C++ 数据结构之栈【2017.3.31更新】
更新日志
栈作为最常用的数据结构之一,一直是算法竞赛中最基础的内容,但是它和递归一起算是初学者的噩梦,我在此也就秉着复习知识加造福新人的初衷,写一篇关于栈的基础详解。
栈也叫后进先出表,LIFO表,其实可以想象成一摞书,先搁上去的会被压在最底下,而最上面的书却是最后摞上去的。
这样讲还是比较抽象,我这里附图解释吧:
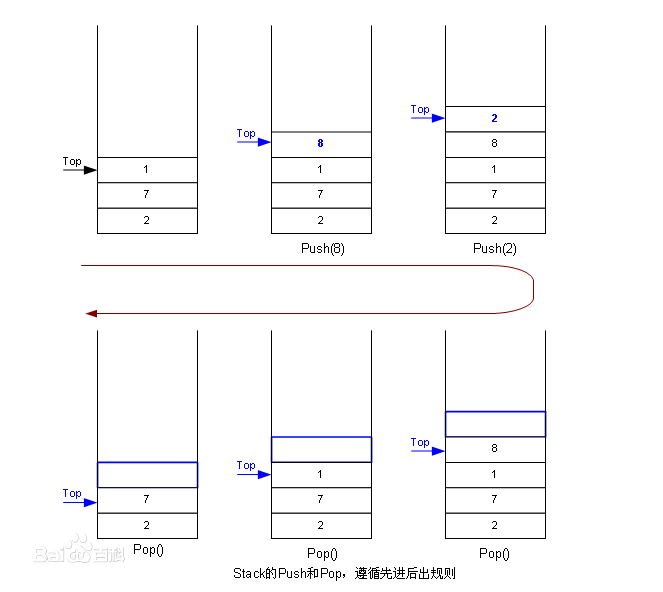
首先原始的栈中元素从下至上为“2,7,1”,而执行“压入8”之后最上层多了一个元素“8”,而后的push(2)则同理。执行pop()会弹出最上层的元素,执行三次后栈中元素还剩下“2,7”。
为了让大家更好的理解,这里附上手写栈的代码。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n, top = 0; int a[105]; int Do[105]; int Top()//返回栈顶元素 { return a[top - 1]; } void pop()//弹栈 { if (top > 0) a[top] = 0; } void push(int x)//压栈 { a[top] = x; top++; } int main() { cin >> n; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> Do[i];//操作命令数组 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (Do[i] == 1)//1压2弹 push(i); else if (top > 0) pop();//栈非空才弹,否则错误 else cout << "Error"; } cout << Top();//输出栈顶 }
这只是个“婴幼儿版本”的手写栈,目的只是便于理解罢了,漏洞还是很多的,比如没有判空函数,而是用一个假指针来判断等等,权当做一个理解工具罢了,实际上做题时一般会使用头函数<stack>中的自带栈。
下面上几道题来辅助理解。
Codevs 2058 括号序列

样例输入
2
{()}<<>>
{{{{{}}}}
样例输出
TRUE
FALSE
这是道很经典的栈题,只需要用数组模拟栈就行,把左括号压栈,如果匹配到右括号就弹,若空则合法。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<cstring> using namespace std; char s[2000001],a[2000001]; int top=0; int i,j,n; int main() { cin>>n; for( i = 1; i <= n; i++) { bool f = 