串口协议解析实战:以 R60ABD1 雷达为例,详解 MicroPython 驱动中数据与业务逻辑的分离设计
串口协议解析实战:以 R60ABD1 雷达为例,详解 MicroPython 驱动中数据与业务逻辑的分离设计
摘要:
本文以 R60ABD1 雷达为实战案例,详解 MicroPython 环境下自定义串口通信协议架构的设计与分析方法,聚焦数据解析与业务逻辑分离核心,拆解协议封装、指令交互等关键环节,提供可复用的嵌入式串口驱动开发思路。
原文链接:
正文
一、R60ABD1 数据手册核心信息解析

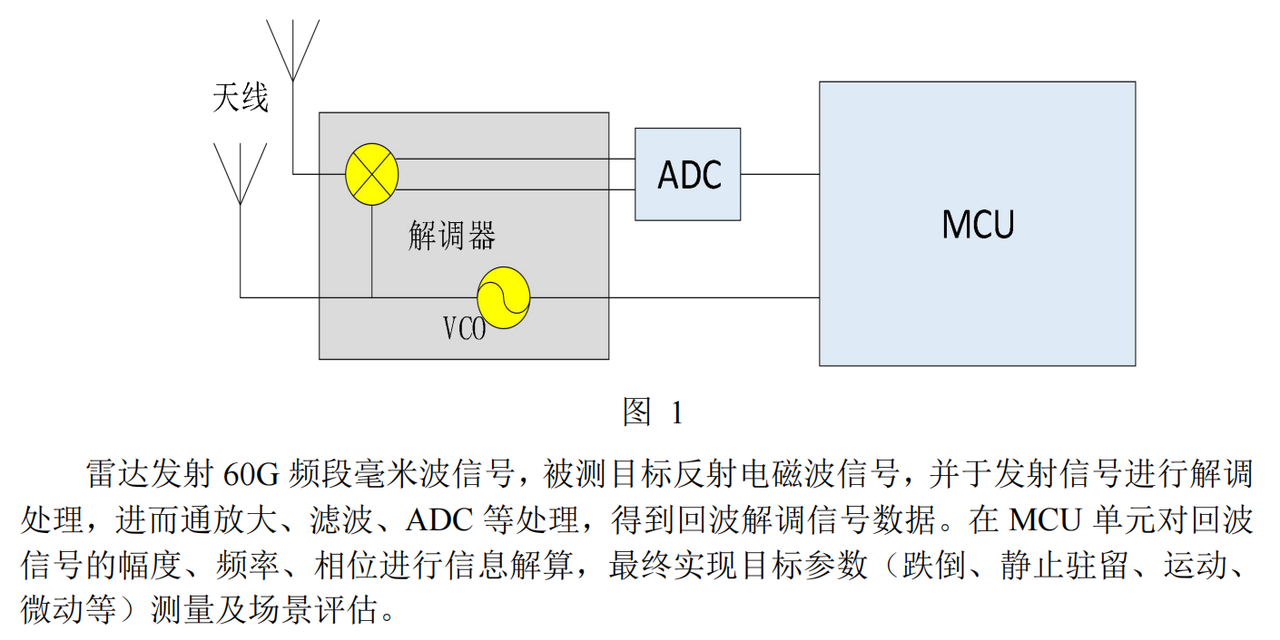
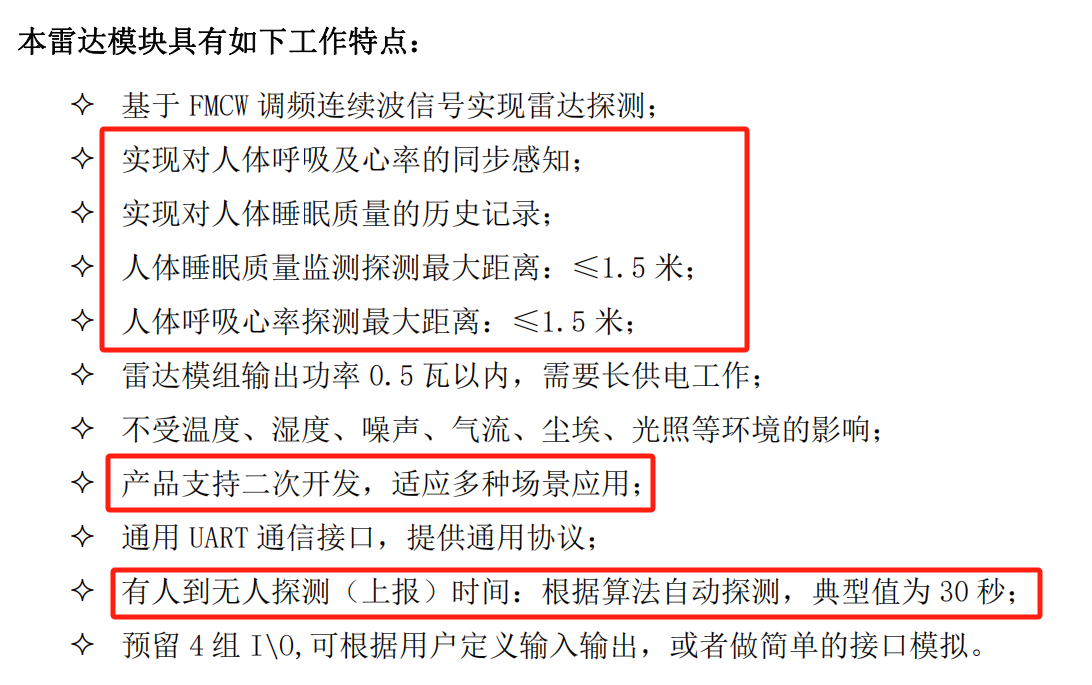
这里,首先我们需要阅读手册相关,可以看到其提供了 UART 接口,并且采用了自定义串口协议:
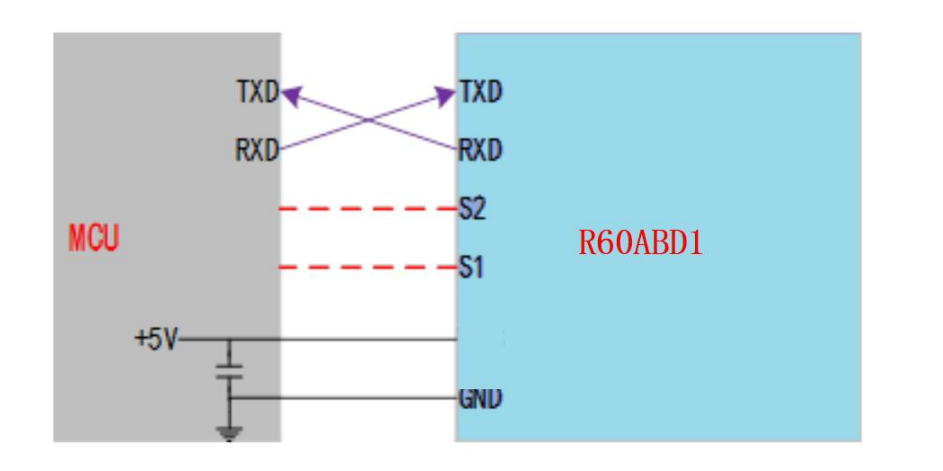
基于该协议,我们可从协议解析层和业务逻辑层进行分层设计,以实现模块化、易维护的 MicroPython 驱动:
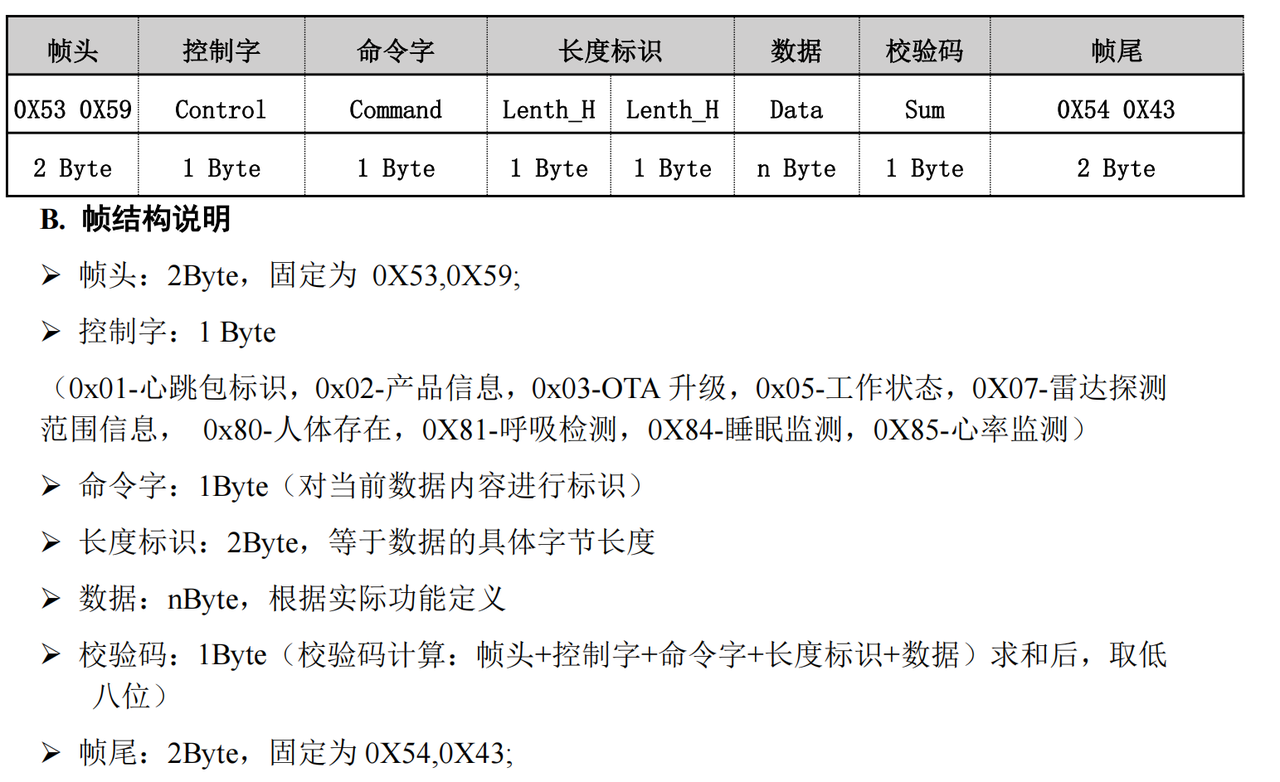
- 在协议解析层,首先需实现帧提取逻辑:通过循环读取串口数据,匹配固定帧头
0X53 0X59来定位一帧的起始;再根据 “长度标识” 字段(2 字节,由Lenth_H和Lenth_L组成,代表数据段的字节长度)确定后续需读取的字节数;最后校验帧尾0X54 0X43,确保整帧数据的完整性,避免断帧、粘帧问题。 - 在业务逻辑层,则封装设备的控制指令(如发送 “配置呼吸监测模式”“查询设备状态” 的指令)和数据应用接口(如实时获取呼吸率、判断人体存在状态、解析睡眠监测结果),使上层业务代码无需关注底层协议的细节,只需调用封装好的方法即可完成设备交互与数据应用。
相关协议可看:

接下来,我们将基于这个分层架构,手把手教大家如何实现 MicroPython 驱动中数据与业务逻辑的分离设计。
二、硬件连接与调试环境搭建(必要前置环节)
在面对任何基于自定义串口协议的设备(如 R60ABD1 呼吸睡眠监测雷达)时,启动二次开发前,有两个 “前置验证环节” 必须优先落地 —— 这不是可有可无的步骤,而是避免后期陷入 “代码逻辑正确却始终跑不通” 的关键:
-
用串口助手逐指令实测: 设备手册对串口协议的描述(如指令格式、响应规则、数据帧结构)本质是 “理论约定”,但实际开发中,受固件版本迭代、生产批次差异甚至文档笔误影响,“手册描述” 与 “设备实际行为” 可能存在偏差。串口助手的核心价值,就是用最直接的 “发送 - 接收” 交互,验证协议细节的真实性。具体操作需围绕三个维度展开:
- 指令完整性验证:按手册定义的格式(帧头、控制字、命令字、参数、校验码、帧尾)手工组装每一条指令(如 R60ABD1 的 “开启呼吸监测” 指令
0x53 0x59 0x01 0x01 0x00 0x00 [校验码] 0x54 0x43),通过串口助手发送后,重点观察返回帧是否符合预期 —— 帧头是否正确(如0x53 0x59)、帧尾是否匹配(如手册写0x54 0x43,实测可能为0x54 0x44)、长度字段是否与数据段字节数一致(避免因长度计算错误导致后续解析丢帧)。 - 响应逻辑验证:测试 “指令 - 响应” 的因果关系是否闭环。例如发送 “配置采样率为 10Hz” 的指令后,观察设备输出数据的频率是否真的变为 10Hz;发送 “查询设备版本号” 指令后,返回数据段的字节是否能解析出合理的版本信息(如
V1.2.3对应的 ASCII 码)。若出现 “发送指令无响应” 或 “响应与指令无关”,需优先排查接线(TX/RX 是否反接)、波特率(是否与设备默认值一致,如 R60ABD1 可能为 115200)、校验方式(是否漏算校验码或计算规则错误)。 - 校验机制有效性验证:故意破坏指令的完整性(如修改某一字节的值、篡改校验码),发送后观察设备是否拒绝响应或返回错误帧 —— 这能验证设备的校验逻辑是否生效。例如 R60ABD1 的校验规则为 “帧头到数据段所有字节累加和的低 8 位”,若修改数据段某字节后设备仍正常响应,说明校验机制可能未启用或手册描述有误,需以实测结果调整解析逻辑。
- 指令完整性验证:按手册定义的格式(帧头、控制字、命令字、参数、校验码、帧尾)手工组装每一条指令(如 R60ABD1 的 “开启呼吸监测” 指令
-
挖掘官方上位机工具: 设备厂商提供的上位机工具是经过官方验证的 “标准交互模板”,其价值远不止于 “可视化显示数据”,更能为驱动开发提供 “锚点式参考”。具体可从三个层面利用上位机工具:
- 设备基础状态确认:通过上位机能否正常连接设备、显示实时数据(如 R60ABD1 的呼吸频率、心率曲线),可快速排除硬件层面的问题 —— 若上位机能正常工作,说明供电(电压是否稳定在 3.3V)、串口接线(电平是否匹配,避免 3.3V 设备接 5V 烧坏)、设备本身(是否故障)均无问题,后续开发可聚焦于软件逻辑;反之,若上位机也无法通信,则需优先排查硬件连接。
- 原始数据日志对照:部分上位机支持 “串口数据日志” 功能(可记录设备收发的每一字节原始数据)。例如启动 R60ABD1 的睡眠监测模式后,上位机日志中会记录设备输出的完整数据帧序列,将这些原始帧与自己用串口助手收到的帧对比:若一致,说明数据接收链路正常,解析错误大概率是逻辑问题;若不一致,需检查串口参数(如停止位是否为 1 位)或缓存机制(是否因接收速度慢导致数据丢失)。
- 协议细节反向推导:当手册对某字段描述模糊,可通过上位机的可视化结果反向映射这种 “现象 → 数据” 的推导,比单纯依赖手册更高效、准确。
这里,在下面的网址中,我们可以找到其上位机:
https://www.micradar.cn/technology-21-208-1.html
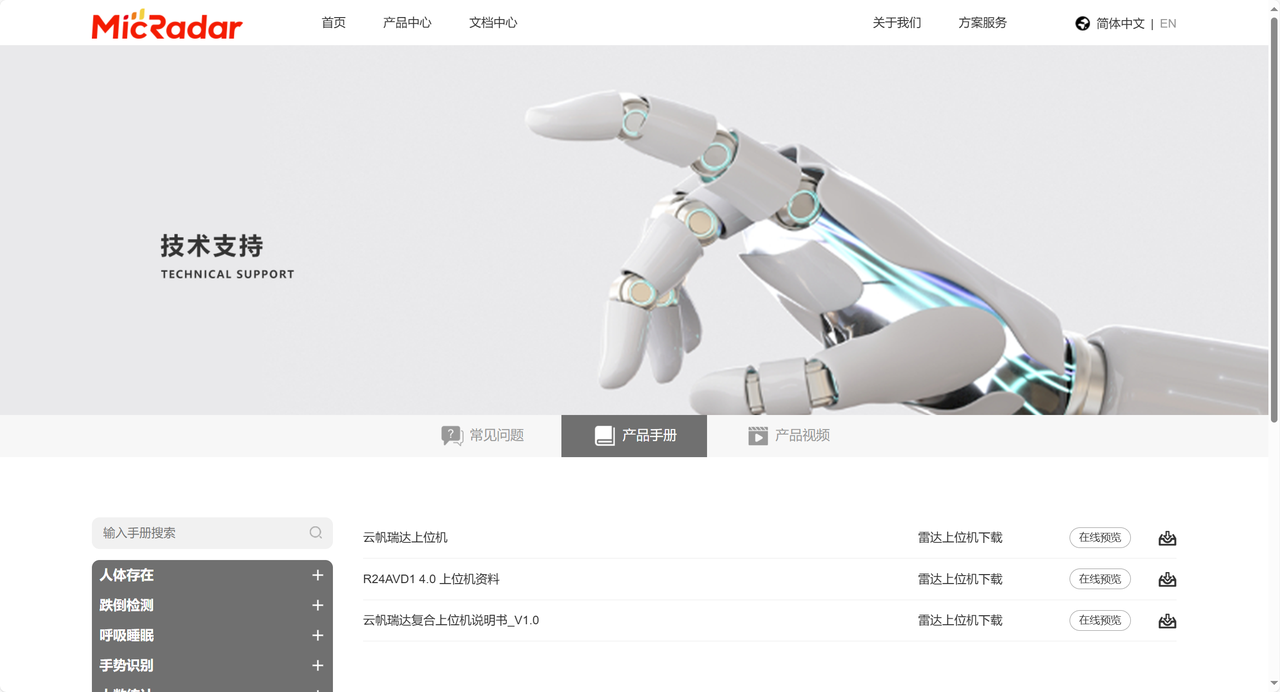
2.1 R60ABD1 指令实测总结
在将模块和 USB 转 TTL 模块连接后,实测相关指令及其响应如下所示:
2.1.1 基础指令信息查询和设置
-
心跳包查询: 53 59 01 80 00 01 0F 3D 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 01 80 00 01 0F 3D 54 43
-
模组复位: 53 59 01 02 00 01 0F BF 54 43
- 回复样例:
53 59 01 02 00 01 0F BF 54 43 # 模组首先原样返回下发的复位指令,作为指令接收确认
53 59 05 01 00 01 0F C2 54 43 # 初始化完成上报
53 59 85 00 00 01 00 32 54 43 # 心率监测功能状态上报。数据 00 表示该功能默认关闭。
53 59 81 00 00 01 00 2E 54 43 # 呼吸监测功能状态上报。数据 00 表示该功能默认关闭。
53 59 84 00 00 01 01 32 54 43 # 睡眠监测功能状态上报。数据 01 表示该功能默认开启。
53 59 84 13 00 01 00 44 54 43 # 人体存在功能状态上报。数据 00 表示该功能默认关闭。
53 59 84 14 00 01 01 46 54 43 # 无人计时功能开关打开
53 59 80 00 00 01 00 2D 54 43 # 人体存在功能打开
53 59 84 0F 00 01 01 41 54 43 # 未知指令
53 59 02 02 00 08 30 2E 30 2E 31 00 00 00 A5 54 43 # 产品 ID 上报,数据 30 2E 30 2E 31 00 转换为 ASCII 是 0.0.1
53 59 02 04 00 10 47 36 30 53 4D 31 53 59 76 30 31 30 33 30 39 00 8F 54 43 # 固件版本上报,数据转换为 ASCII 是 G60SM1SYv010309
53 59 02 03 00 05 52 36 30 41 00 AF 54 43 # 硬件版本上报。数据 52 36 30 41 00 转换为 ASCII 是 R60A。
53 59 84 15 00 01 1E 64 54 43 # 无人计时时长设置为 0x1E (30 分钟)
53 59 84 01 00 01 00 32 54 43 # 入床/离床状态为 00 (离床)
53 59 84 02 00 01 03 36 54 43 # 睡眠状态为 03 (无睡眠状态)
53 59 84 03 00 02 00 00 35 54 43 # 清醒时长为 0000 (0 分钟)
53 59 84 04 00 02 00 00 36 54 43 # 浅睡时长为 0000 (0 分钟)
53 59 84 05 00 02 00 00 37 54 43 # 深睡时长为 0000 (0 分钟)
53 59 84 06 00 01 00 37 54 43 # 睡眠质量评分为 00 (0 分)
53 59 84 0C 00 08 00 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 47 54 43 # 睡眠综合状态数据全 0
53 59 84 0D 00 0C 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 49 54 43 # 睡眠统计数据全 0
53 59 84 0E 00 01 03 42 54 43 # 睡眠异常状态为 0x03 (无)
53 59 84 10 00 01 00 41 54 43 # 睡眠质量评级为 0x00 (无)
53 59 84 16 00 01 0A 51 54 43 # 睡眠截止时长设置为 0x0A 分钟(即 10 分钟)
53 59 84 12 00 01 01 44 54 43 # 无人计时状态为 0x01 (正常)
-
产品型号查询: 53 59 02 A1 00 01 0F 5F 54 43
- 回复样例:
53 59 02 A1 00 08 52 36 30 41 53 4D 31 00 21 54 43R60ASM1(16进制为52 36 30 41 53 4D 31 00)b'R60ASM1\x00'
- 回复样例:
-
产品ID查询: 53 59 02 A2 00 01 0F 60 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 02 A2 00 08 30 2E 30 2E 31 00 00 00 45 54 43
b'0.0.1\x00\x00\x00'
-
硬件型号查询: 53 59 02 A3 00 01 0F 61 54 43
- 回复样例:
53 59 02 A3 00 05 52 36 30 41 00 4F 54 43R60A(16进制为52 36 30 41 00)b'R60A\x00'
- 回复样例:
-
固件版本查询: 53 59 02 A4 00 01 0F 62 54 43
- 回复样例:
53 59 02 A4 00 10 47 36 30 53 4D 31 53 59 76 30 31 30 31 30 37 00 2B 54 43G60SM1SYv010107(16进制为47 36 30 53 4D 31 53 59 76 30 31 30 31 30 37 00)b'G60SM1SYv010309\x00'
- 回复样例:
-
初始化是否完成查询: 53 59 05 81 00 01 0F 42 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 05 81 00 01 01 34 54 43
-
雷达探测范围信息位置越界状态查询: 53 59 07 87 00 01 0F 4A 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 07 87 00 01 00 3B 54 43
2.1.2 人体存在指令信息查询和设置
-
开关人体存在功能
- 打开人体存在功能: 53 59 80 00 00 01 01 2E 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 00 00 01 01 2E 54 43
- 关闭人体存在功能: 53 59 80 00 00 01 00 2D 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 00 00 01 00 2D 54 43
- 打开人体存在功能: 53 59 80 00 00 01 01 2E 54 43
-
查询人体存在开关: 53 59 80 80 00 01 0F BC 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 80 00 01 00 AD 54 43
-
存在信息查询: 53 59 80 81 00 01 0F BD 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 81 00 01 01 AF 54 43
-
运动信息查询: 53 59 80 82 00 01 0F BE 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 82 00 01 02 B1 54 43
-
体动参数查询: 53 59 80 83 00 01 0F BF 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 83 00 01 05 B5 54 43
-
人体距离查询: 53 59 80 84 00 01 0F C0 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 84 00 02 00 2F E1 54 43
-
人体方位查询: 53 59 80 85 00 01 0F C1 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 80 85 00 06 80 0F 00 2C 00 00 72 54 43
2.1.3 心率监测指令信息查询和设置
-
开关心率监测功能
- 打开心率监测功能: 53 59 85 00 00 01 01 33 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 00 00 01 01 33 54 43
- 关闭心率监测功能: 53 59 85 00 00 01 00 32 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 00 00 01 00 32 54 43
- 打开心率监测功能: 53 59 85 00 00 01 01 33 54 43
-
查询心率监测开关: 53 59 85 80 00 01 0F C1 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 80 00 01 00 B2 54 43
-
心率波形上报开关设置
- 打开心率波形上报开关: 53 59 85 0A 00 01 01 3D 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 0A 00 01 01 3D 54 43
- 关闭心率波形上报开关: 53 59 85 0A 00 01 00 3C 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 0A 00 01 00 3C 54 43
- 打开心率波形上报开关: 53 59 85 0A 00 01 01 3D 54 43
