml_example.fxml文件,在GridPane布局的标记末尾添加样式表元素,如示例6-8所示.Example 6-8 Style Sheet
<stylesheets> <URL value="@Login.css" /> </stylesheets> </GridPane>The @ symbol before the name of the style sheet in the URL indicates that the style sheet is in the same directory as the FXML file.
URL中样式表名称前的@符号表示样式表与FXML文件位于同一目录中。
-
To use the root style for the grid pane, add a style class to the markup for the
GridPanelayout as shown in Example 6-9.要使用网格窗格的根样式,请向“GridPane”布局的标记中添加样式类,如示例6-9所示.
Example 6-9 Style the GridPane
<GridPane fx:controller="fxmlexample.FXMLExampleController" xmlns:fx="http://javafx.com/fxml" alignment="center" hgap="10" vgap="10" styleClass="root"> -
Create a
welcome-textID for the WelcomeTextobject so it uses the style#welcome-textdefined in the CSS file, as shown in Example 6-10.为welcome“text”对象创建一个“欢迎文本”ID,使其使用CSS文件中定义的样式“#welcome-text”,如示例6-10所示.
Example 6-10 Text ID
<Text id="welcome-text" text="Welcome" GridPane.columnIndex="0" GridPane.rowIndex="0" GridPane.columnSpan="2"/> -
Run the application. Figure 6-5 shows the stylized application. If you run into problems, then take a look at the code that is included in the downloadable FXMLExample.zip file
运行应用程序。图6-5显示了程式化的应用程序。如果您遇到问题,请查看可下载的FXMLExample.zip中包含的代码文件
Figure 6-5 Stylized Login Application
Where to Go from Here
Now that you are familiar with FXML, look at Introduction to FXML, which provides more information on the elements that make up the FXML language. The document is included in the javafx.fxml package in the API documentation.
既然您已经熟悉了FXML,请看FXML简介,它提供了有关构成FXML语言的元素的更多信息。该文档包含在API文档中的javafx.fxml包中.
You can also try out the JavaFX Scene Builder tool by opening the fxml_example.fxml file in Scene Builder and making modifications. This tool provides a visual layout environment for designing the UI for JavaFX applications and automatically generates the FXML code for the layout. Note that the FXML file might be reformatted when saved. See the Getting Started with JavaFX Scene Builder for more information on this tool. The Skinning with CSS and the CSS Analyzer section of the JavaFX Scene Builder User Guide also gives you information on how you can skin your FXML layout.
您还可以通过在场景生成器中打开fxml_example.fxml文件并进行修改来尝试JavaFX场景生成器工具。此工具为JavaFX应用程序的UI设计提供了一个可视化布局环境,并自动生成布局的FXML代码。请注意,保存FXML文件时可能会重新格式化。有关此工具的更多信息,请参阅JavaFX场景生成器入门。JavaFX场景构建器用户指南的CSS蒙皮和CSS分析器部分还为您提供了如何蒙皮FXML布局的信息。
7 Animation and Visual Effects in JavaFX
You can use JavaFX to quickly develop applications with rich user experiences. In this Getting Started tutorial, you will learn to create animated objects and attain complex effects with very little coding.
您可以使用JavaFX快速开发具有丰富用户体验的应用程序。在本入门教程中,您将学习如何创建动画对象,并使用很少的编码获得复杂的效果。
Figure 7-1 shows the application to be created.
图7-1显示要创建的应用程序。
Figure 7-1 Colorful Circles Application
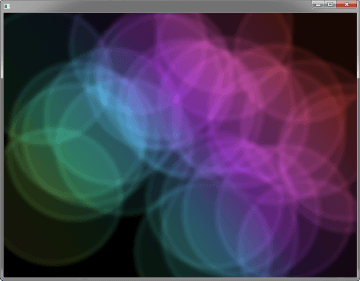
Description of "Figure 7-1 Colorful Circles Application"
Figure 7-2 shows the scene graph for the ColorfulCircles application. Nodes that branch are instantiations of the Group class, and the nonbranching nodes, also known as leaf nodes, are instantiations of the Rectangle and Circle classes.
