spirngMVC注解
笔记
1.@Controller
(1)作用:表示类是一个控制器
(2)源码:作用目标 => 类
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
value(为controller命名)
(3)使用:结合请求处理器@RequestMapper
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
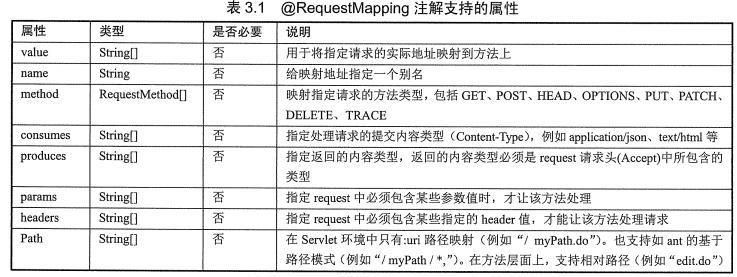
2.@RequestMapper
(1)作用:处理控制器处理的请求动作(访问的url路径)
(2)源码:作用目标 => 类,方法
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}
(3)使用:
value
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
method
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
所有支持的请求方法:
public enum RequestMethod {
GET,
HEAD,
POST,
PUT,
PATCH,
DELETE,
OPTIONS,
TRACE;
consumes
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",consumes = "application/json")
支持提交的内容类型: 百度搜索=>HTTP content-type
produces
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",produces = "application/json")
支持返回的的内容类型与content-type相同
params
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",params = "x=9")
访问需要带上参数x=9
http://localhost:8080/hello?x=9
访问:http://localhost:8080/hello?x=2
返回400
info:Parameter conditions "x=9" not met for actual request parameters: x={2}
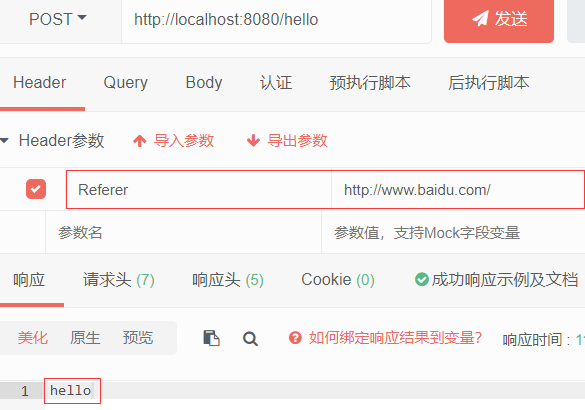
headers
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",headers = "Referer=http://www.baidu.com/")
页面访问:http://localhost:8080/hello
返回404
通过ApiPost发送请求添加请求头
成功返回结果
3.@ResponseBody
(1)作用:此注解标注之后不会再走视图处理器,而是直接将数据写入到输入流中
(2)源码:作用目标 => 类,方法
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ResponseBody {
}
(3)使用
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/res")
@ResponseBody
public String res(Model model){
return "2";
}
4.@RestController
(1)作用:
(2)源码:作用目标=>
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Controller.class
)
String value() default "";
}
(3)使用
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/res")
public String res(){
return "2";
}
等价于
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/res")
@ResponseBody
public String res(){
return "2";
}
5.@RequestParam
(1)作用:将指定的请求参数赋值给方法中的形参
(2)源码:作用目标 => 参数
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestParam {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}
(3)使用
@GetMapping("/param")
@ResponseBody
public String param(@RequestParam(name = "name",required = false,defaultValue = "默认值") String userName){
return userName;
}
6.@PathVariable
(1)作用:获得请求url中的动态参数
(2)源码: 作用目标 => 参数
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface PathVariable {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean required() default true;
}
(3)使用
@GetMapping("/get/{name}")
public String get(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return name;
}
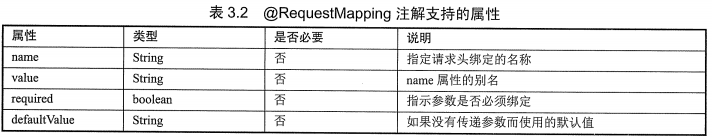
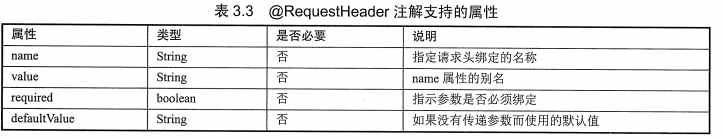
7.@RequestHeader
(1)作用:将请求的头信息数据映射到方法的参数上
(2)源码:作用目标 =>参数
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestHeader {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}
(3)使用
@GetMapping("/get/{name}")
@ResponseBody
public String get(@PathVariable("name") String name,@RequestHeader("User-Agent")String userAgent) {
return name + " [ " + userAgent + " ] ";
}
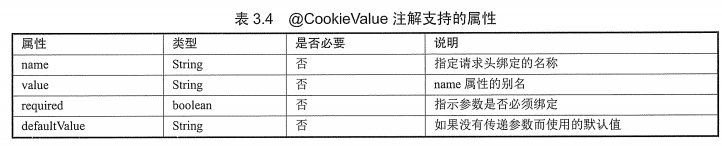
8.@CookieValue
(1)作用:将请求的cookie数据映射到方法的参数上
(2)源码:作用目标=>参数
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CookieValue {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}
(3)使用
@GetMapping("/get")
@ResponseBody
public String get(@CookieValue(value = "JSESSIONID",defaultValue = "")String sessionId) {
return sessionId;
}
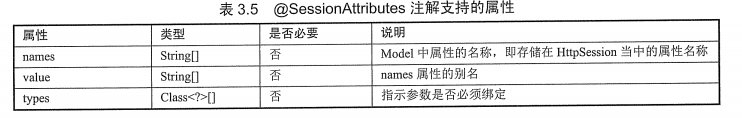
9.@SessionAttributes
(1)作用:指定Model中的哪些属性转存到HttpSession对象当中
(2)源码:作用目标=>类
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface SessionAttributes {
@AliasFor("names")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] names() default {};
Class<?>[] types() default {};
}
(3)使用
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value = "saveName",types = String.class)
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(Model model){
model.addAttribute("saveName","session测试");
return "2";
}
10.@ModelAttribute
(1)作用:向Model对象添加参数
(2)源码:作用目标 => 参数,方法
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ModelAttribute {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean binding() default true;
}
(3)使用
@ModelAttribute
public void myModel(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","myModel");
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String hello1(Model model){
String name = (String)model.asMap().get("name");
return name;
}
时间花在哪里,成就就在哪里


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号