-
心率波形上报开关查询: 53 59 85 8A 00 01 0F CB 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 8A 00 01 00 BC 54 43
-
心率数值查询: 53 59 85 82 00 01 0F C3 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 82 00 01 50 04 54 43
-
心率波形查询: 53 59 85 85 00 01 0F C6 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 85 85 00 05 C1 BE AA 90 8A FE 54 43
2.1.4 呼吸监测指令信息查询和设置
-
开关呼吸监测功能:
- 打开呼吸监测功能: 53 59 81 00 00 01 01 2F 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 00 00 01 01 2F 54 43
- 关闭呼吸监测功能: 53 59 81 00 00 01 00 2E 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 00 00 01 00 2E 54 43
- 打开呼吸监测功能: 53 59 81 00 00 01 01 2F 54 43
-
查询呼吸监测开关: 53 59 81 80 00 01 0F BD 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 80 00 01 00 AE 54 43
-
低缓呼吸判读设置(默认值 0x0A): 数值范围
10~20(0x0A~0x14),可替换数据字段为其他值,需重新计算校验和。- 设置为20: 53 59 81 0B 00 01 14 4D 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 81 8B 00 01 14 CD 54 43
- 设置为10: 53 59 81 0B 00 01 0A 43 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 81 8B 00 01 0A C3 54 43
- 设置为20: 53 59 81 0B 00 01 14 4D 54 43
-
低缓呼吸判读查询: 53 59 81 8B 00 01 0F C8 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 8B 00 01 0A C3 54 43
-
呼吸信息查询: 53 59 81 81 00 01 0F BE 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 81 00 01 01 B0 54 43
-
呼吸数值查询: 53 59 81 82 00 01 0F BF 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 82 00 01 16 C6 54 43
-
呼吸波形上报开关设置:
- 打开呼吸波形上报开关: 53 59 81 0C 00 01 01 3B 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 0C 00 01 01 3B 54 43
- 关闭呼吸波形上报开关: 53 59 81 0C 00 01 00 3A 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 0C 00 01 00 3A 54 43
- 打开呼吸波形上报开关: 53 59 81 0C 00 01 01 3B 54 43
-
呼吸波形上报开关查询: 53 59 81 8C 00 01 0F C9 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 8C 00 01 00 BA 54 43
-
呼吸波形查询: 53 59 81 85 00 01 0F C2 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 81 85 00 05 C9 60 18 40 9A D2 54 43
2.1.5 睡眠监测指令信息查询和设置
-
开关睡眠监测功能
- 打开睡眠监测功能: 53 59 84 00 00 01 01 32 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 00 00 01 01 32 54 43
- 关闭睡眠监测功能: 53 59 84 00 00 01 00 31 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 00 00 01 00 31 54 43
- 打开睡眠监测功能: 53 59 84 00 00 01 01 32 54 43
-
查询睡眠监测开关: 53 59 84 80 00 01 0F C0 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 80 00 01 00 B1 54 43
-
异常挣扎状态开关设置
- 打开异常挣扎状态: 53 59 84 13 00 01 01 45 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 13 00 01 01 45 54 43
- 关闭异常挣扎状态: 53 59 84 13 00 01 00 44 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 13 00 01 00 44 54 43
- 打开异常挣扎状态: 53 59 84 13 00 01 01 45 54 43
-
异常挣扎状态开关查询: 53 59 84 93 00 01 0F D3 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 93 00 01 00 C4 54 43
-
异常挣扎状态查询: 53 59 84 91 00 01 0F D1 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 91 00 01 00 C2 54 43(0x00 无 0x01 正常状态 0x02 异常挣扎状态)
-
挣扎状态判读设置(灵敏度中 = 0x01):
0x00=低,0x01=中,0x02=高- 设置为0x01: 53 59 84 1A 00 01 01 4C 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 84 1A 00 01 01 4C 54 43
- 设置为0x01: 53 59 84 1A 00 01 01 4C 54 43
-
挣扎状态判读查询: 53 59 84 9A 00 01 0F DA 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 9A 00 01 01 CC 54 43
-
无人计时功能开关设置
- 打开无人计时功能开关: 53 59 84 14 00 01 01 46 54 43
- 回复样例:
- 53 59 84 15 00 01 1E 64 54 43
- 53 59 84 14 00 01 01 46 54 43
- 回复样例:
- 关闭无人计时功能开关: 53 59 84 14 00 01 00 45 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 14 00 01 00 45 54 43
- 打开无人计时功能开关: 53 59 84 14 00 01 01 46 54 43
-
无人计时功能开关查询: 53 59 84 94 00 01 0F D4 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 94 00 01 00 C5 54 43
-
无人计时时长设置(默认值 30分钟 = 0x1E) :数值范围 30-180分钟(
0x1E~0xB4),步长10分钟- 设置为30: 53 59 84 15 00 01 1E 64 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 84 15 00 01 1E 64 54 43
- 设置为30: 53 59 84 15 00 01 1E 64 54 43
-
无人计时时长查询: 53 59 84 95 00 01 0F D5 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 84 95 00 01 1E E4 54 43
-
无人计时状态查询: 53 59 84 92 00 01 0F D2 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 84 92 00 01 01 C4 54 43
-
睡眠截止时长设置(默认值 5分钟 = 0x05): 数值范围 5-120分钟(
0x05~0x78)- 设置为5: 53 59 84 16 00 01 05 4C 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 84 16 00 01 05 4C 54 43
- 设置为10: 53 59 84 16 00 01 0A 51 54 43
- 回复样例: 53 59 84 16 00 01 0A 51 54 43
- 设置为5: 53 59 84 16 00 01 05 4C 54 43
-
睡眠截止时间查询: 53 59 84 96 00 01 0F D6 54 43
- 回复样例:
- 53 59 84 96 00 01 0A D1 54 43
- 53 59 84 9A 00 01 01 CC 54 43
- 回复样例:
-
入床/离床状态查询: 53 59 84 81 00 01 0F C1 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 81 00 01 01 B3 54 43
-
睡眠状态查询: 53 59 84 82 00 01 0F C2 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 82 00 01 02 B5 54 43
-
清醒时长查询: 53 59 84 83 00 01 0F C3 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 83 00 02 00 32 E7 54 43
-
浅睡时长查询: 53 59 84 84 00 01 0F C4 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 84 00 02 00 00 B6 54 43
-
深睡时长查询: 53 59 84 85 00 01 0F C5 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 85 00 02 00 00 B7 54 43
-
睡眠质量评分查询: 53 59 84 86 00 01 0F C6 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 86 00 01 00 B7 54 43
-
睡眠综合状态查询: 53 59 84 8D 00 01 0F CD 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 8D 00 08 01 02 12 4B 00 26 3E 00 89 54 43
-
睡眠异常查询: 53 59 84 8E 00 01 0F CE 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 8E 00 01 03 C2 54 43
-
睡眠统计查询: 53 59 84 8F 00 01 0F CF 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 8F 00 0C 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 CB 54 43
-
睡眠质量评级查询: 53 59 84 90 00 01 0F D0 54 43
- 回复样例:53 59 84 90 00 01 00 C1 54 43
2.2 R60ABD1相关问题总结
在实际测试过程中,我们实际上发现了以下问题,在后续驱动代码编写中需要注意,这里我记录了问题的情况和具体版本号。
2.2.1 关闭四项主动上报后重启,单独开启任一功能无数据响应
在新版固件(G60SM1SYv010309)上,发现一个异常操作序列:
- 第N次操作:依次关闭人体存在、心率、呼吸、睡眠这四项功能的主动上报后,对毫米波雷达模组执行断电再上电。
- 第N+1次操作:模组重启后,此时单独开启其中任一功能,均无法收到相应的主动上报数据。
- 第N+2次操作:将四项功能的主动上报全部开启,并再次对模组执行断电重启。此后,所有主动上报功能均恢复正常工作,且在此次上电周期内,任意开启或关闭单一功能,都能得到预期的响应。
如下为在新版固件(G60SM1SYv010309)上进行测试的过程:
如下,为在旧版本固件(G60SM1SYv010107)上进行的相同测试:
可以看到当所有主动上报功能被禁用后,模组在断电重启过程中未能正确初始化其功能状态机或配置寄存器,导致系统进入了一个功能“静默”的异常状态。
这里,笔者猜测根本原因可能源于固件的状态管理逻辑存在缺陷。具体分析如下:
- 配置存储与加载异常:
- 推测:设备的使能状态标志可能存储于非易失性存储器中。当所有功能关闭时,存储的或许是一个特殊的“全关”状态值。模组在下次启动加载该配置时,固件可能错误地将此状态解析为“不进行任何上报”,而非“等待用户指令”,从而阻塞了所有上报通道。
- 佐证:只有再次“全部开启”并重启后,存储的状态被更新,系统才恢复正常。这表明正确的配置在第二次重启后被成功加载。
- 功能状态机死锁:
- 推测:各个上报功能可能共享一个公共的使能逻辑或硬件资源。当所有功能被禁用时,该逻辑可能错误地进入了一个休眠或锁死状态。此时,通过指令单独开启某一功能,无法有效触发状态机的解锁。而同时开启所有功能,则发送了一个足够强的“全局唤醒”信号,重置了整个状态机。
- 底层驱动或中间件漏洞:
- 推测:负责管理雷达传感器核心功能的底层驱动或中间件,可能存在一个边界条件漏洞。当它检测到没有任何主动上报功能需要服务时,可能会彻底关闭数据采集或中断服务例程。而重新激活该采集流程需要一个更高级别的初始化命令(即“全部开启”),而非单个功能的开关指令。
2.2.2 开启无人计时功能时响应与手册所写不一致
在新版固件(G60SM1SYv010309)上,发现一个异常操作序列,版本信息如下:
- 固件版本:
G60SM1SYv010309(16进制为47 36 30 53 4D 31 53 59 76 30 31 30 33 30 39 00) - 产品型号:
R60ASM1(16进制为52 36 30 41 53 4D 31 00) - 硬件版本:
R60A(16进制为52 36 30 41 00)
问题如下:
- 预期行为(根据手册):
- 主机下发设置指令:53 59 84 14 00 01 01 ...
