pTransE算法的学习
论文的阅读
来源于Modeling Relation Paths for Representation Learning of Knowledge Bases
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.00379.pdf
摘要部分
- We argue that multiple-step relation paths also contain rich inference patterns between entities, and propose a path-based representation learning model.
- Since not all relation paths are reliable,we design a path-constraint resource allocation algorithm to measure the reliability of relation paths.
- We represent relation paths via semantic composition of relation embeddings.
引言部分
1. multiple-step relation paths: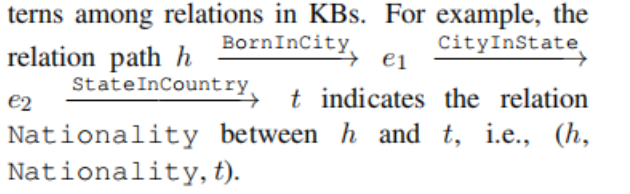
2. we aim at extending TransE to model relation paths for representation learning of KBs, and propose path-based TransE (PTransE).
3. Take the 2-step path
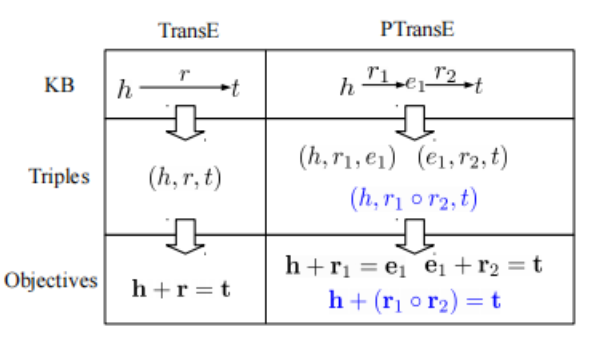
4.Relation Path Reliability:it is inappropriate to consider all relation paths in our model.we propose a path-constraint resource allocation algorithm to measure the reliability of relation paths. Afterwards, we select the reliable relation paths for representation learning
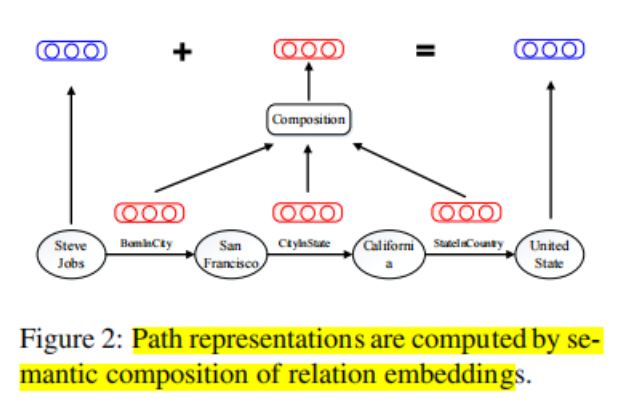
5.Relation Path Representation:

提出PTransE模型
1.Our model is expected to return a low energy score when the relation holds, and a high one otherwise.