1; cin >> s; int l = strlen(s); for(j = 0; j < l; j++) { if(s[j]=='('||s[j]=='{'||s[j]=='['||s[j]=='<') { top++; a[top]=s[j]; } else if((s[j]==')')&&(a[top]=='(')&&(top>0)) top--; else if(s[j]==']'&&a[top]=='['&&top>0) top--; else if(s[j]=='>'&&a[top]=='<'&&top>0) top--; else if(s[j]=='}'&&a[top]=='{'&&top>0) top--; else { f=0; break; } } if(f==0) cout<<"FALSE"<<endl; else if(top>0) cout<<"FALSE"<<endl; else cout<<"TRUE"<<endl; top=0; } return 0; }
Codevs 2821 天使之城
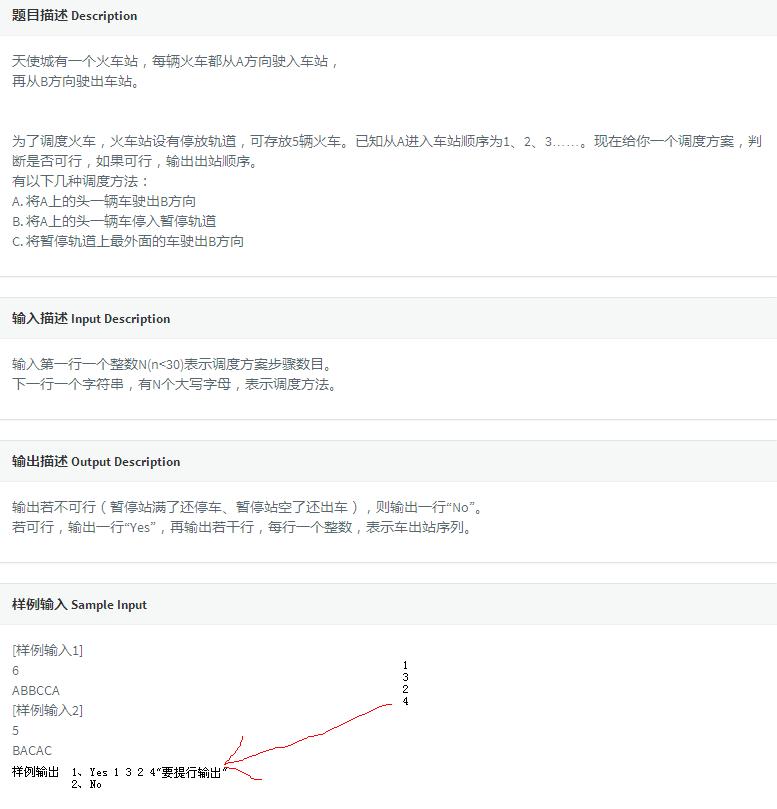
一样利用栈来模拟暂停站区,常规进行压弹栈操作就好。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int p = 1; int n, cnt; int ans[105]; char a[105]; stack<int>s; int main() { scanf("%d", &n); scanf("%s", a+1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (a[i] == 'A') { ans[p] = p; p++; continue; } else if (a[i] == 'B') { s.push(i); cnt++; if (cnt > 5) { cout << "No"; return 0; } continue; } else if (a[i] == 'C') { if (s.empty() == 1) { cout << "No"; return 0; } else { ans[p] = s.top(); p++; s.pop(); cnt--; } continue; } } cout << "Yes\n"; for (int i = 1; i < p; i++) cout << ans[i] << endl; return 0; }
Codevs 1531 山峰
样例输出
5
这道题在Codevs上评级是钻石,但也就是题意隐藏的比较深罢了,肛道理其实难度不比天使之城高多少。我最开始看到这道题的时候其实想的是更新最高峰的值,去维护S,但这么做明显没有用栈更优,那么用栈怎么做呢?
