【论文阅读】Chinese relation extraction based on lattice network improved with BERT model[ICMAI2020]
论文地址:https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3395260.3395276
代码地址:
ABSTRACT
关系分类是自然语言处理领域的一项基本而重要的任务。关于英语数据集的研究已经很多,而对汉语数据集的研究却很少。由于汉语的特殊性,现有的方法大多存在着切分错误和多义现象两大问题。综上所述,许多模型都能很好地解决切分误差问题,以格点模型为例,该模型能精确地切分中文单词。但是一词多义的问题还没有得到足够的重视。本文利用BERT模型来处理多义现象。实验结果表明,该模型取得了很好的效果,优于基线模型。
1. INTRODUCTION
基于中文数据集的关系抽取研究相对较少。传统的中文关系抽取方法主要有两种,一种是基于字符的方法,另一种是基于单词的方法。但是,它们都有自己的缺点。基于字符的模型忽略了单词级特征,这对于后续任务非常有用。
NLP任务(Named Entity Recognition,NER)中,分割越精确,模型的效果越好,反之越差。也就是说,它可能会导致错误传播。如何准确地分割和处理多义词是汉语关系抽取的两个关键问题,也是大多数模型必须解决的两个问题。
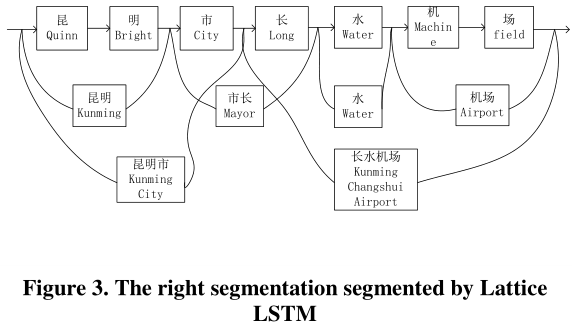
值得注意的是,Zhang等人[1]提出了格LSTM模型,通过改进LSTM结构[2],该模型能够准确地分割汉语句子。如图3所示,该模型可以分割汉语句子昆明市长水机场(昆明长水机场)“以正确的结果,这是令人印象深刻的。但该模型忽略了一词多义的问题。
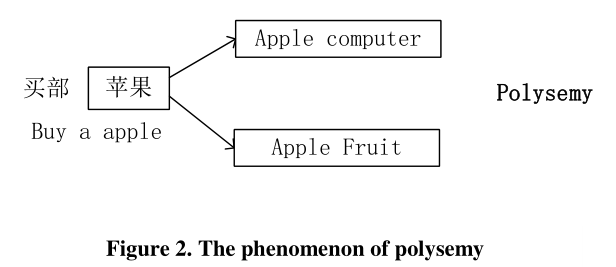
为了解决这两个问题,本文提出了一种用BERT模型改进的格型网络[3]。而且我们不使用任何NLP工具,所以我们避免了错误传播。
本文的主要贡献是引入BERT模型来解决汉语一词多义的难题。实验结果表明,该模型对中文关系抽取有很好的处理效果,优于基线模型。
2. RELATED WORK
根据数据集标注是否准确,关系抽取可分为完全监督模型和远程监督模型。全监督学习是基于完美的标注数据建立起来做的,数据量小。于是人们开始思考如何在大型数据集上进行关系抽取。
Mintz等人[4]创造性地将远程监督学习的概念应用到关系抽取任务中,提出了一个著名的假设,即“如果两个实体在一个已知的知识库中有关系,那么所有提到这两个实体的句子都会以某种方式表达这种关系”。随后,进行了一系列的研究。Ji等人[5]引入了额外的实体描述信息来增强嵌入学习,尽管这两部分的融合有点简单和暴力,本质上是在原始基础上增加了范式约束。但是这个方法提供了一个好主意,而且它的可扩展性非常强。Mintz等人[6]介绍了关系之间的依赖关系。由于本文使用的是所有正确的标注数据,所以本文主要讨论了全监督方法。