2.评分公式:
这条公式其实可以看成是两个分数的结合,一个是单一embedding的分数,一个是路径预测的分数。而这个算法的目标就是要优化这些分数的表达能力
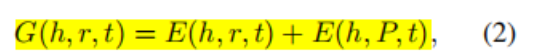
一连串的p表示path,path是有relation组成

基于head,relation,tail的差距优化,同时优化head,relation,tail向量
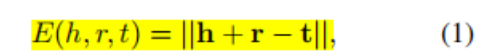
基于path_relation与relation差距的优化,其实也在优化relation向量
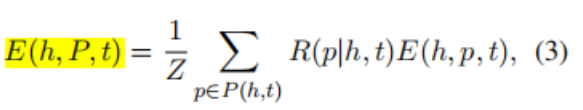
其实这里的R可以看作是概率,后面的可以看作是一个三元组的分数,执行累加,相当于是求当前路径的期望,然后除Z,相当于是加权平均

3.如何解决Relation Path Reliability
这部分代码的实现与论文的描述有出入,代码是用每一条的概率进行连乘作为路径的概率,随后除path推relation的次数,这个值作为path推relation的Reliability,这个Reliabilty就是一个路径的度量方式

4.如何解决Relation Path Representation
用path去逼近真正的relation
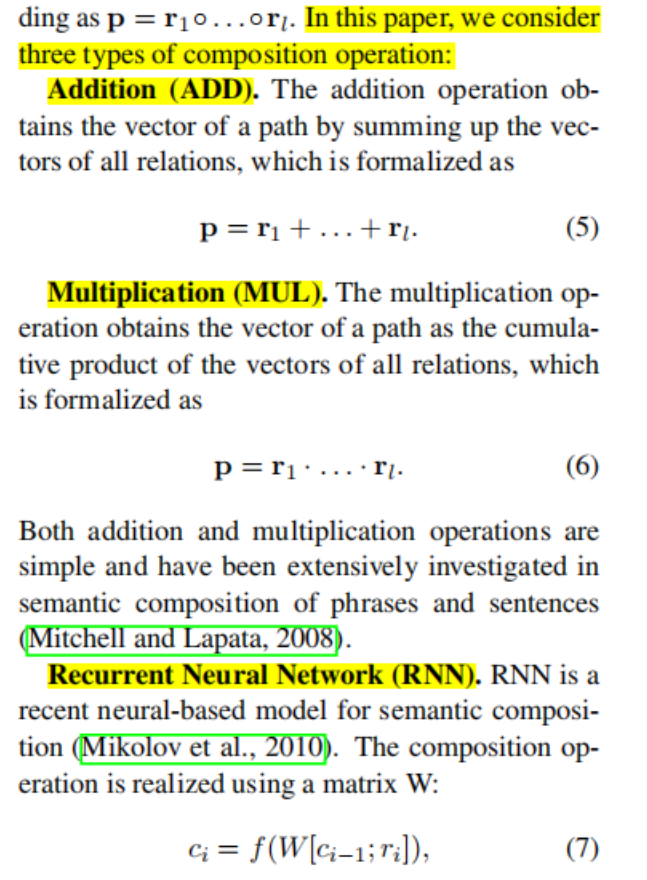
文章提出了三种方式,做了对比实验,其中最好的是adding
5.对head,relation,tail的向量进行优化 (参考TransE);对path与relation的向量进行优化
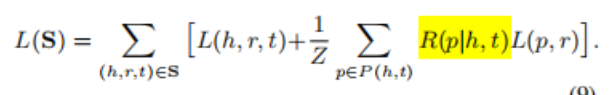
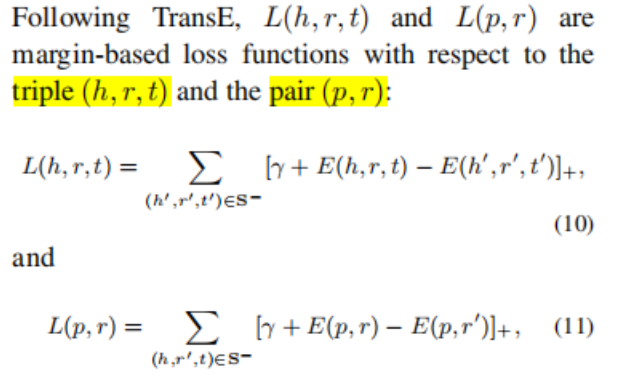
6.方向的说明
方向都采用正向

7.参数的说明
只采用最大的path长度为3,另外reliability的值应该>0.01

Java代码的学习
源码地址,https://github.com/MaximTian/TransX
数据集 使用的是三国演义人物关系图,对其进行了整理得到相应的三元组,一共有173条数据
入口函数
public class Main {
private static void PCRA_run() throws IOException {
File f = new File("resource/path_data/confident.txt");
if (!f.exists()) {
PCRA pcra = new PCRA();
pcra.run();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Train or test? y/n");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean train_flag;
train_flag = sc.next().equals("y");
if (train_flag) {
PCRA_run();
TrainRun trainRun = new TrainRun();
trainRun.train_run();
} else {
TestRun testRun = new TestRun();
testRun.test_run();
}
}
}
初始化变量
relation2id,id2relation,relation_num,head_relation2tail,head_tail2relation,head_tail2path
是用不同的格式存储数据的变量,方便后续的遍历
paths,path2relation,path_valid
是用于拓展路径的变量。paths变量只记录路径中的Relation,而不记录里面的Entity
- paths:用于统计paths的次数
- path2relation:用于统计path推理head的次数
- path_valid: 用于统计满足阈值的路径
public class PCRA {
private Map<String, Integer> relation2id;
private Map<Integer, String> id2relation;
private int relation_num;
private Map<String, Map<Integer, Set<String>>> head_relation2tail; // (头实体,关系) -> (尾实体)
private Map<String, HashSet<Integer>> head_tail2relation; // (头实体,尾实体) -> (关系)
private Map<String, Map<String, Double>> head_tail2path; // (头实体,尾实体) -> (关系路径)
private Map<String, Integer> paths; // 记录每条路径,以及该路径出现的次数
private Map<String, Integer> path2relation; // 记录每个路径推理的边("path->rel"),已经对应出现的次数
private Set<String> path_valid; // 存储符合条件的路径
private void init() {
relation2id = new HashMap<>();
id2relation = new HashMap<>();
head_relation2tail = new HashMap<>();
head_tail2relation = new HashMap<>();
head_tail2path = new HashMap<>();
paths = new HashMap<>();
path2relation = new HashMap<>();
path_valid = new HashSet<>();
}
拓展路径,计算概率
public void run() throws IOException {
init();
prepare();
ArrayDeque<String> cur_entity_list = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (String head: head_relation2tail.keySet()) {
cur_entity_list.addFirst(head);
Map<Integer, Set<String>> visit_relation_tail = head_relation2tail.get(head);//获取满足head的relation和tail
ArrayDeque<Integer> cur_relation_list = new ArrayDeque<>();
dfs(cur_entity_list, visit_relation_tail, cur_relation_list, 0, 1, 1.0);
dfs(cur_entity_list, visit_relation_tail, cur_relation_list, 0, 2, 1.0);
cur_entity_list.removeFirst();
}
Write_Path();//path的数量,path的长度,path_relation的内容,概率,path的长度,path_relation的内容,path_relation的概率
Write_Confident();//path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,换行,head_relation的个数,head_relation,path_relation推出head_relation的次数*path出现的概率