- 从设备回复确认帧:53 59 84 14 00 01 01 ... (原样返回,作为操作成功的确认)
- 观察到的实际行为:
- 主机下发设置指令:53 59 84 14 00 01 01 46 54 43 (开启无人计时功能)
- 从设备回复了两条信息:
- 第一条:53 59 84 15 00 01 1E 64 54 43 (这是一个对命令字 0x15 ——“无人计时时长查询”的响应,数据 1E 表示时长为30分钟)
- 第二条:53 59 84 14 00 01 01 46 54 43 (这才是手册中描述的,对设置命令的正确确认帧)
这种行为不符合典型的“命令-应答”模式,当开启无人计时功能时,固件内部自动触发了一次无人计时时长的查询操作。
2.2.3 设置睡眠截止时长时响应与手册所写不一致
在新版固件(G60SM1SYv010309)上,发现一个异常操作序列,版本信息如下:
- 固件版本:G60SM1SYv010309(16进制为 47 36 30 53 4D 31 53 59 76 30 31 30 33 30 39 00)
- 产品型号:R60ASM1(16进制为 52 36 30 41 53 4D 31 00)
- 硬件版本:R60A(16进制为 52 36 30 41 00)
问题如下:在设置睡眠截止时长后,进行查询操作时,观察到的实际通信序列与手册说明存在不一致:
- 设置睡眠截止时长(10分钟):
- 发送指令:53 59 84 16 00 01 0A 51 54 43
- 收到确认回复:53 59 84 16 00 01 0A 51 54 43(符合预期,设备原样返回确认帧)。 - 后续查询操作:
- 发送睡眠截止时间查询指令:53 59 84 96 00 01 0F D6 54 43
- 收到两条回复:- 第一条回复:53 59 84 96 00 01 0A D1 54 43(预期中的查询回复,数据 0A 表示睡眠截止时长为10分钟)。
- 第二条回复:53 59 84 9A 00 01 01 CC 54 43(非预期的回复,对应命令字 0x9A,即“挣扎状态判读查询”的回复,数据 01 表示灵敏度为中)。
在睡眠截止时间查询后,设备额外返回了一个“挣扎状态判读”的回复帧,而主机并未发送该查询指令。
三、MicroPython 驱动整体架构设计
3.1 整体架构设计
整体架构采用 “数据解析与业务逻辑分离” 的设计思路,核心包含两个组件:DataFlowProcessor与 R60ABD1,通过明确分工实现模块化协作:
DataFlowProcessor专注于 “数据管道” 的底层处理:负责从串口读取原始字节流,维护缓冲区以应对粘包、半包问题,通过帧头、帧尾标识拆分出完整数据帧,并从帧中解析出DP标识(数据点ID)与对应原始数据,最终输出 (dp_id,raw_data) 结构。这一组件完全不涉及业务逻辑,例如它不会处理 “dp_id=1对应有人 / 无人状态” 这类映射,仅负责数据的流转与格式提取,实现了与业务的彻底解耦。这种设计带来显著的复用价值 —— 若更换同系列传感器(帧头、帧尾等基础协议一致,仅DP定义不同),可直接复用该组件,只需修改上层业务逻辑即可。R60ABD1组件则聚焦于业务属性管理:它持有DataFlowProcessor实例,通过定时器触发数据读取流程,接收其输出的 (dp_id,raw_data) 后,负责将原始数据转换为具体业务属性(例如将raw_data=0x01映射为 “有人状态”),并提供简洁的属性查询接口(如获取当前人体存在状态、心率值等)。两者通过组合关系协作,使整体逻辑更清晰精简,符合嵌入式开发的 “功能模块化” 思想。
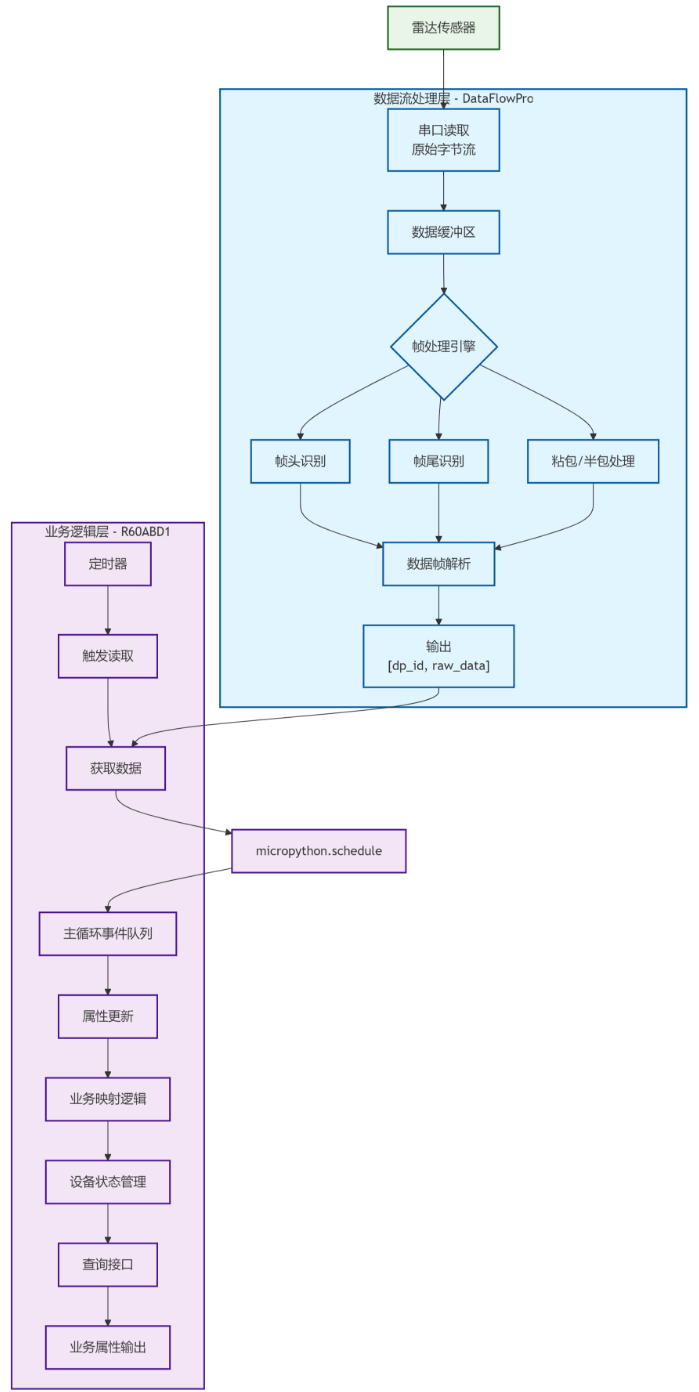
此外,设计中引入 micropython.schedule 机制保障系统稳定性:定时器回调属于中断上下文,若直接在其中执行属性更新(_update_properties,可能涉及内存操作或复杂计算),易引发中断嵌套、资源竞争等问题,甚至导致系统崩溃。而 schedule 会将更新操作放入主循环的事件队列,在合适时机执行,避免了中断上下文的风险。
对于缓冲区中出现的粘包或半包数据,考虑到雷达输出的是实时监测数据,无需保留历史不完整帧,直接丢弃即可。这种处理方式可简化缓冲区逻辑,避免复杂的帧恢复机制,同时因实时数据会持续输出,后续完整帧能快速补充,不影响监测的连续性。
3.2 DataFlowProcessor类的设计与性能验证
在R60ABD1呼吸睡眠监测毫米波雷达的MicroPython驱动开发中,数据解析层与业务逻辑层的分离设计是确保代码可维护性与性能的关键。以下从定时周期确定、DataFlowProcessor功能架构、性能测试验证三个维度,详解其设计与实现逻辑。
3.2.1 定时器调用周期的确定:匹配设备数据输出频率
要确保串口数据无丢失、无积压,需先明确设备的数据帧输出间隔。通过串口助手对R60ABD1的实时数据监测,发现两个数据帧之间的最短间隔约为 100ms(主动上报情况下,如果是命令-响应模式最短30ms左右)。
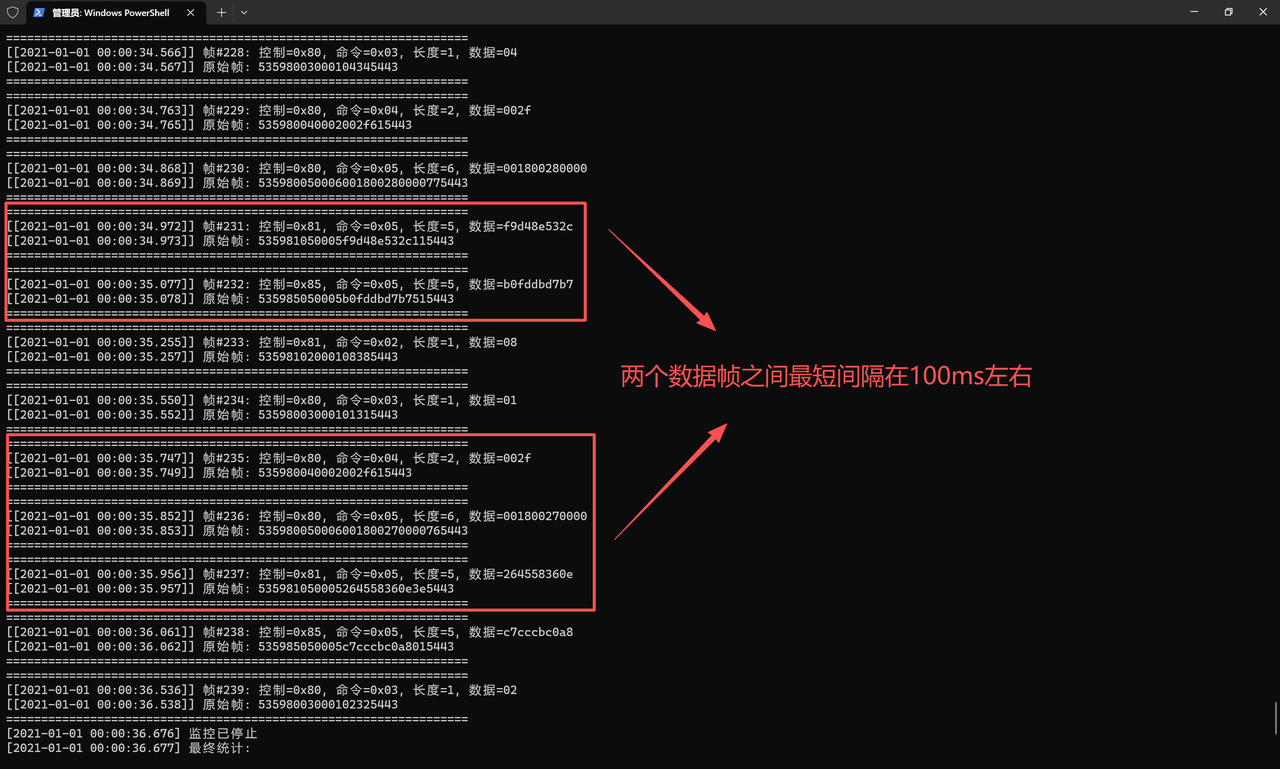
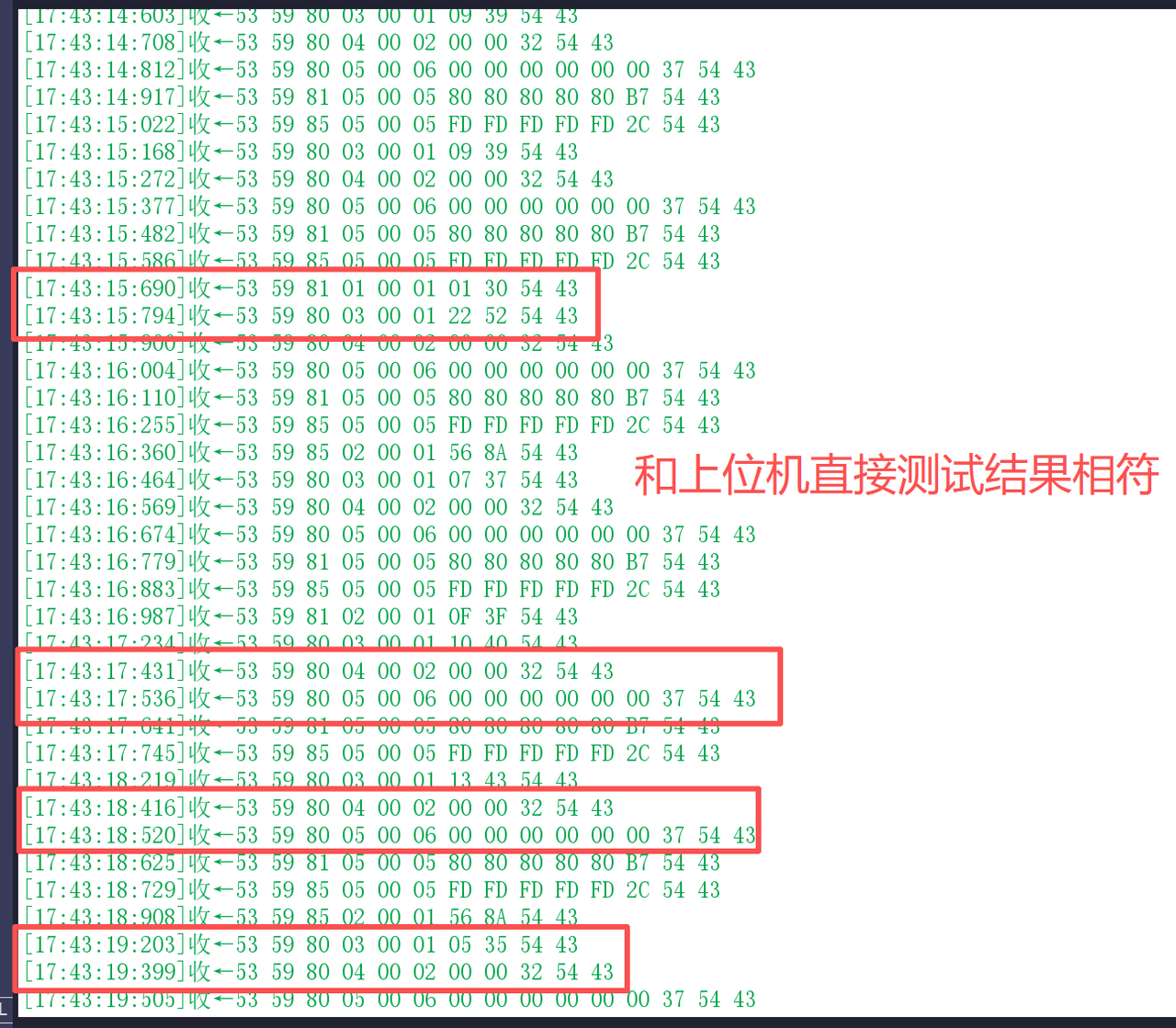
基于此,与DataFlowProcessor实例配合的定时器触发周期需设置为 小于 100ms (例如 50ms)。这样既能及时读取串口缓冲区数据,又不会因触发过于频繁占用过多系统资源,从而实现数据的高效、无丢失采集。
3.2.2 DataFlowProcessor类-解耦数据管道与业务逻辑的核心组件
DataFlowProcessor类是 “数据解析层” 的核心,专注于串口数据的流转与协议解析,完全与业务逻辑(如 “呼吸率映射为具体数值”)解耦。其设计遵循 “高内聚、低耦合” 的模块化思想,以下从属性定义和方法功能两方面展开说明。
3.2.2.1 核心属性:承载数据与状态
class DataFlowProcessor:
def __init__(self, uart):
self.uart = uart # 串口通信实例,负责底层收发
self.buffer = bytearray() # 数据缓冲区,处理粘包/半包
self.stats = { # 统计信息,用于调试与异常分析
'total_bytes_received': 0,
'total_frames_parsed': 0,
'crc_errors': 0,
'frame_errors': 0,
'invalid_frames': 0
}
self.max_buffer_size = 128 # 缓冲区容量限制,防止内存溢出
# 帧结构常量(与协议强绑定)
self.HEADER = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
self.TRAILER = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
# 各字段长度定义(帧头、控制字、命令字等)
self.HEADER_LEN = 2
self.CONTROL_LEN = 1
self.COMMAND_LEN = 1
self.LENGTH_LEN = 2
self.CRC_LEN = 1
self.TRAILER_LEN = 2
self.MIN_FRAME_LEN = self.HEADER_LEN + self.CONTROL_LEN + self.COMMAND_LEN + self.LENGTH_LEN + self.CRC_LEN + self.TRAILER_LEN
3.2.2.2 核心方法:从 “数据读取” 到 “帧解析” 的完整链路
3.2.2.2.1 read_and_parse 数据读取与帧解析的入口
该方法是数据处理的 “主流程”,负责:
- 从串口读取数据(每次最多读 32 字节,避免阻塞);
- 管理缓冲区(防止溢出,清理已解析数据);
- 循环提取完整数据帧,执行帧头识别、长度解析、帧尾验证、CRC 校验;
- 返回解析成功的帧列表,供上层业务逻辑使用。
def read_and_parse(self):
data = self.uart.read(32) # 单次读取32字节,平衡效率与阻塞风险
if not data:
return []
self.stats['total_bytes_received'] += len(data)
self.buffer.extend(data) # 数据存入缓冲区
frames = []
processed_bytes = 0
while len(self.buffer) - processed_bytes >= self.MIN_FRAME_LEN:
# 查找帧头(_find_header)
header_pos = self._find_header(processed_bytes)
if header_pos == -1:
break
# 解析数据长度(_parse_data_length)
length_pos = header_pos + self.HEADER_LEN + self.CONTROL_LEN + self.COMMAND_LEN
data_len = self._parse_data_length(length_pos)
total_frame_len = self.HEADER_LEN + self.CONTROL_LEN + self.COMMAND_LEN + self.LENGTH_LEN + data_len + self.CRC_LEN + self.TRAILER_LEN
# 提取并验证完整帧(帧尾_validate_trailer、CRC_validate_crc)
frame_data = self.buffer[header_pos:header_pos+total_frame_len]
if not self._validate_trailer(frame_data):
self.stats['frame_errors'] += 1
processed_bytes = header_pos + 1
continue
if not self._validate_crc(frame_data):
self.stats['crc_errors'] += 1
processed_bytes = header_pos + total_frame_len
continue
# 解析单帧(_parse_single_frame)
parsed_frame = self._parse_single_frame(frame_data)
if parsed_frame:
frames.append(parsed_frame)
self.stats['total_frames_parsed'] += 1
else:
self.stats['invalid_frames'] += 1
processed_bytes = header_pos + total_frame_len
# 清理已处理数据
if processed_bytes > 0:
self.buffer = self.buffer[processed_bytes:]
return frames
3.2.2.2.2 帧头、长度、帧尾、CRC 的辅助解析方法
相关方法如下:
_find_header(start_pos):在缓冲区中线性搜索帧头0x53 0x59,定位一帧的起始位置;_parse_data_length(length_pos):按大端格式解析 “数据长度” 字段,确定数据段的字节数;_validate_trailer(frame_data):验证帧尾0x54 0x43,确保帧结构完整;_validate_crc(frame_data):对 “帧头到数据段” 的所有字节求和,取低 8 位与帧中 CRC 字段比对,过滤无效帧;_parse_single_frame(frame_data):将完整帧拆解为 “帧头、控制字、命令字、数据、CRC、帧尾” 等字段,封装为字典返回。
3.2.2.2.3 指令发送与工具方法
相关方法如下:
build_and_send_frame(control_byte, command_byte, data):按协议格式组装指令帧(包含帧头、控制字、命令字、长度、数据、CRC、帧尾),并通过串口发送,支持设备配置(如切换监测模式);get_stats():返回数据流转的统计信息(接收字节数、解析帧数、各类错误数),用于调试;clear_buffer():清空缓冲区,在异常恢复或重连时使用。
3.2.2.2.4 完整代码
如下所示:
# Python env : MicroPython v1.23.0
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/11/4 下午6:38
# @Author : 李清水
# @File : data_flow_processor.py
# @Description : 用于处理R60ABD1雷达设备串口通信协议的数据流处理器类相关代码
# @License : CC BY-NC 4.0
# ======================================== 导入相关模块 =========================================
# ======================================== 全局变量 ============================================
# ======================================== 功能函数 ============================================
# ======================================== 自定义类 ============================================
class DataFlowProcessor:
"""
R60ABD1 雷达设备串口通信协议的数据流处理器类。
负责处理雷达设备的串口数据通信,包括数据帧的接收、解析、校验和发送。
Attributes:
uart (UART): 串口通信实例,用于数据收发。
buffer (bytearray): 数据缓冲区,用于存储接收到的原始字节数据。
stats (dict): 数据流转与解析统计信息字典,包含:
total_bytes_received (int): 总接收字节数
total_frames_parsed (int): 总解析帧数
crc_errors (int): CRC校验错误次数
frame_errors (int): 帧结构错误次数
invalid_frames (int): 无效帧次数
max_buffer_size (int): 缓冲区最大容量限制。
Methods:
__init__(uart): 初始化数据流处理器。
read_and_parse(): 读取串口数据并解析完整帧。
_find_header(start_pos=0): 在缓冲区中查找帧头位置。
_parse_data_length(length_pos): 解析数据长度(大端格式)。
_validate_trailer(frame_data): 验证帧尾。
_validate_crc(frame_data): 验证CRC校验码。
_parse_single_frame(frame_data): 解析单个数据帧。
get_stats(): 获取数据流转与解析统计信息。
clear_buffer(): 清空缓冲区。
build_and_send_frame(control_byte, command_byte, data=b''): 构建并发送数据帧。
_calculate_crc(data_bytes): 计算CRC校验码。
==========================================
Data flow processor class for R60ABD1 radar device UART communication protocol.
Handles UART data communication for radar devices, including data frame reception,
parsing, validation, and transmission.
Attributes:
uart (UART): UART communication instance for data transmission and reception.
buffer (bytearray): Data buffer for storing received raw byte data.
stats (dict): Data flow and parsing statistics dictionary containing:
total_bytes_received (int): Total bytes received
total_frames_parsed (int): Total frames parsed
crc_errors (int): CRC validation error count
frame_errors (int): Frame structure error count
invalid_frames (int): Invalid frame count
max_buffer_size (int): Maximum buffer capacity limit.
Methods:
__init__(uart): Initialize data flow processor.
read_and_parse(): Read UART data and parse complete frames.
_find_header(start_pos=0): Find frame header position in buffer.
_parse_data_length(length_pos): Parse data length (big-endian format).
_validate_trailer(frame_data): Validate frame trailer.
_validate_crc(frame_data): Validate CRC checksum.
_parse_single_frame(frame_data): Parse single data frame.
get_stats(): Get data flow and parsing statistics.
clear_buffer(): Clear buffer.
build_and_send_frame(control_byte, command_byte, data=b''): Build and send data frame.
_calculate_crc(data_bytes): Calculate CRC checksum.
