JDBC04----预编译语句介绍
sql的拼接很麻烦,且容易出错,因此就可以使用预编译语句。
接口java.sql.Statement有两个子接口:CallableStatement,PreparedStatement
有两种类型的sql语句:
1.静态sql
在执行之前就知道了sql语句的形式。
2.动态sql
一. Statement接口的实现类
1. PreparedStatement
- PreparedStatement用于预编译模板SQL语句,在运行时接受SQL输入参数。eg:PreparedStatement ps=conn.preparedStatement(sql);
- 在性能和代码灵活性上有显著的提高
- PreparedStatement对象使用?作为占位符,即参数标记;eg: select *from stu where id=?; insert into stu value(?,?,?);
- 使用setXXX(index,value)方法将值绑定到参数中,每个参数标记是其顺序位置引用,注意index从1开始;eg:ps.setInt(1,stu.getId());
- PreparedStatement对象执行sql语句:executeQuery()、executeUpdate(),注意,他们没有参数; eg:ps.executeUpdate();
2. 举例
public Stu get(int id) { ResultSet resultSet=null; Connection connection=null; PreparedStatement pStatement=null; Stu student=new Stu(); try { Class.forName(JDBCUtil.driverName); connection=JDBCUtil.getConnection(); String sql="select *from stu where id=?"; pStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); pStatement.setInt(1, id);//note这里的id时传入的,如果传入参数是student,就可以改成pStatement.setInt(1,student.getId()) resultSet=pStatement.executeQuery(); if(resultSet.next()) { student.setId(resultSet.getInt("id")); student.setName(resultSet.getString("name")); student.setAge(resultSet.getInt("age")); return student; } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtil.close(connection, pStatement, resultSet); } return null; }
3. 如果没有使用预编译语句
如果没有使用预编译语句的话,假设已经有一个静态的sql语句了,每一次查找的age不同,都会往预编池中写入一次数据。