calculate_prob("train");//head,tail,relation,换行,path_relation的个数,path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,path_relation的概率
calculate_prob("test");//
}
1.执行deep-first-search,搜索路径。遍历train数据的head,拓展路径
private void dfs(ArrayDeque<String> entity_list, Map<Integer, Set<String>> relation_tail,
ArrayDeque<Integer> relation_list, int depth, int max_depth, double prob) {
/**
* entity_list: record those visited entities, to prevent visiting again
* relation_tail: record the relation_set needed to visit, which is from the last_entity in the entity_list
* realtion_list: record those visited relations
*/
if (relation_tail == null && depth < max_depth) {
return;
}
if (depth == max_depth) {
String head = entity_list.getFirst();
String tail = entity_list.getLast();
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
for (int relation_id: relation_list) {
if (path.length() > 0) {
path.append(" ");
}
path.append(String.valueOf(relation_id));
}
map_add_path(paths, path.toString());//存储路径,和统计路径的出现次数,paths当中只包含路径中的relation
if (head_tail2relation.containsKey(head + " " + tail)) {
Set<Integer> relation_set = head_tail2relation.get(head + " " + tail);
add_Path2Relation(path2relation, path.toString(), relation_set);// 记录每个路径推理的边("path->rel"),rel是头部的relation
}
map_add_RelationPath(head_tail2path, head, tail, path.toString(), prob);// 存储符合条件的路径,存储格式(head,tail),只含relation的path,路径的概率
return;
}
for (int relation_id: relation_tail.keySet()) {
Set<String> tail_set = relation_tail.get(relation_id);//获取当前relation的tail
relation_list.addLast(relation_id);//记录路径中的relation
double cur_prob = prob * (1.0 / tail_set.size());//前一环节的概率,乘当前环节的概率
for (String tail: tail_set) {
if (!entity_list.contains(tail)) {//不能与前面的重复
entity_list.addLast(tail);//记录路径中的entity
Map<Integer, Set<String>> visit_relation_tail = head_relation2tail.get(tail);//获取下一节点的内容
dfs(entity_list, visit_relation_tail, relation_list, depth + 1, max_depth, cur_prob);
entity_list.removeLast();
}
}
relation_list.removeLast();
}
}
2.计算概率
每一跳的概率相乘
Set<String> tail_set = relation_tail.get(relation_id);//获取当前relation的tail
relation_list.addLast(relation_id);//记录路径中的relation
double cur_prob = prob * (1.0 / tail_set.size());//前一环节的概率,乘当前环节的概率
3.统计path的次数
map_add_path(paths, path.toString());//存储路径,和统计路径的出现次数,paths当中只包含路径中的relation
static void map_add_path(Map<String, Integer> map, String path) {
if (!map.containsKey(path)) {
map.put(path, 0);
}
map.put(path, map.get(path) + 1);
}
4.用path2relation统计path与head的关系
path2relation统计path推出head的数量
add_Path2Relation(path2relation, path.toString(), relation_set);// 记录每个路径推理的边("path->rel"),rel是头部的relation
static void add_Path2Relation(Map<String, Integer> path2relation_set, String path, Set<Integer> relation_set) {
for (int relation: relation_set) {
String path_relation = path + "->" + relation;
map_add_path(path2relation_set, path_relation);
}
}
static void map_add_path(Map<String, Integer> map, String path) {
if (!map.containsKey(path)) {
map.put(path, 0);
}
map.put(path, map.get(path) + 1);
}
5.统计训练数据对应的路径,以及匹配path的概率和
以一个head_tail为单位,对其中中相同path的概率求和
这里的head,tail不一定是数据集当中存在的三元组,只是拓展的多跳路径中存在
map_add_RelationPath(head_tail2path, head, tail, path.toString(), prob);// 存储符合条件的路径,存储格式(head,tail),只含relation的path,路径的概率
static void map_add_RelationPath(Map<String, Map<String, Double>> map, String head, String tail,
String relation_path, double prob) {
String head_tail = head + " " + tail;