Liu等[7]首次尝试将CNN神经网络用于关系分类,取得了很好的效果。利用同义词嵌入(随机初始化的查找表)的工作可以引入一些附加信息,但是完全忽略了单词嵌入的语义信息。曾等[8]也尝试利用CNN来处理这一问题,他们创新性地引入了位置特征,并取得了一些成果。但该模型的缺点是卷积核只使用一个窗口大小,导致得到的信息太小,结构相对简单。Santos等人[9]提出了一个基于CNN的模型。损失函数是主要贡献。他们不再使用softmax和交叉熵函数,而是提出了全新的损失函数,即基于边际的耙损函数raking-loss function that based on margin。实验表明,排序损失函数的效果优于交叉熵损失函数。
Zhang等人[10]首次提出了使用RNN进行关系分类的尝试,可以达到与Zeng等人相同的效果,文中的一些实验表明,RNN的记忆优势可以在长文本建模中得到体现。Zhou等人[11]仍然使用RNN进行关系分类。与Zhang等人不同的是,它引入了注意机制,取得了比Zhang等人更好的结果。
利用CNN的另一个尝试是由Wang等人[12]。主要贡献是引入了多层注意,取得了一定的效果,但模型复杂度太高,性能相对较差。
格网The lattice network是李等[13]提出的,它完全解决了汉语分词错误,却忽略了汉语多义的影响。
据我们所知,我们是第一个使用BERT模型改进格型网络进行关系抽取的人。
3. MODEL
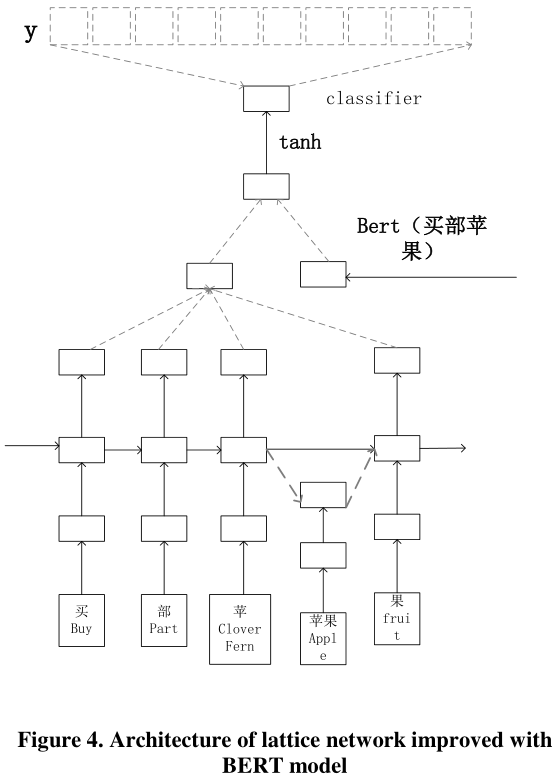
给定一个句子和对应的两个实体,我们的模型可以预测两个实体之间的关系。现在,我们将分别从四个方面介绍我们的模型,包括输入表示、格型LSTM编码器、BERT模型、分类。我们遵循最经典的工作方法。汉语句子$s$可以表示为$s=c_1,c_2,…c_m$, 其中$c_i$表示第$i$个汉字。也可以表示为$s=w_1,w_2, …w_m$, 其中$w_i$表示可由FudanNLP标记器获取的第$i$个汉语单词。FudanNLP标记器可以在http://code.google.com/p/fudannlp/. 我们的模型架构如下图所示:
3.1 Input Representation
3.1.1 Char-level Representation
We use skip-gram model [14] to map each Chinese character $c_i$ to a vector of $d^c$ , which can be denoted as follow:
$x_j^c=Model_{skip-gram}(c_j)$
$x_j^c$ is the character embedding.
