CompTIA_Security+_1.4_Explain the importance of using appropriate cryptographic solutions.
1.4 解释使用适当的加密解决方案的重要性
摘要
- 1.4.1 Public key infrastructure (PKI)(公钥基础设施)
- Public key(公钥)
- Private key(私钥)
- Key escrow(密钥托管)
- 1.4.2 Encryption(加密)
- Level(等级)
- Full-disk(全盘)
- Partition(分割)
- File(文件)
- Volume(卷)
- Database(数据库)
- Record(记录)
- Transport/communication(传输/通信)
- Asymmetric(非对称)
- Symmetric(对称)
- Key exchange(密钥交换)
- Algorithms(算法)
- Key length(密钥长度)
- Level(等级)
- 1.4.3 Tools(工具)
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM)(可信平台模块)
- Hardware security module (HSM)(硬件安全模块)
- Key management system(密钥管理系统)
- Secure enclave(安全区域)
- 1.4.4 Obfuscation(混淆)
- Steganography(隐写术)
- Tokenization(令牌化)
- Data masking(数据屏蔽)
- 1.4.5 Hashing(哈希算法)
- 1.4.6 Salting(加盐算法)
- 1.4.7 Digital signatures(数字签名)
- 1.4.8 Key stretching(密钥拉伸)
- 1.4.9 Blockchain(区块链)
- 1.4.10 Open public ledger(公开账本)
- 1.4.11 Certificates(证书)
- Certificate authorities(证书颁发机构)
- Certificate revocation lists (CRLs)(证书吊销列表)
- Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)(在线证书状态协议)
- Self-signed(自签名)
- Third-party(第三方)
- Root of trust(信任根)
- Certificate signing request (CSR) generation− Wildcard(证书签名请求生成——通配符)
1.4.1 Public key infrastructure (PKI)(公钥基础设施)
- 通常指 Policies, Procedures, hardware, software, people
- Digital certifcates: create, distribute, manage, store, revoke(撤销)
- 在公司内部需要大量规划及决策。
- 也指将公钥与人或设备绑定。
- Certificate authority(CA, 证书颁发机构)
- 与信任相关
Symmetric encryption(对称加密)
- Encrypt(加密)与 decrypt(解密)使用相同密钥
- 也称为 secret key algorithm(密钥算法)或 shared secret(共享秘密)
- 分发密钥具有挑战性
- 与非对称加密相比开销小且速度快
- 通常同时使用对称加密与非对称加密
Asymmetric encryption(非对称加密)
- Public key cryptography(公钥密码)
- 两个或更多 mathematically(数学上)相关的密码,在同一过程中同时创建
- Private key(私钥):保密
- Public key:任何人可查看
- 公钥加密的数据仅对应私钥可解密,且无法通过公钥推出私钥
The key pair(密钥对)
- Asymmetric encryption: Public Key Cryptography
- Key generate(密钥生成)
- 同时创建 public key 和 private key
- 涉及大量randomization(随机数)、large prime numbers(大素数)及大量数学
- 每个人都可以获得 public key,但仅密钥拥有者持有 private key
- Private key 通常保存在本地,且分配有密码保护
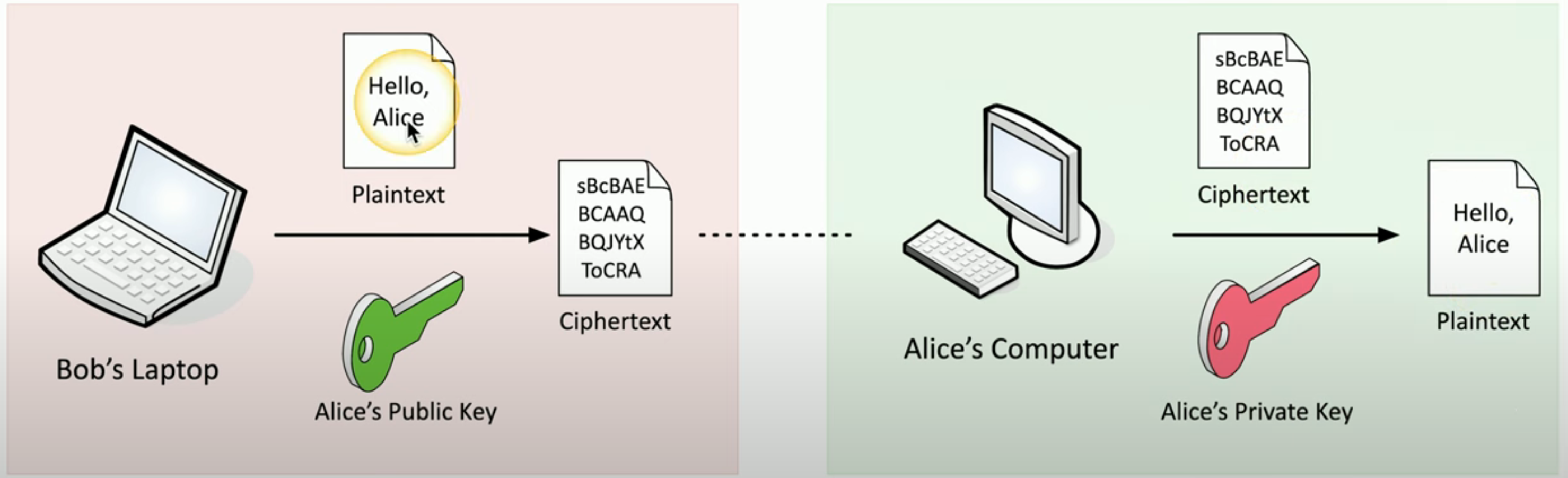
Key escrow(密钥托管)
你的 private key 由第三方(如你的所属组织)持有。
- 这可能是合法的业务场景需要:如员工设备丢失后企业需解密其数据以保障业务连续性,或政府机构出于国家安全等需求对合作方数据进行解密。
- 争议性:可能导致隐私泄露或权力滥用。
1.4.2 Encryption(加密)
Encrypting stored date(加密存储数据)
保护存储数据及传输过程中的数据。
- Full-disk(全盘)和 Partition(分割)/ Volume(卷)encryption
- BitLocker(Windows)
- FileVault(MacOS)
- etc.
- File(文件)encryption
- EFS(Encrypting File System)(Windows):内置于 NTFS 文件系统的文件级加密
- 文件或文件夹 -> 属性 -> 高级属性 -> Encrypt contents to secure data(Windows)
- third-party utilities(其他操作系统)
- EFS(Encrypting File System)(Windows):内置于 NTFS 文件系统的文件级加密
- Database(数据库)encryption
- Transparent encryption(透明加密)
使用 symmetric key 对所有数据库信息加密。- 对授权用户和应用程序透明:加密和解密过程自动、无缝地在后台完成。
- 对未授权访问和恶意行为者不透明:黑客、未经授权的用户或恶意软件试图绕过正常权限直接访问存储数据的文件或磁盘,看到的只是一堆毫无意义的加密乱码。
- Transparent encryption(透明加密)
- Record(记录)-level encryption
- 加密独立的 column(列)。
- 对 each column使用 separate symmetric keys 。
Transport/communication(传输/通信)encryption
- Encryption in the application
- Browsers(浏览器) can communicate using HTTPS
- VPN(Virtual Private Network,虚拟专用网络)
- Encrypts all data transmitted over the network, regardless(无论)of the application
- Client-based VPN using SSL/TLS
- Site-to-Site VPN using IPsec
Encryption algorithms(加密算法)
- 加密数据有多种不同方式
- 双方在加密数据前确定算法
- 细节通常对最终用户隐藏
- 算法各有优缺点
- Security level, speed, complexity of implementation(实现复杂度), etc.