if (!map.containsKey(head_tail)) {
map.put(head_tail, new HashMap<>());
}
Map<String, Double> path_set = map.get(head_tail);
if (!path_set.containsKey(relation_path)) {//若map中不存在这条路径,先初始化
path_set.put(relation_path, 0.0);
}
path_set.put(relation_path, path_set.get(relation_path) + prob);
}
6.将前面统计的结果写入文件当中
Write_Path();//path的数量,path的长度,path_relation的内容,概率,path的长度,path_relation的内容,path_relation的概率
Write_Confident();//path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,换行,head_relation的个数,head_relation,path_relation推出head_relation的次数*path出现的概率
calculate_prob("train");//head,tail,relation,换行,path_relation的个数,path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,path_relation的概率
calculate_prob("test");//
7.将满足的path值写入path.txt文件当中
在写入path之前,要对path进行筛选。以head_tail为单位,对它所附属的path进行归一化,然后检查path是否满足阈值。head_tail2path的key是head和tail,value是多条path以及path对应的概率
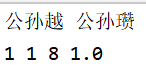
path.txt的内容如下图所示.包含headtail与path的关系
head tail 换行
path的个数,path的长度,path的内容,path的概率

private void Write_Path() throws IOException {
File f = new File("resource/path_data/path.txt");
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(f), "UTF-8");
int i=0;
int j=0;
Set<String> sets=new HashSet<>();
sets.addAll(head_relation2tail.keySet());
sets.addAll(tail_relation2head.keySet());
for (String head: sets) {
for (String tail: sets) {
if (head.equals(tail)) {
continue;
}
String head_tail = head + " " + tail;
if (head_tail2path.containsKey(head_tail)) {//从head_tail2path选出合适的路径
i++;
Map<String, Double> path_prob_valid = generate_valid_path(head_tail2path, head_tail);
writer.write(head_tail + "\n");
writer.write(String.valueOf(path_prob_valid.size()));
for (String path: path_prob_valid.keySet()) {
path_valid.add(path);//path_relation
String[] split_path = path.split(" ");
writer.write(" " + String.valueOf(split_path.length) + " " + path
+ " " + String.valueOf(path_prob_valid.get(path)));//path的长度,relation_path的内容,概率+" "+path的长度,relation_path的内容,概率
}
writer.write("\n");
writer.flush();
}
}
// System.out.println(i);
}
}
static Map<String, Double> generate_valid_path(Map<String, Map<String, Double>> head_tail2path, String head_tail) {
Map<String, Double> path_prob = new HashMap<>(); // 记录所有路径以及相应的路径概率
Map<String, Double> path_prob_valid = new HashMap<>(); // 记录符合概率阈值的路径
double sum = 0.0; // 用于归一化
Map<String, Double> path_set = head_tail2path.get(head_tail);
for (String path: path_set.keySet()) {
double prob = path_set.get(path);
path_prob.put(path, prob);
sum += prob;
}
for (String path: path_prob.keySet()) {
double prob = path_prob.get(path) / sum;
path_prob.put(path, prob);
if (prob > 0.01) { // 筛选条件
path_prob_valid.put(path, prob);
}
}
return path_prob_valid;
}
8.计算path的confidence,将满足的写入confident.txt文件中
代码中有几个变量值得注意
- prob:1/path出现的次数
- path2relation.get(tmp_path2relation):path推导出head的次数
- confidence: path2relation.get(tmp_path2relation)*prob
confident.txt的文件格式如下,包含path与headrelation关系的内容
path的长度 path的内容 换行
path可推导的headrelation的个数 headrelation的内容 path推headrelation的概率

Write_Confident();//path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,换行,head_relation的个数,head_relation,path_relation推出head_relation的次数*path出现的概率
private void Write_Confident() throws IOException {
/**
* path_length, path
* relation counts, (relation, prob) ...
*/
File f = new File("resource/path_data/confident.txt");
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(f), "UTF-8");
