JDBC 和 事务回滚
一,连接数据库的六步
//方式一:
// DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
//方式二(推荐):
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");2,获取数据库的
//DriverManger.getConnection("数据库的连接地址","用户名","密码");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库","root","123");
3,获取数据库的操作对象
//1,Statement对象(不安全,存在sql注入问题)
//Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//2,PreparedStatement对象(继承自Statement类,不存在sql注入问题,但是需要占位符)
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement();
4,执行sql语句
//执行查询的sql语句 的操作
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//执行DML的操作
//int count = ps.executeUpdate();
5,处理查询的结果集
while(rs.next()){
//表示获取第几个字段
//rs.getInt(1);
//rs.getString(2);
//rs.getString(3);
//rs.getString(4);
//传字段名(推荐)
rs.getInt("id");
rs.getString("username");
rs.getString("pasword");
rs.getString("eamil");
}
6,释放资源(关闭连接)
rs.close();
ps.close();
conn.close();
二,示例
1,Statement示例
查询操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1,注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2,获取数据连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book_management", "root", "Wping3014");
//3,获取数据库操作对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4,执行sql
String sql = "select * from user where id = 1 ";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5,处理结果集
//rs.next()方法:判断是不是还有下一条数据,默认指标停在第一条数据之前
while (rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String username = rs.getString("username");
String password = rs.getString("password");
String email = rs.getString("email");
System.out.println(id+" "+username+" "+password+" "+email);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//6,,释放资源
if (rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
DML操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//1,注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2,获取数据连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book_management", "root", "Wping3014");
//3,获取数据库操作对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4,执行sql
//String sql = "insert into user(username,password,email) values('demo222',123,'demo222@qq.com') ";
//String sql = "update user set username = '黄祖贤' where id = 5 ";
String sql = "delete from user where id = 5";
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count);
//5,处理结果集
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//6,,释放资源
if (stmt != null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2,PreparedStatement示例
查询操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1,注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2,获取数据连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book_management", "root", "Wping3014");
String sql = "select * from user where id = ? ";
//3,获取数据库操作对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//填充占位符
ps.setInt(1,3);
//4,执行sql
rs = ps.executeQuery();
//5,处理结果集
//rs.next()方法:判断是不是还有下一条数据,默认指标停在第一条数据之前
while (rs.next()){
//获取遍历的自动的数据
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String username = rs.getString("username");
String password = rs.getString("password");
String email = rs.getString("email");
System.out.println(id+" "+username+" "+password+" "+email);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//6,,释放资源
if (rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null){
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
DML操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//1,注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2,获取数据连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book_management", "root", "Wping3014");
String sql = "insert into user(username,password,email) values(?,?,?)";
//3,获取数据库操作对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//填充占位符
ps.setString(1,"张三");
ps.setString(2,"123");
ps.setString(3,"zs@qq.com");
//4,执行sql
int i = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i);
//5,处理结果集
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//6,,释放资源
if (ps != null){
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
三,JDBC封装成工具类
public class JDBCUtils {
//注册驱动
static {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//建立数据库连接
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book_management", "root", "Wping3014");
}
//释放资源
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs){
if (rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
四,事务
事务的三个方法:
1,设置事务的提交方式
setAutoCommit(boolean b);
2,提交事务
commit();
3,回滚事务
rollback();
事务回滚示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟转账
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConn();
//setAutoCommit(boolean b);默认:默认为true
//true:自动提交事务,false:手动提交事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);//把事务条件改为手动提交
System.out.println(conn);
//甲方20000-10000
String sql1 = "update t_act set balance = 10000 where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps.setInt(1,111);
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
int temp = 10 /0;//算术异常
//乙方0+10000
String sql2 = "update t_act set balance = 10000 where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
ps.setInt(1,222);
count += ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
//提交事务
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtils.close(conn,null,null);
}
}
![]()
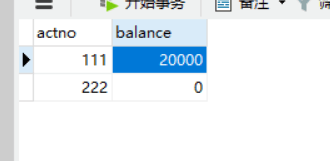
如果没有事务回滚,转账的甲方在转账时遇见了异常,会显示转账成功并且余额减少了,收账的乙方却没有收到钱。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号