"""
def __init__(self, uart):
"""
初始化数据流处理器。
Args:
uart (UART): 已初始化的串口实例,用于数据收发。
Returns:
None
Note:
- 初始化时创建空缓冲区和统计信息字典。
- 定义帧结构相关常量,包括帧头、帧尾、各字段长度等。
- 设置缓冲区最大容量为128字节,防止内存溢出。
==========================================
Initialize data flow processor.
Args:
uart (UART): Initialized UART instance for data transmission and reception.
Returns:
None
Note:
- Creates empty buffer and statistics dictionary during initialization.
- Defines frame structure constants including header, trailer, field lengths, etc.
- Sets maximum buffer capacity to 128 bytes to prevent memory overflow.
"""
self.uart = uart
self.buffer = bytearray()
self.stats = {
'total_bytes_received': 0,
'total_frames_parsed': 0,
'crc_errors': 0,
'frame_errors': 0,
'invalid_frames': 0
}
self.max_buffer_size = 128
# 帧结构常量定义
self.HEADER = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
self.TRAILER = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
self.HEADER_LEN = 2
self.CONTROL_LEN = 1
self.COMMAND_LEN = 1
self.LENGTH_LEN = 2
self.CRC_LEN = 1
self.TRAILER_LEN = 2
self.MIN_FRAME_LEN = self.HEADER_LEN + self.CONTROL_LEN + self.COMMAND_LEN + self.LENGTH_LEN + self.CRC_LEN + self.TRAILER_LEN
def read_and_parse(self):
"""
读取串口数据并解析完整帧。
Args:
无
Returns:
list: 解析成功的数据帧列表,每个元素为解析后的帧字典。
[]: 无完整帧或解析失败时返回空列表。
Raises:
Exception: 底层串口操作可能抛出的异常会向上传播。
Note:
- 每次读取最多32字节数据,避免阻塞时间过长。
- 采用滑动窗口方式处理缓冲区,逐步解析完整帧。
- 自动处理CRC校验和帧结构验证,统计各类错误信息。
- 方法执行期间会更新统计信息,调用get_stats()可获取最新状态。
==========================================
Read UART data and parse complete frames.
Args:
None
Returns:
list: List of successfully parsed data frames, each element is a parsed frame dictionary.
[]: Returns empty list when no complete frames or parsing fails.
Raises:
Exception: Underlying UART operations may raise exceptions that propagate upward.
Note:
- Reads up to 32 bytes per call to avoid long blocking times.
- Uses sliding window approach to process buffer and gradually parse complete frames.
- Automatically handles CRC validation and frame structure verification, statistics various error types.
- Updates statistics during execution, call get_stats() to get latest status.
"""
# 读取串口数据
data = self.uart.read(32)
if not data:
return []
# 更新统计信息
self.stats['total_bytes_received'] += len(data)
# 检查缓冲区大小
if len(self.buffer) > self.max_buffer_size:
self.clear_buffer()
# 将数据添加到缓冲区
self.buffer.extend(data)
frames = []
processed_bytes = 0
while len(self.buffer) - processed_bytes >= self.MIN_FRAME_LEN:
# 查找帧头
header_pos = self._find_header(processed_bytes)
if header_pos == -1:
# 没有找到更多帧头,跳出循环
break
# 从找到的帧头位置开始
current_pos = header_pos
# 检查是否有足够数据解析长度字段
if current_pos + self.HEADER_LEN + self.CONTROL_LEN + self.COMMAND_LEN + self.LENGTH_LEN > len(self.buffer):
break
# 解析数据长度(大端格式)
length_pos = current_pos + self.HEADER_LEN + self.CONTROL_LEN + self.COMMAND_LEN
data_len = self._parse_data_length(length_pos)
# 计算完整帧长度
total_frame_len = self.HEADER_LEN + self.CONTROL_LEN + self.COMMAND_LEN + self.LENGTH_LEN + data_len + self.CRC_LEN + self.TRAILER_LEN
# 检查是否有完整的帧
if current_pos + total_frame_len > len(self.buffer):
break
# 提取完整帧数据
frame_end = current_pos + total_frame_len
frame_data = self.buffer[current_pos:frame_end]
# 验证帧尾
if not self._validate_trailer(frame_data):
self.stats['frame_errors'] += 1
# 帧尾错误,跳过这个帧头,继续查找下一个
processed_bytes = current_pos + 1
continue
# 验证CRC
if not self._validate_crc(frame_data):
self.stats['crc_errors'] += 1
# CRC错误,跳过这个帧,继续查找下一个
processed_bytes = current_pos + total_frame_len
continue
# 解析单帧
parsed_frame = self._parse_single_frame(frame_data)
if parsed_frame:
frames.append(parsed_frame)
self.stats['total_frames_parsed'] += 1
else:
self.stats['invalid_frames'] += 1
# 移动到下一帧
processed_bytes = current_pos + total_frame_len
# 清理已处理的数据
if processed_bytes > 0:
self.buffer = self.buffer[processed_bytes:]
return frames
def _find_header(self, start_pos=0):
"""
在缓冲区中查找帧头位置。
Args:
start_pos (int): 起始搜索位置,默认为0。
Returns:
int: 找到的帧头位置索引,未找到返回-1。
Note:
- 帧头为固定字节序列 [0x53, 0x59]。
- 搜索范围从start_pos到缓冲区末尾-1(需要连续两个字节)。
- 采用线性搜索算法,时间复杂度O(n)。
==========================================
Find frame header position in buffer.
Args:
start_pos (int): Starting search position, defaults to 0.
Returns:
int: Found header position index, returns -1 if not found.
Note:
- Frame header is fixed byte sequence [0x53, 0x59].
- Search range from start_pos to buffer end-1 (requires two consecutive bytes).
- Uses linear search algorithm with O(n) time complexity.
"""
for i in range(start_pos, len(self.buffer) - 1):
if self.buffer[i] == self.HEADER[0] and self.buffer[i + 1] == self.HEADER[1]:
return i
return -1
def _parse_data_length(self, length_pos):
"""
解析数据长度(大端格式)。
Args:
length_pos (int): 长度字段在缓冲区中的起始位置。
Returns:
int: 解析出的数据长度值,解析失败返回0。
Note:
- 长度字段采用大端格式存储:高字节在前,低字节在后。
- 需要确保length_pos+1不超出缓冲区范围。
- 返回值为数据部分的实际字节长度。
==========================================
Parse data length (big-endian format).
Args:
length_pos (int): Starting position of length field in buffer.
Returns:
int: Parsed data length value, returns 0 if parsing fails.
Note:
- Length field uses big-endian format: high byte first, low byte last.
- Ensures length_pos+1 does not exceed buffer bounds.
- Return value is the actual byte length of data portion.
"""
if length_pos + 1 >= len(self.buffer):
return 0
# 大端格式:高字节在前,低字节在后
return (self.buffer[length_pos] << 8) | self.buffer[length_pos + 1]
def _validate_trailer(self, frame_data):
"""
验证帧尾。
Args:
frame_data (bytes|bytearray): 完整帧数据。
Returns:
bool: 帧尾验证通过返回True,否则返回False。
Note:
- 帧尾为固定字节序列 [0x54, 0x43]。
- 检查帧数据最后两个字节是否匹配帧尾。
- 帧尾验证失败表明帧结构不完整或数据损坏。
==========================================
Validate frame trailer.
Args:
frame_data (bytes|bytearray): Complete frame data.
Returns:
bool: Returns True if trailer validation passes, False otherwise.
Note:
- Frame trailer is fixed byte sequence [0x54, 0x43].
- Checks if last two bytes of frame data match trailer.
- Trailer validation failure indicates incomplete frame structure or data corruption.
"""
if len(frame_data) < 2:
return False
return (frame_data[-2] == self.TRAILER[0] and
frame_data[-1] == self.TRAILER[1])
def _validate_crc(self, frame_data):
"""
验证CRC校验码。
Args:
frame_data (bytes|bytearray): 完整帧数据。
Returns:
bool: CRC验证通过返回True,否则返回False。
Note:
- CRC校验范围:帧头到数据部分(不包括CRC字节和帧尾)。
- 计算方式:对校验数据求和后取低8位。
- CRC位于帧数据倒数第3个字节位置。
==========================================
Validate CRC checksum.
Args:
frame_data (bytes|bytearray): Complete frame data.
Returns:
bool: Returns True if CRC validation passes, False otherwise.
Note:
- CRC check range: from header to data portion (excluding CRC byte and trailer).
- Calculation method: sum check data and take lower 8 bits.
- CRC is located at the third last byte of frame data.
"""
if len(frame_data) < 3:
return False
# 计算校验和(不包括CRC字节和帧尾)
data_to_check = frame_data[:-3]
calculated_crc = sum(data_to_check) & 0xFF
received_crc = frame_data[-3]
return calculated_crc == received_crc
def _parse_single_frame(self, frame_data):
"""
解析单个数据帧。
Args:
frame_data (bytes|bytearray): 完整帧数据。
Returns:
dict|None: 解析成功返回帧信息字典,解析失败返回None。
Raises:
Exception: 解析过程中发生异常时记录错误信息。
Note:
- 按协议格式依次解析:帧头→控制字→命令字→长度字段→数据→CRC→帧尾。
- 返回字典包含所有解析出的字段和原始数据。
- 解析失败会记录到invalid_frames统计中。
==========================================
Parse single data frame.
Args:
frame_data (bytes|bytearray): Complete frame data.
Returns:
dict|None: Returns frame information dictionary on success, None on failure.
Raises:
Exception: Records error information when exceptions occur during parsing.
Note:
- Parses sequentially according to protocol format: header→control→command→length→data→CRC→trailer.
- Return dictionary contains all parsed fields and raw data.
- Parsing failures are recorded in invalid_frames statistics.
"""
try:
pos = 0
# 解析帧头 (2字节)
header = bytes(frame_data[pos:pos + 2])
pos += 2
# 控制字 (1字节)
control_byte = frame_data[pos]
pos += 1
# 命令字 (1字节)
command_byte = frame_data[pos]
pos += 1
# 长度标识 (2字节)
data_length = (frame_data[pos] << 8) | frame_data[pos + 1]
pos += 2
# 数据 (n字节)
data_end = pos + data_length
if data_end > len(frame_data) - 3: # -3 为CRC(1)+帧尾(2)
return None
data = bytes(frame_data[pos:data_end])
pos = data_end
# CRC (1字节)
crc = frame_data[pos]
pos += 1
# 帧尾 (2字节)
trailer = bytes(frame_data[pos:pos + 2])
# 构建解析结果
parsed_frame = {
'header': header,
'control_byte': control_byte,
'command_byte': command_byte,
'data_length': data_length,
'data': data,
'crc': crc,
'trailer': trailer,
'raw_data': bytes(frame_data)
}
return parsed_frame
except Exception as e:
print(f"Frame parsing error: {e}")
return None
def get_stats(self):
"""
获取数据流转与解析统计信息。
Args:
无
Returns:
dict: 包含所有统计信息的字典副本。
Note:
- 返回统计信息的深拷贝,防止外部修改影响内部数据。
- 统计信息包括:接收字节数、解析帧数、各类错误计数等。
==========================================
Get data flow and parsing statistics.
Args:
None
Returns:
dict: Dictionary containing all statistics information (copy).
Note:
- Returns deep copy of statistics to prevent external modifications affecting internal data.
- Statistics include: received bytes, parsed frames, various error counts, etc.
"""
return self.stats.copy()
def clear_buffer(self):
"""
清空缓冲区。
Args:
无
Returns:
None
Note:
- 将缓冲区重置为空bytearray。
- 通常在缓冲区过大或需要重新开始解析时调用。
==========================================
Clear buffer.
Args:
None
Returns:
None
Note:
- Resets buffer to empty bytearray.
- Typically called when buffer is too large or need to restart parsing.
"""
self.buffer = bytearray()
def build_and_send_frame(self, control_byte, command_byte, data=b''):
"""
构建并发送数据帧。
Args:
control_byte (int): 控制字,1字节无符号整数。
command_byte (int): 命令字,1字节无符号整数。
data (bytes): 数据部分,默认为空字节。
Returns:
bytes|None: 构建好的完整帧数据(用于调试),发送失败返回None。
Raises:
Exception: 帧构建或发送过程中发生异常时记录错误信息。
Note:
- 按照协议格式构建完整帧:帧头→控制字→命令字→长度→数据→CRC→帧尾。
- 自动计算数据长度和CRC校验码。
- 通过串口发送构建好的帧数据。
==========================================
Build and send data frame.
Args:
control_byte (int): Control byte, 1-byte unsigned integer.
command_byte (int): Command byte, 1-byte unsigned integer.
data (bytes): Data portion, defaults to empty bytes.
Returns:
bytes|None: Built complete frame data (for debugging), returns None on send failure.
Raises:
Exception: Records error information when exceptions occur during frame building or sending.
Note:
- Builds complete frame according to protocol format: header→control→command→length→data→CRC→trailer.
- Automatically calculates data length and CRC checksum.
- Sends built frame data via UART.
"""
try:
# 帧头
header = self.HEADER
# 控制字和命令字
control = bytes([control_byte])
command = bytes([command_byte])
# 数据长度(大端格式)
data_length = len(data)
length_bytes = bytes([(data_length >> 8) & 0xFF, data_length & 0xFF])
# 组装除CRC和帧尾的部分
frame_without_crc = header + control + command + length_bytes + data
# 计算CRC
crc = self._calculate_crc(frame_without_crc)
# 帧尾A
trailer = self.TRAILER
# 完整帧
complete_frame = frame_without_crc + bytes([crc]) + trailer
# 发送帧
self.uart.write(complete_frame)
return complete_frame
except Exception as e:
print(f"Frame building and sending error: {e}")
return None
def _calculate_crc(self, data_bytes):
"""
计算CRC校验码。
Args:
data_bytes (bytes): 需要计算CRC的数据字节序列。
Returns:
int: 计算出的CRC校验码(1字节)。
Note:
- 校验码计算:对输入数据所有字节求和后,取低8位。
- 此CRC算法为简单求和校验,适用于基本错误检测。
- CRC校验范围通常为帧头到数据部分。
==========================================
Calculate CRC checksum.
Args:
data_bytes (bytes): Data byte sequence for CRC calculation.
Returns:
int: Calculated CRC checksum (1 byte).
Note:
- Checksum calculation: sum all input data bytes and take lower 8 bits.
- This CRC algorithm uses simple sum check, suitable for basic error detection.
- CRC check range typically from header to data portion.
