比赛链接:
https://codeforces.com/contest/1619
A. Square String?
题目大意:
A string is called square if it is some string written twice in a row.
For a given string s determine if it is square.
思路:
首先字符串长度要是偶数,然后直接循环判断字符串前半段和后半段是否相等就可以了。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int mod = 1;
LL T, n;
string s;
void solve(){
cin >> s;
int f = 1;
if (s.length() % 2 != 0){
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() / 2; i++){
if (s[i] != s[i + s.length() / 2]){
f = 0;
break;
}
}
cout << (f ? "YES\n" : "NO\n");
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
B. Squares and Cubes
题目大意:
计算 1 到 \(n\) 的平方数和立方数的个数。
思路:
数据范围只有 1e9,直接暴力跑出来 1 到 \(n\) 的平方数和立方数放到 \(set\) 里面就可以了。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int mod = 1;
int T, n;
void solve(){
cin >> n;
set <int> a;
for (int i = 1; i * i <= n; i++)
a.insert(i * i);
for (int i = 1; i * i * i <= n; i++)
a.insert(i * i * i);
cout << a.size() << "\n";
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
C. Wrong Addition
题目大意:
两个数相加,首先将长度较短的数补上前导零,使长度相等。然后从右至左对每一位做正常加法,得出来的数直接写到结果里面。
题目中的例子
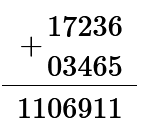
6 + 5 = 11,直接就写到结果中去了。
现给出 \(a\) 和 \(s\),要求找到一个 \(b\),按照上述加法,使 \(a + b = s\),找不到输出 -1.
思路:
直接将 \(a\) 和 \(s\) 的最后一位拿出来计算,分别记为 \(x 和 y\)。
当 \(x <= y\) 时,显然 \(b\) 的最后一位就是 \(y - x\)。
当 \(x > y\) 时,说明 \(a 和 b\) 某位相加之后大于 10,那么我们再取 \(s\) 的下一位,\(y\) 就变成这个两位数,然后判断这个两位数是不是 >= 10 并且 <= 18(两个一位数相加,肯定 <= 18 的),若是,说明 \(b\) 的这一位也是 \(y - x\),否则说明 \(b\) 不存在。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int mod = 1;
LL T, n, a, s;
void solve(){
cin >> a >> s;
vector <int> b;
while (s){
int x = a % 10, y = s % 10;
if (x <= y) b.emplace_back(y - x);
else {
s /= 10;
y += 10 * (s % 10);
if (x < y && y >= 10 && y <= 18) b.emplace_back(y - x);
else {
cout << "-1\n";
return;
}
}
a /= 10;
s /= 10;
}
if (a) cout << "-1\n";
else {
while (b.back() == 0) b.pop_back();
for (int i = b.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << b[i];
cout << "\n";
}
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
D. New Year's Problem
题目大意:
\(Vlad\) 有 \(n\) 个朋友,他打算给每位朋友买一个新年礼物,现在有 \(m\) 个商店,在第 \(i\) 个商店买给第 \(j\) 个朋友的礼物会给这个朋友带来 \(p[i][j]\) 个快乐值,他最多只能去 \(n - 1\) 个商店买礼物,他想知道朋友中快乐值的最小值最大是多少。
思路一:
如果最大值能是 \(x\),说明 \(x\) - 1 也能实现,而当 \(x\) 不能时,\(x\) + 1 也不能,所以想到二分去猜最大值。
猜最大值为 \(x\),要实现最大值是 \(x\) 的话,需要满足两个条件:
首先,每个朋友至少能获得一个带来 \(x\) 及以上快乐值的玩具。
其次,因为只去了 \(n\) - 1 个商店,而我们要买 \(n\) 个商品,所以有一个商店买了两个玩具,即某个商店中有两个 >= \(x\) 的快乐值的玩具。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int T = 1, n, m;
