Python数据分析-数据导出
1. 主要内容
- 导出为.xlsx文件
- 导出为.csv文件
说明:当然,主要内容不仅仅这些,因为数据分析主要基于数据库、Excel表格这类常见的文件,所以此篇主要学习.csv和.xlsx这两个后缀的文件
2. 导出为.xlsx文件
常用函数df.to_excel(),语法如下:
DataFrame.to_excel(excel_writer, *, sheet_name='Sheet1', na_rep='', float_format=None, columns=None, header=True, index=True, index_label=None, startrow=0, startcol=0, engine=None, merge_cells=True, inf_rep='inf', freeze_panes=None, storage_options=None, engine_kwargs=None)
Write object to an Excel sheet.
To write a single object to an Excel .xlsx file it is only necessary to specify a target file name. To write to multiple sheets it is necessary to create an ExcelWriter object with a target file name, and specify a sheet in the file to write to.
Multiple sheets may be written to by specifying unique sheet_name. With all data written to the file it is necessary to save the changes. Note that creating an ExcelWriter object with a file name that already exists will result in the contents of the existing file being erased.
参数说明:
- excel_writer:path-like, file-like, or ExcelWriter object
File path or existing ExcelWriter.
- sheet_name:str, default ‘Sheet1’
Name of sheet which will contain DataFrame.
- na_rep:str, default ‘"’
Missing data representation.
- float_format:str, optional
Format string for floating point numbers. For example float_format="%.2f" will format 0.1234 to 0.12.
- columns:sequence or list of str, optional
Columns to write.
- header:bool or list of str, default True
Write out the column names. If a list of string is given it is assumed to be aliases for the column names.
- index:bool, default True
Write row names (index).
- index_label:str or sequence, optional
Column label for index column(s) if desired. If not specified, and header and index are True, then the index names are used. A sequence should be given if the DataFrame uses MultiIndex.
- startrow:int, default 0
Upper left cell row to dump data frame.
- startcol:int, default 0
Upper left cell column to dump data frame.
- engine:str, optional
Write engine to use, ‘openpyxl’ or ‘xlsxwriter’. You can also set this via the options io.excel.xlsx.writeror io.excel.xlsm.writer.
- merge_cells:bool, default True
Write MultiIndex and Hierarchical Rows as merged cells.
- inf_rep:str, default ‘inf’
Representation for infinity (there is no native representation for infinity in Excel).
- freeze_panes:tuple of int (length 2), optional
Specifies the one-based bottommost row and rightmost column that is to be frozen.
- storage_options:dict, optional
Extra options that make sense for a particular storage connection, e.g. host, port, username, password, etc. For HTTP(S) URLs the key-value pairs are forwarded to urllib.request.Request as header options. For other URLs (e.g. starting with “s3://”, and “gcs://”) the key-value pairs are forwarded to fsspec.open.
- engine_kwargs:dict, optional
Arbitrary keyword arguments passed to excel engine.
注意:
For compatibility with to_csv(), to_excel serializes lists and dicts to strings before writing.
Once a workbook has been saved it is not possible to write further data without rewriting the whole workbook.