"""
return sum(data_bytes) & 0xFF
# ======================================== 初始化配置 ==========================================
# ======================================== 主程序 ===========================================
3.2.3 性能验证
为确保 DataFlowProcessor 在 MicroPython 环境下的可靠性,需从解析耗时方面验证。
相关测试代码如下:
# Python env :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/11/4 下午5:33
# @Author : 李清水
# @File : main.py
# @Description :
from machine import UART, Pin, Timer
import time
from data_flow_processor import DataFlowProcessor
frame_count = 0
# 存储解析到的数据帧
parsed_frames_buffer = []
# 初始化UART0:TX=16, RX=17,波特率115200
uart = UART(0, baudrate=115200, tx=Pin(16), rx=Pin(17), timeout=0)
# 创建DataFlowProcessor实例
processor = DataFlowProcessor(uart)
# ======================================== 功能函数 ============================================
# 计时装饰器,用于计算函数运行时间
def timed_function(f: callable, *args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> callable:
_"""_
_ 计时装饰器,用于计算并打印函数/方法运行时间。_
_ Args:_
_ f (callable): 需要传入的函数/方法_
_ args (tuple): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的位置参数_
_ kwargs (dict): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的关键字参数_
_ Returns:_
_ callable: 返回计时后的函数_
_ """_
_ _myname = str(f).split(' ')[1]
def new_func(*args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> any:
t: int = time.ticks_us()
result = f(*args, **kwargs)
delta: int = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_us(), t)
print('Function {} Time = {:6.3f}ms'.format(myname, delta / 1000))
return result
return new_func
def format_time():
_"""格式化当前时间为 [YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.sss] 格式"""_
_ _t = time.localtime()
ms = time.ticks_ms() % 1000
return f"[{t[0]}-{t[1]:02d}-{t[2]:02d} {t[3]:02d}:{t[4]:02d}:{t[5]:02d}.{ms:03d}]"
@timed_function
def timer_callback(timer):
_"""定时器回调函数,每50ms触发一次,直接解析数据帧"""_
_ _global frame_count, parsed_frames_buffer
# 直接调用解析方法
frames = processor.read_and_parse()
# 将解析到的帧添加到缓冲区
for frame in frames:
frame_count += 1
parsed_frames_buffer.append({
'frame_number': frame_count,
'control': frame['control_byte'],
'command': frame['command_byte'],
'data_length': frame['data_length'],
'data_hex': frame['data'].hex() if frame['data'] else "",
'raw_hex': frame['raw_data'].hex(),
'timestamp': format_time()
})
# 初始化50ms定时器
timer = Timer(-1)
timer.init(period=50, mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=timer_callback)
try:
while True:
# 检查是否需要打印缓冲区中的帧(每10个打印一次)
if len(parsed_frames_buffer) >= 10:
print("=====================================================")
for frame_data in parsed_frames_buffer:
print("[%s] Frame#%d: Control=0x%02X, Command=0x%02X, Length=%d, Data=%s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['frame_number'], frame_data['control'], frame_data['command'], frame_data['data_length'], frame_data['data_hex']))
print("[%s] Raw frame: %s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['raw_hex']))
print("-" * 60)
print("=====================================================")
# 清空缓冲区
parsed_frames_buffer = []
# 小延迟,避免占用太多CPU
time.sleep(0.01)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# 停止定时器
timer.deinit()
# 打印剩余未输出的帧
if parsed_frames_buffer:
print("=====================================================")
print("[%s] Final output %d parsed frames:" % (format_time(), len(parsed_frames_buffer)))
for frame_data in parsed_frames_buffer:
print("[%s] Frame#%d: Control=0x%02X, Command=0x%02X, Length=%d, Data=%s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['frame_number'], frame_data['control'], frame_data['command'], frame_data['data_length'], frame_data['data_hex']))
print("[%s] Raw frame: %s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['raw_hex']))
print("-" * 60)
# 输出最终统计信息
stats = processor.get_stats()
print("[%s] Final statistics:" % format_time())
print(" Total bytes received: %d" % stats['total_bytes_received'])
print(" Total frames parsed: %d" % stats['total_frames_parsed'])
print(" CRC errors: %d" % stats['crc_errors'])
print(" Frame errors: %d" % stats['frame_errors'])
print(" Invalid frames: %d" % stats['invalid_frames'])
测试结果如下:
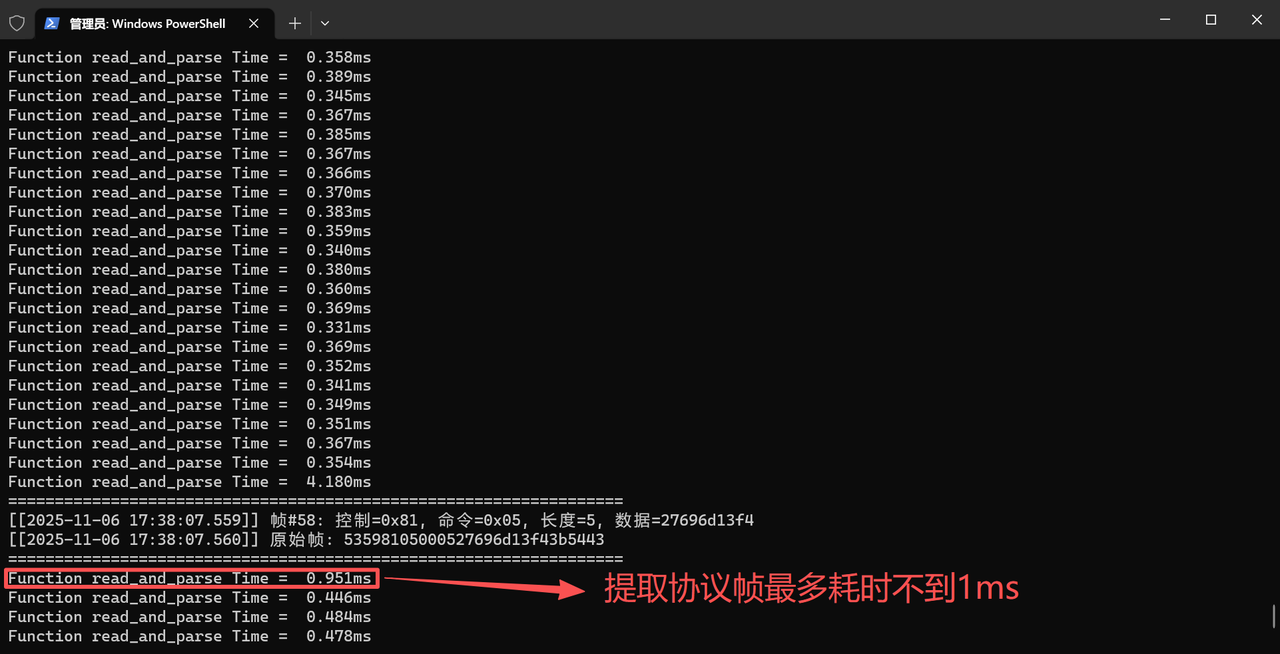
通过在 read_and_parse() 方法中插入时间统计,发现单帧解析耗时最多不到 1ms,远小于数据帧的最短间隔(100ms)。这意味着即使在 MicroPython 的解释性执行环境下,该组件也能及时处理数据,不会因解析耗时导致数据积压或丢失。
3.3 R60ABD1 类的设计:业务逻辑层的模块化封装
R60ABD1 类作为业务逻辑层的核心,负责将 DataFlowProcessor 解析出的原始数据映射为可读的业务属性(如呼吸率、心率、睡眠状态等),并提供设备控制接口。其设计遵循 “功能模块化、状态清晰化” 的原则,以下从实例属性、类属性与常量、私有解析方法、测试验证四个维度展开说明。
3.3.1 实例属性设计:按功能模块分层隔离
根据手册下面的描述,我们首先归纳实例属性包括哪些:
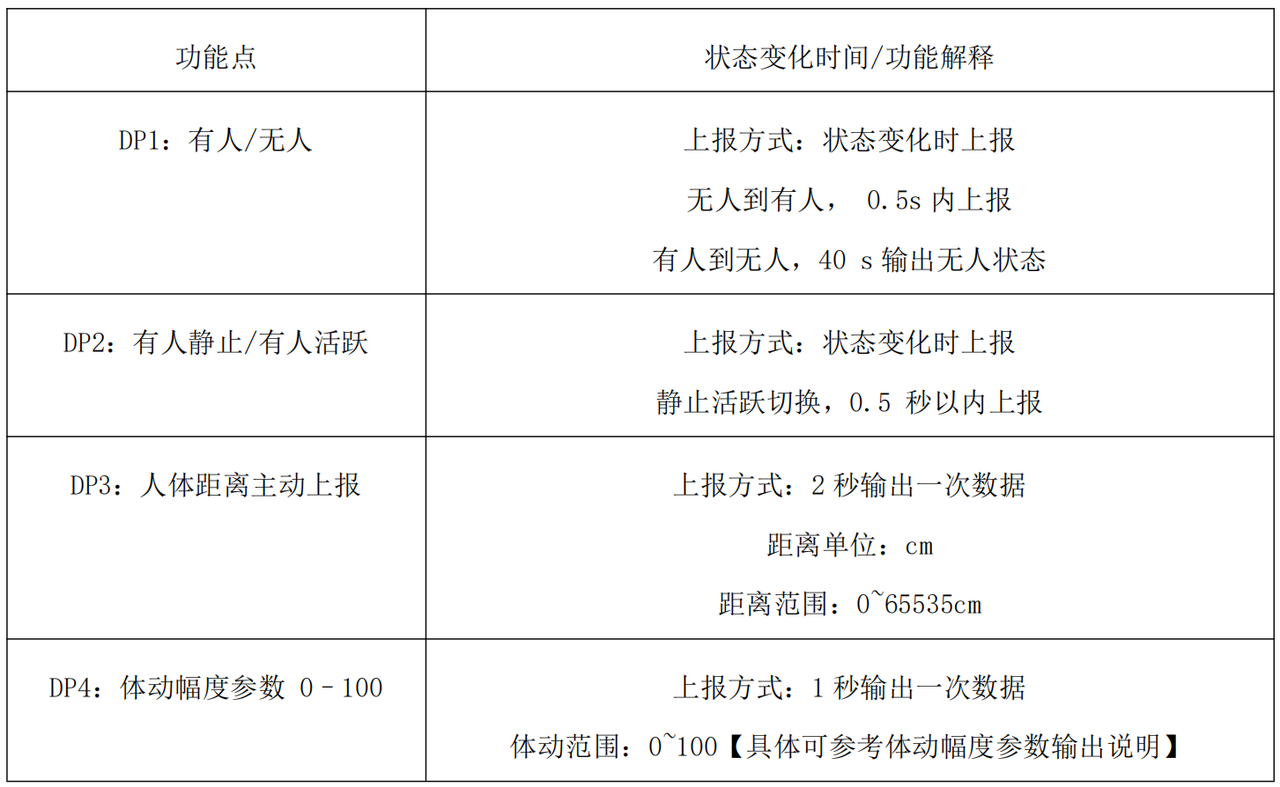
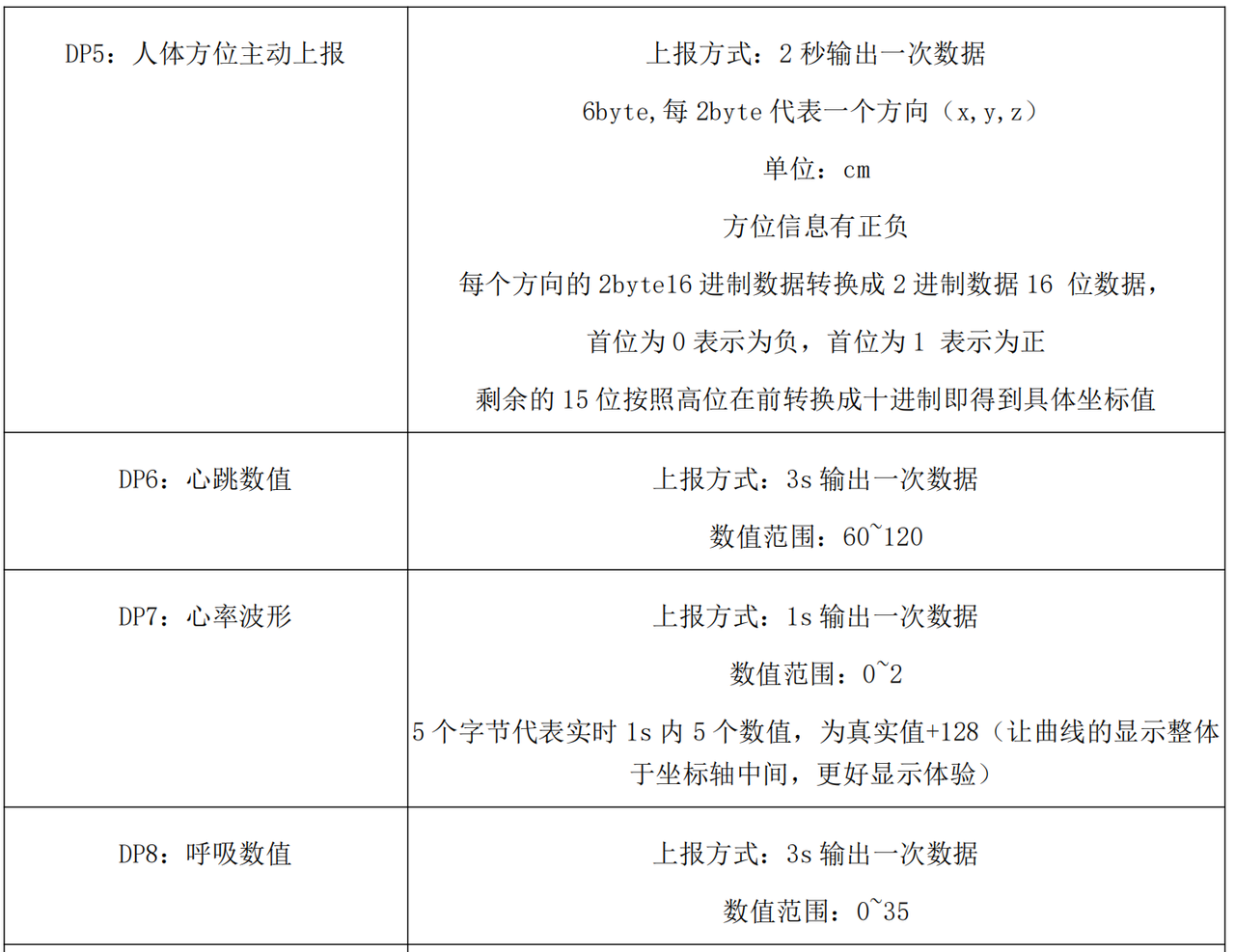
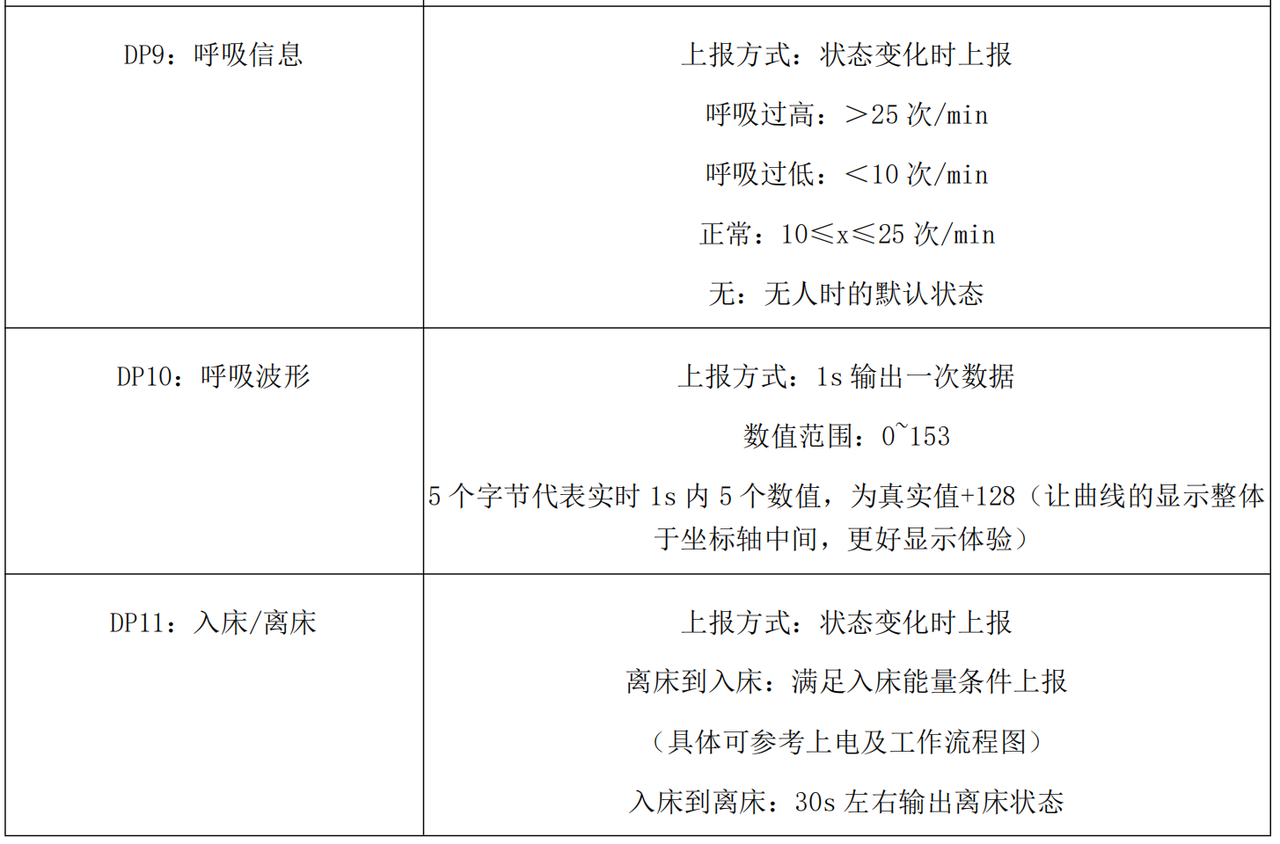
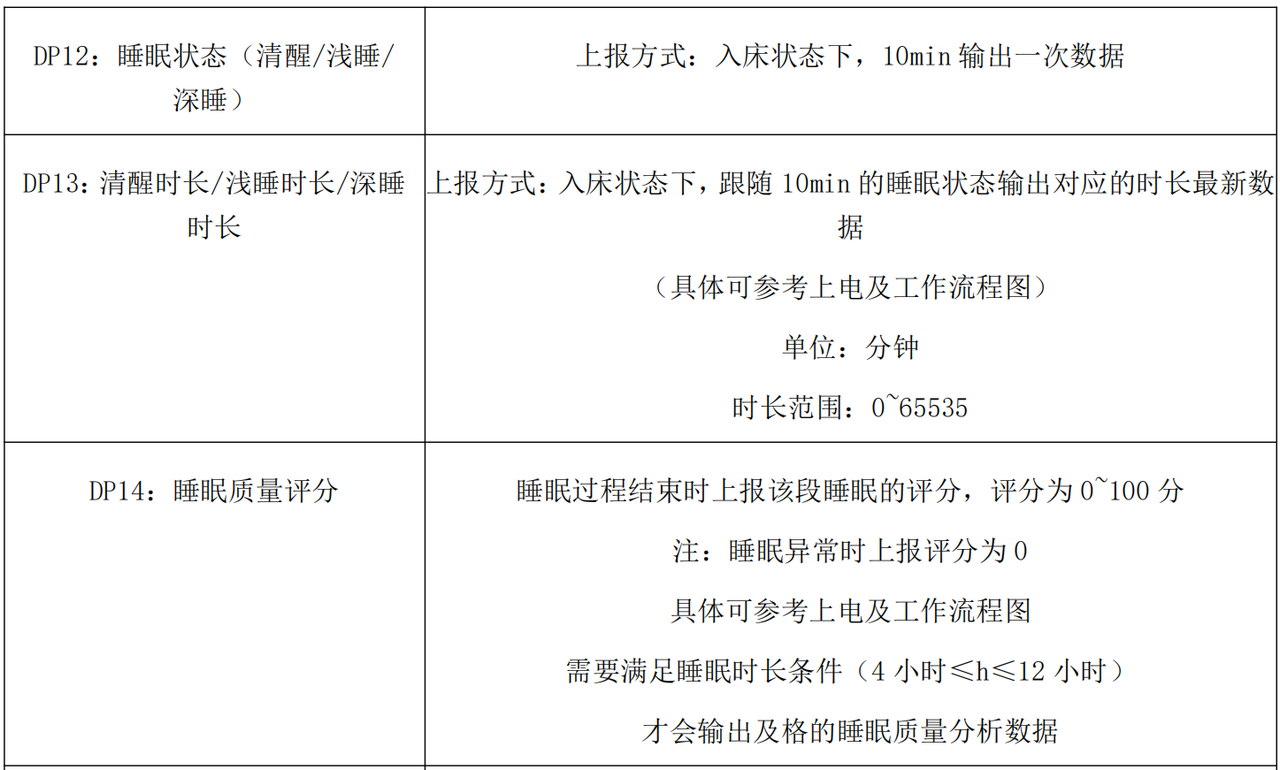
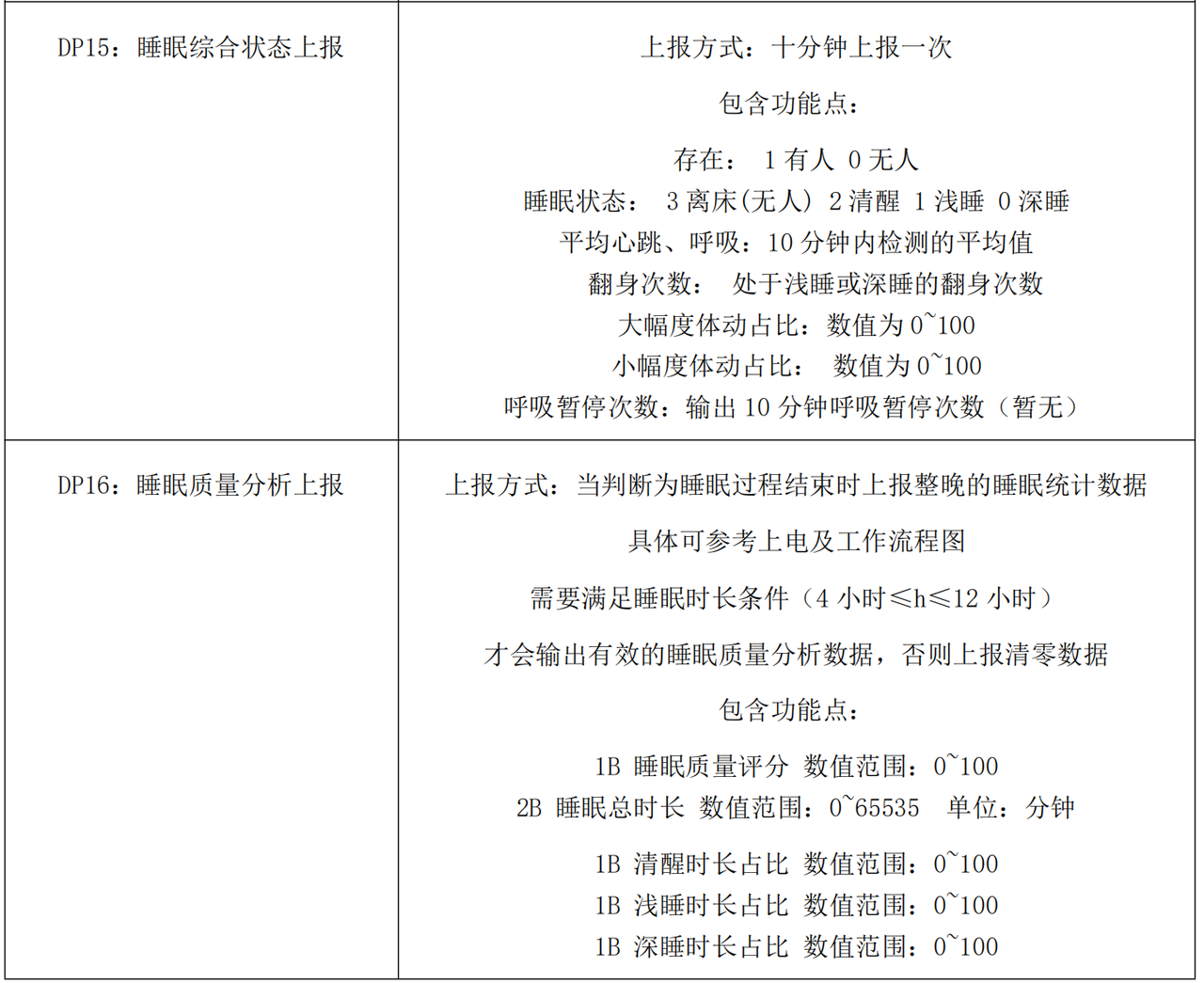
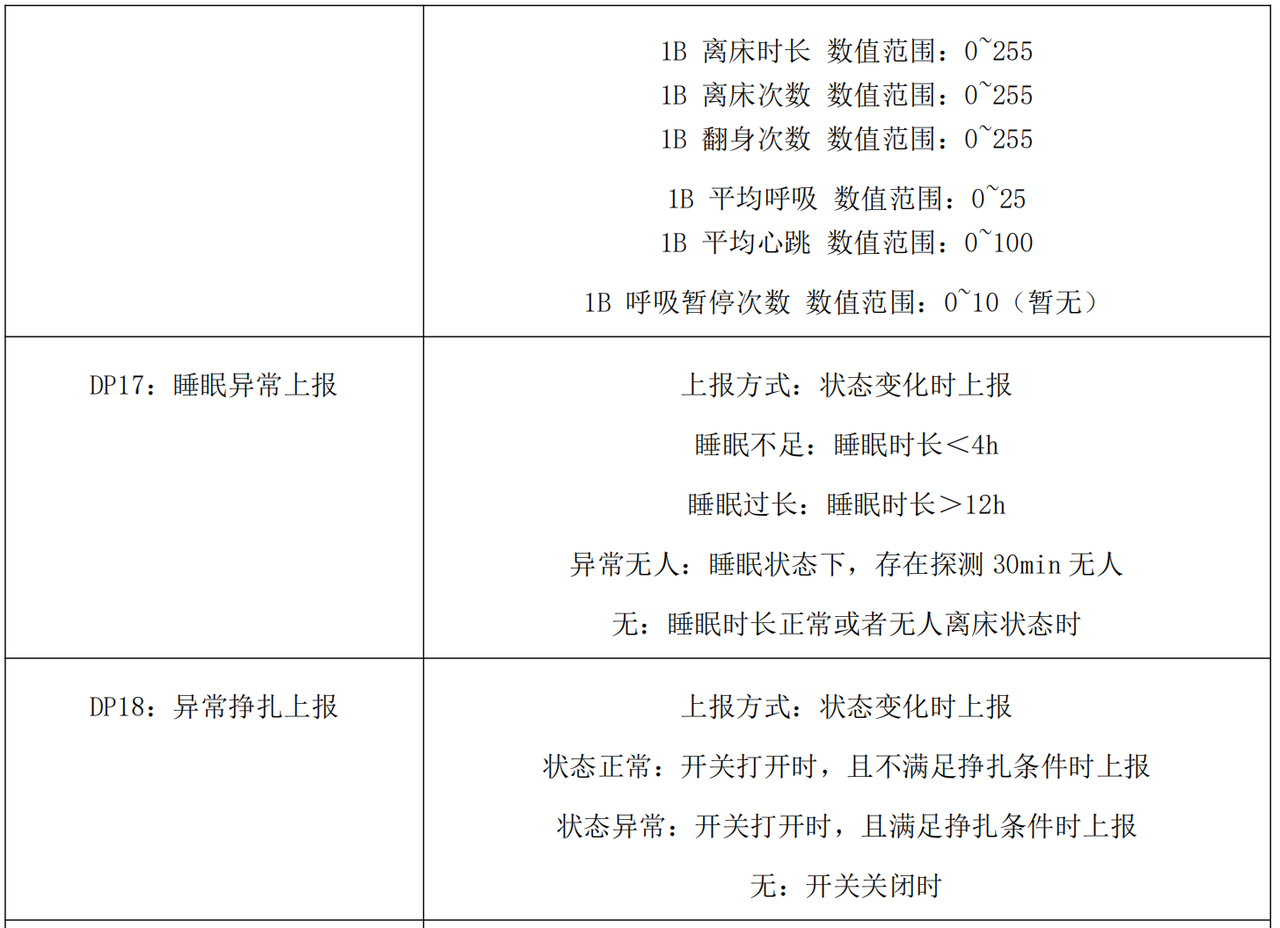
为了让业务逻辑更清晰、可维护,R60ABD1 的实例属性按功能领域进行分层设计,每个模块的属性专注于特定业务场景:
3.1.1.1 系统控制与状态属性
self.parse_interval = parse_interval # 数据解析周期,适配设备数据输出频率
self.max_retries = max_retries # 指令重试次数,保障通信可靠性
self.retry_delay = retry_delay # 重试间隔,避免频繁重试导致设备负载过高
self.init_timeout = init_timeout # 初始化超时时间,防止设备未响应时无限等待
# 运行状态标志
self._is_running = False # 设备是否处于运行状态
self._initialization_complete = False # 初始化是否完成
self._configuration_errors = [] # 配置错误记录,用于异常排查
这类属性用于设备全局控制(如初始化、重试策略),是保障设备稳定运行的基础。
3.1.1.2 系统级监控属性
# 心跳包监控
self.heartbeat_last_received = 0 # 最后接收心跳包的时间戳(ms)
self.heartbeat_timeout_count = 0 # 心跳超时累计次数
self.heartbeat_interval = 0 # 实际心跳间隔统计(ms)
# 系统状态
self.system_initialized = False # 初始化完成状态
self.system_initialized_timestamp = 0 # 初始化完成时间戳(ms)
self.module_reset_flag = False # 模组复位状态标记
self.module_reset_timestamp = 0 # 模组复位时间戳(ms)
# 产品信息
self.product_model = "" # 产品型号(如“R60ABD1”)
self.product_id = "" # 产品ID(唯一标识)
self.hardware_model = "" # 硬件型号
self.firmware_version = "" # 固件版本(如“G60SM1SYv010309”)
这类属性用于设备健康度与身份识别,帮助开发者快速定位设备状态(如是否初始化、固件版本是否兼容)。
3.1.1.3 雷达探测与人体存在属性
# 位置状态
self.radar_in_range = False # 是否在雷达探测范围内
# 人体存在基本状态
self.presence_enabled = presence_enabled # 人体存在功能开关
self.presence_status = 0 # 存在状态(0=无人,1=有人)
self.motion_status = 0 # 运动状态(0=无,1=静止,2=活跃)
# 量化数据
self.movement_parameter = 0 # 体动参数(0-100)
self.human_distance = 0 # 人体距离(0-65535 cm)
self.human_position_x = 0 # 人体X坐标(有符号)
self.human_position_y = 0 # 人体Y坐标(有符号)
self.human_position_z = 0 # 人体Z坐标(有符号)
这类属性聚焦人体存在与运动监测,是雷达 “环境感知” 能力的直接体现。
3.1.1.4 呼吸监测属性
# 功能配置
self.breath_monitoring_enabled = breath_monitoring_enabled # 呼吸监测开关
self.breath_waveform_enabled = False # 呼吸波形上报开关
self.low_breath_threshold = 10 # 低缓呼吸阈值(10-20次/min)
# 监测数据
self.breath_status = 0 # 呼吸状态(1=正常,2=过高,3=过低,4=无)
self.breath_value = 0 # 呼吸数值(0-35次/分)
self.breath_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 5字节呼吸波形数据
这类属性围绕呼吸健康监测,覆盖 “功能开关 → 实时数值 → 波形数据” 的完整链路。
3.1.1.5 心率监测属性
# 功能配置
self.heart_rate_enabled = heart_rate_enabled # 心率监测开关
self.heart_rate_waveform_enabled = False # 心率波形上报开关
# 监测数据
self.heart_rate_value = 0 # 心率数值(60-120次/分)
self.heart_rate_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 5字节心率波形数据
这类属性与 “呼吸监测” 结构对称,确保心率数据的一致性管理。
3.1.1.6 睡眠监测属性
# 基础状态
self.sleep_monitoring_enabled = sleep_monitoring_enabled # 睡眠监测开关
# 入床/离床与睡眠状态
self.bed_status = 0 # 床状态(0=离床,1=入床,2=无)
self.sleep_status = 0 # 睡眠状态(0=深睡,1=浅睡,2=清醒,3=无)
# 时长统计
self.awake_duration = 0 # 清醒时长(分钟)
self.light_sleep_duration = 0 # 浅睡时长(分钟)
self.deep_sleep_duration = 0 # 深睡时长(分钟)
# 睡眠质量与异常
self.sleep_quality_score = 0 # 睡眠质量评分(0-100)
self.sleep_quality_rating = 0 # 睡眠质量评级
self.sleep_comprehensive_status = {} # 睡眠综合状态(8字段字典)
self.sleep_anomaly = 0 # 睡眠异常状态
self.abnormal_struggle_status = 0 # 异常挣扎状态
self.no_person_timing_status = 0 # 无人计时状态
# 配置参数
self.abnormal_struggle_enabled = abnormal_struggle_enabled # 异常挣扎开关
self.no_person_timing_enabled = no_person_timing_enabled # 无人计时开关
self.no_person_timing_duration = no_person_timing_duration # 无人计时时长
self.sleep_cutoff_duration = sleep_cutoff_duration # 睡眠截止时长
self.struggle_sensitivity = struggle_sensitivity # 挣扎灵敏度
这类属性是睡眠监测的核心载体,从 “状态 → 时长 → 质量 → 异常” 多维度刻画睡眠健康。
3.1.1.7 查询与定时器管理属性
# 查询状态管理
self._query_in_progress = False # 是否有查询在进行中
self._query_response_received = False # 是否收到查询响应
self._query_result = None # 查询结果
self._current_query_type = None # 当前查询类型
self._query_timeout = 200 # 默认查询超时时间(ms)
# 内部定时器
self._timer = Timer(-1) # 用于周期性任务(如心跳检测、数据解析)
这类属性用于设备交互的底层管理(如查询流程、定时器调度),对上层业务透明。
3.3.2 类属性与常量:业务规则的集中化定义
为了避免硬编码、提升代码可读性,R60ABD1 通过类属性与常量封装业务规则、指令类型和状态映射:
3.3.2.1 调试与状态常量
# 是否启用调试(全局开关,便于日志输出与问题排查)
DEBUG_ENABLED = False
# 运动、呼吸、睡眠等状态的枚举映射
MOTION_NONE, MOTION_STATIC, MOTION_ACTIVE = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
BREATH_NORMAL, BREATH_HIGH, BREATH_LOW, BREATH_NONE = (0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04)
BED_LEAVE, BED_ENTER, BED_NONE = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
SLEEP_DEEP, SLEEP_LIGHT, SLEEP_AWAKE, SLEEP_NONE = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03)
# ... 其他状态枚举(如睡眠异常、质量评级等)
这些常量将 “数值 → 业务含义” 的映射集中化,例如 MOTION_ACTIVE 直接对应 “人体活跃状态”,避免代码中散落的字面量。