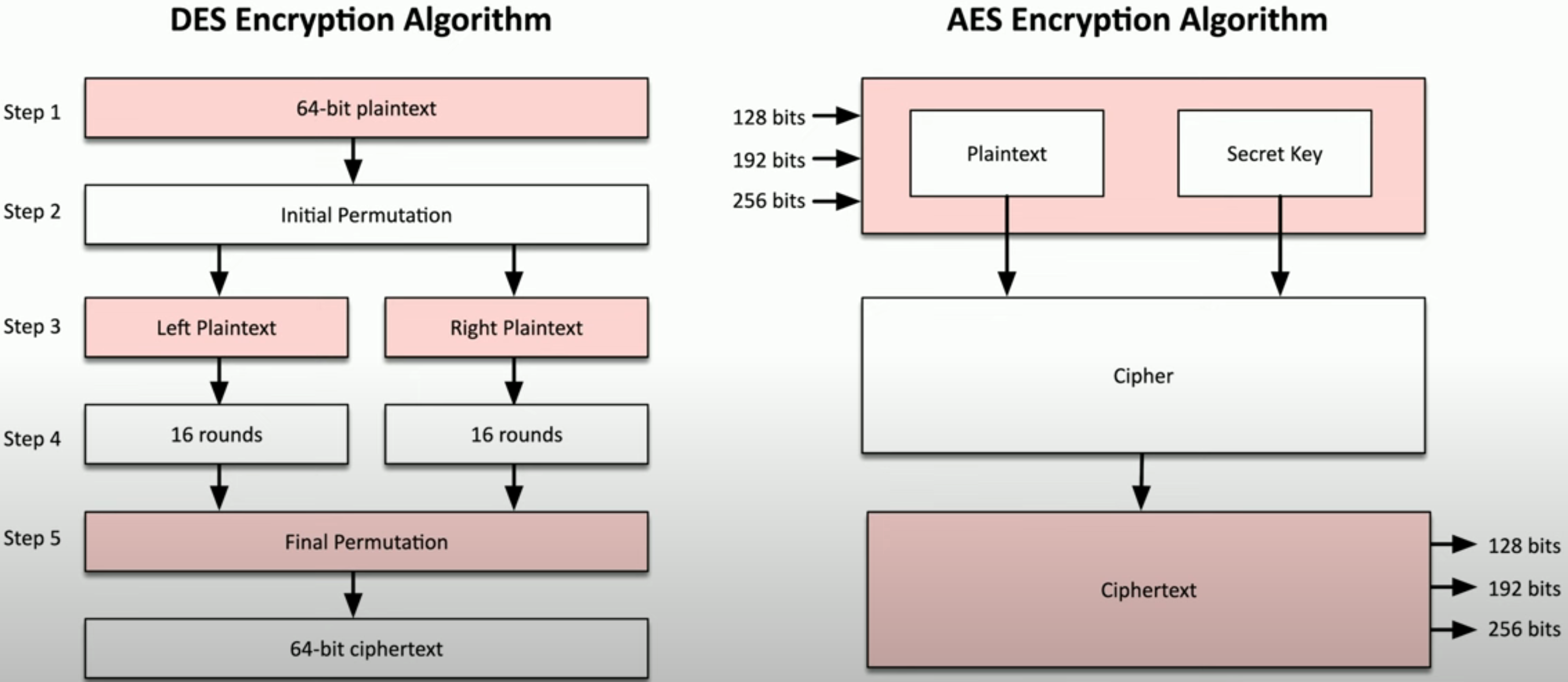
- Security level, speed, complexity of implementation(实现复杂度), etc.
Cryptographic keys(加密密钥)
- 加密算法公开,但密钥需要保密。
- 这是保护数据的唯一实体。
- The key determines(决定)the output
- Encrypted data
- Hash value
- Digital signature
Key length(密钥长度)
加解密密钥容易受到 brute force attacks(暴力攻击)。
Symmetric encryption(对称加密)
128-bit 或更大的对称密钥很常见,随着未来处理器能力提升,这些数字会变得更大。
Asymmetric encryption(非对称加密)
- Complex calculations of prime numbers(质数的复杂计算)
- Larger keys than symmetric encryption
- Common to see key lengths of 3,072 bits or larger
Key stretching(密钥拉伸)
或 Key strengthening(密钥强化)。
- Weak key(弱密钥)本身并不安全。
- 通过多次执行过程强化 Weak key
- 如连续多次 Hash,brute force attacks 需要破解每次 Hash,花销更大。
Key Exchange(密钥交换)
用于解决如何在两个人之间不通过互联网等不安全的媒介物理传输加密密钥。
Key Exchange
- Out-of-band key exchange(带外密钥交换)
- 不在网络上发送 symmetric key
- 可通过 Courier(快递)、Telephone(电话)或亲自交换密钥等方式来完成。
- In-band Key Exchange(带内密钥交换)
- On the network
- Use asymmetric encryption to deliver a symmetric key
Real-time encryption/decryption(实时加密/解密)
Without compromising(损害)the security part.
- Share a symmetric session key using asymmetric encryption(使用非对称加密共享对称会话密钥)
- Client: encrypts a random (symmetric) key ← server's public key
- Server: decrypts this share key, uses it to encrypt data
- 小心实现 session keys
- 对每个会话生成一个新的 Session Key
- unpredictable(不可预测)
Symmetric key from asymmetric keys(对称密钥来自非对称密钥)
Use Public and private key cryptography to create a symmetric key
- 将对方的 Public Key 和自己的 Private Key 结合算出 Symmentic Key
- 无需通过网络发送对称密钥
*拓展-经典算法
- Diffie-Hellman(DH)
- 原理:双方选择一个公开的大素数 \(p\) 和一个整数 \(g\)(\(g\) 是 \(p\) 的原根)。
- 过程:
- 一方选择一个秘密整数 \(a\) 作为私钥,计算公钥 \(A=g^a \mod p\),然后将 \(A\) 公开给对方。
- 另一方选择一个秘密整数 \(b\) 作为私钥,计算公钥 \(B=g^b \mod p\),然后将 \(B\) 公开给对方。
- 一方用对方的公钥 \(B\) 和私钥 \(a\),计算共享密钥 \(K=B^a \mod p\)。
- 另一方用对方的公钥 \(A\) 和自己的私钥 \(b\) 计算共享密钥 \(K=A^b \mod p\)。
- 结果:双方计算出的密钥 \(K\) 相同(\(K=(g^b)^a \mod p=(g^a)^b \mod p = g^{ab} \mod p\)),而窃听者只能获得 \(A\) 和 \(B\),无法在不进行离散对数运算的情况下计算出共享密钥。
- 前向安全:是
- 常用场景:IPSec
- RSA
- 原理:客户端使用服务器的公钥加密一个随机生成的会话密钥,然后服务器用对应的私钥解密该会话密钥。
- 特点:这种方式不具备前向安全(Forward Secrecy),一旦服务器的私钥泄露,所有历史通信都会破解。
- 常用场景:较少使用
- ECDHE
- 原理:基于椭圆曲线的 Diffie-Hellman 算法。
- 特点:具备前向安全,即每次会话都使用临时生成的密钥对进行交换,即使服务器私钥泄露,也不能解密之前的通信历史。
- 注意事项
- 密钥交换与加密:密钥交换算法的目的是建立一个安全的共享密钥,而不是直接用来加密通信内容。
- 后续使用:建立共享密钥后,双方会使用该密钥来执行对称加密算法(如 AES)来加密和解密实际的通信消息。
1.4.3 Encryption Technologies(加密技术)
Trust Platform Module (TPM)(可信平台模块)
- A specification for cryptographic functions
- Cryptography hardware on a device
- cryptographic processor(加密处理器)
- random number generator, key generators
- Persistent memory(持久的内存)
- Unique keys burned in durning manufacturing(制造过程中烧制的唯一密钥)
- Versatile memory(多才多艺的内存)
- Storage keys, hardware configuration information
- Securely store BitLocker keys
- Password protected
- No dictionary attacks
Hardware Security Module (HSM)(硬件安全模块)
- Used in a large environments
- Clusters(集群), redundant power(冗余电源)
- Securely store thousands of cryptographic keys
- High-end cryptographic hardware(高端加密硬件)
- Plug-in card(插卡)or separate hardware device
- Key backup
- Secure storage in hardware
- Cryptographic accelerators(加密加速器)
- Offload(卸载)that CPU overhead(开销)from other devices
Key management system(密钥管理系统)
- Services are everywhere
- On-premises(本地), cloud-based(云端)
- Many different keys for many different services
- Manage all keys from a centralized(集中的)manager
- Often provided as third-party software
- Separate the encryption keys from the data
- All key management from one console(控制台)
- Create key for a specific service or cloud provider (SSL/TLS, SSH, ect.)
- Associate keys with specific users(将密钥与特定用户关联)
- Rotate(轮换)keys on regular intervals(时间间隔)
- Log key use and important events
Secure enclave(安全隔离区)—— Keeping data private
- A protected area for our secrets
- Often implemented(实现)as a hardware processor(处理器)
- Isolated from the main processor(与主处理器隔离)
- Many different technologies and names
- Provides extensive(广泛的)security features
- Has its own boot(启动)ROM(read-only memory,只读存储器)
- Monitors the system boot process
- True random number generator
- Real-time memory encryption
- Root cryptographic keys
- Performs AES encryption in hardware
- And more…
1.4.4 Obfuscation(混淆)
- The process of making something unclear(不清楚)
- It's now much more difficult to understand
- But it's not impossible to understand
- If you know how to read it
- Hide information in plain sight(显眼的地方)
- Store payment(支付)information without storing a credit card number
- Hide information inside of an image
- Steganography
Steganography(隐写术)
- Greek for "concealed writing"(希腊语的意思是“隐藏的书写”)
- Security through obscurity(隐藏)
- Message is invisible(不可见的), But it's really there.