代码示例:
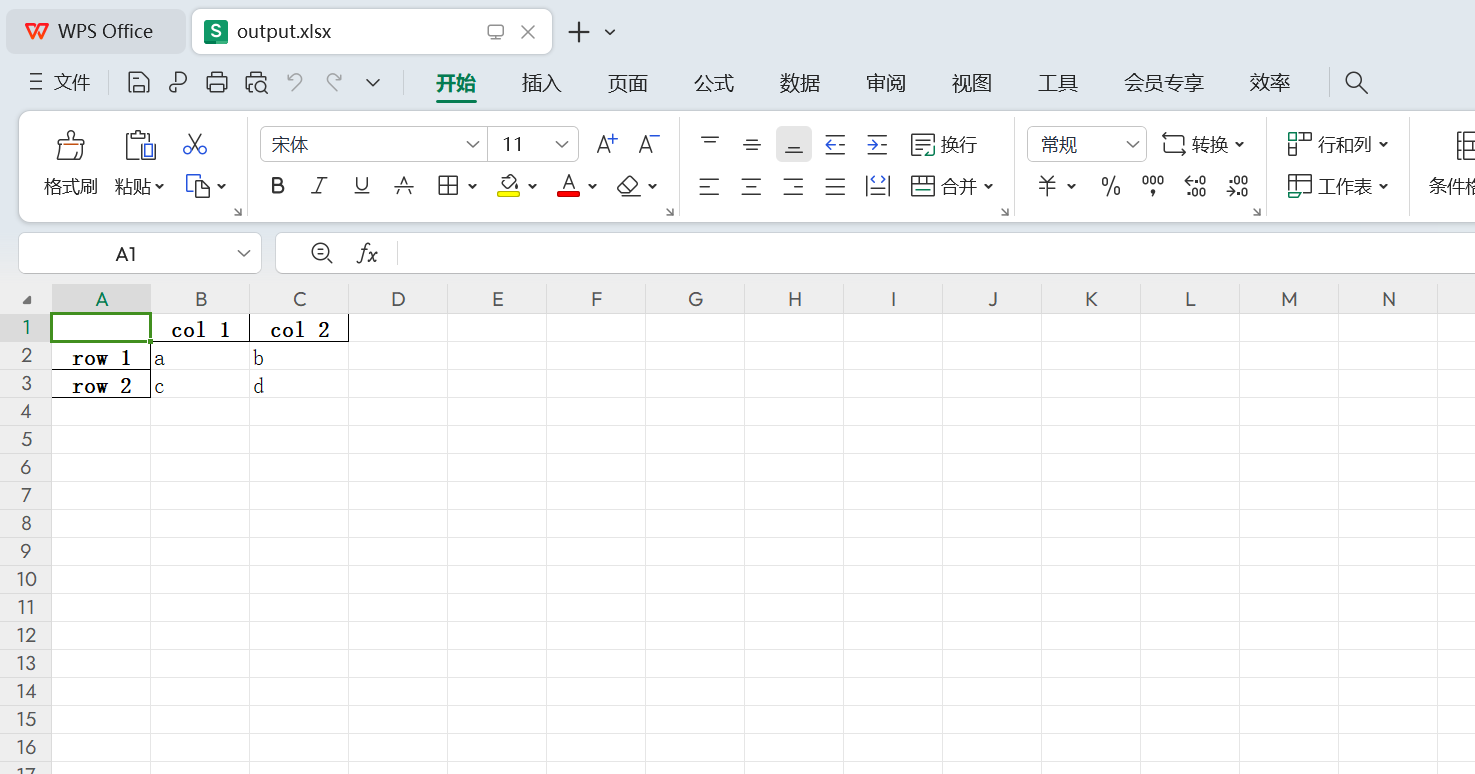
1 df1 = pd.DataFrame([['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']], index=['row 1', 'row 2'], columns=['col 1', 'col 2']) 2 df1.to_excel("output.xlsx") 3 4 ### 结果 5 # 如下图

其他代码示例:
1 # 指定工作表名称 2 df1.to_excel("output.xlsx", sheet_name='Sheet_name_1')
1 # 如果您希望在工作簿中写入多个工作表,则必须指定一个ExcelWriter对象 2 df2 = df1.copy() 3 with pd.ExcelWriter('output.xlsx') as writer: 4 df1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Sheet_name_1') 5 df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Sheet_name_2')
1 # ExcelWriter还可以用于向现有的Excel文件追加内容 2 with pd.ExcelWriter('output.xlsx', mode='a') as writer: 3 df1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Sheet_name_3')
1 # 要设置用于写入Excel文件的库,可以传递engine关键字(根据文件扩展名自动选择默认引擎) 2 df1.to_excel('output1.xlsx', engine='xlsxwriter')
3. 导出为.csv文件
常用函数df.to_csv(),语法如下:
DataFrame.to_csv(path_or_buf=None, *, sep=',', na_rep='', float_format=None, columns=None, header=True, index=True, index_label=None, mode='w', encoding=None, compression='infer', quoting=None, quotechar='"', lineterminator=None, chunksize=None, date_format=None, doublequote=True, escapechar=None, decimal='.', errors='strict', storage_options=None)
参数说明:
- path_or_buf:str, path object, file-like object, or None, default None
String, path object (implementing os.PathLike[str]), or file-like object implementing a write() function. If None, the result is returned as a string. If a non-binary file object is passed, it should be opened with newline=’’, disabling universal newlines. If a binary file object is passed, mode might need to contain a ‘b’.
