2.24~3.2
牛客周赛81
A
题目

签到
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if(a==b && b==c) cout <<"Yes\n";
else if(a+1==b && b+1==c) cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
B
题目

一颗完全二叉树,如果每个节点的两个子节点都不小于它,那么这称颗二叉树是“平衡的”。数据量不大,把树储存在二维数组里,逐节点判断即可
如果某个节点满足G[i][j] > G[i+1][j] || G[i][j] > G[i+1][j+1]则不行
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int G[1005][1005];
void solve(int* n){
for(int i=1;i<*n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
if(G[i][j] > G[i+1][j] || G[i][j] > G[i+1][j+1]){
cout << "No\n";
return;
}
cout << "Yes\n";
return;
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t,n;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
cin >> G[i][j];
solve(&n);
}
return 0;
}
C
题目

看到本题的数据量,就知道不能用B的方法模拟树来找,会爆栈。
本题应用二分找到 l 和 r 的层数,如果 l 和 r 在同一层,那么颠倒后一样平衡。容易想不到的是 l 和 r 在相邻层,且 l + i(层数) > r 时同样平衡
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e9;
int t,n,li,ri;
int erfen(int li){
int l=1,r=(1<<30),mid,x2 = 2*li;
while(l<r){
mid = (l+r)>>1;
int x1 = mid*(mid+1);
if(x1 < x2)
l = mid+1;
else if(x1 > x2)
r = mid;
else return mid;
}
return l;
}
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n >> li >> ri;
int c1 = erfen(li), c2 = erfen(ri);
if(c1 == c2) cout << "Yes\n";
else if(c1+1 == c2 && li+c1 > ri) cout << "Yes\n";
else cout << "No\n";
}
return 0;
}
D
题目

对于 构造 这一类题,很多都是贪心
本体也贪,要使得塔平衡,就要使得每一层数字在满足条件的情况下尽可能小
模拟这颗树,每一层与上一层的数相比,用lower_bound()好使
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector <vector<int>> G(n,vector<int>(n));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
cin >> G[i][j];
sort(G[i].begin(),G[i].end());
}
int pos = 0;
vector <int>::iterator it;
vector <int> vec1,vec2 = {G[0][0]};
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
it = lower_bound(G[i].begin()+pos,G[i].end(),vec2[j]);
if(it == G[i].end()){
cout << i << '\n';
return;
}
vec1.push_back(*it);
pos = it-G[i].begin()+1;
}
if(n > pos-1)
vec1.push_back(G[i][pos]);
else{
cout << i << '\n';
return;
}
vec2 = vec1;
}
cout << n << '\n';
return;
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
牛客周赛82
A
题目

代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
string s;
cin >> s;
if(s[0] == s[2]) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
签到
B
题目

代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int n,cache;
cin >> n;
set <int> s;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin >> cache;
s.insert(cache);
}
if(s.size() == n) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
题目如图
观察发现,拍不了照的情况就是:你在本窗口拍照时,还有别的窗口的队伍是空的。
所以,能拍照的条件就是,每一条队伍的人数都互不相同
C
题目

代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5+1;
pair<int,int> a[maxn];
map<int,int> ma;
bool cpa(pair<int,int> a,pair<int,int> b){
return a.first < b.first;
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int n,cache,pd=1;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin >> cache;
a[i] = {cache,i+1};
if(!ma[cache]) ma[cache]++;
else pd=0;
}
if(pd){
sort(a,a+n,cpa);
cout << "YES\n";
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cout << a[i].second << ' ';
}
else cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
与B题差不多
先将队伍人数从小到大排序,然后输出每个队伍的ID即可
D
题目

题目如图
由于排列是递减的,所以一旦有第i项大于第i-1项的情况,为0
对输入的排列进行逐项判断,后一项与前一项不同,更新ave
后一项与前一项相同,ans *= ave,ave--
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int sup = 1e9+1;
const int maxn = 2e5+1;
const int mod = 998244353;
int prefix[maxn],t,n;
void solve(){
int ans=1, ave=n-prefix[1];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(prefix[i] == prefix[i-1]){
ans *= ave;
ave--;
}
else if(prefix[i] > prefix[i-1]){
cout << "0\n";
return;
}
else ave += prefix[i-1] - prefix[i] -1;
}
ans %= mod;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> t;
prefix[0] = sup;
while(t--){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin >> prefix[i];
solve();
}
return 0;
}
洛谷FAOI-R4
A
题目