Common steganography techniques
- Network based
- Embed(嵌入)messages in TCP packets
- Use an image
- Embed the message in the image itself
- Invisible watermarks
- Yellow dots on printers

- Yellow dots on printers
Other steganography types
- Audio steganography
- Modify the digital audio file
- Interlace(穿插)a secret message within the audio
- Similar technique to image steganography
- Video steganography
- A sequence(组)of images
- Use image steganography on a large scale(范围)
- Manage the signal to noise ratio(信噪比)
- Potentially transfer much more information(潜在地传递更多的信息)
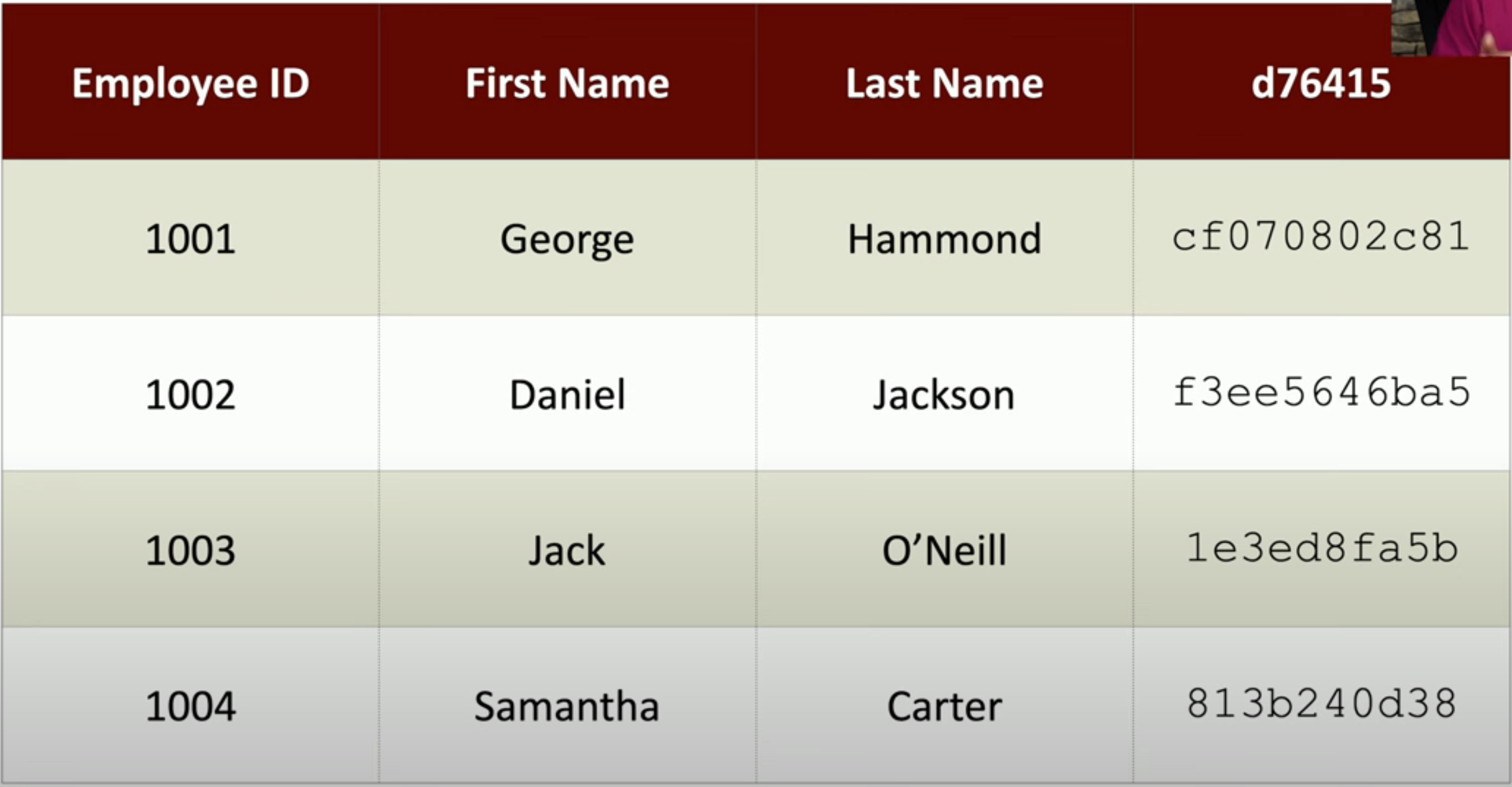
Tokenization(令牌化)
- Replace sensitive data with a non-sensitive placeholder(非敏感占位符)
- SSN 266-12-1112 is now 691-61-8539
- Common with credit card processing
- Use a temporary token during payment(付款)
- An attacker capturing the card numbers can't use them later
- This isn't encryption or hashing
- The original data and token aren't mathematically(在数学上)related
- The original data and token aren't mathematically(在数学上)related
Data masking(数据屏蔽)
- Data obfuscation(模糊)
- Hide some of the original data
- Protects PII(Personally Identifiable Information, 个人可识别信息)
- And other sensitive data
- May only be hidden from view(也许只是隐藏在视线之外)
- The data may still be intact(完整的)in storage
- Control the view based on permissions