3.1.2 Word-level Representation
$w_{b,e}$ represents a string that begins with Chinese character b and ends with Chinese character e. Then we leverage word2vec to convert word $w_{b,e}$ to a real-valued vector $x_{b,e}^w$ as follow:
$x_{b,e}^w \in R^{d^w}$
But word2vec map each word to only one single embedding so it ignores the phenomenon of polysemy(一词多义) in Chinese words. And then we will introduce BERT model to deal with this problem.
3.2 Lattice LSTM Encoder
LSTM(Long-Short-Term Memory)是一种设计良好的结构,称为“门”,门包括一个sigmoid神经网络层和逐点乘法运算,可以用来去除或增加向单元传输信息的能力。sigmoid层输出一个介于0和1之间的值,描述每个部分将通过的数量。0表示“不允许任何内容通过”,1表示“允许任何内容通过”。
LSTM总共有三个门,第一个是遗忘门$f_j$:决定将从单元状态中丢弃哪些信息。第二个是输入门$i_j$:决定将哪些新信息放入单元状态。第三个是输出门$o_j$:根据单元格状态输出结果。还有一个单元格更新状态值$c_j^c$它记录到当前时间的所有历史信息流。
LSTM的函数可用以下公式表示:略
As we've already discussed, for the input word $w_{b,e}$, we can convert it to $x_{b,e]^w$ as follow:
$w_{b,e}^w=e^w(w_{b,e})$
$w_{b,e}$ 表示以汉字$b$开头,以汉字$e$结尾的字符串。$e^w$ 是一个查找表。$c_j^c$表示从句首到第$j$个字符的信息流。然后,通过计算构造出lattice LSTM编码器$c_j^c$和词级表示$x_{b,e}^w$:
$\left[ \begin{matrix} i_{b,e}^w\\f_{b,e}^w\\\tilde{c}_{b,e}^w \end{matrix} \right]=\left[ \begin{matrix} \sigma \\\sigma \\tanh \end{matrix} \right] (w^{w^T}*x_{b,e}^w+w^{w^T}*h_b^c+b^w)$
$c_{b,e}^w=f_{b,e}^w\bigotimes c_b^c+i_{b,e}^w\bigotimes \tilde{c}_{b,e}^w$
$c_{b,e}^w$ represses the memory cell state of $x_{b,e}^w,x_{b,e}^i$ is input gate and $f_{b,e}^w$ is forget gate.The i-th character’s cell state is influenced by the words that ends in index e, which is $w_{b,e}$ with $b\in \{ b^{'}|w_{b^{'},e}\in D\} $.A new gate is leveraged to control the contribution of each word:
$i_{b,e}^c=\sigma(wx_{e}^c+Uc_{b,e}^w+b^l)$
So, the cell $i$-th character’s cell value can be computed by:
$c_e^c=\sum \alpha_{b,e}^c\bigotimes c_{b,e}^w+\alpha_e^c\bigotimes \tilde{c}_e^c$
$\alpha_{b,e}^c= \frac{exp(i_{b,e}^c)}{exp(i_e^c)+\sum_{b^{'}}exp(i_{b^{'},e}^c)}$
$b^{'}\in \{b^{''}|w_{b^{''},e}\in D\}$
Where $\alpha_{b,e}^c,\alpha_{e}^c$ are Regularization parameter. Finally, we will get the final hidden state vectors h use Eq16. This structure is also used in [3]and [13].
3.3 BERT Model
BERT的全称是Transformers的双向编码器表示,这是Google在2018年提出的一个新模型,它可以处理多义问题,在11个NLP任务中取得了最先进的结果。BERT模型的优点有两点:一是采用了蒙面语言模型(MLM)Masked Language Model[3]和下一句预测(NSP)Next Sentence Prediction[3]作为新的训练任务;其次,谷歌使用了大量的数据和计算能力来满足伯特的训练强度。
MLM可以从文本中进行双向学习,使得模型能够根据相邻单词的上下文来学习每个单词的上下文,这对于传统的方法是不可能的。MLM预训任务将文本转换为符号,并使用符号表示作为训练的输入和输出。在训练过程中对随机的符号子集(15%)进行掩蔽mask,并用目标函数预测符号识别的准确率。具体措施如下,比如my dog is bob→ my dog is [MASK].。在这里,bob is masked,无监督学习被用来预测被蒙蔽的单词。
However, there is a problem with this method, because the percent of masked words account for 15% which is already high number relatively, and it will lead to some words that have never been seen in the fine-tuning stage. In order to solve this problem, the author makes the following treatment. 80% of the time it's [mask], my dog is hairy → my dog is [mask]. 10% of the time, a word was randomly taken in place of the mask word, my dog is hairy -> my dog is apple. And the rest 10% of the time it stays the original word, my dog is hairy -> my dog is hairy.