仔细思考一下,会发现这道题的数据类型很符合栈的特点:后入先出。将之前走过的山峰压入栈,记当前山峰为i,若i比栈顶元素大,则弹出当前栈顶元素,直到栈中元素都比i大为止,然后压入x,则可以保证当前栈总元素-1为开心值的最大值。这道题很有思考的必要,AC了的话栈基本就没什么问题了。下面上代码;
#include <stack> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define INF 1000000000 #define readin(x) scanf("%d", &x) #define put(x) printf("%d\n", x) #define Enter cout << endl using namespace std; int n, cnt; int main() { readin(n); stack<int>mon; mon.push(INF);//栈底元素初始化,记住这步很重要!很重要!很重要! for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int x; cnt += mon.size() - 1;//当前开心值为栈元素量-1 readin(x);//读入第i个山峰高度 while (x > mon.top())//如果当前山峰比最高山峰还高 mon.pop();//弹到有一个山峰比当前山峰高为止 mon.push(x);//压入x } put(cnt); }
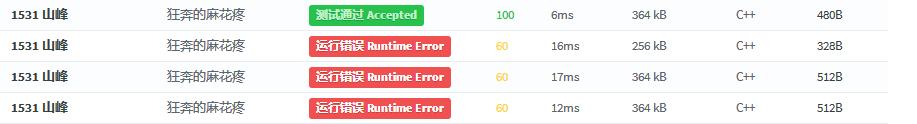
↑这就是不加初始化的后果→_→,因为山峰的高度可能会超过此前所有山,这样就会出现空栈弹栈的情况,自然会RE咯,其实加一条判断栈是否空来避免RE,但这样可能会调用empty函数很多次,肯定是没有设初值更优的。
Codevs 1051 接龙游戏
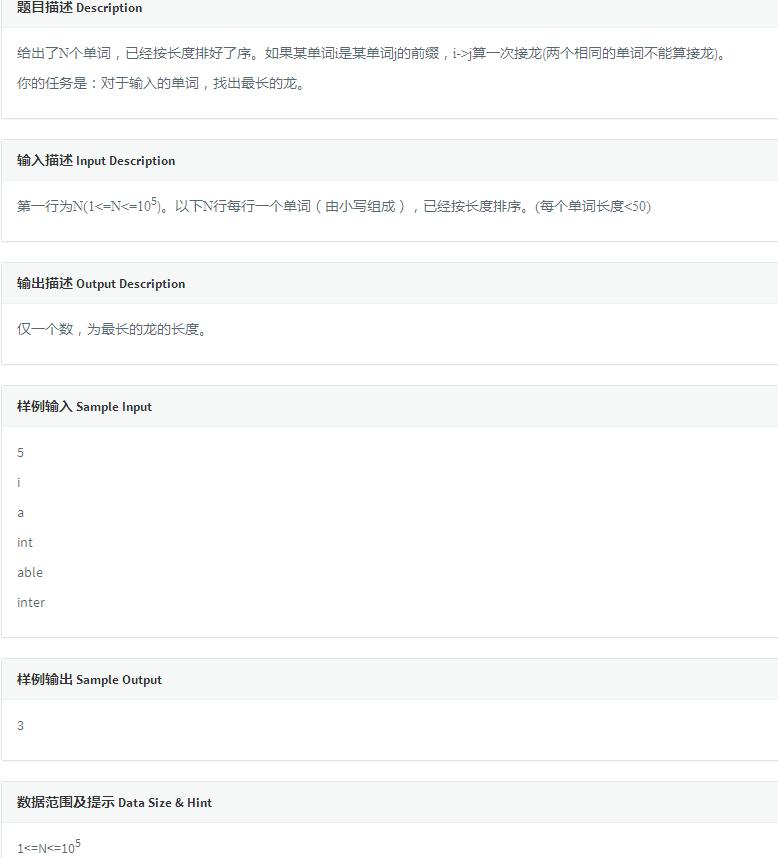
这道题乍一看很有可能会想到用KMP诶,或者是后缀数组啥的字符串知识,其实没有那么复杂。抛开字符串,这道题和山峰其实有异曲同工之妙,维护一个有序栈就好,只是对于前后缀的处理可能会比较富有技巧性。
#include <stack> #include <string> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define readin(x) scanf("%d", &x) #define put(x) printf("%d\n", x) using namespace std; int n; int maxn; string str[100010]; stack<string>s; int main() { readin(n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> str[i]; sort(str+1, str+n+1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (s.empty()) { s.push(str[i]); if (s.size() > maxn) maxn = s.size(); } else if (strstr(&str[i][0], &s.top()[0]) != NULL && str[i] != s.top()) { s.push(str[i]); if (s.size() > maxn) maxn = s.size(); } else if (str[i] == s.top()) continue; else { s.pop(); i--; } } put(maxn); }
关于这个代码,需要注意的是strstr函数是用来找子序列的,前参数是要找的子序列,后参数是要找子序列的序列,返回值若为NULL则没有子序列,
这个代码里用来判断栈顶字符串和待处理字符串之间有无子序列,其他的都是一些常规操作,不难理解。
自此栈的基础总结也算是告一段落了,这四道题难度由易到难,加以思考搞清楚不难搞通栈,所以这篇博文我也不太会再更新了,可能以后会单独开一片栈的进阶内容。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号