- Many different techniques
- Substituting(替换), shuffling(变换), encrypting, masking out, ect.
1.4.5 Hashing(哈希算法)
Hashes
- Represent data as a short string of text
- A message digest, a fingerprint
- One-way trip(单向不可逆)
- Impossible to recover the original message from the digital
- Used to store passwords / confidentiality
- Verify a downloaded document is the same as the original -> Integrity(完整性)
- Can be a digital signature -> Authentication(认证), non-repudiation(不可否认性)and integrity
- Exemple - SHA256 hash
256 bits / 64 hexadecimal characters- My name is Professor Messer. -> 19da9a2e26f3bff67f0522f962851c42542b8659333ac53397c8d65aa7a3f871
- My name is Professor Messer! -> 54381cae1eea10892d81c8688d06d1928b4ee8495061a792864f83092b033aea
Collision(碰撞)
- Hash functions
- Take an input of any size and create a fixed size string
- Message digest(消息摘要), checksum(校验和)
- The hash should be unique(唯一的)
- Different inputs should never create the same hash
- If they do, it's a collision
- MD5 has a collision problem

Practical hashing(实际的哈希)
-
Verify a downloaded file
- Hashes may be provided on the download site
- Compare the downloaded file hash with the posted hash value

-
Password storage
- Instead of storing the password, store a salted hash(加盐的散列)
- Compare hashes during the authentication process
- Nobody ever knows your actual password