图7-2显示了“ColorfulCircles”应用程序的场景图。分支的节点是“Group”类的实例化,非分支节点,也称为叶子节点,是“Rectangle”和“Circle”类的实例。
Figure 7-2 Colorful Circles Scene Graph
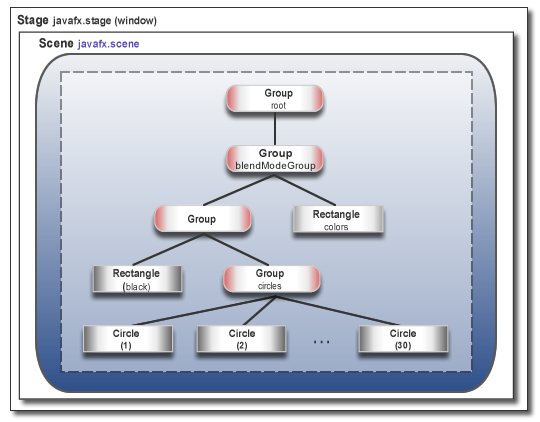
Description of "Figure 7-2 Colorful Circles Scene Graph"
The tool used in this Getting Started tutorial is NetBeans IDE. Before you begin, ensure that the version of NetBeans IDE that you are using supports JavaFX 8. See the Certified System Configurations section of the Java SE Downloads page for details.
本入门教程中使用的工具是NetBeans IDE。在开始之前,请确保您使用的NetBeans IDE版本支持JavaFX 8。请参阅Java SE下载页面的认证系统配置部分了解详情。
Set Up the Application
Set up your JavaFX project in NetBeans IDE as follows:
在NetBeans IDE中设置JavaFX项目,如下所示:
-
From the File menu, choose New Project.
从“文件”菜单中,选择“新建项目”。
-
In the JavaFX application category, choose JavaFX Application. Click Next.
在JavaFX应用类别中,选择JavaFX应用程序。单击下一步。
-
Name the project ColorfulCircles and click Finish.
将项目命名为ColorfulCircles,然后单击Finish。
-
Delete the import statements that NetBeans IDE generated.
删除NetBeans IDE生成的导入语句。
You can generate the import statements as you work your way through the tutorial by using either the code completion feature or the Fix Imports command from the Source menu in NetBeans IDE. When there is a choice of import statements, choose the one that starts with
javafx.您可以在教程中使用代码完成功能或NetBeans IDE中“源”菜单中的“修复导入”命令来生成导入语句。当有导入语句可供选择时,请选择以“javafx”开头的语句。
Set Up the Project
Delete the ColorfulCircles class from the source file that NetBeans IDE generated and replace it with the code in Example 7-1.
从NetBeans IDE生成的源文件中删除“ColorfulCircles”类,并将其替换为示例7-1中的代码.
Example 7-1 Basic Application
public class ColorfulCircles extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
Group root = new Group();
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 800, 600, Color.BLACK);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
For the ColorfulCircles application, it is appropriate to use a group node as the root node for the scene. The size of the group is dictated by the size of the nodes within it. For most applications, however, you want the nodes to track the size of the scene and change when the stage is resized. In that case, you use a resizable layout node as the root, as described in Creating a Form in JavaFX.
对于ColorfulCircles应用程序,使用组节点作为场景的根节点是合适的。组的大小由组内节点的大小决定。但是,对于大多数应用程序,您希望节点跟踪场景的大小,并在调整舞台大小时进行更改。在这种情况下,您可以使用可调整大小的布局节点作为根,如在JavaFX中创建表单中所述.
You can compile and run the ColorfulCircles application now, and at each step of the tutorial, to see the intermediate results. If you run into problems, then take a look at the code in the ColorfulCircles.java file, which is included in the downloadable ColorfulCircles.zip file. At this point, the application is a simple black window.
现在,您可以编译并运行ColorfulCircles应用程序,并在教程的每个步骤中查看中间结果。如果您遇到问题,请查看可下载的ColorfulCircles.zip]中包含的ColorfulCircles.java文件中的代码文件。此时,应用程序是一个简单的黑色窗口。
Add Graphics
Next, create 30 circles by adding the code in Example 7-2 before the primaryStage.show() line.
接下来,通过添加示例7-2中的代码创建30个圆圈在primaryStage.show()行之前。
Example 7-2 30 Circles
Group circles = new Group();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
Circle circle = new Circle(150, Color.web("white", 0.05));
circle.setStrokeType(StrokeType.OUTSIDE);
circle.setStroke(Color.web("white", 0.16));
circle.setStrokeWidth(4);
circles.getChildren().add(circle);
}
root.getChildren().add(circles);
This code creates a group named circles, then uses a for loop to add 30 circles to the group. Each circle has a radius of 150, fill color of white, and opacity level of 5 percent, meaning it is mostly transparent.
