实验1 C语言输入输出和简单程序编写
实验1(用的markdown编辑器没法用line标,下次用HTML的)
实验任务1
task1-1.c
源代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main1()
{
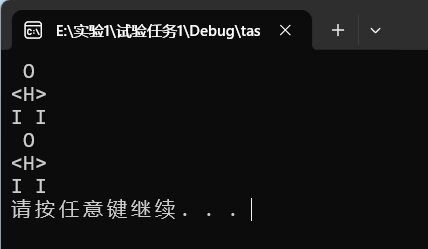
printf(" O \n");
printf("<H>\n");
printf("I I\n");
printf(" O \n");
printf("<H>\n");
printf("I I\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
task1-2.c
源代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main1()
{
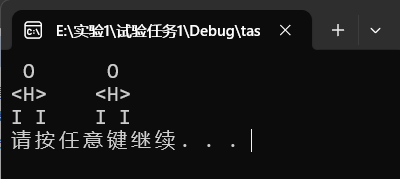
printf(" O O \n");
printf("<H> <H>\n");
printf("I I I I\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
实验任务2
task2.c源代码
//判断构成三角形
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
double a,b,c;
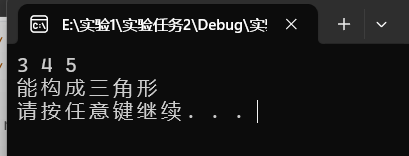
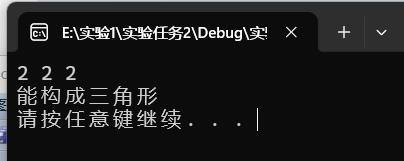
scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c);
if(a+b>c && a+c>b && b+c>a )
printf("能构成三角形\n");
else
printf("不能构成三角形");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/*注
1. line11的格式控制符%lf,是字母L的小写l, 不是数字1。
2. double类型的数据,在输入时必须使用格式符%lf, 输出时可以使用%f,也可以使用%lf
*/
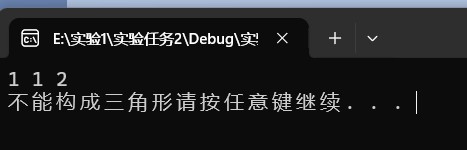
运行结果截图
实验任务3
task3.c源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
char ans1,ans2;
printf("预习复习了吗(输入y/Y表示有,输入n或N表示没有):");
ans1=getchar();//输入一个字符,赋值给ans1
getchar();
printf("\n动手敲代码实践了没? (输入y或Y表示敲了,输入n或N表示没敲) : ");
ans2=getchar();
if((ans1=='y'||ans1=='Y')&&(ans2=='Y'||ans2=='y'))
printf("/n罗马不是一天建成的,继续保持噢:)\n");
else
printf("\n罗马不是一天毁灭的,我们来建设吧");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
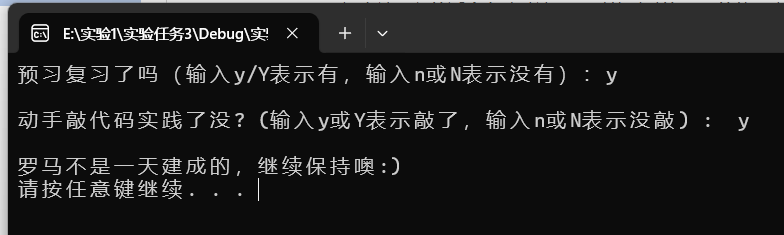
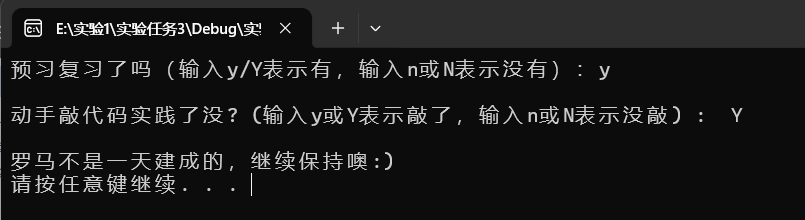
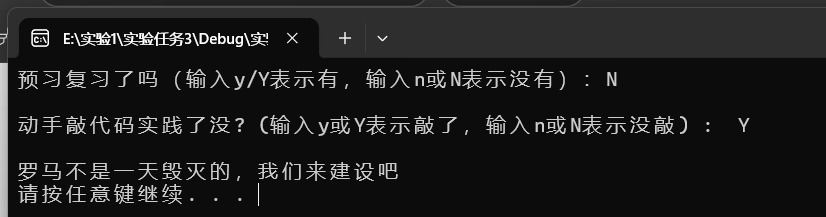
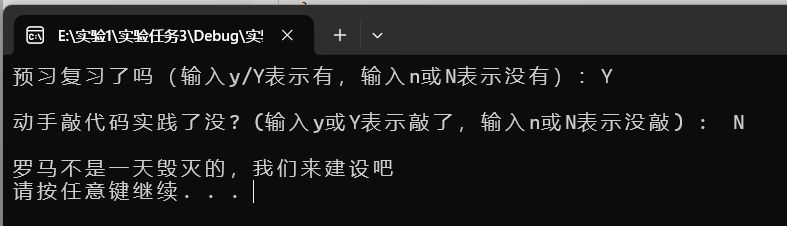
回答问题
因为前面在给ans1赋值时getchar中暂存了两个数据,第二个是换行符号,所以如果去掉getchar()则ans2得到的数据就是回车,导致输入ans1后直接会得出结果,加上getchar()这行代码后则会输出暂存的回车这个数据。
实验任务4
源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
double x, y;
char c1, c2, c3;
int a1, a2, a3;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a1, &a2, &a3);//源代码中a1,a2,a3前面没加占位符&
printf("a1 = %d, a2 = %d, a3 = %d\n", a1,a2,a3);
scanf("%c%c%c", &c1, &c2, &c3);