3.3.2.2 指令类型与映射表
# 指令类型常量(区分查询、控制、设置操作)
TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT = 0 # 心跳包查询
TYPE_MODULE_RESET = 1 # 模组复位
TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL = 2 # 产品型号查询
# ... 人体存在、心率、呼吸、睡眠等模块的指令类型(共60+种)
# 指令映射表:将指令类型映射为“控制字、命令字、数据”的协议参数
COMMAND_MAP = {
TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT: {
'control_byte': 0x01,
'command_byte': 0x80,
'data': bytes([0x0F])
},
# ... 其他指令的协议参数映射
}
# 查询类型到名称的映射(用于调试输出,提升日志可读性)
QUERY_NAME_MAP = {
TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT: "Heartbeat",
TYPE_MODULE_RESET: "Module Reset",
# ... 其他指令的名称映射
}
这类映射表是 “业务指令 → 底层协议” 的翻译层,例如业务层调用 “查询产品型号” 时,可通过 COMMAND_MAP 直接获取对应的串口帧参数,无需关注协议细节。
3.3.3 私有解析方法:原始数据到业务属性的转换
R60ABD1 通过一系列私有方法将 DataFlowProcessor 解析出的原始字节转换为业务属性,这些方法聚焦 “数据格式解析”,与业务逻辑解耦:
3.3.3.1 人体位置解析(带符号 16 位特殊格式)
def _parse_human_position_data(self, data_bytes):
"""解析人体方位数据(6字节:X(2B)、Y(2B)、Z(2B)),支持特殊符号位格式"""
if len(data_bytes) != 6:
return (0, 0, 0)
x = self._parse_signed_16bit_special(data_bytes[0:2])
y = self._parse_signed_16bit_special(data_bytes[2:4])
z = self._parse_signed_16bit_special(data_bytes[4:6])
return (x, y, z)
def _parse_signed_16bit_special(self, two_bytes):
"""解析特殊有符号16位数据(首位为符号位,后15位为数值)"""
if len(two_bytes) != 2:
return 0
unsigned_value = (two_bytes[0] << 8) | two_bytes[1]
sign_bit = (unsigned_value >> 15) & 0x1
magnitude = unsigned_value & 0x7FFF
return -magnitude if sign_bit else magnitude
例如,原始字节 0x80 0x0F 会被解析为 -32753(符号位为 1,数值位为 0x000F),精准还原人体坐标的正负与数值。
3.3.3.2 波形数据解析(心率、呼吸通用逻辑)
def _parse_heart_rate_waveform_data(self, data_bytes):
"""解析心率波形数据(5字节,还原实时波形数值)"""
if len(data_bytes) != 5:
return (128, 128, 128, 128, 128)
return (data_bytes[0], data_bytes[1], data_bytes[2], data_bytes[3], data_bytes[4])
def _parse_breath_waveform_data(self, data_bytes):
"""解析呼吸波形数据(5字节,逻辑与心率波形一致)"""
if len(data_bytes) != 5:
return (128, 128, 128, 128, 128)
return (data_bytes[0], data_bytes[1], data_bytes[2], data_bytes[3], data_bytes[4])
这类方法将原始字节直接映射为波形数值(如 0xC1→193),为 “波形可视化” 等上层功能提供基础数据。
3.3.3.3 睡眠数据解析(综合状态与统计信息)
def _parse_sleep_comprehensive_data(self, data_bytes):
"""解析睡眠综合状态数据(8字节,多维度睡眠信息)"""
if len(data_bytes) != 8:
return (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
return (
data_bytes[0], # 存在状态
data_bytes[1], # 睡眠状态
data_bytes[2], # 平均呼吸
data_bytes[3], # 平均心跳
data_bytes[4], # 翻身次数
data_bytes[5], # 大幅度体动占比
data_bytes[6], # 小幅度体动占比
data_bytes[7] # 呼吸暂停次数
)
def _parse_sleep_statistics_data(self, data_bytes):
"""解析睡眠统计信息数据(12字节,时长、质量等汇总)"""
if len(data_bytes) != 12:
return (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
total_sleep_duration = (data_bytes[1] << 8) | data_bytes[2]
return (
data_bytes[0], # 睡眠质量评分
total_sleep_duration, # 睡眠总时长
data_bytes[3], # 清醒时长占比
data_bytes[4], # 浅睡时长占比
data_bytes[5], # 深睡时长占比
data_bytes[6], # 离床时长
data_bytes[7], # 离床次数
data_bytes[8], # 翻身次数
data_bytes[9], # 平均呼吸
data_bytes[10], # 平均心跳
data_bytes[11] # 呼吸暂停次数
)
这类方法将复杂的睡眠数据拆解为可读的业务指标,例如 “睡眠总时长” 由两个字节的大端数据拼接而成。
3.3.3.4 产品与固件信息解析(字符串处理)
def _parse_product_info_data(self, data_bytes):
"""解析产品信息(含空字节的字符串处理)"""
try:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Raw product data: {data_bytes}, hex: {data_bytes.hex()}")
# 截取空字节前的有效部分
if b'\x00' in data_bytes:
null_index = data_bytes.index(b'\x00')
valid_data = data_bytes[:null_index]
else:
valid_data = data_bytes
return (valid_data.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore').strip(),)
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Product info parse error: {e}, data: {data_bytes}")
return ("",)
def _parse_firmware_version_data(self, data_bytes):
"""解析固件版本(逻辑与产品信息一致)"""
try:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Raw firmware data: {data_bytes}, hex: {data_bytes.hex()}")
if b'\x00' in data_bytes:
null_index = data_bytes.index(b'\x00')
valid_data = data_bytes[:null_index]
else:
valid_data = data_bytes
return (valid_data.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore').strip(),)
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Firmware version parse error: {e}, data: {data_bytes}")
return ("",)
这类方法处理 “带空字节的字符串” 场景,确保产品型号、固件版本等信息能被正确解析为 Python 字符串。
3.3.4 解析逻辑的测试验证:REPL 环境下的正确性校验
为确保解析方法的可靠性,需在 MicroPython 的 REPL 环境中进行数据一致性测试,验证 “原始字节 → 业务属性” 的转换是否符合预期:
# 模拟DataFlowProcessor(仅用于测试)
class MockDataProcessor:
pass
# 初始化R60ABD1实例
device = R60ABD1(MockDataProcessor())
# 测试用例1:人体方位数据解析
human_position_data = bytes([0x80, 0x0F, 0x00, 0x2C, 0x00, 0x00])
result = device._parse_human_position_data(human_position_data)
print("人体方位数据:", result)
# 预期输出:(-32753, 44, 0) (验证符号位与数值的正确转换)
# 测试用例2:心率波形数据解析
heart_rate_waveform_data = bytes([0xC1, 0xBE, 0xAA, 0x90, 0x8A])
result = device._parse_heart_rate_waveform_data(heart_rate_waveform_data)
print("心率波形数据:", result)
# 预期输出:(193, 190, 170, 144, 138) (验证字节到数值的直接映射)
# 测试用例3:呼吸波形数据解析
breath_waveform_data = bytes([0xC9, 0x60, 0x18, 0x40, 0x9A])
result = device._parse_breath_waveform_data(breath_waveform_data)
print("呼吸波形数据:", result)
# 预期输出:(201, 96, 24, 64, 154) (逻辑与心率波形一致)
# 测试用例4:睡眠综合状态解析
sleep_comprehensive_data = bytes([0x01, 0x02, 0x12, 0x4B, 0x00, 0x26, 0x3E, 0x00])
result = device._parse_sleep_comprehensive_data(sleep_comprehensive_data)
print("睡眠综合状态数据:", result)
# 预期输出:(1, 2, 18, 75, 0, 38, 62, 0) (多维度睡眠信息的正确拆解)
# 测试用例5:睡眠统计信息解析
sleep_statistics_data = bytes([0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00])
result = device._parse_sleep_statistics_data(sleep_statistics_data)
print("睡眠统计信息数据:", result)
# 预期输出:(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) (全零场景的兼容性)
测试结果正常,如下所示:
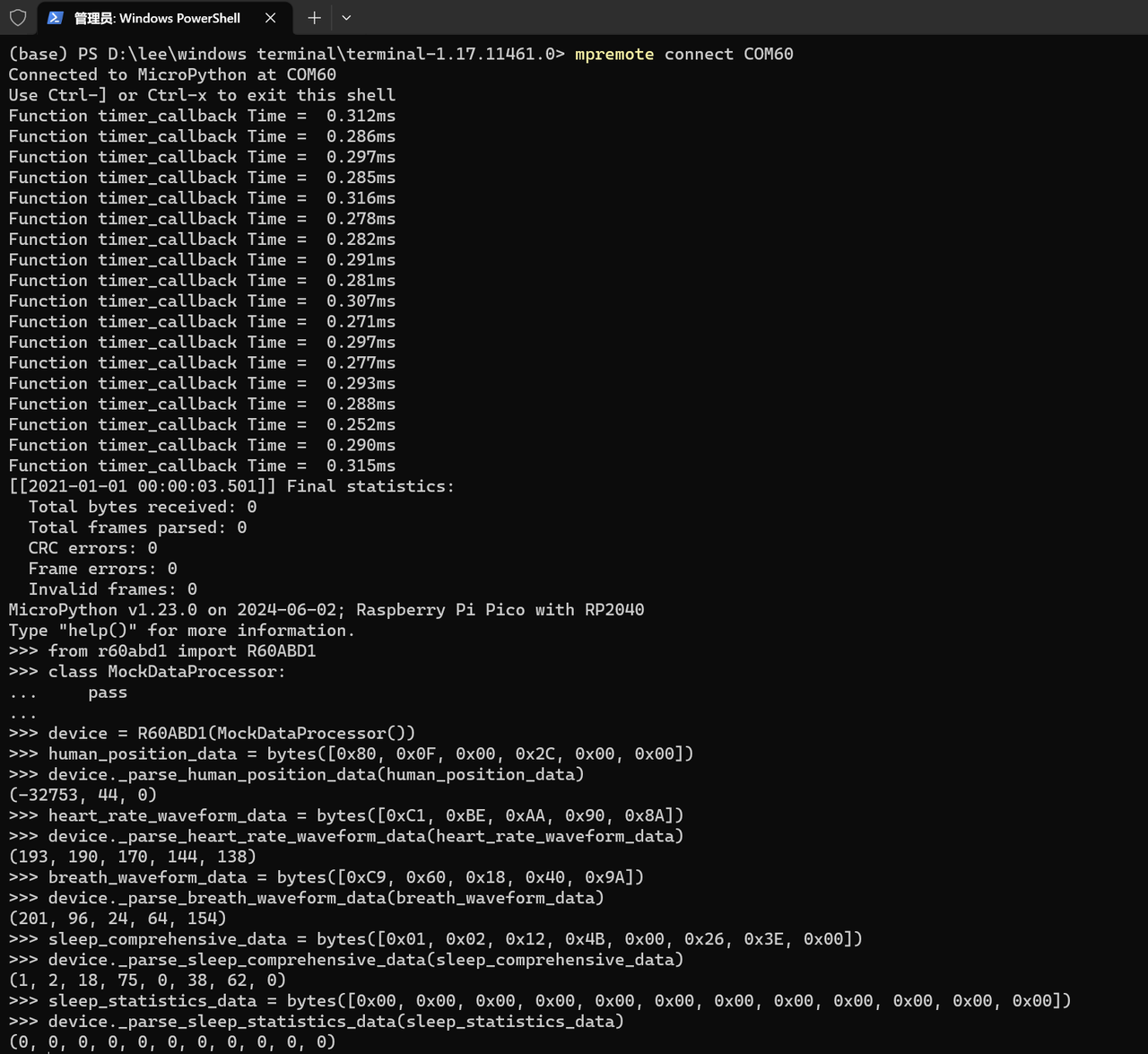
通过上述测试,可验证所有解析方法能精准转换原始字节为业务属性,为后续 update_properties_from_frame 方法的实现奠定了可靠基础。
3.3.5 update_properties_from_frame 方法:业务属性的更新入口
update_properties_from_frame 是 R60ABD1 类衔接 “数据解析层” 与 “业务逻辑层” 的核心方法,负责将 DataFlowProcessor 解析的原始帧数据映射为可读的业务属性,并实现属性的分层、实时更新。
3.3.5.1 方法设计目的:数据到业务的 “翻译器”
该方法承担 “原始帧数据 → 业务属性” 的翻译与更新职责 ,是业务逻辑层感知设备状态的 “桥梁”。它接收 DataFlowProcessor 输出的帧字典,通过 控制字 和 命令字 的组合判断,将字节数据转换为结构化的业务属性(如呼吸率、心率、人体存在状态等),最终支撑设备的健康监测、状态分析等上层应用。
3.3.5.2 属性更新时机的分层策略:匹配数据频率
为平衡 “实时性” 与 “资源消耗”,建议调用驱动库的开发者需根据数据输出频率分层处理属性更新:
- 高频数据(<100ms):如人体存在状态、运动状态。这类数据变化快,需立即更新属性,确保业务层实时感知环境变化。
- 中频数据(1-3s):如呼吸 / 心率波形、体动参数。这类数据用于趋势分析(如波形可视化),更新频率稍缓但需保证数据完整性。
- 低频数据(>10s):如睡眠状态、质量评分。这类数据为汇总性指标,更新间隔较长,收到帧时一次性处理即可。
3.3.5.3 方法具体实现:模块化分支解析
这里,为了快速测试可行性,我们在 mian.py 中进行测试,用全局变量模拟属性值,在相关函数中通过 控制字+命令字 的组合判断,将不同类型的帧数据路由到对应属性的更新逻辑中:
# Python env :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/11/4 下午5:33
# @Author : 李清水
# @File : main.py
# @Description :
from machine import UART, Pin, Timer
import time
from data_flow_processor import DataFlowProcessor
import micropython
frame_count = 0
# 存储解析到的数据帧
parsed_frames_buffer = []
# 初始化UART0:TX=16, RX=17,波特率115200
uart = UART(0, baudrate=115200, tx=Pin(16), rx=Pin(17), timeout=0)
# 创建DataFlowProcessor实例
processor = DataFlowProcessor(uart)
# ======================================== 功能函数 ============================================
# 计时装饰器,用于计算函数运行时间
def timed_function(f: callable, *args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> callable:
_"""_
_ 计时装饰器,用于计算并打印函数/方法运行时间。_
_ Args:_
_ f (callable): 需要传入的函数/方法_
_ args (tuple): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的位置参数_
_ kwargs (dict): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的关键字参数_
_ Returns:_
_ callable: 返回计时后的函数_
_ """_
_ _myname = str(f).split(' ')[1]
def new_func(*args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> any:
t: int = time.ticks_us()
result = f(*args, **kwargs)
delta: int = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_us(), t)
print('Function {} Time = {:6.3f}ms'.format(myname, delta / 1000))
return result
return new_func
def format_time():
_"""格式化当前时间为 [YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.sss] 格式"""_
_ _t = time.localtime()
ms = time.ticks_ms() % 1000
return f"[{t[0]}-{t[1]:02d}-{t[2]:02d} {t[3]:02d}:{t[4]:02d}:{t[5]:02d}.{ms:03d}]"
@timed_function
def timer_callback(timer):
_"""定时器回调函数,每50ms触发一次,直接解析数据帧"""_
_ _global frame_count, parsed_frames_buffer
# 直接调用解析方法
frames = processor.read_and_parse()
# 将解析到的帧添加到缓冲区
for frame in frames:
frame_count += 1
parsed_frames_buffer.append({
'frame_number': frame_count,
'control': frame['control_byte'],
'command': frame['command_byte'],
'data_length': frame['data_length'],
'data_hex': frame['data'].hex() if frame['data'] else "",
'raw_hex': frame['raw_data'].hex(),
'timestamp': format_time()
})
# 更新属性
micropython.schedule(update_properties_from_frame, frame)
@timed_function
def update_properties_from_frame(frame):
_"""根据解析的帧更新属性值"""_
_ _global heartbeat_last_received, presence_status, motion_status, movement_parameter
global human_distance, human_position_x, human_position_y, human_position_z
global breath_status, breath_value, breath_waveform
global heart_rate_value, heart_rate_waveform
global radar_in_range, system_initialized