签到,字符串处理,如果输入的字符串的首字母为数字,那么输出时就加上P,否则直接输出
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
string wz = "https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/";
string k = "PBCASUT";
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
string inp;
cin >> inp;
int pd = 1;
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
if(inp[0] == k[i]){
cout << wz << inp << '\n';
pd = 0;
break;
}
if(pd) cout << wz << 'P' << inp << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
B
题目
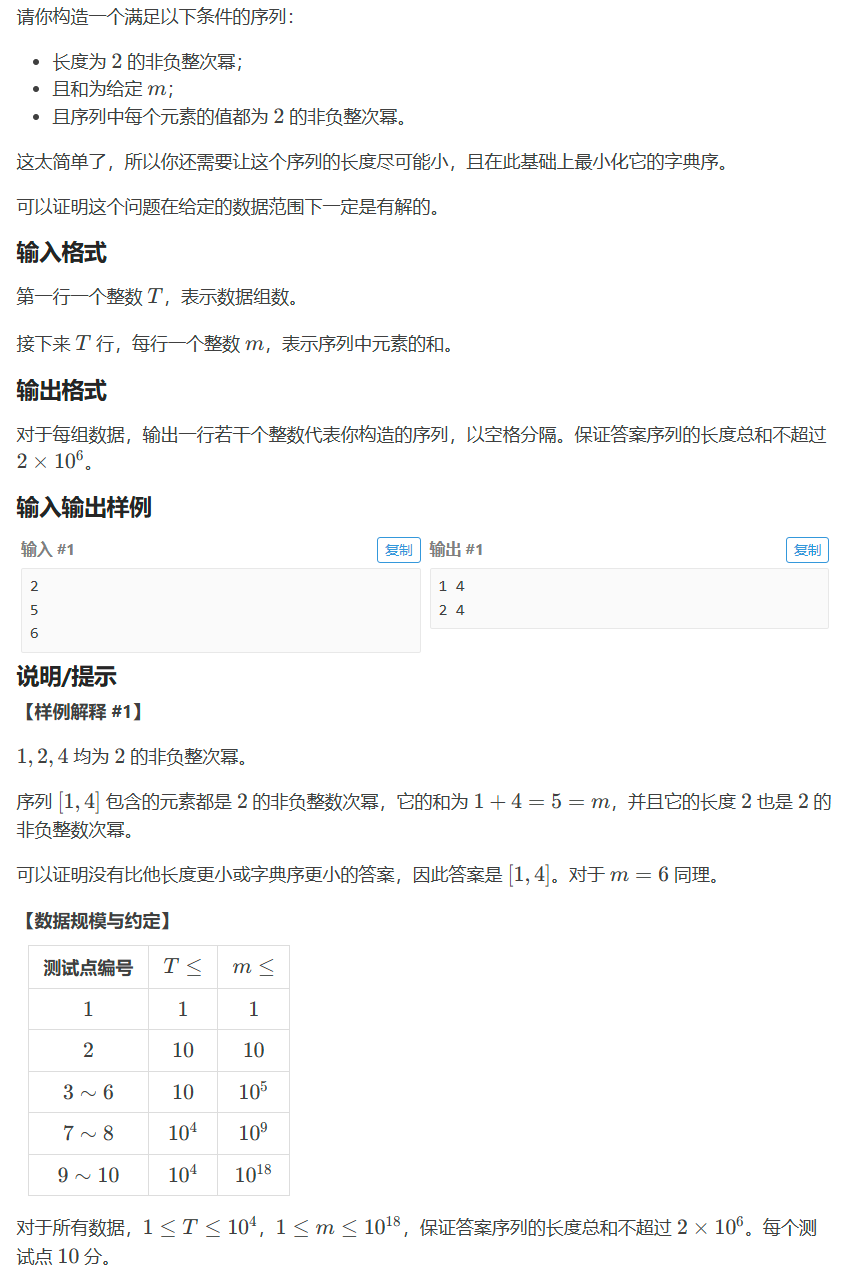
题目如图
限制条件有点多,很容易看漏/想漏...qwq...
先把m拆为二进制数的形式,再判断m的长度是否为二次幂,对于这个判断,我先做个预处理打表,判断时查表。如果m长度不是二次幂,那么从最小位开始,把m拆开,遇到1就跳过,直到长度为二次幂为止,这个过程用deque实现
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e6+1;
vector <int> er;
deque <int> q;
bool biao[maxn];
void yu(){
int sup = maxn/2;
for(int i=1;i<=sup;i*=2)
biao[i] = true;
}
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
yu();
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int m;
cin >> m;
while(m>0){
int yu = m%2;
er.push_back(yu);
m/=2;
}
int si = er.size(),pd=0;
for(int i=0;i<si;i++)
if(er[i])
q.push_back(pow(2,i));
si = q.size();
while(!biao[si]){
int temp = q.front();
q.pop_front();
if(temp == 1){
cout << 1 << ' ';
continue;
}
temp/=2;
si++;
q.push_front(temp);
q.push_front(temp);
}
for(auto it:q)
cout << it << ' ';
cout << '\n';
er.clear();
q.clear();
}
return 0;
}
树状数组
可以高效率地查询和维护前缀和(或区间和);当序列是动态变化的时,如果改变其中一个元素ai的值,那么后面的前缀和都要重新计算,查询一次的复杂度就会变成O(n)。但是树状数组可以用简短的代码大大提高效率,查询和维护的复杂度都为O(log2n)。
lowbit(x)
找x的二进制数的最后一个1对应的十进制是多少。
lowbit(x) = x & -x
例如,lowbit(5) = 5 & -5 = 1,
lowbit(6) = 6 & -6 = 2,lowbit(8) = 8 & -8 = 8
编码