这段代码创建了一个名为“circles”的组,然后使用“for”循环将30个圆添加到该组中。每个圆的半径为150,填充颜色为白色,不透明度为5%,这意味着它基本上是透明的。
To create a border around the circles, the code includes the StrokeType class. A stroke type of OUTSIDE means the boundary of the circle is extended outside the interior by the StrokeWidth value, which is 4. The color of the stroke is white, and the opacity level is 16 percent, making it brighter than the color of the circles.
为了在圆圈周围创建边框,代码中包含了StrokeType类。“OUTSIDE”的笔划类型意味着圆的边界通过“StrokeWidth”值向外延伸,即“4”。笔划的颜色为“白色”,不透明度为“16%”,使其比圆圈的颜色更亮。
The final line adds the circles group to the root node. This is a temporary structure. Later, you will modify this scene graph to match the one shown in Figure 7-2.
最后一行将“circles”组添加到根节点。这是一个临时结构。稍后,您将修改此场景图以匹配图7-2中所示的场景图.
Figure 7-3 shows the application. Because the code does not yet specify a unique location for each circle, the circles are drawn on top of one another, with the upper left-hand corner of the window as the center point for the circles. The opacity of the overlaid circles interacts with the black background, producing the gray color of the circles.
图7-3显示应用程序。因为代码还没有为每个圆指定唯一的位置,所以这些圆是一个接一个地绘制的,窗口的左上角是圆的中心点。重叠圆的不透明度与黑色背景相互作用,产生圆的灰色。
Figure 7-3 Circles

Description of "Figure 7-3 Circles"
Add a Visual Effect
Continue by applying a box blur effect to the circles so that they appear slightly out of focus. The code is in Example 7-3. Add this code before the primaryStage.show() line.
继续对圆圈应用长方体模糊效果,使其看起来稍微失焦。代码在示例7-3中. 在primaryStage.show()行之前添加此代码。
Example 7-3 Box Blur Effect
circles.setEffect(new BoxBlur(10, 10, 3));
This code sets the blur radius to 10 pixels wide by 10 pixels high, and the blur iteration to 3, making it approximate a Gaussian blur. This blurring technique produces a smoothing effect on the edge of the circles, as shown in Figure 7-4.
此代码将模糊半径设置为“10”像素宽乘以“10”个像素高,模糊迭代设置为“3”,使其近似于高斯模糊。这种模糊技术在圆的边缘产生平滑效果,如图7-4所示.
Figure 7-4 Box Blur on Circles

Description of "Figure 7-4 Box Blur on Circles"
Create a Background Gradient
Now, create a rectangle and fill it with a linear gradient, as shown in Example 7-4.
现在,创建一个矩形并用线性渐变填充它,如示例7-4所示.
Add the code before the root.getChildren().add(circles) line so that the gradient rectangle appears behind the circles.
在root.getChildren().Add(circles)行之前添加代码,使渐变矩形出现在圆圈后面。
Example 7-4 Linear Gradient
Rectangle colors = new Rectangle(scene.getWidth(), scene.getHeight(),
new LinearGradient(0f, 1f, 1f, 0f, true, CycleMethod.NO_CYCLE, new
Stop[]{
new Stop(0, Color.web("#f8bd55")),
new Stop(0.14, Color.web("#c0fe56")),
new Stop(0.28, Color.web("#5dfbc1")),
new Stop(0.43, Color.web("#64c2f8")),
new Stop(0.57, Color.web("#be4af7")),
new Stop(0.71, Color.web("#ed5fc2")),
new Stop(0.85, Color.web("#ef504c")),
new Stop(1, Color.web("#f2660f")),}));
colors.widthProperty().bind(scene.widthProperty());
colors.heightProperty().bind(scene.heightProperty());
root.getChildren().add(colors);
This code creates a rectangle named colors. The rectangle is the same width and height as the scene and is filled with a linear gradient that starts in the lower left-hand corner (0, 1) and ends in the upper right-hand corner (1, 0). The value of true means the gradient is proportional to the rectangle, and NO_CYCLE indicates that the color cycle will not repeat. The Stop[] sequence indicates what the gradient color should be at a particular spot.
