C#3.0笔记(二)预备知识之委托与事件
2009-04-25 22:50 Henry Cui 阅读(1587) 评论(6) 收藏 举报在上篇blog中简单地介绍了委托的基础知识,在这片文章中会介绍下委托跟事件之间的联系。
事件的由来
我们可以看到在使用委托进行回调的实现的时候,我们往往需要再定义一个委托对象,以及一个对外公开的辅助方法来添加委托的方法,这样子会使我们感觉比较繁琐。C#提供了event关键字来减轻直接使用委托的负担,编译器会自动提供注册、取消注册的方法和委托必要的成员。首先来看看定义事件的步骤:
1.先定义委托类型;
2.通过event关键字定委托类型的事件。
public delegate int Caculate(int x, int y); public event Caculate OnCaculate;
看看编译器帮我们定义了什么
首先我们可以看到帮我们定义了一个Caculate对象,其次定义了两个方法add_OnCaculate跟remove_OnCaculate。我们可以在看看add_OnCaculate两个方法里面的一些核心的东西。add_OnCaculate:
IL_0008: call class [mscorlib]System.Delegate [mscorlib]System.Delegate::Combine(class [mscorlib]System.Delegate, class [mscorlib]System.Delegate)
很明显地看到add_OnCaculate方法调用的就是委托的Combine方法,从而我们也可以想到remove_OnCaculate方法调用的是Remove方法。从上面我们可以看到其实event关键字只是提供给我们了一种语法上的便利措施。
一个稍微完整的例子
这个例子参考的是《C#与.NET3.0高级程序设计》上面的。使用Car来举例的,当车子加速时到一定限制值时会触发一个预警事件,当超过某一个速度时会触发一个车子爆炸事件。首先看委托跟事件:
public delegate void CarEventHandler(string msg); public event CarEventHandler AbortToBlow; public event CarEventHandler Exploded;
EventCar类中有两个事件一个是AbortToBlow一个是Exploded。下面是Car的几个属性以及字段:
private const int MaxSpeed = 180; public int CurrSpeed { get; private set; } public bool IsDead { get; private set; } public string Name { get; private set; }
其中IsDead是表示车子是否已经报废了。下面是一个加速的方法:
public void Accelerate(int addSpeed) { if (IsDead) { if (this.Exploded!= null) Exploded("The Car Is Dead"); } else { CurrSpeed += addSpeed; if (10 == MaxSpeed - CurrSpeed &&AbortToBlow != null) { AbortToBlow("Careful!Bona blow!"); } if (CurrSpeed >= MaxSpeed) IsDead = true; else Console.WriteLine("CurrentSpeed:{0}", CurrSpeed); } }
完整代码:
public class EventCar { public delegate void CarEventHandler(string msg); public event CarEventHandler AbortToBlow; public event CarEventHandler Exploded; private const int MaxSpeed = 180; public int CurrSpeed { get; private set; } public bool IsDead { get; private set; } public string Name { get; private set; } public EventCar() { } public EventCar(string carName, int currSpeed) { if (currSpeed > MaxSpeed) IsDead = true; else { Name = carName; CurrSpeed = currSpeed; } } public void Accelerate(int addSpeed) { if (IsDead) { if (this.Exploded!= null) Exploded("The Car Is Dead"); } else { CurrSpeed += addSpeed; if (10 == MaxSpeed - CurrSpeed &&AbortToBlow != null) { AbortToBlow("Careful!Bona blow!"); } if (CurrSpeed >= MaxSpeed) IsDead = true; else Console.WriteLine("CurrentSpeed:{0}", CurrSpeed); } } }
客户端调用:
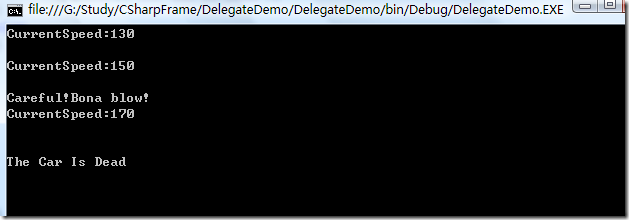
static void Main(string[] args) { EventCar bmw = new EventCar("Henllyee", 110); bmw.AbortToBlow += new EventCar.CarEventHandler(CarAboutToBlow); bmw.Exploded += new EventCar.CarEventHandler(CarExploede); for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) { bmw.Accelerate(20); Console.ReadLine(); } } public static void CarAboutToBlow(string msg) { Console.WriteLine(msg); } public static void CarExploede(string msg) { Console.WriteLine(msg); }
运行效果:
规范的事件与匿名方法
我们看我们定义的事件似乎跟底层的事件有点不一样,底层的委托的第一个参数一般为System.Object类型的,第二个参数一般为派生自System.EventArgs类型的。第一个参数一般表示发送事件的对象,第二个参数表示与该事件相关的参数。我们可以定义个CarEventArgs:
public class CarEventArgs : EventArgs { public readonly string msg; public CarEventArgs(string Msg) { msg = Msg; } }
委托就可以修改成:
public delegate void CarEventHandler(object send, CarEventArgs e);
使用时:
if (IsDead) { if (this.Exploded!= null) Exploded(this,new CarEventArgs("The Car Is Dead")); }
在上面的时候我们当监听事件的时候都是通过定义一个唯一的与委托签名匹配的方法,在有的时候我们监听的方法也许只需要处理一段简单的逻辑,所以每次都定义个方法毕竟比较麻烦。大都时候我们可以通过匿名方法来监听事件,如:
bmw.AbortToBlow += delegate(object sender, CarEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("Message:{0}",e.msg); };
总结
这篇中分析了下事件跟委托的关系,其实事件只是语法定义上的方便,关键还是理解了委托就行。
现在经常出差,一个月有20天在外面,写点东西不容易,后悔以前没勤奋点,呵呵



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号