vector < vector <int> > p;
bool judge(int x){
vector<bool> v(n + 1);
bool f = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int c = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (p[i][j] >= x){
v[j] = true;
c++;
}
if (c > 1) f = true;
}
if (!f && n > 1) return false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!v[i]) return false;
return true;
}
void solve() {
scanf("%d %d", &m, &n);
p.assign(m + 1, vector<int> (n + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
scanf("%d", &p[i][j]);
int l = 1, r = 1e9 + 5;
while (l < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (judge(mid)) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid;
}
cout << l - 1 << "\n";
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
思路二:
直接贪,因为一定有个商店买了两个玩具,所以我们先去玩具带来的快乐值中次大值最大的那个商店,将这个玩具送给朋友,然后我们再买其他人的玩具。求出最小值,就是答案。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
int T = 1, n, m;
void solve() {
scanf("%d %d", &m, &n);
int ans = 0;
vector <vector<int>> p(m, vector <int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
scanf("%d", &p[i][j]);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){
vector <int> t = p[i];
sort(all(t), greater<int>());
ans = max(ans, t[1]);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int mx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
mx = max(mx, p[i][j]);
ans = min(ans, mx);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
E. MEX and Increments
题目大意:
给定一个长为 \(n\) 的非负整数序列,每一步操作中可以任选一个 \(j\),使 \(a_j\) +1,求使 \(MEX = i\)(\(i = 0, 1, 2... n\)) 的最小操作次数,若无法实现,输出 -1。(\(MEX\) 即序列中未出现的非负整数)
思路:
要使 \(MEX\) = \(i\),就要使 0 到 \(i - 1\) 全部都存在,同时将所有的 \(i\) 都增大。因为要求最小的步数,那么最贪的方式就是使 \(i\) 增大 1。
我们可以发现使序列的 \(MEX\) 等于 \(i\) 的这个状态不会对后面造成影响,同时,它也可以从前一个状态转移过来,即我们可以在通过最小的操作次数使 \(MEX\) 等于 \(i - 1\) 的基础上,再用最小的操作次数使 \(MEX\) 等于 \(i\)。
所以对于 \(i\) 的状态,我们只需要考虑序列中等于 \(i - 1\) 的数是不是 0 即可。
如果是 0,我们就要从前面多余的数中取一个去补上,如果没有多余的数,那后面所有的都是 -1。
如果不是 0,那就不用再操作前面的数,只需要将所有等于 \(i\) 的数 +1 就好了。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int T = 1, n;
void solve(){
scanf("%d", &n);
vector <int> a(n), cnt(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
cnt[a[i]]++;
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
stack <int> s;
LL sum = 0;
vector <LL> ans(n + 1, -1);
ans[0] = cnt[0];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if (cnt[i - 1] == 0){
if (s.empty()) break;
sum += i - 1 - s.top();
s.pop();
}
ans[i] = sum + cnt[i];
while (cnt[i - 1] > 1){
cnt[i - 1]--;
s.push(i - 1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == n];