control = frame['control_byte']
command = frame['command_byte']
data = frame['data']
current_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 心跳包 (0x01)
if control == 0x01 and command == 0x01:
heartbeat_last_received = current_time
print("[%s] Heartbeat received" % format_time())
# 系统初始化状态 (0x05)
elif control == 0x05 and command == 0x01:
if data and len(data) > 0:
system_initialized = (data[0] == 0x01)
print("[%s] System initialized: %s" % (format_time(), "Yes" if system_initialized else "No"))
# 雷达探测范围 (0x07)
elif control == 0x07 and command == 0x07:
if data and len(data) > 0:
radar_in_range = (data[0] == 0x01)
print("[%s] Radar in range: %s" % (format_time(), "Yes" if radar_in_range else "No"))
# 人体存在状态 (0x80)
elif control == 0x80:
if command == 0x01: # 存在信息
if data and len(data) > 0:
presence_status = data[0]
status_text = "No one" if presence_status == 0 else "Someone"
print("[%s] Presence status: %s" % (format_time(), status_text))
elif command == 0x02: # 运动信息
if data and len(data) > 0:
motion_status = data[0]
status_text = ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][motion_status] if motion_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print("[%s] Motion status: %s" % (format_time(), status_text))
elif command == 0x03: # 体动参数
if data and len(data) > 0:
movement_parameter = data[0]
print("[%s] Movement parameter: %d" % (format_time(), movement_parameter))
elif command == 0x04: # 人体距离
if data and len(data) >= 2:
human_distance = data[0] | (data[1] << 8)
print("[%s] Human distance: %d cm" % (format_time(), human_distance))
elif command == 0x05: # 人体方位
if data and len(data) >= 6:
human_position_x = data[0] | (data[1] << 8)
human_position_y = data[2] | (data[3] << 8)
human_position_z = data[4] | (data[5] << 8)
print("[%s] Human position: X=%d, Y=%d, Z=%d" % (
format_time(), human_position_x, human_position_y, human_position_z))
# 呼吸监测 (0x81)
elif control == 0x81:
if command == 0x01: # 呼吸状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
breath_status = data[0]
status_text = ["Normal", "High", "Low", "None"][
breath_status - 1] if 1 <= breath_status <= 4 else "Unknown"
print("[%s] Breath status: %s" % (format_time(), status_text))
elif command == 0x02: # 呼吸数值
if data and len(data) > 0:
breath_value = data[0]
print("[%s] Breath value: %d" % (format_time(), breath_value))
elif command == 0x05: # 呼吸波形
if data and len(data) >= 5:
breath_waveform = list(data[:5])
print("[%s] Breath waveform updated" % format_time())
# 心率监测 (0x85)
elif control == 0x85:
if command == 0x02: # 心率数值
if data and len(data) > 0:
heart_rate_value = data[0]
print("[%s] Heart rate: %d" % (format_time(), heart_rate_value))
elif command == 0x05: # 心率波形
if data and len(data) >= 5:
heart_rate_waveform = list(data[:5])
print("[%s] Heart rate waveform updated" % format_time())
# ======================================== 全局属性变量 ============================================
# 1. 系统级属性
heartbeat_last_received = 0
heartbeat_timeout_count = 0
heartbeat_interval = 0
system_initialized = False
system_initialized_timestamp = 0
module_reset_flag = False
module_reset_timestamp = 0
product_model = ""
product_id = ""
hardware_model = ""
firmware_version = ""
# 2. 雷达探测属性
radar_in_range = False
radar_in_range_timestamp = 0
# 3. 人体存在检测属性
presence_enabled = True
presence_status = 0
presence_status_timestamp = 0
motion_status = 0
motion_status_timestamp = 0
movement_parameter = 0
movement_parameter_timestamp = 0
human_distance = 0
human_distance_timestamp = 0
human_position_x = 0
human_position_y = 0
human_position_z = 0
human_position_timestamp = 0
# 4. 呼吸监测属性
breath_monitoring_enabled = True
breath_waveform_enabled = False
low_breath_threshold = 10
breath_status = 0
breath_status_timestamp = 0
breath_value = 0
breath_value_timestamp = 0
breath_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
breath_waveform_timestamp = 0
# 5. 心率监测属性
heart_rate_enabled = True
heart_rate_waveform_enabled = False
heart_rate_value = 0
heart_rate_value_timestamp = 0
heart_rate_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
heart_rate_waveform_timestamp = 0
# 6. 睡眠监测属性
sleep_monitoring_enabled = True
bed_status = 0
bed_status_timestamp = 0
sleep_status = 0
sleep_status_timestamp = 0
awake_duration = 0
light_sleep_duration = 0
deep_sleep_duration = 0
sleep_quality_score = 0
sleep_quality_rating = 0
sleep_comprehensive_status = {}
sleep_anomaly = 0
abnormal_struggle_status = 0
no_person_timing_status = 0
abnormal_struggle_enabled = False
no_person_timing_enabled = False
no_person_timing_duration = 30
sleep_cutoff_duration = 120
struggle_sensitivity = 1
# ======================================== 主程序 ============================================
# 初始化50ms定时器
timer = Timer(-1)
timer.init(period=50, mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=timer_callback)
# 测试计数器
test_counter = 0
last_print_time = time.ticks_ms()
try:
while True:
current_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 检查是否需要打印缓冲区中的帧(每10个打印一次)
if len(parsed_frames_buffer) >= 10:
print("=====================================================")
for frame_data in parsed_frames_buffer:
print("[%s] Frame#%d: Control=0x%02X, Command=0x%02X, Length=%d, Data=%s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['frame_number'], frame_data['control'], frame_data['command'], frame_data['data_length'], frame_data['data_hex']))
print("[%s] Raw frame: %s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['raw_hex']))
print("-" * 60)
print("=====================================================")
# 清空缓冲区
parsed_frames_buffer = []
# 每5秒打印一次属性状态摘要
if time.ticks_diff(current_time, last_print_time) >= 5000:
last_print_time = current_time
test_counter += 1
print("[%s] Property Status Summary (Test #%d)" % (format_time(), test_counter))
print("******************************************************************************************")
# 系统状态
print("System: Heartbeat=%d, Initialized=%s" % (
heartbeat_last_received, "Yes" if system_initialized else "No"))
# 雷达状态
print("Radar: InRange=%s" % ("Yes" if radar_in_range else "No"))
# 人体存在
presence_text = "No one" if presence_status == 0 else "Someone"
motion_text = ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][motion_status] if motion_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print("Presence: Status=%s, Motion=%s, Distance=%dcm" % (presence_text, motion_text, human_distance))
# 呼吸监测
breath_status_text = ["Normal", "High", "Low", "None"][
breath_status - 1] if 1 <= breath_status <= 4 else "Unknown"
print("Breath: Status=%s, Value=%d" % (breath_status_text, breath_value))
print("******************************************************************************************")
# 心率监测
print("Heart Rate: Value=%d" % heart_rate_value)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# 停止定时器
timer.deinit()
# 打印剩余未输出的帧
if parsed_frames_buffer:
print("=====================================================")
print("[%s] Final output %d parsed frames:" % (format_time(), len(parsed_frames_buffer)))
for frame_data in parsed_frames_buffer:
print("[%s] Frame#%d: Control=0x%02X, Command=0x%02X, Length=%d, Data=%s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['frame_number'], frame_data['control'], frame_data['command'], frame_data['data_length'], frame_data['data_hex']))
print("[%s] Raw frame: %s" % (frame_data['timestamp'], frame_data['raw_hex']))
print("-" * 60)
# 输出最终统计信息
stats = processor.get_stats()
print("[%s] Final statistics:" % format_time())
print(" Total bytes received: %d" % stats['total_bytes_received'])
print(" Total frames parsed: %d" % stats['total_frames_parsed'])
print(" CRC errors: %d" % stats['crc_errors'])
print(" Frame errors: %d" % stats['frame_errors'])
print(" Invalid frames: %d" % stats['invalid_frames'])
3.3.5.4 性能测试
烧录代码,打开终端:

可以看到 update_properties_from_frame 函数对单帧数据来说,耗时 1.2ms 左右,时间上是充沛的。
接下来,我们开始将 update_properties_from_frame 函数放到 R60ABD1 类中,代码如下:
def update_properties_from_frame(self, frame):
_"""_
_ 根据解析的帧更新属性值_
_ Args:_
_ frame: DataFlowProcessor解析后的帧数据字典_
_ """_
_ _control = frame['control_byte']
command = frame['command_byte']
data = frame['data']
# 心跳包 (0x01)
if control == 0x01:
# 心跳包上报
if command == 0x01:
self.heartbeat_last_received = time.ticks_ms()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Heartbeat] Received")
# 系统初始化状态 (0x05)
elif control == 0x05:
if command == 0x01: # 初始化完成信息
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.system_initialized = (data[0] == 0x01)
self.system_initialized_timestamp = time.ticks_ms()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status = "completed" if self.system_initialized else "not completed"
print(f"[System] Initialization {status}")
# 雷达探测范围 (0x07)
elif control == 0x07:
if command == 0x07: # 位置越界状态上报
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.radar_in_range = (data[0] == 0x01)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status = "in range" if self.radar_in_range else "out of range"