printf("c1 = %c, c2 = %c, c3 = %c\n", c1, c2, c3);
scanf("%lf,%lf", &x, &y);//源代码中第一个是用的%f,但是双精度型的数据应该是用%lf
printf("x = %f, y = %lf\n",x, y);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
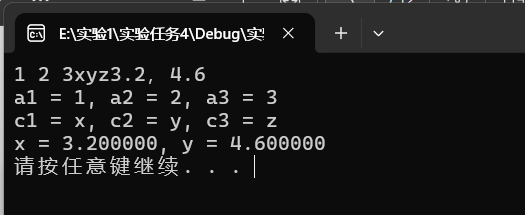
实验任务5
源代码
// 计算10亿秒约等于多少年,并打印输出
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int year;
int t=1000000000;// 补足代码
year=t/(60*60*24*365);// ×××
printf("10亿秒约等于%d年\n", year);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
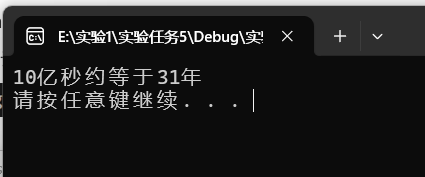
实验任务6
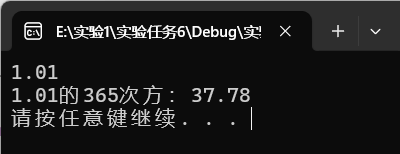
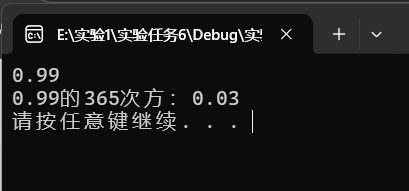
task6—1源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x,ans;
scanf("%lf",&x);
ans=pow(x,365);
printf("%.2f的365次方:%.2f\n",x,ans);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
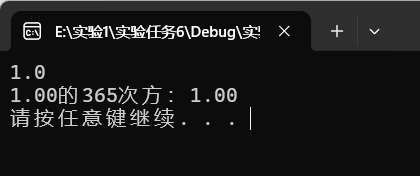
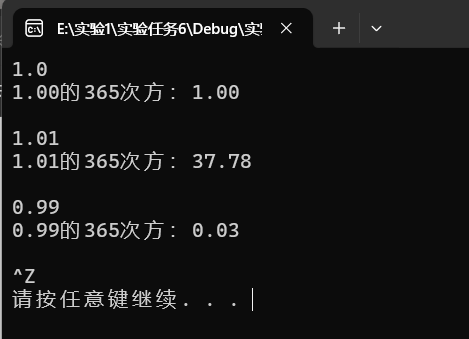
task6-2源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x,ans;
while(scanf("%lf",&x) != EOF)
{
ans=pow(x,365);
printf("%.2f的365次方:%.2f\n",x,ans);
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
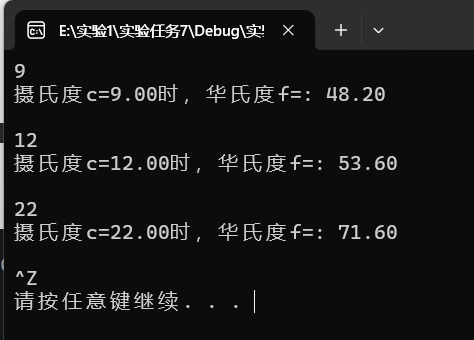
实验任务7
源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
double F,C;
while(scanf("%lf", &C) != EOF)
{
F=1.8*C+32;
printf("摄氏度c=%.2f时,华氏度f=: %.2f\n", C, F);
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
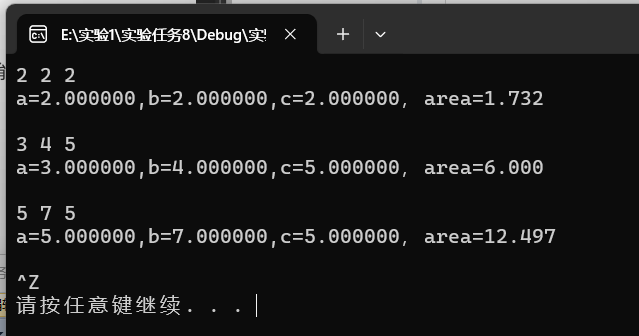
实验任务8
源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double a,b,c,s,p;
while(scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c) != EOF)
{
s=(a+b+c)/2;
p=pow(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c),0.5);
printf("a=%f,b=%f,c=%f,area=%.3f\n\n",a,b,c,p);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果截图
实验总结
每个程序都要重复写头文件什么的,比较烦,我后面会在一个文件中提前编好框架,后面新建项目需要敲代码可以直接打开那个提前尊卑好的文件进行编写,还有运行框一闪而过的话是因为运行的太快了,可以加个system(“pausse”)(记得加头文件)这样就会停留在结果页面。这次实验让我对scanf的语法规则有了深刻理解,比如输入时的分隔符要严格遵守源代码中写的分隔符,比如实验4最后输入的3.2和4.6我源文件中分割号写的是逗号,我输入时分隔号也应该是逗号,不然就会结果就会错乱等等。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号