- sep:str, default ‘,’
String of length 1. Field delimiter for the output file.
- na_rep:str, default ‘’
Missing data representation.
- float_format:str, Callable, default None
Format string for floating point numbers. If a Callable is given, it takes precedence over other numeric formatting parameters, like decimal.
- columns:sequence, optional
Columns to write.
- header:bool or list of str, default True
Write out the column names. If a list of strings is given it is assumed to be aliases for the column names.
- index:bool, default True
Write row names (index).
- index_label:str or sequence, or False, default None
Column label for index column(s) if desired. If None is given, and header and index are True, then the index names are used. A sequence should be given if the object uses MultiIndex. If False do not print fields for index names. Use index_label=False for easier importing in R.
- mode:{‘w’, ‘x’, ‘a’}, default ‘w’
Forwarded to either open(mode=) or fsspec.open(mode=) to control the file opening. Typical values include:
- ‘w’, truncate the file first.
- ‘x’, exclusive creation, failing if the file already exists.
- ‘a’, append to the end of file if it exists.
- encoding:str, optional
A string representing the encoding to use in the output file, defaults to ‘utf-8’. encoding is not supported if path_or_buf is a non-binary file object.
- compression:str or dict, default ‘infer’
For on-the-fly compression of the output data. If ‘infer’ and ‘path_or_buf’ is path-like, then detect compression from the following extensions: ‘.gz’, ‘.bz2’, ‘.zip’, ‘.xz’, ‘.zst’, ‘.tar’, ‘.tar.gz’, ‘.tar.xz’ or ‘.tar.bz2’ (otherwise no compression). Set to None for no compression. Can also be a dict with key 'method' set to one of {'zip', 'gzip', 'bz2', 'zstd', 'xz', 'tar'} and other key-value pairs are forwarded to zipfile.ZipFile, gzip.GzipFile, bz2.BZ2File, zstandard.ZstdCompressor, lzma.LZMAFile or tarfile.TarFile, respectively. As an example, the following could be passed for faster compression and to create a reproducible gzip archive: compression={'method': 'gzip', 'compresslevel': 1, 'mtime': 1}.
- quoting:optional constant from csv module
Defaults to csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL. If you have set a float_format then floats are converted to strings and thus csv.QUOTE_NONNUMERIC will treat them as non-numeric.
- quotechar:str, default ‘"’
String of length 1. Character used to quote fields.
- lineterminator:str, optional
The newline character or character sequence to use in the output file. Defaults to os.linesep, which depends on the OS in which this method is called (’\n’ for linux, ‘\r\n’ for Windows, i.e.).
- chunksize:int or None
Rows to write at a time.
- date_format:str, default None
Format string for datetime objects.
- doublequote:bool, default True
Control quoting of quotechar inside a field.
- escapechar:str, default None
String of length 1. Character used to escape sep and quotechar when appropriate.
- decimal:str, default ‘.’
Character recognized as decimal separator. E.g. use ‘,’ for European data.
- errors:str, default ‘strict’
Specifies how encoding and decoding errors are to be handled. See the errors argument for open() for a full list of options.
- storage_options:dict, optional
Extra options that make sense for a particular storage connection, e.g. host, port, username, password, etc. For HTTP(S) URLs the key-value pairs are forwarded to urllib.request.Request as header options. For other URLs (e.g. starting with “s3://”, and “gcs://”) the key-value pairs are forwarded to fsspec.open.
代码示例:
1 df = pd.DataFrame({'name': ['Raphael', 'Donatello'], 2 'mask': ['red', 'purple'], 3 'weapon': ['sai', 'bo staff']}) 4 df.to_csv('out.csv', index=False)
1 # 创建包含out.csv文件的out.zip文件 2 compression_opts = dict(method='zip', archive_name='out.csv') 3 df.to_csv('out.zip', index=False, compression=compression_opts)
1 # 要将csv文件写入新文件夹或嵌套文件夹,首先需要使用Pathlib或os创建它 2 from pathlib import Path 3 filepath = Path('folder/subfolder/out.csv') 4 filepath.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) 5 df.to_csv(filepath) 6 7 #################################################### 8 9 import os 10 os.makedirs('folder/subfolder', exist_ok=True) 11 df.to_csv('folder/subfolder/out.csv')
时间:2024年2月8日

 Python数据分析-数据导出
Python数据分析-数据导出

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号