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
F. Let's Play the Hat?
题目大意:
\(n\) 个人在 \(m\) 张桌子上玩 \(k\) 场游戏,每场游戏中坐在每张桌子的人数为 \(\lceil \frac{n}{m} \rceil\) 或 \(\lfloor \frac{n}{m} \rfloor\),输出一种方案,使得任何两人坐在人数为 \(\lceil \frac{n}{m} \rceil\) 的次数差不超过 1。
思路:
第 \(i\) 轮坐在大桌子上的人,下一轮肯定要尽可能坐在小桌子上,这样子才能让每个人坐在大桌子上的次数趋向平衡。
所以考虑一个循环,设 \(c\) 为大桌子上的人数,\(f\) 为小桌子上的人数,\(res\) 为大桌子的数量,人的序号从 0 开始。
将坐在小桌子上的人按照顺序向前移动,即每一轮之后 \(a[i] = a[(i + res * f) % n]\)。
循环输出就可以了。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int T, n, m, k;
void solve(){
cin >> n >> m >> k;
vector <int> a(n), t(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
a[i] = i + 1;
int c = (n + m - 1) / m, f = n / m, res = n % m;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i ++ ){
for (int j = 0; j < res; j ++ ){
cout << c << " ";
for (int u = j * c; u < (j + 1) * c; u ++ )
cout << " " << a[u];
cout << "\n";
}
for (int j = 0; j < m - res; j ++ ){
cout << f << " ";
for (int u = res * c + j * f; u < res * c + (j + 1) * f; u ++ )
cout << " " << a[u];
cout << "\n";
}
t = a;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++ )
a[j] = t[( j + res * c ) % n];
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cin >> T;
while ( T -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
G. Unusual Minesweeper
题目大意:
已知 \(n\) 颗地雷的坐标以及它们爆炸的时间(从 0 开始),每一颗地雷爆炸,会引爆垂直和水平(两条垂线)的距离小于等于 \(k\) 的所有地雷,每一秒可以主动引爆一颗地雷(不管它本来是什么时候引爆的),问最少多少秒使所有地雷爆炸。
思路:
一颗地雷引爆后可能会导致很多地雷引爆,通过并查集将一起爆炸的地雷连通,同时可以计算出这一个块最小的爆炸时间。
然后遍历每一个块,找到使得所有地雷引爆的最小时间。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int T, n, k, fa[N];
int find(int x){
if (fa[x] == x) return x;
return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void join(int a, int b){
int aa = find(a), bb = find(b);
if (aa == bb) return;
fa[bb] = aa;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n >> k;
vector <int> x(n), y(n), t(n), p(n), a(n, 1e9 + 1), b;
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
iota(fa, fa + n, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
cin >> x[i] >> y[i] >> t[i];
sort(p.begin(), p.end(), [&](int i, int j){
if (x[i] != x[j]) return x[i] < x[j];
return y[i] < y[j];
});
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ){
int a = p[i], b = p[i + 1];
if (x[a] == x[b] && y[a] + k >= y[b])
join(a, b);
}
sort(p.begin(), p.end(), [&](int i, int j){
if (y[i] != y[j]) return y[i] < y[j];
return x[i] < x[j];
});
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ){
int a = p[i], b = p[i + 1];
if (y[a] == y[b] && x[a] + k >= x[b])
join(a, b);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
int u = find(i);
a[u] = min(a[u], t[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
if (find(i) == i)
b.push_back(a[i]);
sort(b.begin(), b.end());
int ans = b.size() - 1; //引爆所有地雷所花的时间(时间从 0 开始计算)
for (int i = 0; i < b.size(); i ++ )
ans = min(ans, max(b[i], (int)b.size() - i - 2)); //该地雷及之前的地雷自然引爆,后面的地雷手动引爆
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cin >> T;
while (T -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
H. Permutation and Queries
题目大意:
给定一个长为 \(n\) 的排列,\(q\) 次询问:
1、交换两个位置的数,\(p_x\) 和 \(p_y\)。
2、输出进行 \(k\) 次 \(i = p_i\) 操作后的结果。
思路:
每个数的变化最多是一个长为 \(n\) 的环,直接暴力操作 \(k\) 次肯定超时。
通过分块的思想,预处理每个数操作 \(\sqrt{n}\) 次后的结果,同时建一个链表,存下来每个数前 \(\sqrt{n}\) 和后 \(\sqrt{n}\) 的数。
每次交换过后,要更新链表。
每次查询的时候,以 \(\sqrt{n}\) 的步长来找即可。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m, q, op, x, y, pre[N], to[N], f[N];
void link(int x){
int y = x;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
y = to[y];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ){
f[x] = y;
x = pre[x];
y = pre[y];
}
}
void update(int x, int y){
int a = to[x], b = to[y];
to[x] = b, to[y] = a;
pre[b] = x, pre[a] = y;
link(x), link(y);
}
int query(int x, int y){
int t = 0;
while (t + m <= y){
x = f[x];
t += m;
}
while (t < y){
t ++ ;
x = to[x];
}
return x;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> q;
m = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
cin >> to[i];
pre[to[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if (!f[i])
link(i);
while (q -- ){
cin >> op >> x >> y;
if (op == 1) update(x, y);
else cout << query(x, y) << "\n";
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号