传统方法以单向预测为目标,包括从左到右和从右到左的训练。因此,利用MLM的效果要优于传统的方法。
NSP通过预测下一个句子是否连贯,使BERT能够获得句子之间的关系。给出50%正确的上下句对,再加上50%随机的上下句对,然后训练模型。
由于word2vec不考虑一词多义,本文引入BERT模型从整个输入语句中提取特征,具体如下:
$Vec_s=BERT(S)$
S represses the input Chinese sentence.$Vec_s$ is the feature vector of the input Chinese sentence, which has eliminated the problem of polysemy.
3.4 Classification
When the hidden state of an instance $h$ is learned, due to lattice LSTM ignored the problem of polysemy, so we concatenate $h$ and $Vec_s$ as follow :
$H=[h\oplus Vec_s]$
Then, we use tanh activation function which can nonlinear the neural network.
$H^{*}=tanh(H)$
The classifier takes the hidden state $H^{*}$ as input:
$p(y^{'}|s)=softmax(wH^{*}+b)$
Where $y^{'}$ is the predicted possibility for each type. $W$ and $b$ are a transformation matrix and a bias vector respectively.
Finally, we use cross-entropy as the objective function as follows:
$J(\theta)=\sum log p(y^{(i)}|S^{(i)},\theta)$
Where $S^{(i)},y^{(i)}$ are training examples and $\theta$ indicates all parameters of our model.
4. EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Dataset
我们在SanWen数据集[15]上执行我们的模型。数据集的句子来源于837篇中文文献,包含Unknow, Create, Use, Near,Social, Located, Ownership, General-Special, Family, Part-Whole 9种类型。我们利用85%的数据集进行培训,10%的数据集进行测试,其余5%用于验证。
4.2 Evaluation Metrics
In our experiments, there are two evaluation metrics including F1score and area under the curve(AUC)are applied. So our model can be estimated more comprehensively.
4.3 Parameter Settings
We use grid searching网格搜索 on the validation dataset to tune the parameters of our model. For Adam optimizer[16], We leverage grid searching to select optimal learning rate λ in ${0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005}$.Table 1 shows the best hyper-parameters’ value in our experiments. About other Parameter Settings, we use conventional settings.
4.4 Final Results
The char-based and word-based baseline model are using BiLSTM, which can achieve 41.23% and 42.03% F1-score respectively. After that, some new models were proposed and achieved better results. Zeng et al. puts forward a CNN model which can get 59.42% F1-score and 47.8% AUC. Piece-wise CNN model were proposed by Zeng et al. [17], which achieves 61% F1-score and 48.26% AUC. On the basic of PCNN model, Lin et al. [18] added selective attention mechanism to it and achieved 60.55% F1-score and 50.41% AUC. Our model yields 63.13% F1score and 56.34% AUC, which outperforms above models.

5. CONCLUSION
分词错误和一词多义这两大问题长期以来一直困扰着许多研究者。因此,如何处理这两个问题是众多研究者共同关注的目标。本文提出了一种新的关系分类模型,该模型在格LSTM的基础上利用BERT模型来解决多义现象。实验结果表明,该模型取得了很好的效果,优于基线模型。
观后感:说服力不是很强,解决了词的多义问题起码举几个例子增强说服力啊喂



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号