这段代码创建了一个名为“colors”的矩形。矩形的宽度和高度与场景相同,并填充有从左下角(0,1)开始到右上角(1,0)结束的线性渐变。“true”的值表示渐变与矩形成正比,“NO_CYCLE”表示颜色循环不会重复。“Stop[]”序列指示特定位置的渐变颜色应该是什么。
The next two lines of code make the linear gradient adjust as the size of the scene changes by binding the width and height of the rectangle to the width and height of the scene. See Using JavaFX Properties and Bindings for more information on binding.
接下来的两行代码通过将矩形的宽度和高度绑定到场景的宽度和高,使线性渐变随着场景大小的变化而调整。请参阅使用JavaFX属性和绑定有关绑定的更多信息。
The final line of code adds the colors rectangle to the root node.
最后一行代码将“colors”矩形添加到根节点。
The gray circles with the blurry edges now appear on top of a rainbow of colors, as shown in Figure 7-5.
现在,边缘模糊的灰色圆圈出现在彩虹色之上,如图7-5所示.
Figure 7-5 Linear Gradient

Description of "Figure 7-5 Linear Gradient"
Figure 7-6 shows the intermediate scene graph. At this point, the circles group and colors rectangle are children of the root node.
图7-6显示了中间场景图。此时,“圆形”组和“颜色”矩形是根节点的子节点。
Figure 7-6 Intermediate Scene Graph

Description of "Figure 7-6 Intermediate Scene Graph"
Apply a Blend Mode
Next, add color to the circles and darken the scene by adding an overlay blend effect. You will remove the circles group and the linear gradient rectangle from the scene graph and add them to the new overlay blend group.
接下来,为圆圈添加颜色,并通过添加叠加混合效果使场景变暗。您将从场景图中删除“圆形”组和线性渐变矩形,并将其添加到新的叠加混合组中。
-
Locate the following two lines of code:
找到以下两行代码:
root.getChildren().add(colors); root.getChildren().add(circles); -
Replace the two lines of code from Step 1 with the code in Example 7-5.
Example 7-5 Blend Mode
Group blendModeGroup = new Group(new Group(new Rectangle(scene.getWidth(), scene.getHeight(), Color.BLACK), circles), colors); colors.setBlendMode(BlendMode.OVERLAY); root.getChildren().add(blendModeGroup);
The group blendModeGroup sets up the structure for the overlay blend. The group contains two children. The first child is a new (unnamed) Group containing a new (unnamed) black rectangle and the previously created circles group. The second child is the previously created colors rectangle.
“blendModeGroup”组为叠加混合设置结构。这个小组有两个孩子。第一个子对象是一个新的(未命名的)“组”,其中包含一个新(未命名)的黑色矩形和之前创建的“圆圈”组。第二个子对象是之前创建的“colors”矩形。
The setBlendMode() method applies the overlay blend to the colors rectangle. The final line of code adds the blendModeGroup to the scene graph as a child of the root node, as depicted in Figure 7-2.
setBlendMode()方法将叠加混合应用于colors矩形。最后一行代码将“blendModeGroup”作为根节点的子节点添加到场景图中,如图7-2所示.
An overlay blend is a common effect in graphic design applications. Such a blend can darken an image or add highlights or both, depending on the colors in the blend. In this case, the linear gradient rectangle is used as the overlay. The black rectangle serves to keep the background dark, while the nearly transparent circles pick up colors from the gradient, but are also darkened.
叠加混合是平面设计应用程序中常见的效果。这种混合可以使图像变暗或添加高光,或两者兼而有之,具体取决于混合中的颜色。在这种情况下,使用线性梯度矩形作为覆盖。黑色矩形用于保持背景黑暗,而近乎透明的圆圈从渐变中吸收颜色,但也会变暗。
Figure 7-7 shows the results. You will see the full effect of the overlay blend when you animate the circles in the next step.