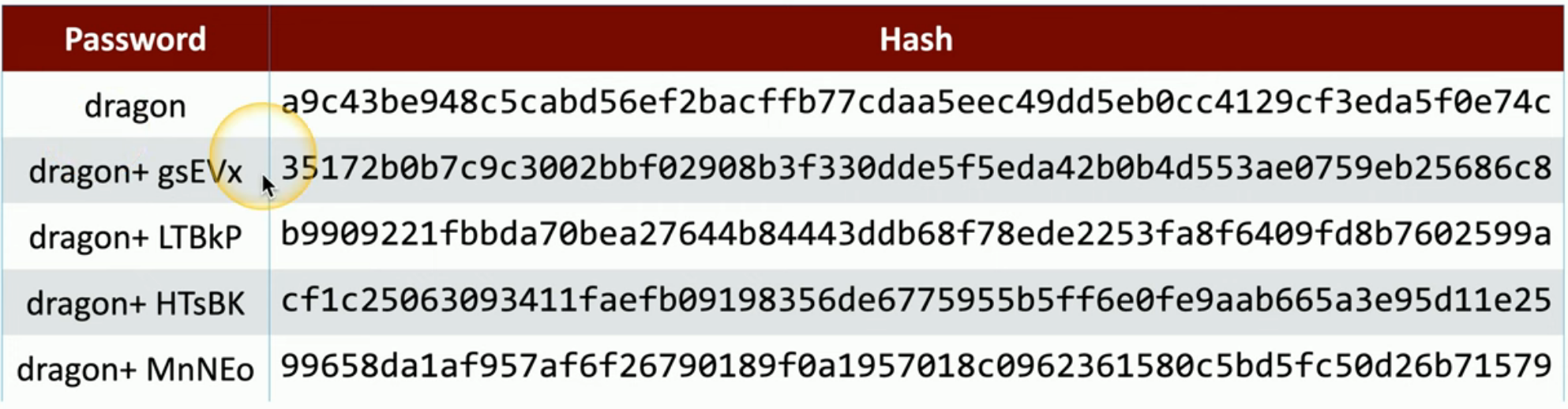
1.4.6 Salting(加盐算法)
- Salt
- Random date added to a password when hashing
- Every user gets their own random salt
- The salt is commonly stored with the password
- Rainbow tables won't work with salted hashes
- Addetional random valus added to the original password
- This slows(减慢)things down the brute force(暴力破解)process
- It doesn't completely stop the reverse engineering(逆向工程)
- Each user gets a different random hash with the same password
1.4.7 Digital signatures(数字签名)
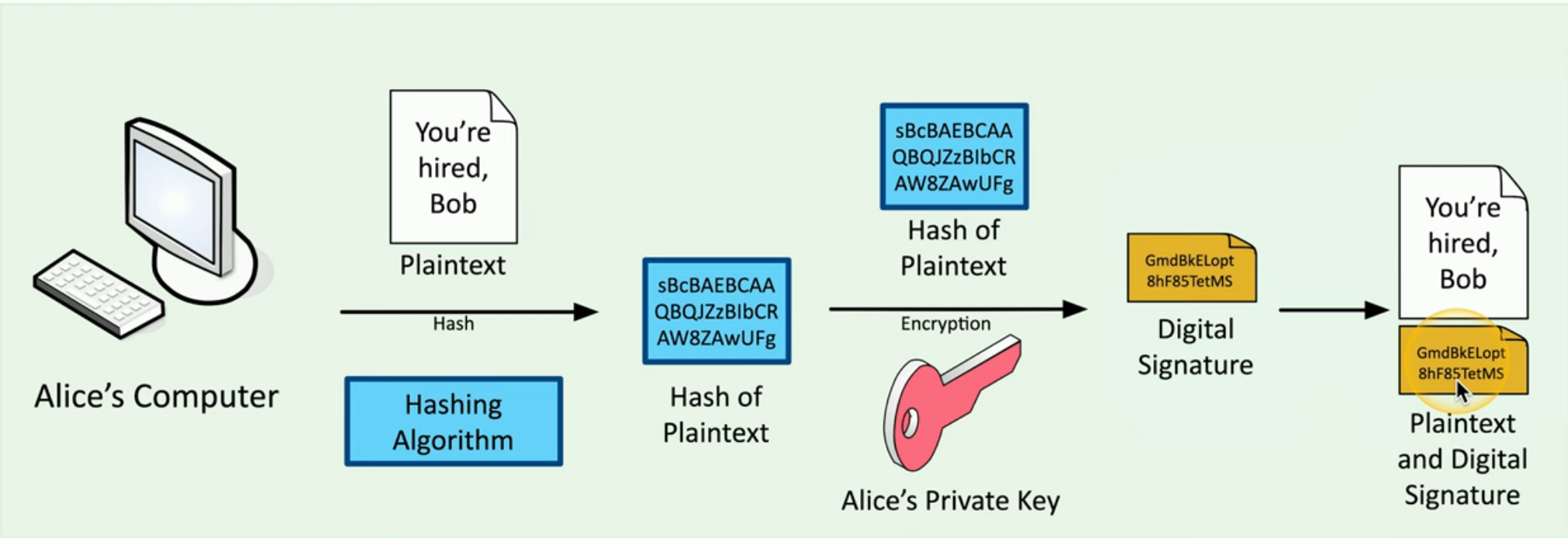
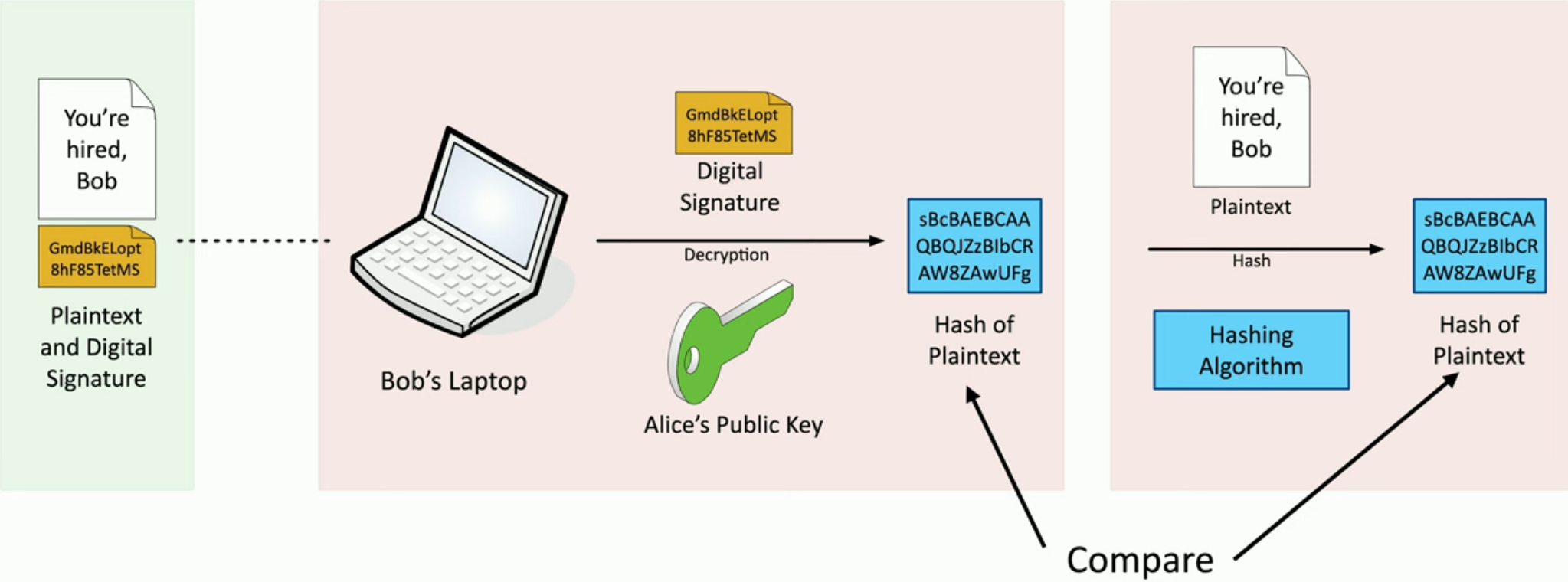
Digital signatures
- Prove the message was not changed -> Integrity
- Prove the source of the message -> Authentication
- Make sure the signature isn't fake -> Non-repudiation
- Sign with the private key and verify with the public key
- The message doesn't need to be encrypted
- Nobody else can sign this (obviously(显然))
- Any change in the message will invalidate the signature(使签名无效)
Creating and verifying a digital signature
Creating:
Verifying
1.4.8 Key stretching(密钥拉伸)
1.4.9 Blockchain Technology(区块链技术)
Blockchain(区块链)
- A distributed ledger(分布式账本)
- Keep track of transactions(用于记录/追踪交易)
- Everyone on the blockchain network maintains the ledger(账本)
- Records and replicates to anyone and everyone(记录并全网同步)
- Many practical applications(实际应用)