4. 如果使用预编译语句
参数统一用?表示,这样预编译池中就不会多次写入数据了。---------(当很多人操作数据库时,这回很麻烦的)
note: mysql不支持预编译池,oracle支持预编译池。
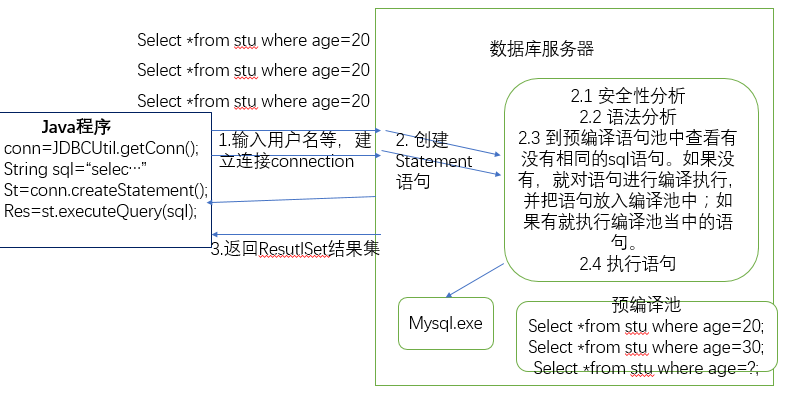
6. 使用预编译可以防止SQL注入。
(1)什么是SQL注入(note: 后面文章还会补充关于SQL注入以及如何防止SQL注入的知识!!!,这里只是先简单了解下)
就是通过把SQL命令插入到WEB表单提交或输入域名或页面请求的查询字符串,最终达到欺骗服务器执行恶意的SQL语句。(说人话:就是一些错误的sql语句,导致了错误的sql语义被执行了)
(2)SQL注入举例
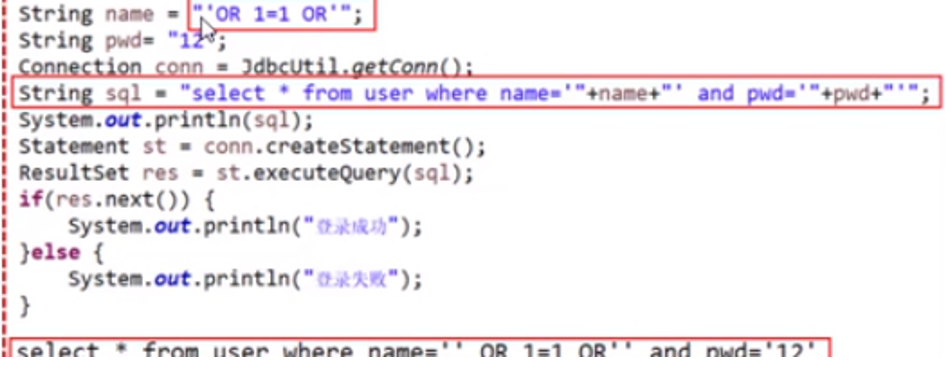
上面是一个用户登陆的代码,当用户名如上定义时,虽然表中没有这个用户,但是最终的结果会发现打印了登陆成功。打印出这一条sql语句:
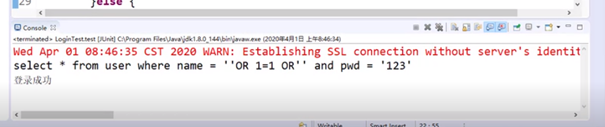
因此,看到拼接结果可以知道前面那个条件已经满足了,就不会管or后面的语句了:即name=‘’已经成立了。
如果使用预编译,因为它执行的时候会把单引号转义。----也就是防止SQL注入的根源
如果使用预编译:
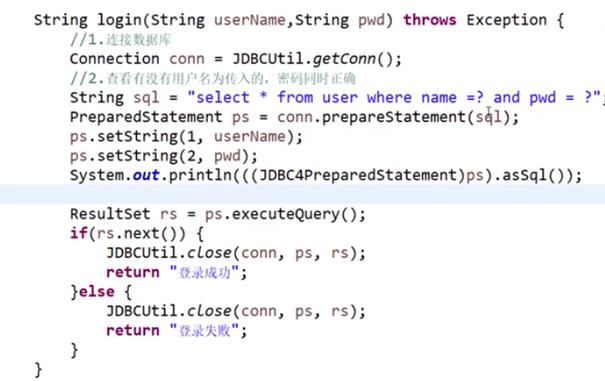
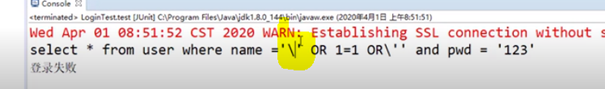
(3)为什么PrepareStaet就能防止注入
是因为它把单引号转义了,变成了\,这样一来,就无法截断SQL语句,进而无法拼接SQL语句,基本上没有办法注入了。
二. JDBC调用输出参数存储过程----CallableStatement
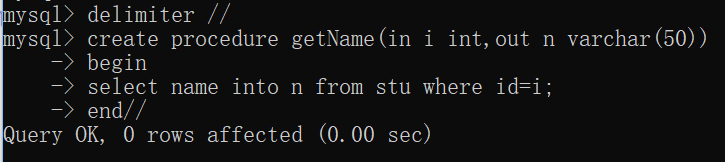
1. 创建一个存储过程
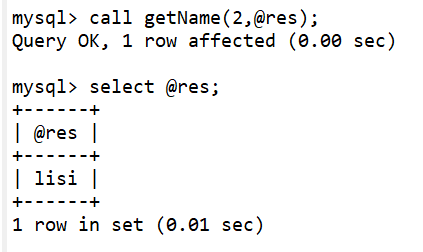
测试下:
2. 使用Java程序来实现调用
public void call(){ Connection connection=JDBCUtil.getConnection(); CallableStatement cStatement; try { cStatement = connection.prepareCall("{call getName(?,?)}"); cStatement.setInt(1, 2); cStatement.registerOutParameter(2, Types.VARCHAR); cStatement.execute(); String name=cStatement.getString(2); System.out.println(name); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }
参考文献
https://ke.qq.com/course/339214





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号