for (String path: path_valid) {//path_relation
List<String> out_list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < relation_num; i++) {
String tmp_path2relation = String.format("%s->%d", path, i);
if (path2relation.containsKey(tmp_path2relation)) {//("path->rel"),path是body的relation,rel是头部的relation
double prob = 1.0 / paths.get(path);//path出现的次数
String str = String.format(" %d %f", i, path2relation.get(tmp_path2relation) * prob);//head_relation,path_relation推出head_relation的次数*path出现的概率
out_list.add(str);
}
}
if (!out_list.isEmpty()) {
writer.write(String.format("%d %s\n", path.split(" ").length, path));//path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,换行
writer.write(String.valueOf(out_list.size()));//head_relation的个数
for (String out: out_list) {
writer.write(out);//head_relation,path_relation推出head_relation的次数*path出现的概率
}
writer.write("\n");
writer.flush();
}
}
}
9.对前面的数据进行过滤,将数据写入train_prob.txt与test_prob.txt
仅保存训练集或者测试集当中存在的数据
存储格式如下图所示

head tail relationid 换行
path的个数,path的长度,path的内容,path的概率
calculate_prob("train");//head,tail,relation,换行,path_relation的个数,path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,path_relation的概率
calculate_prob("test");//
private void calculate_prob(String file_name) throws IOException {
File f = new File(String.format("resource/data/%s.txt", file_name));
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(f),"UTF-8"));
f = new File(String.format("resource/path_data/%s_prob.txt", file_name));
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(f), "UTF-8");
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {//读取train_data的数据
String[] split_data = line.split("\t");
String head = split_data[0];
String tail = split_data[1];
int relation_id = relation2id.get(split_data[2]);
String head_tail = head + " " + tail;
Map<String, Double> path_prob_valid = new HashMap<>(); // 记录符合概率阈值的路径
if (head_tail2path.containsKey(head_tail)) {
path_prob_valid = generate_valid_path(head_tail2path, head_tail);//path,概率
}
writer.write(String.format("%s %s %d\n", head, tail, relation_id));//head,tail,relation,换行
writer.write(String.valueOf(path_prob_valid.size()));//path_relation的个数
for (String path: path_prob_valid.keySet()) {
String[] split_path = path.split(" ");
writer.write(String.format(" %d %s %f", split_path.length, path, path_prob_valid.get(path)));//path_relation的长度,path_relation的内容,path_relation的概率
}
writer.write("\n");
/**
* to do reverse
*/
writer.flush();
}
}
训练的部分
1.训练函数的入口
public void train_run() throws IOException {
int nepoch = 1200;
int nbatches = 150;
System.out.printf("iteration times = %s\n", nepoch);
System.out.printf("nbatches = %s\n", nbatches);
train = new Train();
prepare();
train.run(nepoch, nbatches);
}
2.读取前面PCRA部分生成的文件
读取的格式如下所示,head,relation,tail,path以及path对应的概率
其中有几个变量值得注意
fb_h:所有的head节点fb_r:所有的relation节点fb_l: 所有的tail节点fb_path2prob:路径列表和它对应的概率head_relation2tail: key是head和relation,value是tailpath_confidence: path推导relation, path推导relation的概率
train.add(head_id, relation_id, tail_id, path2prob_list);
private void prepare() throws IOException {
GlobalValueInit();
entity_num = Read_Data("resource/data/entity2id.txt", entity2id, id2entity);
relation_num = Read_Data("resource/data/relation2id.txt", relation2id, id2relation);
File f = new File("resource/path_data/train_prob.txt");
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(f),"UTF-8"));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] split_data = line.split(" ");