#incldue <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000;
#define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x))
int tree[N] = {0};
void update(int x,int d){ //单点修改:修改元素a[x], a[x] = a[x] + d;
while(x <= N){
tree[x] += d;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int sum(int x){ //查询前缀和:返回前缀和sum[x] = a[1] + a[2] +...+ a[x]
int ans = 0;
while(x > 0){
ans += tree[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
//以上是树状数组相关
int a[11] = {0,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13} //注意a[0]拿来占位的,不用
int main(){
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
update(i,a[i]); //初始化tree[]数组
cout << "old:[5,8] = "<< sum(8) - sum(4) << '\n'; //查询区间和[5,8] = 38
update(5,100); //修改a[5]增加100
cout << "new:[5,8] = "<< sum(8) - sum(4) << '\n'; //查询新和 = 138
return 0;
}
以HDU 1556 为例
题目
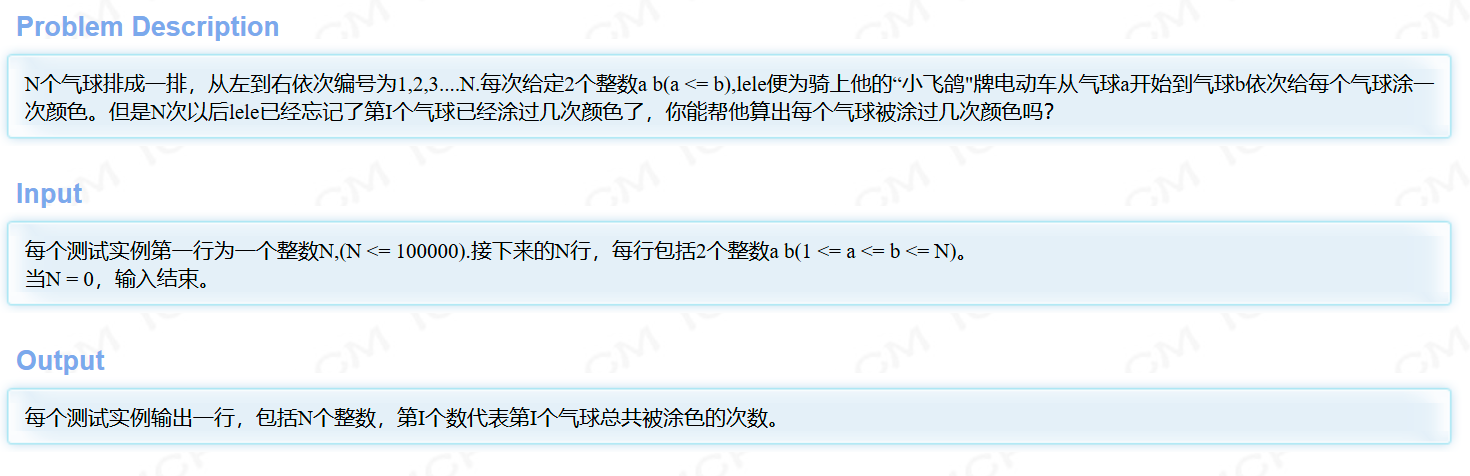
总所周知,差分是前缀和的逆运算,求某点维护后的值,相当于求差分的前缀和。
树状数组正好适合来处理前缀和。
这里用树状数组tree[]来模拟差分,最后的sum(i)就相当于输出a[i]
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x))
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100002;
int N,tree[maxn];
void update(int x,int d){
while(x <= N){
tree[x] += d;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int sum(int x){
int ans = 0;
while(x > 0){
ans += tree[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
while(cin >> N){
memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree));
int a,b;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
cin >> a >> b;
update(a,1);
update(b+1,-1);
}
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
cout << sum(i) << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号