- Payment processing(支付处理)
- Digital identification
- Supply chain monitoring(供应链监控)
- Digital voting(数字投票)
The blockchain process(区块链流程)
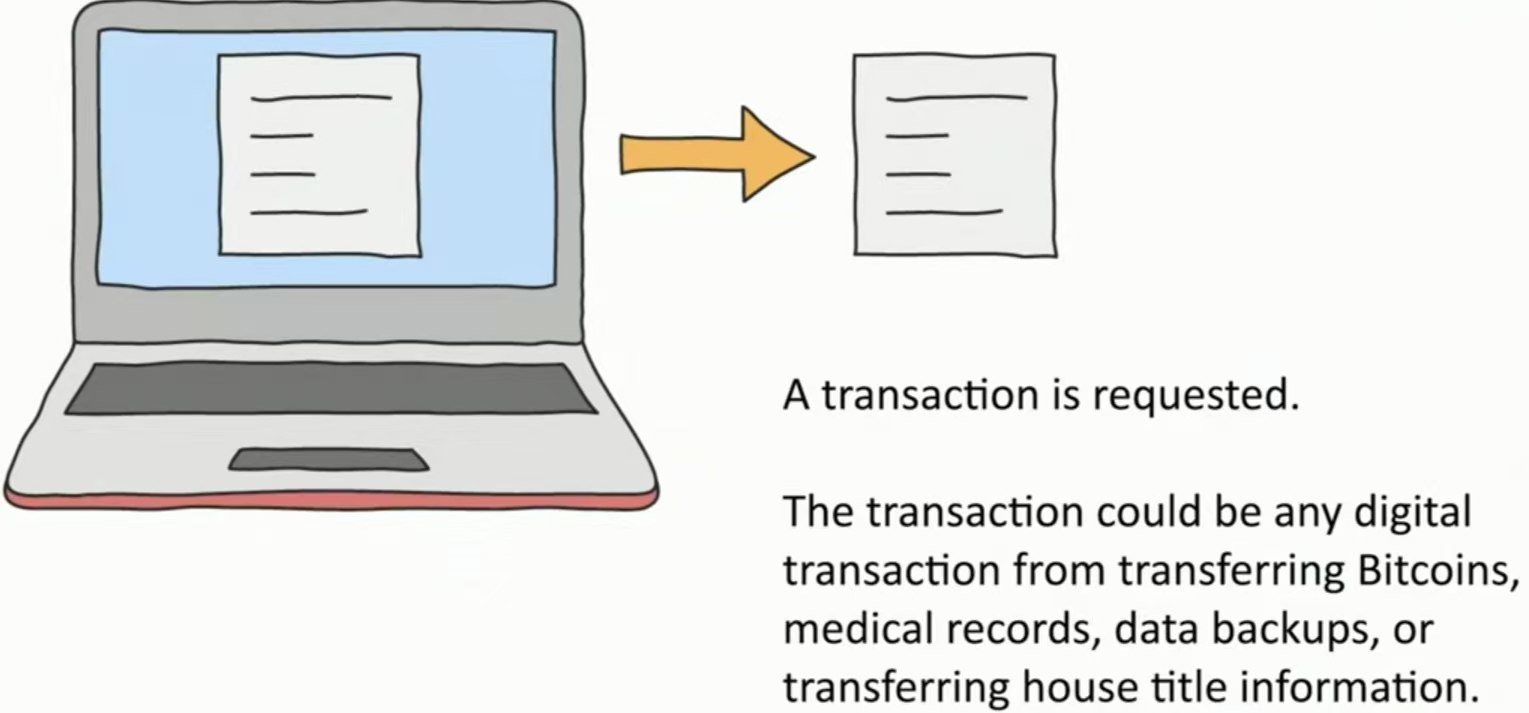
请求一个事务。
交易发生:交易可以是任何数字交易,从转移比特币、医疗记录、数据备份到转移房屋所有权信息。
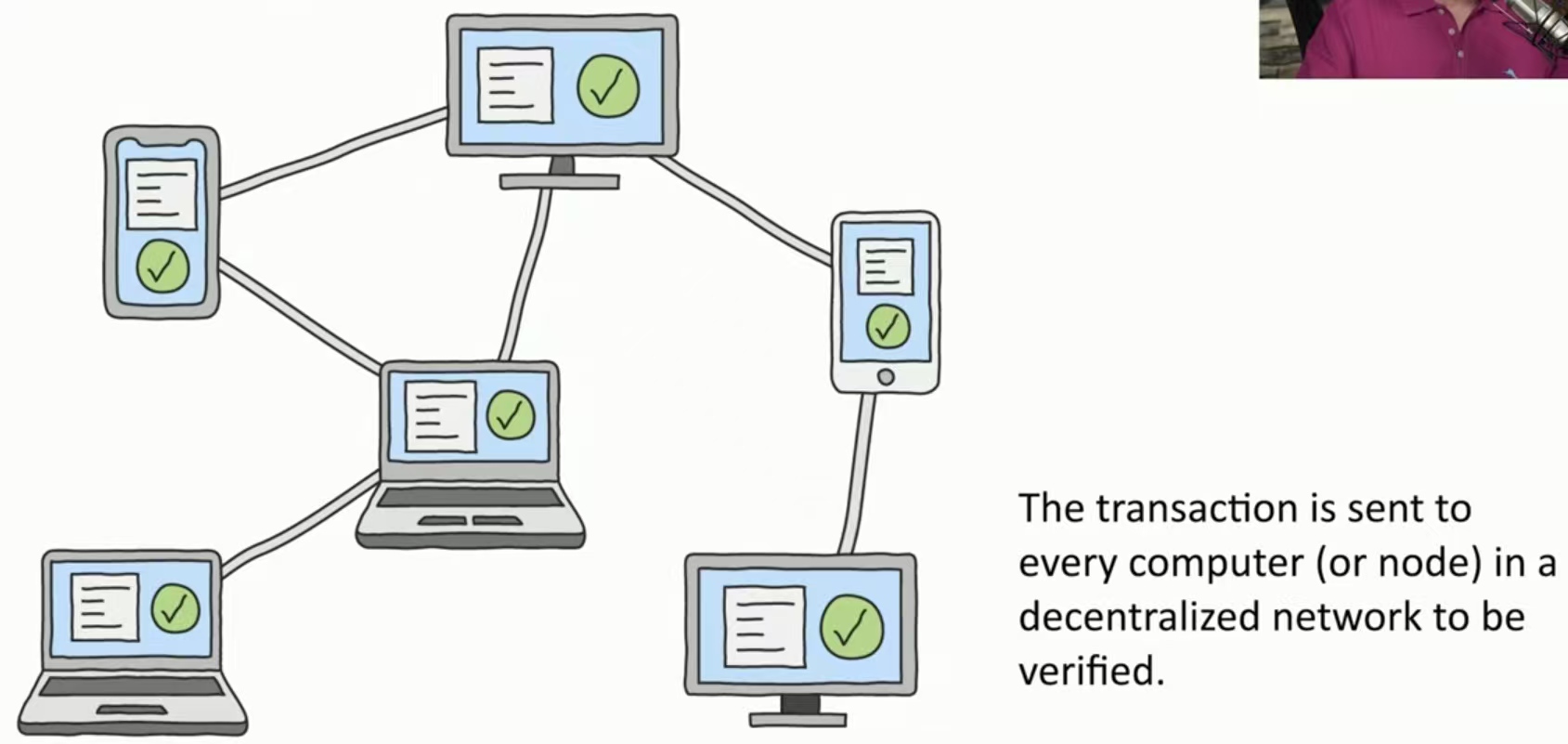
广播与验证:交易被发送到分散网络中的每台计算机(或节点)进行验证。
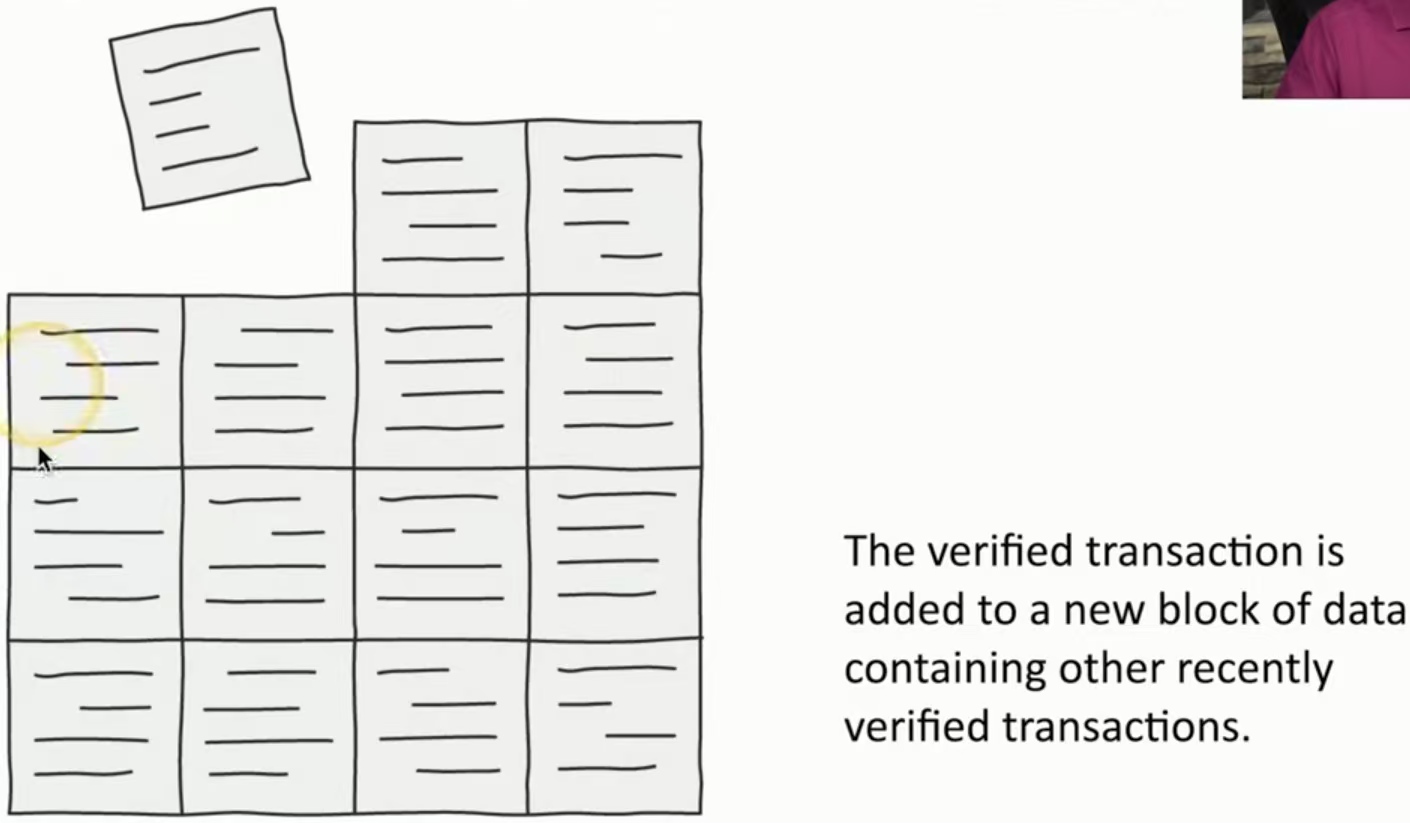
打包成块:经过验证的事务被添加到包含其他最近验证的事务的新数据块中。
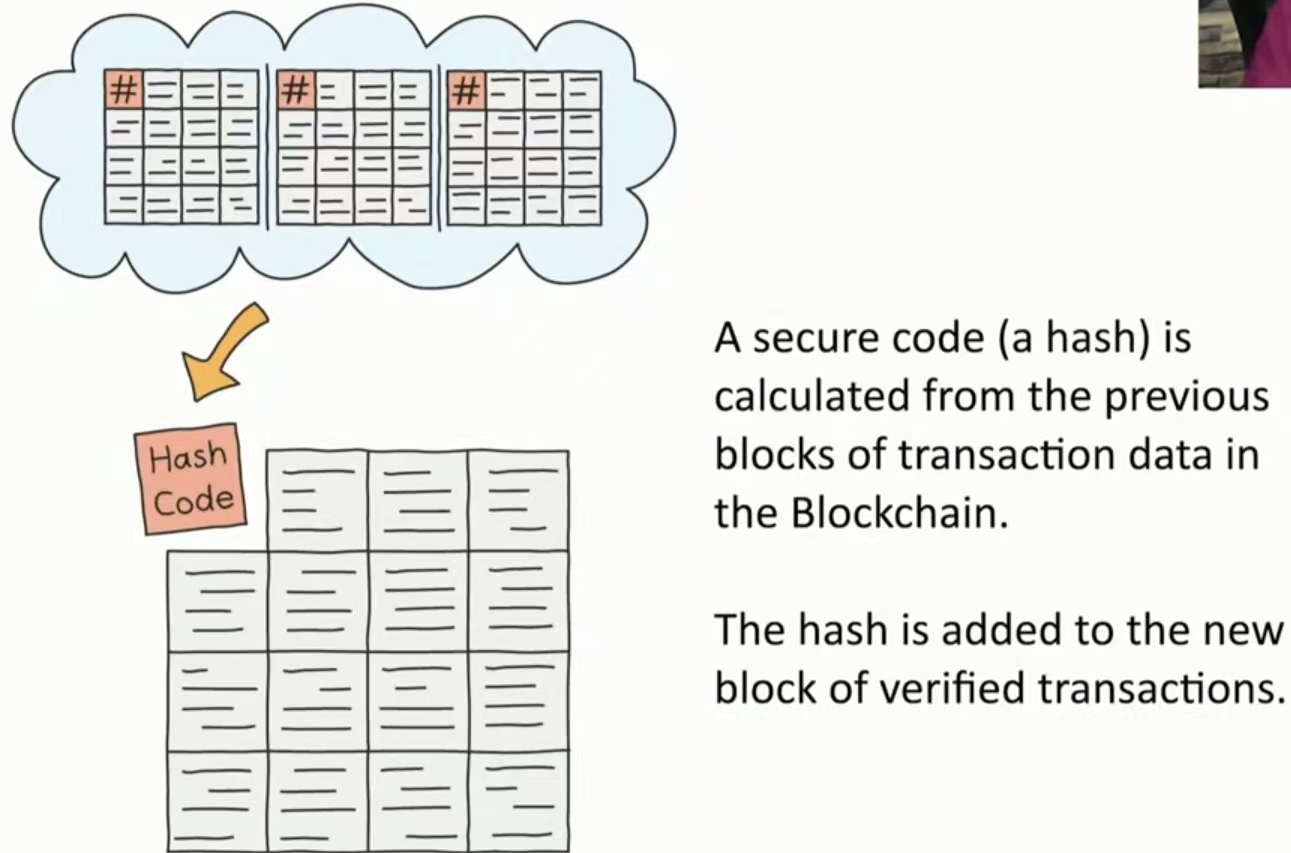
链式添加:安全代码(哈希)是从区块链中以前的事务数据块中计算出来的。
哈希值被添加到经过验证的交易的新块中。
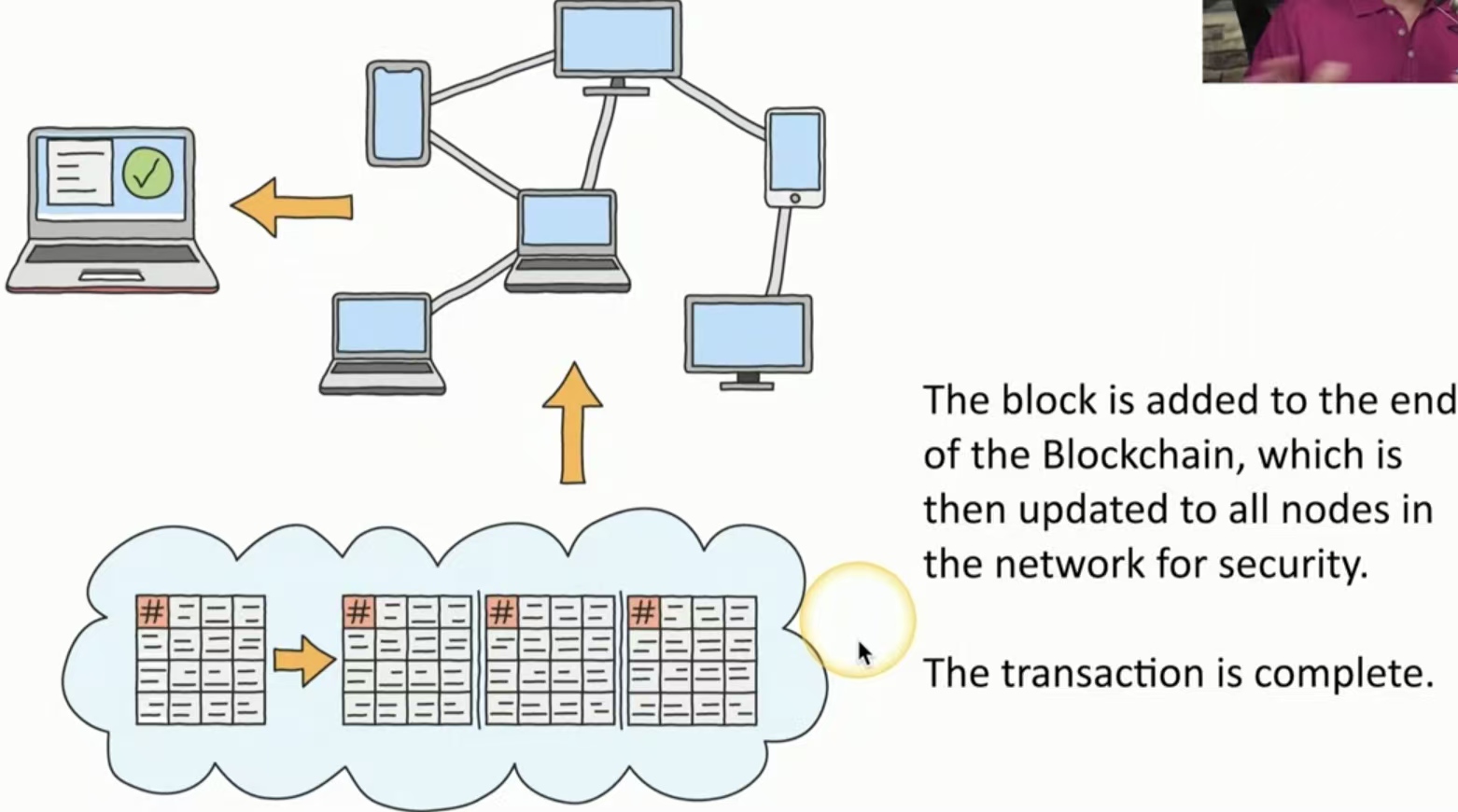
全网同步:块被添加到区块链的末尾,然后为了安全起见,将其更新到网络中的所有节点。
交易完成。
如果任何块被改变,它的哈希值和链中的所有后续哈希值都会自动重新计算。
修改后的链将不再与网络其他部分存储的链匹配,并将被拒绝。
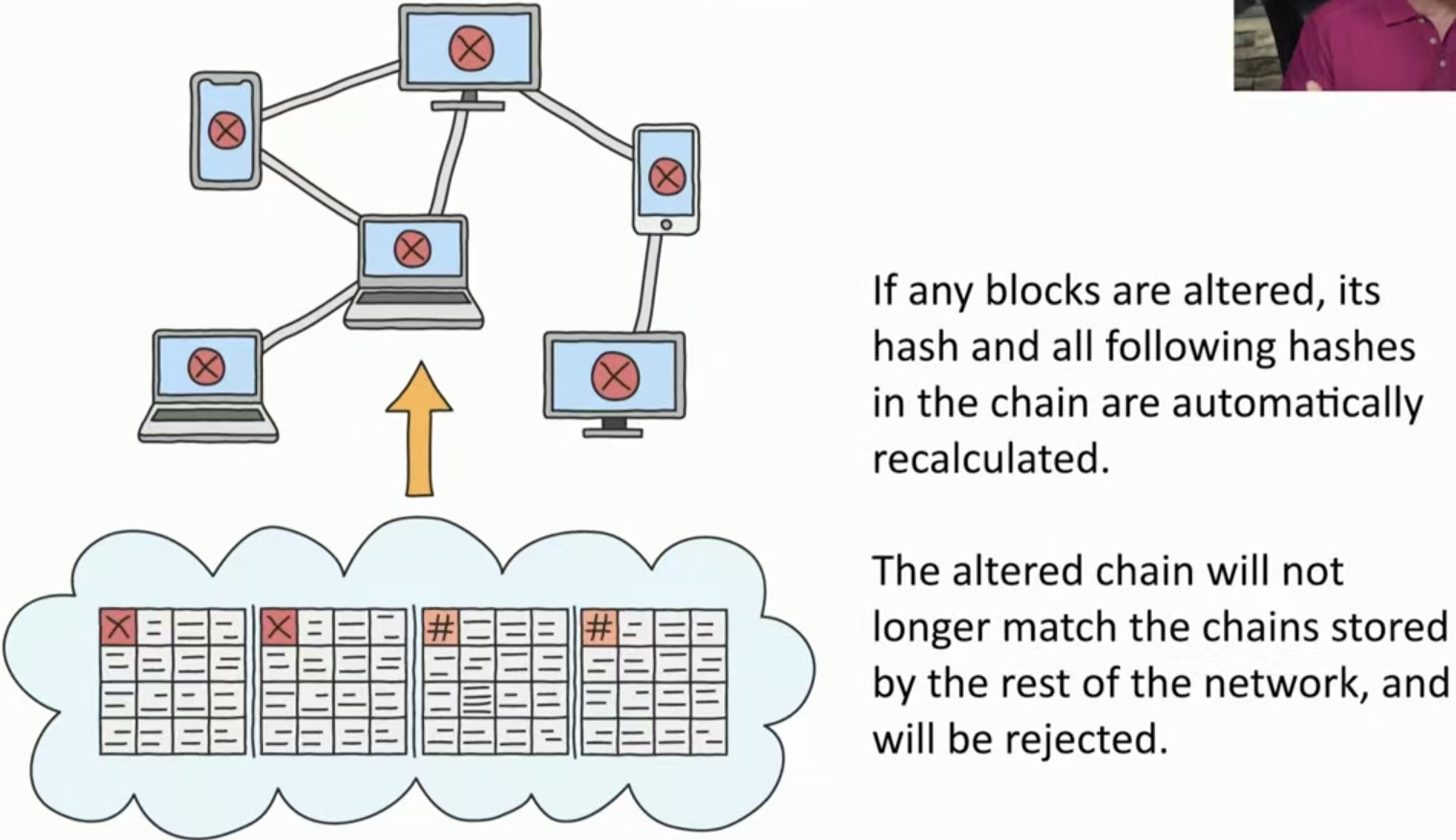
1.4.10 Open public ledger(开放公共账本)
开放公共账本是目标:就像一本“任何人都能查阅、但无法私自涂改的公共账簿”最终呈现的状态。
区块链流程是方法:就是为了实现上述目标而设计的 “如何记账、如何核对、如何装订成册以防止篡改” 的一整套具体规则和步骤。
from DeepSeek,后续将进行补充
参考:https://clocked-out.com/what-is-a-open-public-ledger/
1.4.11 Certificates(证书)
Digital certificates
- A public key certificate
- Binds(绑定)a pubic key with a digital signature
- And other details about the key holder
- A digital signature adds trust(信任)
- PKI uses Certificate Authorities for additional trust
- Web of Trust(信任网络)adds other users for additional trust
- Certificate creation can be built into the OS
- Part of Windows Domain services(域服务)
- Many 3rd-party options
What's in a digital certificate?