int head_id = entity2id.get(split_data[0]);
int tail_id = entity2id.get(split_data[1]);
int relation_id = Integer.valueOf(split_data[2]);
String[] path_info = reader.readLine().split(" ");
List<Pair<List<Integer>, Double>> path2prob_list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i < path_info.length;) {
int path_length = Integer.valueOf(path_info[i]);
List<Integer> relation_id_list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 1; j <= path_length; j++) {
relation_id_list.add(Integer.valueOf(path_info[i + j]));
}
double prob = Double.valueOf(path_info[i + path_length + 1]);
Pair<List<Integer>, Double> path2prob = new Pair<>(relation_id_list, prob);
path2prob_list.add(path2prob);
i += path_length + 2;
}
train.add(head_id, relation_id, tail_id, path2prob_list);
}
f = new File("resource/path_data/confident.txt");
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(f),"UTF-8"));
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] line_split = line.split(" ");
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1; i < line_split.length; i++) {
if (path.length() > 0) path.append(" ");
path.append(line_split[i]);
}
String[] path_info = reader.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i < path_info.length; i += 2) {
int relation_id = Integer.valueOf(path_info[i]);
double prob = Double.valueOf(path_info[i + 1]);
Pair<String, Integer> path2relation = new Pair<>(path.toString(), relation_id);
path_confidence.put(path2relation, prob);
}
}
System.out.printf("entity number = %s\n", entity_num);
System.out.printf("relation number = %s\n", relation_num);
}
void add(int head, int relation, int tail, List<Pair<List<Integer>, Double>> path2prob_list) {
fb_h.add(head);
fb_r.add(relation);
fb_l.add(tail);
fb_path2prob.add(path2prob_list);
Pair<Integer, Integer> key = new Pair<>(head, relation);
if (!head_relation2tail.containsKey(key)) {
head_relation2tail.put(key, new HashSet<>());
}
Set<Integer> tail_set = head_relation2tail.get(key);
tail_set.add(tail);
}
3.初始化向量
初始化entity向量以及relation的向量,它们的向量长度是相同的
void run(int nepoch, int nbatches) throws IOException {
relation_vec = new double[relation_num][vector_len];
entity_vec = new double[entity_num][vector_len];
for (int i = 0; i < relation_num; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < vector_len; j++) {
relation_vec[i][j] = uniform(-6 / sqrt(vector_len), 6 / sqrt(vector_len));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < entity_num; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < vector_len; j++) {
entity_vec[i][j] = uniform(-6 / sqrt(vector_len), 6 / sqrt(vector_len));
}
norm(entity_vec[i], vector_len);
}
bfgs(nepoch, nbatches);
}
4.计算embedding的损失值,采用随机梯度下降更新向量
类似于TransE
private void bfgs(int nepoch, int nbatches) throws IOException {
int batchsize = fb_h.size() / nbatches;
System.out.printf("Batch size = %s\n", batchsize);
for (int epoch = 0; epoch < nepoch; epoch++) {
// region private members
//loss function value
loss = 0;
for (int batch = 0; batch < nbatches; batch++) {
for (int k = 0; k < batchsize; k++) {
int pos = rand_max(fb_h.size()); // 随机选取一行三元组, 行号
int tmp_rand = rand() % 100;
if (tmp_rand < 25) {
int tail_neg = rand_max(entity_num);
tail_neg = random_tail(pos, tail_neg);
loss = train_kb(fb_h.get(pos), fb_l.get(pos), fb_r.get(pos), fb_h.get(pos), tail_neg, fb_r.get(pos), loss);
norm(entity_vec[tail_neg], vector_len);
} else if (tmp_rand < 50) {