图7-7显示了结果。在下一步中设置圆的动画时,您将看到叠加混合的完整效果。
Figure 7-7 Overlay Blend

Description of "Figure 7-7 Overlay Blend"
Add Animation
The final step is to use JavaFX animations to move the circles:
最后一步是使用JavaFX动画来移动圆圈:
-
If you have not done so already, add
import static java.lang.Math.random;to the list of import statements.如果您还没有这样做,请添加
import static java.lang.Math.random;到进口声明列表。 -
Add the animation code in Example 7-6 before the
primaryStage.show()line.添加例7-6中的动画代码在
primaryStage.show()行之前。Example 7-6 Animation
Timeline timeline = new Timeline(); for (Node circle: circles.getChildren()) { timeline.getKeyFrames().addAll( new KeyFrame(Duration.ZERO, // set start position at 0 new KeyValue(circle.translateXProperty(), random() * 800), new KeyValue(circle.translateYProperty(), random() * 600) ), new KeyFrame(new Duration(40000), // set end position at 40s new KeyValue(circle.translateXProperty(), random() * 800), new KeyValue(circle.translateYProperty(), random() * 600) ) ); } // play 40s of animation timeline.play();
Animation is driven by a timeline, so this code creates a timeline, then uses a for loop to add two key frames to each of the 30 circles. The first key frame at 0 seconds uses the properties translateXProperty and translateYProperty to set a random position of the circles within the window. The second key frame at 40 seconds does the same. Thus, when the timeline is played, it animates all circles from one random position to another over a period of 40 seconds.
动画由时间线驱动,因此此代码创建了一个时间线,然后使用“for”循环将两个关键帧添加到30个圆圈中的每一个。0秒时的第一个关键帧使用属性“translateXProperty”和“translateYProperty”来设置窗口内圆的随机位置。40秒时的第二个关键帧也是如此。因此,当播放时间线时,它会在40秒内将所有圆圈从一个随机位置动画化到另一个。
Figure 7-8 shows the 30 colorful circles in motion, which completes the application. For the complete source code, see the ColorfulCircles.java file, which is included in the downloadable ColorfulCircles.zip file..
图7-8显示了30个运动中的彩色圆圈,从而完成了应用程序。有关完整的源代码,请参阅可下载的ColorfulCircles.zip中包含的ColorfulCircles.java文件文件。
Figure 7-8 Animated Circles

Description of "Figure 7-8 Animated Circles"
Where to Go from Here
Here are several suggestions about what to do next:
以下是关于下一步行动的几点建议:
-
Try the JavaFX samples, which you can download from the JDK Demos and Samples section of the Java SE Downloads page at
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/. Especially take a look at the Ensemble application, which provides sample code for animations and effects.尝试JavaFX示例,您可以从Java SE下载页面的JDK演示和示例部分下载,网址为
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/. 特别是看看Ensemble应用程序,它提供了动画和效果的示例代码。 -
Read Creating Transitions and Timeline Animation in JavaFX. You will find more details on timeline animation as well as information on fade, path, parallel, and sequential transitions.
阅读在JavaFX中创建过渡和时间线动画. 您将找到有关时间线动画的更多详细信息,以及有关淡入淡出、路径、平行和顺序过渡的信息。
-
See Creating Visual Effects in JavaFX for additional ways to enhance the look and design of your application, including reflection, lighting, and shadow effects.
请参阅在JavaFX中创建视觉效果了解增强应用程序外观和设计的其他方法,包括反射、照明和阴影效果。
-
Try the JavaFX Scene Builder tool to create visually interesting applications. This tool provides a visual layout environment for designing the UI for JavaFX applications and generates FXML code. You can use the Properties panel or the Modify option of the menu bar to add effects to the UI elements. See the Properties Panel and the Menu Bar sections of the JavaFX Scene Builder User Guide for information.
尝试JavaFX场景生成器工具来创建视觉上有趣的应用程序。该工具为JavaFX应用程序的UI设计提供了一个可视化布局环境,并生成FXML代码。您可以使用“属性”面板或菜单栏的“修改”选项为UI元素添加效果。有关信息,请参阅《JavaFX场景生成器用户指南》的“属性面板”和“菜单栏”部分。
A background.jpg
This appendix provides a graphical image used in the Using FXML to Create a User Interface.
本附录提供了使用FXML创建用户界面中使用的图形图像.
Legal Terms and Copyright Notice
/*
* Copyright (c) 2008, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
* All rights reserved. Use is subject to license terms.
*
* This file is available and licensed under the following license:
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
*
* - Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* - Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in
* the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* - Neither the name of Oracle nor the names of its
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
* A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
* OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
* SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
* DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
* OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
background.jpg
本文来自博客园,作者:积跬步小流臹千里江海,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Hloveandshare/p/18847814



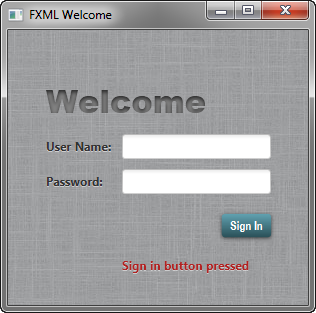


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号