- X.509
- Standard format(标准格式)
- Certificate details
- Serial number
- Version
- Signature Algorithm
- Issuer
- Name of the cert holder
- Public key
- Extensions
- And more...
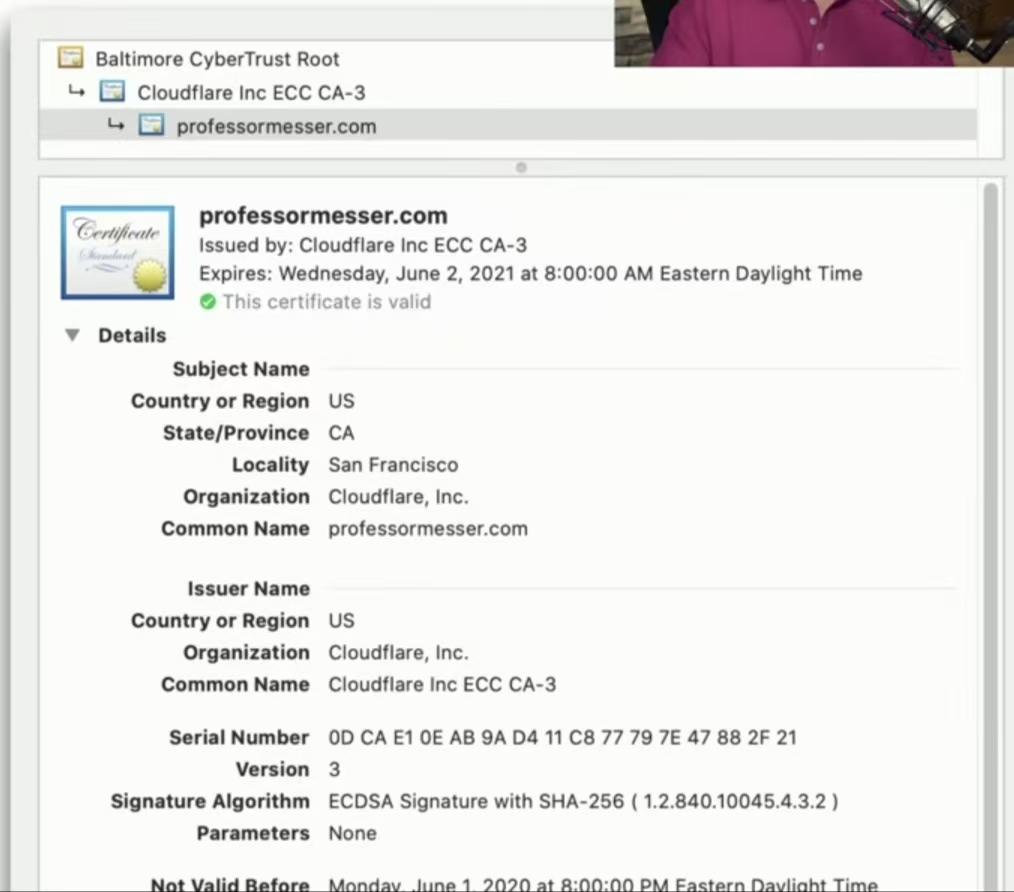
Root of trust
- Everything associated with IT security requires(需要)trust
- A foundational characteristic
- How to build trust from something unknown?
- Someone/something trustworthy(值得信赖的)provides their approval
- Refer to the root of trust
- An inherently(固有)trusted component
- Hardware, software, firmware(固件), or other component
- Hardware security module (HSM), Secure Enclave(隔区), Certificate Authority, ect.
- Secure Enclave
一块拥有独立CPU、存储和加密引擎的专用硬件芯片(或芯片区域),与设备的主操作系统物理隔离。
硬件级隔离 / 专属加密引擎 / 防物理攻击 / 完整性验证。
- Secure Enclave
Certificate Authorities(证书颁发机构)
- Need a good way to trust an unknown entity(实体)
- Use a trusted third-party
- An authority(权威人士)
- Certificate Authority (CA) has digitally signed the website certificate(证书颁发机构(CA)已对网站证书进行数字签名)
- You trust the CA, therefore you trust the website
- Real-time verification
Third-party certificate authorities
- Built-in to your browser
- Any browser
- Purchase your web site certificate
- It will be trusted by everyone's browser
- CA is responsible for vetting(审查)the request
- They will confirm the certificate owner
- Additional verification information may be required by the CA
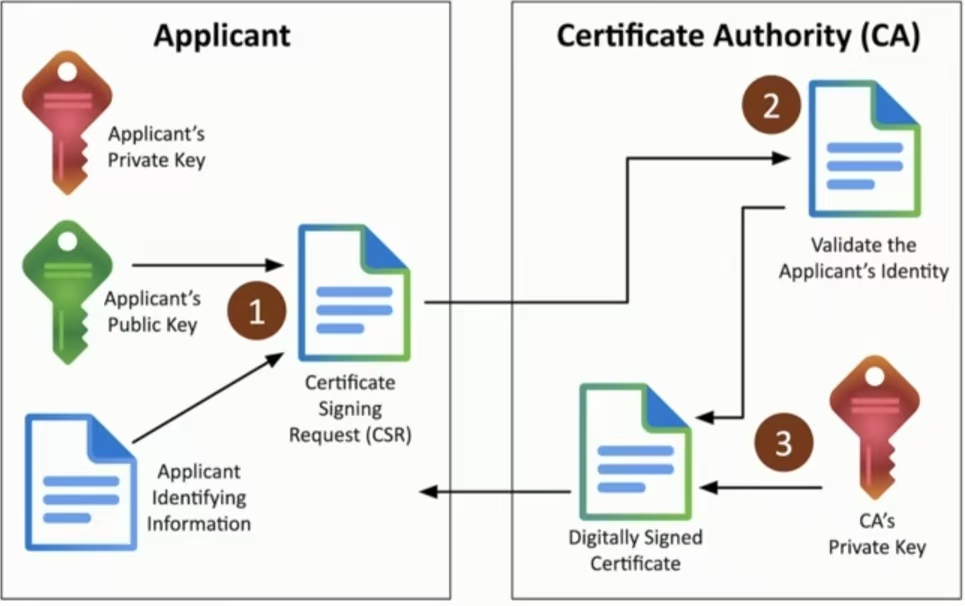
Certificate signing requests (CSR)
- Create a key pair, then send the public key to the CA to be signed
- A certificate signing request (CSR)
- The CA valildates the request
- Confirms DNS emails and website ownership
- CA digital signs the cert
- Returns to the applicant
Private certificate authorities(私人证书颁发机构)
- You are your own CA
- Build it in-house(内部)
- Your devices must trust the internal CA
- Needed for medium-to-large(中型到大型)organizations
- Many web servers and privacy requirements
- Implement(实现)as part of your overall computing strategy(策略)
- Windows Certificate Services, OpenCA
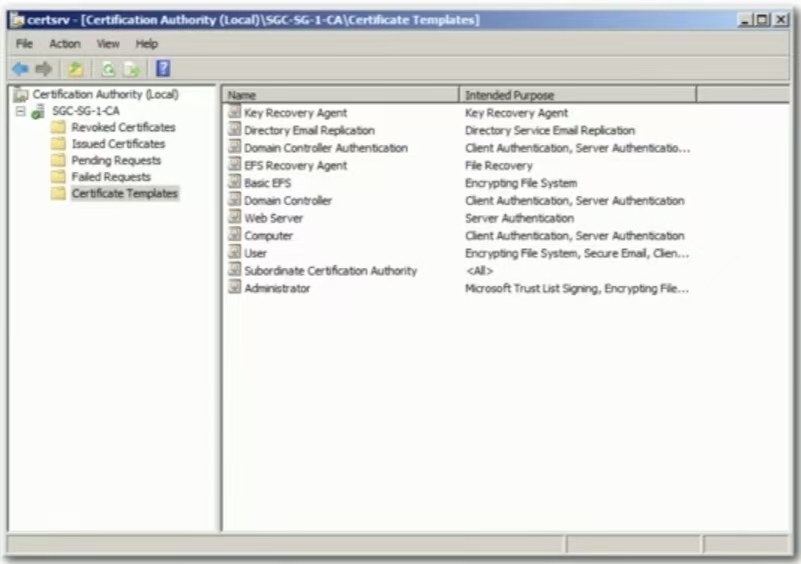
Self-signed certificates
- Internal certificates don't need to be signed by a public CA
- Your company is the only one going to use it