int head_neg = rand_max(entity_num);
head_neg = random_head(pos, head_neg);
loss = train_kb(fb_h.get(pos), fb_l.get(pos), fb_r.get(pos), head_neg, fb_l.get(pos), fb_r.get(pos), loss);
norm(entity_vec[head_neg], vector_len);
} else {
int relation_neg = rand_max(relation_num);
relation_neg = random_relation(pos, relation_neg); // 若某一对实体之间存在所有的关系,则陷入死循环
loss = train_kb(fb_h.get(pos), fb_l.get(pos), fb_r.get(pos), fb_h.get(pos), fb_l.get(pos), relation_neg, loss);
norm(relation_vec[relation_neg], vector_len);
}
update_relation(pos);
norm(relation_vec[fb_r.get(pos)], vector_len);
norm(entity_vec[fb_h.get(pos)], vector_len);
norm(entity_vec[fb_l.get(pos)], vector_len);
}
}
System.out.printf("epoch: %s %s\n", epoch, loss);
}
Write_Vec2File("resource/result/relation2vec.txt", relation_vec, relation_num);
Write_Vec2File("resource/result/entity2vec.txt", entity_vec, entity_num);
}
损失值的计算
static double train_kb(int head_a, int tail_a, int relation_a, int head_b, int tail_b, int relation_b, double res) {
double sum1 = calc_sum(head_a, tail_a, relation_a);
double sum2 = calc_sum(head_b, tail_b, relation_b);
if (sum1 + margin > sum2) {
res += margin + sum1 - sum2;
gradient(head_a, tail_a, relation_a, -1);
gradient(head_b, tail_b, relation_b, 1);
}
return res;
}
static double calc_sum(int e1, int e2, int rel) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vector_len; i++) {
sum += abs(entity_vec[e2][i] - entity_vec[e1][i] - relation_vec[rel][i]);
}
return sum;
}
private static void gradient(int head, int tail, int relation, int beta) {
for (int i = 0; i < vector_len; i++) {
double delta = entity_vec[tail][i] - entity_vec[head][i] - relation_vec[relation][i];
double x = (delta > 0) ? 1 : -1;
relation_vec[relation][i] -= x * learning_rate * beta;
entity_vec[head][i] -= x * learning_rate * beta;
entity_vec[tail][i] += x * learning_rate * beta;
}
}
5.计算路径的损失值
private void update_relation(int pos) {
int relation_neg = rand_max(relation_num);
relation_neg = random_relation(pos, relation_neg);
List<Pair<List<Integer>, Double>> path2prob_list = fb_path2prob.get(pos);
for (Pair<List<Integer>, Double> path2prob: path2prob_list) {
List<Integer> path = path2prob.a;
double prob = path2prob.b;
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
for (int path_id: path) {
if (str.length() > 0) str.append(" ");
str.append(path_id);
}
Pair<String, Integer> tmp_path2rel = new Pair<>(str.toString(), fb_r.get(pos));
double tmp_confidence = 0;
if (path_confidence.containsKey(tmp_path2rel)) {
tmp_confidence = path_confidence.get(tmp_path2rel);
}
tmp_confidence = (0.99 * tmp_confidence + 0.01) * prob;
train_path(fb_r.get(pos), relation_neg, path, tmp_confidence, loss);
}
}
static double train_path(int relation, int neg_relation, List<Integer> path, double alpha, double loss) {
double sum1 = calc_path(relation, path);
double sum2 = calc_path(neg_relation, path);
if (sum1 + margin_relation > sum2) {
loss += alpha * (sum1 + margin_relation - sum2);
gradient_path(relation, path, -1 * alpha);
gradient_path(neg_relation, path, alpha);
}
return loss;
}
计算损失值
一个relation减去多个path同一位置的元素。在更新的时候,假设有这么一对数据(h,r,t),(h,p1,p2,p3,t),更新的时候要更新r,p1,p2,p3,它们都属于relation向量
static private double calc_path(int relation, List<Integer> path) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vector_len; i++) {
double x = relation_vec[relation][i];
for (int path_id : path) {
x -= relation_vec[path_id][i];
}
sum += abs(x);
}
