# 使用np.array()创建一个numpy的array对象
np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])

# 嵌套列表构成多维数组
np.array([range(i, i + 3) for i in [2, 4, 6]])

# 创建一维零矩阵
np.zeros(10)
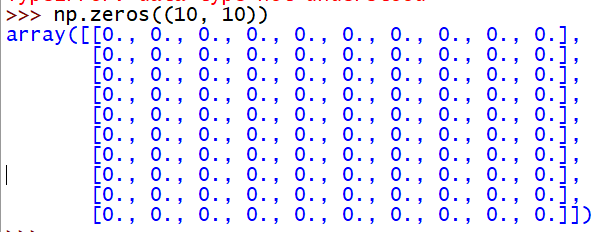
# 创建二维零矩阵
np.zeros((10, 10))
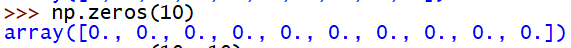
# 创建一个二维全1矩阵
np.ones((3, 5))

# 用一个数填充矩阵
np.full((3, 5), 3.14)

# 创建一个线性序列数组,从0开始,到20结束,步长为2
np.arange(0, 20, 2)
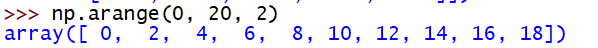
# 创建一个5个元素的数组,均分0-1这个区间
np.linspace(0, 1, 5)

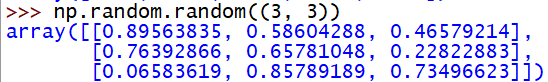
# 创建一个3x3的在01上均匀分布的随机数组成的数组
np.random.random((3, 3))
# 创建一个3x3的均值为0,方差为1的正态分布的随机数组
np.random.normal(0, 1, (3, 3))

# 创建一个3x3的[0, 10)区间的随机整型数组
np.random.randint(0, 10, (3, 3))

# 创建一个由3个整形数组成的未初始化的数组,数组的值是内存空间中的任意值
np.empty(3)

# numpy数组的属性
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
x1 = np.random.randint(10, size=6)
x2 = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 4))
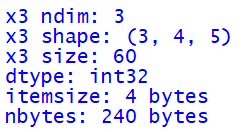
x3 = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 4, 5))
print('x3 ndim:', x3.ndim)
print('x3 shape:', x3.shape)
print('x3 size:', x3.size)
print('dtype:', x3.dtype)
print('itemsize:', x3.itemsize, 'bytes')
print('nbytes:', x3.nbytes, 'bytes')
# 数组索引:获取单个元素
from numpy import *
x1 = array([5, 0, 3, 3, 7, 9])
print('x1[0]:', x1[0])
print('x1[4]:', x1[4])
print('x1[-1]:', x1[-1])
print('x1[-2]:', x1[-2])
x2 = array([[3, 5, 2, 4],
[7, 6, 8, 8],
[1, 6, 7, 7]])
print('x2[0, 0]:', x2[0, 0])
print('x2[2, 0]:', x2[2, 0])
print('x2[2, -1]:', x2[2, -1])
x2[0, 0] = 12
print('x2:', x2)

import numpy as np
x = np.arange(10)
# x[start:stop:step]
print('x:', x)
print('x[:5]:', x[:5]) # 前5个元素
print('x[5:]:', x[5:]) # 索引5之后的元素
print('x[4:7]:', x[4:7]) # 4到7中间的数组
print('x[::2]:', x[::2]) # 每隔一个元素
print('x[1::2]:', x[1::2]) # 每隔一个元素,从索引1开始
print('x[::-1]:', x[::-1]) # 所有元素,逆序的
print('x[5::-2]:', x[5::-2]) # 从索引5开始每隔一个元素逆序
x2 = np.array([[12, 5, 2, 4],
[7, 6, 8, 8],
[1, 6, 7, 7]])
print('x2:', x2)
print('x2[:2, :3]:', x2[:2, :3]) # 两行,三列
print('x2[:3, ::2]:', x2[:3, ::2]) # 所有行,每隔一列
print('x2[::-1, ::-1]:', x2[::-1, ::-1]) # 子数组维度同时被逆序



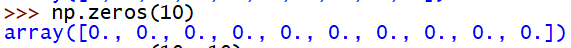



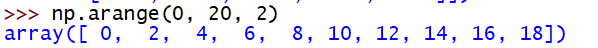











 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号