- No need to purchase trust for devices that already trust you
- Build your own CA
- Issue your own certificates signed by your own CA
- Install the CA certificate/trusted chain on all devices
- They'll now trust any certificates signed by your internal CA
- Works(工作原理)exactly(完全)like(与……相同)a certificate your purchased
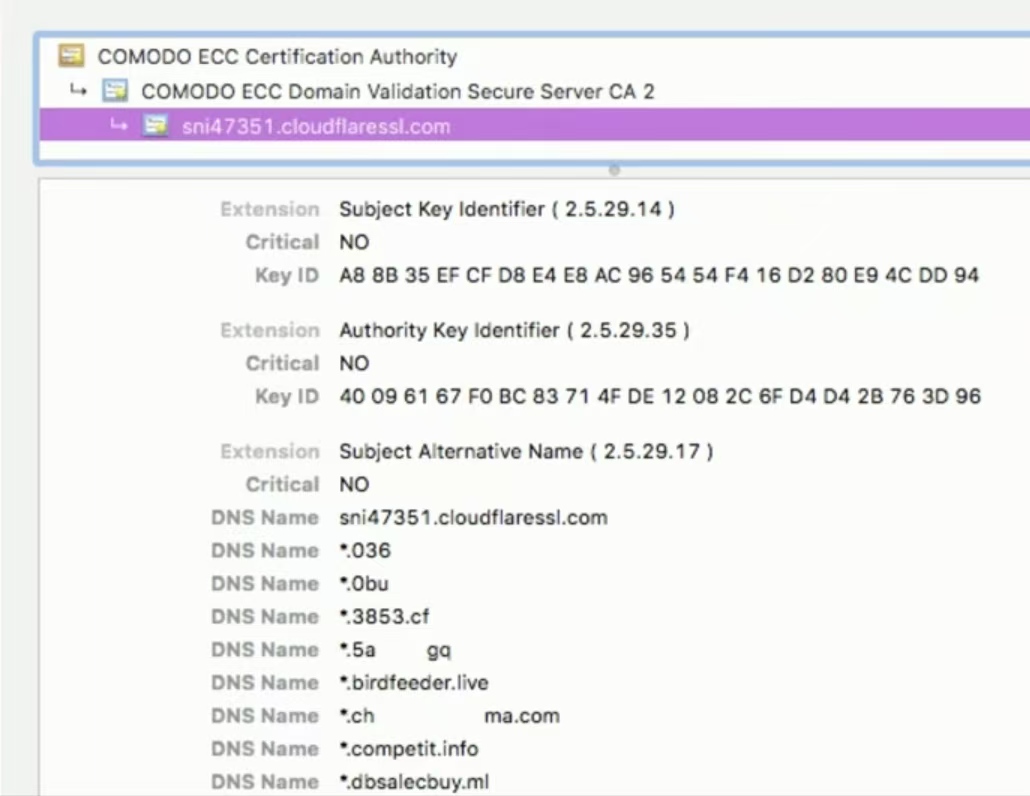
Wildcard certificates(通配符证书)
- Subject Alternative Name (SAN)(主题备用名称)
- Extension to an X.509 certificate
- Lists additional identification information
- Allows a certificate to support many different domains
- e.g. www.example.com
- Wildcard domain
- Certificates are based on the name of the server
- A wildcard domain will apply to all server names in a domain
- e.g. *.example.com
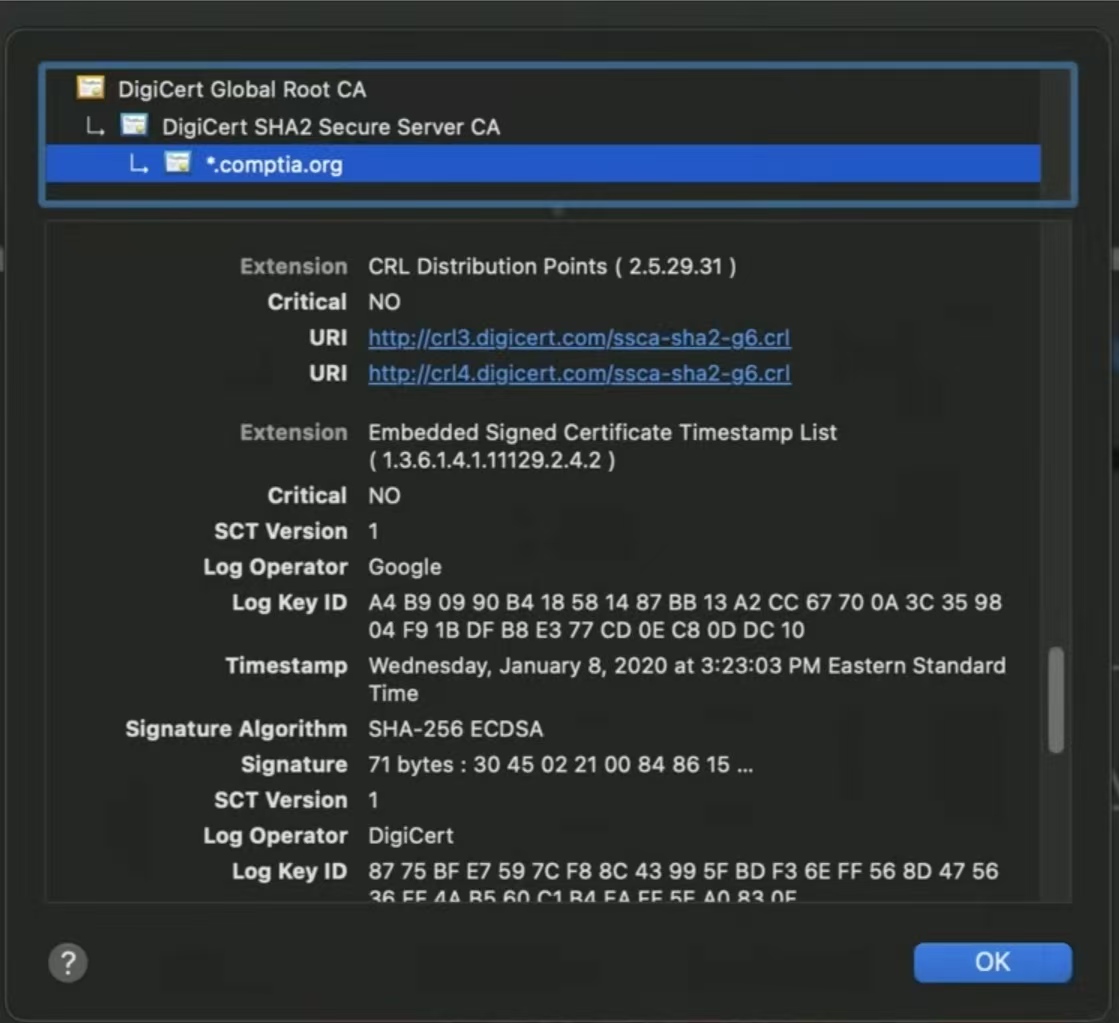
Key revocation(密钥撤销)
- Certificate Revocation List (CRL)(证书撤销列表)
- Maintained by the Certificate Authority (CA)
- Can contain many revocations in a large file
- Many different reasons
- Changes all the time
- April 2014 - CVE-2014-0160
- Heartbleed
- OpenSSL flaw put the private key of affected web servers at risk(OpenSSL漏洞使受影响的web服务器的私钥处于危险之中)
- OpenSSL was patched, every web server certificate was replaced
- Older certificates were moved to the CRL
OCSP stapling(OCSP 装订)
- Online Certificate Status Protocol
- Provides scalability(可伸缩性)for OCSP checks
- The CA is responsible(负责)for responding(响应)to all client OCSP requests
- This may not scale well(很好地扩展)
- Instead(相反), have the certificate holder verify their own status
- Status information is stored on the certificate holder's server
- OCSP status is "stapled" into the SSL/TLS handshake(握手)
- OCSP protocol digitally signed by the CA
Getting revocation details to the browser
- OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol)
- The browser can check certificate revocation
- Messages usually sent to an OCSP responder(响应器)via HTTP
- Easy to support over internet links
- More efficient than downloading a CRL
- Not all browsers/apps support OCSP
- Early Internet Explorer versions did not support OCSP
- Some support OCSP, but don't bother checking(但不会费心去检查)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号