return sum;
}
static private void gradient_path(int relation, List<Integer> path, double beta) {
/**
* 相关联的路径和关系之间的空间位置相近,反之疏远
*/
for (int i = 0; i < vector_len; i++) {
double x = relation_vec[relation][i];
for (int path_id: path) {
x -= relation_vec[path_id][i];
}
int flag = (x > 0) ? 1 : -1;
relation_vec[relation][i] += beta * learning_rate * flag;
for (int path_id : path) {
relation_vec[path_id][i] -= beta * learning_rate * flag;
}
}
}
预测
将预测的过程写入到output_detail.txt文件中
结果将会输出图片所示的内容

public void run() throws IOException {
relation_vec = new double[relation_num][vector_len];
entity_vec = new double[entity_num][vector_len];
Read_Vec_File("resource/result/relation2vec.txt", relation_vec);
Read_Vec_File("resource/result/entity2vec.txt", entity_vec);
int lsum = 0, rsum = 0;
int lp_n = 0, rp_n = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> lsum_r = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> rsum_r = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> lp_n_r = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> rp_n_r = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> rel_num = new HashMap<>();
File out_file = new File("resource/result/output_detail.txt");
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(out_file), "UTF-8");
System.out.printf("Total iterations = %s\n", fb_l.size());
for (int id = 0; id < fb_l.size(); id++) {
System.out.println(id);
int head = fb_h.get(id);
int tail = fb_l.get(id);
int relation = fb_r.get(id);
relation_add(rel_num, relation);
List<Pair<Integer, Double>> head_dist = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < entity_num; i++) {
if (hrt_isvalid(i, relation, tail)) {
continue;
}
double sum = calc_sum(i, tail, relation);//计算所有组合的距离
head_dist.add(new Pair<>(i, sum));
}
Collections.sort(head_dist, (o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.b, o2.b));//对headlist排序
for (int i = 0; i < head_dist.size(); i++) {
int cur_head = head_dist.get(i).a;
if (cur_head == head) {
lsum += i; // 统计小于<h, l, r>距离的数量
map_add_value(lsum_r, relation, i);
if (i <= 10) {
lp_n++;
map_add_value(lp_n_r, relation, 1);
}
String str = String.format("%s %s %s, dist=%f, %d\n\n", id2entity.get(head), id2relation.get(relation),
id2entity.get(tail), calc_sum(head, tail, relation), i);
writer.write(str);
writer.flush();
break;
} else {
String temp_str = String.format("%s %s %s, dist=%f, %d\n", id2entity.get(cur_head), id2relation.get(relation),
id2entity.get(tail), calc_sum(cur_head, tail, relation), i);
writer.write(temp_str);
writer.flush();
}
}
List<Pair<Integer, Double>> tail_dist = new ArrayList<>();//预测尾
for (int i = 0; i < entity_num; i++) {
if (hrt_isvalid(head, relation, i)) {
continue;
}
double sum = calc_sum(head, i, relation);
tail_dist.add(new Pair<>(i, sum));
}
Collections.sort(tail_dist, (o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.b, o2.b));
for (int i = 0; i < tail_dist.size(); i++) {
int cur_tail = tail_dist.get(i).a;
if (cur_tail == tail) {
rsum += i;
map_add_value(rsum_r, relation, i);
if (i <= 10) {
rp_n++;
map_add_value(rp_n_r, relation, 1);
}
break;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("lsum = %s, tail number = %s\n", lsum, fb_l.size());
System.out.printf("left: %s\t%s\n", (lsum * 1.0) / fb_l.size(), (lp_n * 1.0) / fb_l.size());
System.out.printf("right: %s\t%s\n", (rsum * 1.0) / fb_h.size(), (rp_n * 1.0) / fb_h.size());
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号