print(f"[Radar] {status}")
# 人体存在检测 (0x80)
elif control == 0x80:
if command == 0x01: # 存在信息
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.presence_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "No one" if self.presence_status == 0 else "Someone"
print(f"[Presence] {status_text}")
elif command == 0x02: # 运动信息
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.motion_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][
self.motion_status] if self.motion_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Motion] {status_text}")
elif command == 0x03: # 体动参数
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.movement_parameter = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Movement] Parameter: {self.movement_parameter}")
elif command == 0x04: # 人体距离
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.human_distance = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Distance] {self.human_distance} cm")
elif command == 0x05: # 人体方位
if data and len(data) == 6:
x, y, z = self._parse_human_position_data(data)
self.human_position_x = x
self.human_position_y = y
self.human_position_z = z
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Position] X={x}, Y={y}, Z={z}")
# 呼吸监测 (0x81)
elif control == 0x81:
if command == 0x01: # 呼吸状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.breath_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Normal", "High", "Low", "None"][
self.breath_status - 1] if 1 <= self.breath_status <= 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Breath] Status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x02: # 呼吸数值
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.breath_value = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Breath] Value: {self.breath_value}")
elif command == 0x05: # 呼吸波形
if data and len(data) == 5:
waveform = self._parse_breath_waveform_data(data)
self.breath_waveform = list(waveform)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Breath] Waveform updated: {waveform}")
# 心率监测 (0x85)
elif control == 0x85:
if command == 0x02: # 心率数值
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.heart_rate_value = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Heart Rate] Value: {self.heart_rate_value}")
elif command == 0x05: # 心率波形
if data and len(data) == 5:
waveform = self._parse_heart_rate_waveform_data(data)
self.heart_rate_waveform = list(waveform)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Heart Rate] Waveform updated: {waveform}")
# 睡眠监测 (0x84)
elif control == 0x84:
if command == 0x01: # 入床/离床状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.bed_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Leave bed", "Enter bed", "None"][
self.bed_status] if self.bed_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Bed] Status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x02: # 睡眠状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Deep sleep", "Light sleep", "Awake", "None"][
self.sleep_status] if self.sleep_status < 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x03: # 清醒时长
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.awake_duration = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Awake duration: {self.awake_duration} min")
elif command == 0x04: # 浅睡时长
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.light_sleep_duration = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Light sleep duration: {self.light_sleep_duration} min")
elif command == 0x05: # 深睡时长
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.deep_sleep_duration = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Deep sleep duration: {self.deep_sleep_duration} min")
elif command == 0x06: # 睡眠质量评分
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_quality_score = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Quality score: {self.sleep_quality_score}")
elif command == 0x0C: # 睡眠综合状态
if data and len(data) == 8:
comprehensive_data = self._parse_sleep_comprehensive_data(data)
# 更新到字典属性
self.sleep_comprehensive_status = {
'presence': comprehensive_data[0],
'sleep_status': comprehensive_data[1],
'avg_breath': comprehensive_data[2],
'avg_heart_rate': comprehensive_data[3],
'turnover_count': comprehensive_data[4],
'large_movement_ratio': comprehensive_data[5],
'small_movement_ratio': comprehensive_data[6],
'apnea_count': comprehensive_data[7]
}
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Comprehensive status updated")
elif command == 0x0D: # 睡眠质量分析/统计信息
if data and len(data) == 12:
stats_data = self._parse_sleep_statistics_data(data)
# 更新对应的睡眠统计属性
self.sleep_quality_score = stats_data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
# 注意:stats_data[1]是总睡眠时长,需要根据实际情况决定如何分配
print(f"[Sleep] Statistics updated")
elif command == 0x0E: # 睡眠异常
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_anomaly = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Short sleep (<4h)", "Long sleep (>12h)", "No person anomaly", "Normal"][
self.sleep_anomaly] if self.sleep_anomaly < 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Anomaly: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x10: # 睡眠质量评级
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_quality_rating = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["None", "Good", "Normal", "Poor"][
self.sleep_quality_rating] if self.sleep_quality_rating < 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Quality rating: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x11: # 异常挣扎状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.abnormal_struggle_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["None", "Normal", "Abnormal"][
self.abnormal_struggle_status] if self.abnormal_struggle_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Struggle status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x12: # 无人计时状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.no_person_timing_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["None", "Normal", "Abnormal"][
self.no_person_timing_status] if self.no_person_timing_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] No person timing: {status_text}")
接下来,我们修改一下 main.py:
# Python env :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/11/4 下午5:33
# @Author : 李清水
# @File : main.py
# @Description :
from machine import UART, Pin, Timer
import time
from data_flow_processor import DataFlowProcessor
from r60abd1 import R60ABD1, format_time
# 初始化UART0:TX=16, RX=17,波特率115200
uart = UART(0, baudrate=115200, tx=Pin(16), rx=Pin(17), timeout=0)
# 创建DataFlowProcessor实例
processor = DataFlowProcessor(uart)
# 创建R60ABD1实例
device = R60ABD1(processor, parse_interval=50)
# ======================================== 功能函数 ============================================
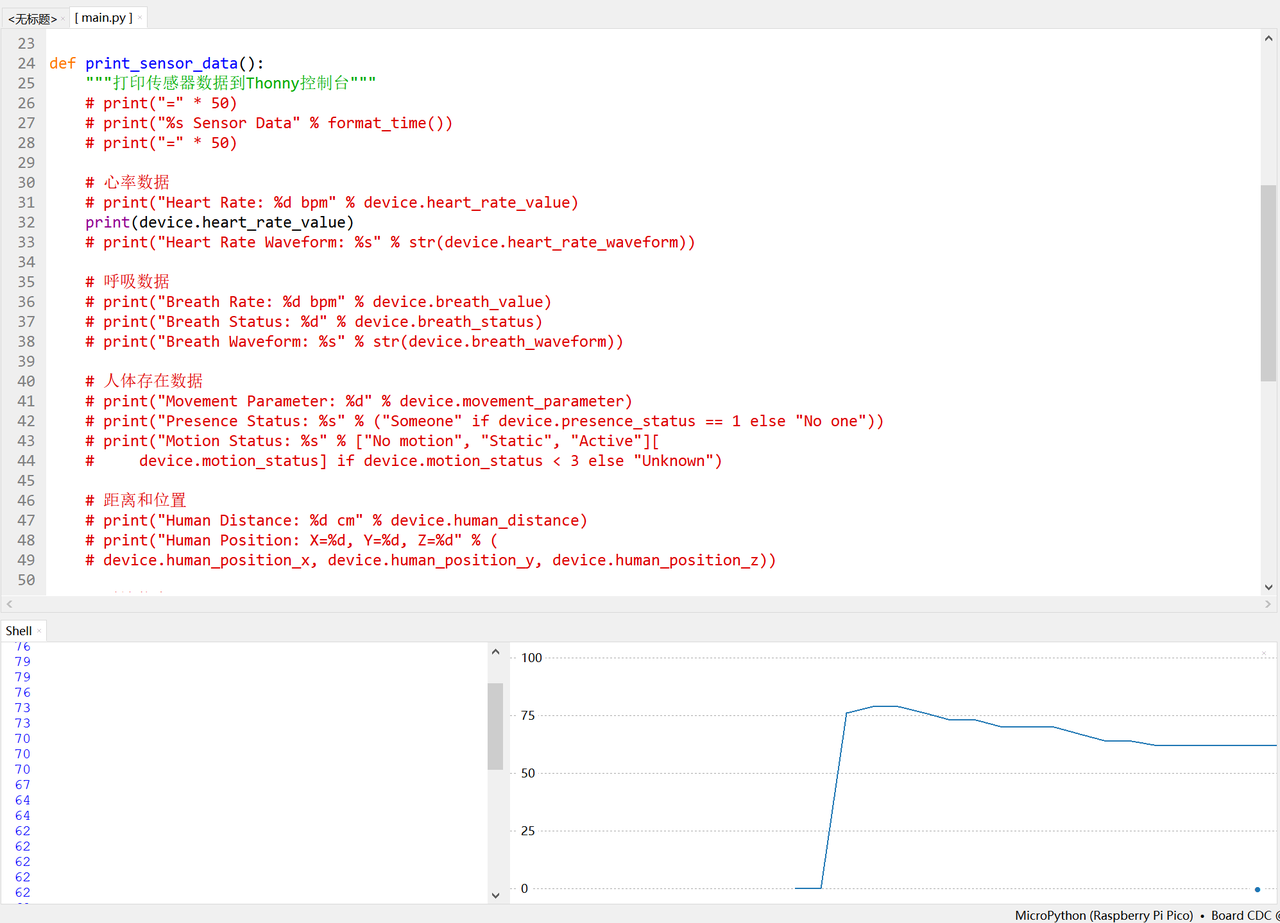
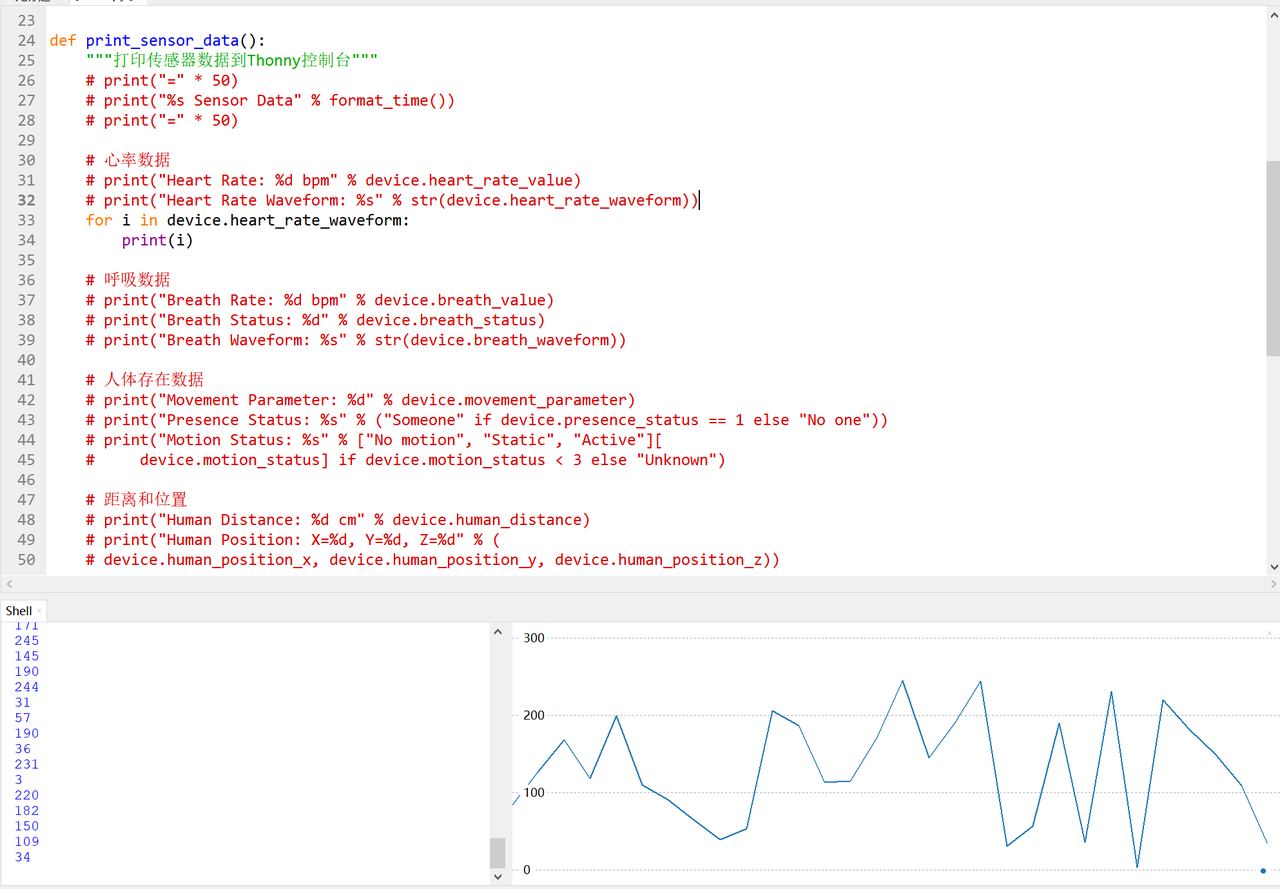
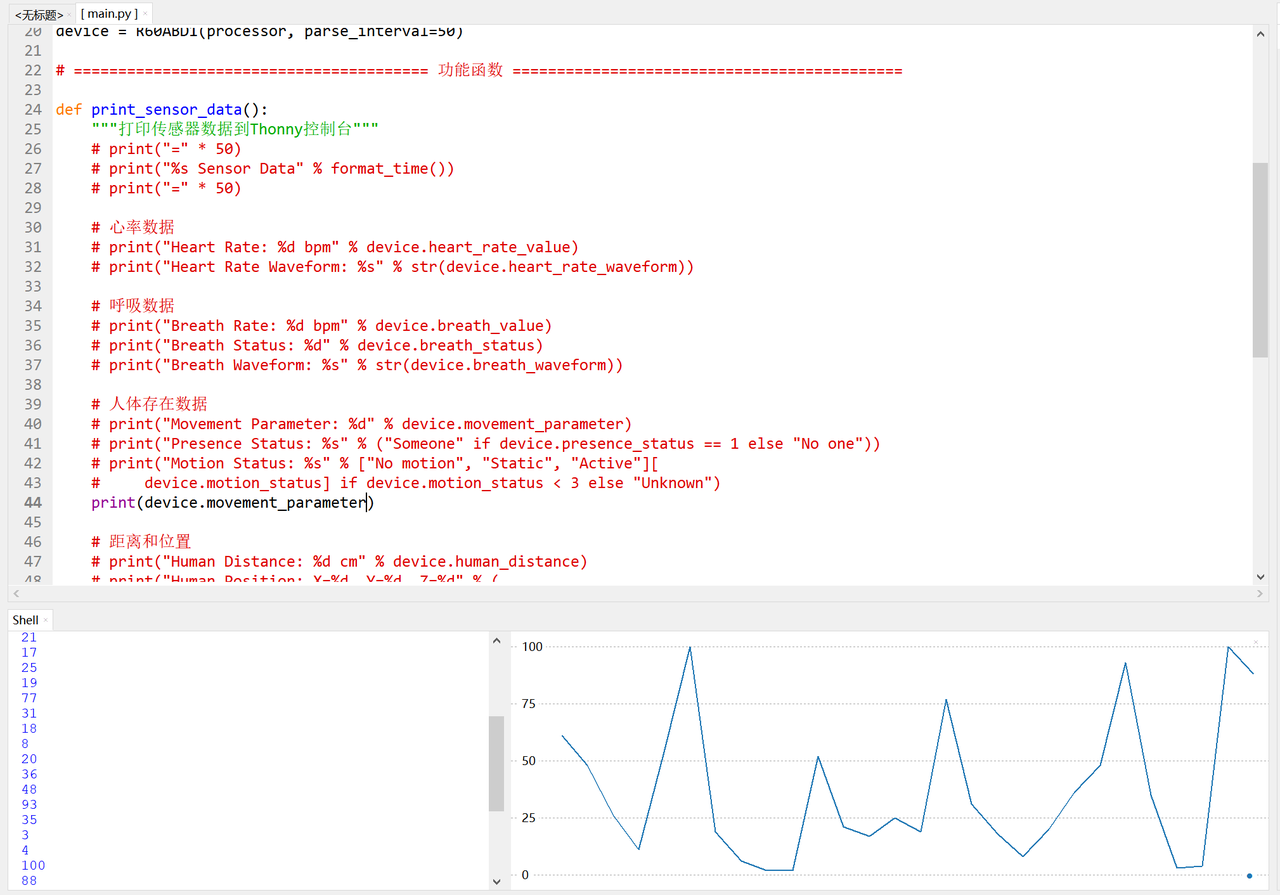
def print_sensor_data():
_"""打印传感器数据到Thonny控制台"""_
_ _print("=" * 50)
print("%s Sensor Data" % format_time())
print("=" * 50)
# 心率数据
print("Heart Rate: %d bpm" % device.heart_rate_value)
print("Heart Rate Waveform: %s" % str(device.heart_rate_waveform))
# 呼吸数据
print("Breath Rate: %d bpm" % device.breath_value)
print("Breath Status: %d" % device.breath_status)
print("Breath Waveform: %s" % str(device.breath_waveform))
# 人体存在数据
print("Movement Parameter: %d" % device.movement_parameter)
print("Presence Status: %s" % ("Someone" if device.presence_status == 1 else "No one"))
print("Motion Status: %s" % ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][
device.motion_status] if device.motion_status < 3 else "Unknown")
# 距离和位置
print("Human Distance: %d cm" % device.human_distance)
print("Human Position: X=%d, Y=%d, Z=%d" % (
device.human_position_x, device.human_position_y, device.human_position_z))
# 雷达状态
print("Radar in Range: %s" % ("Yes" if device.radar_in_range else "No"))
print("=" * 50)
# ======================================== 主程序 ============================================
# 上次打印时间
last_print_time = time.ticks_ms()
print_interval = 2000 # 2秒打印一次
try:
while True:
current_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 定期打印传感器数据
if time.ticks_diff(current_time, last_print_time) >= print_interval:
print_sensor_data()
last_print_time = current_time
# 小延迟,避免占用太多CPU
time.sleep_ms(10)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("%s Program interrupted by user" % format_time())
finally:
# 清理资源
print("%s Cleaning up resources..." % format_time())
device.close()
print("%s Program exited" % format_time())
运行时发现可以正常解析,同时中断代码时也可以:
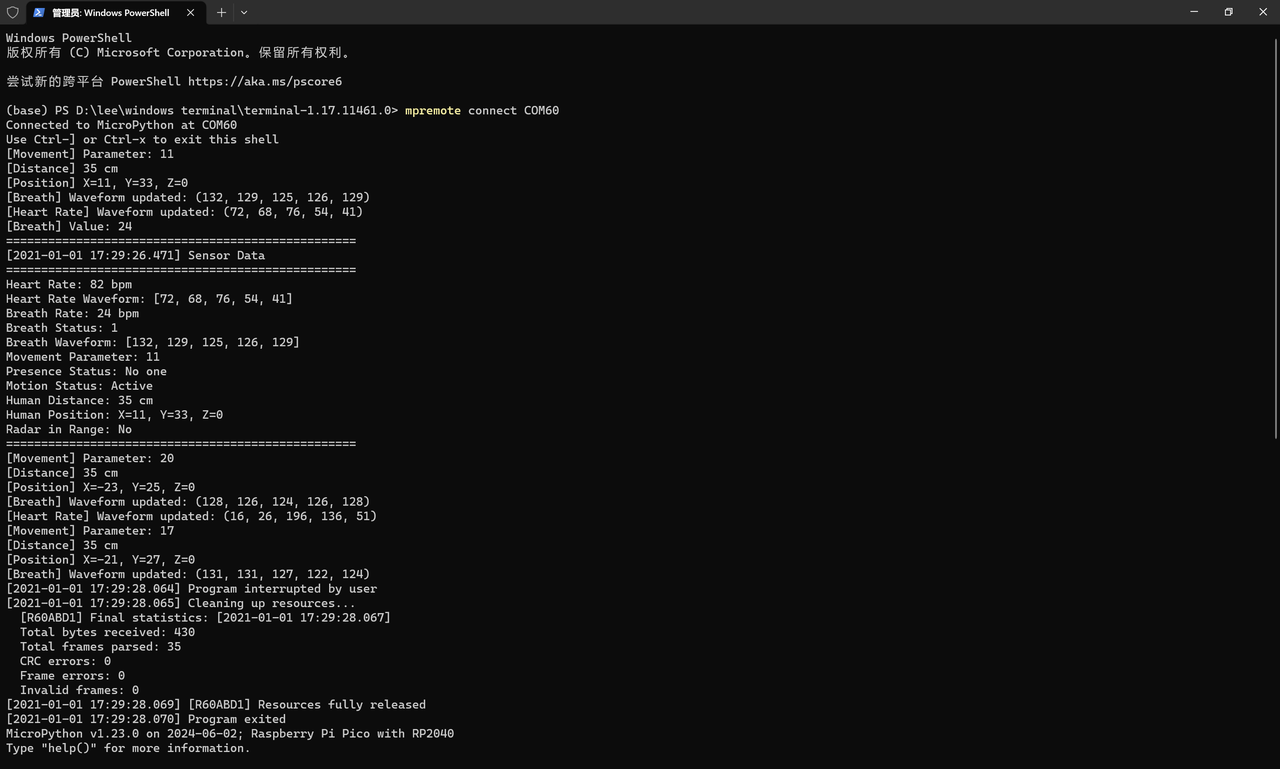
3.3.5.5 实际运行验证:数据一致性与可视化
接下来,我们在 thonny 中看一下值的变化曲线(此时需要设置 DEBUG_ENABLED = False):
同时,需要注意,这里,我们一次只输出一类数值便于查看:
3.3.6 命令响应逻辑设计与实现:主动查询/设置/使能指令交互处理
在 R60ABD1 类的业务逻辑层中,命令响应逻辑负责处理 “主动发起指令 → 接收设备响应 → 更新属性 / 返回结果” 的交互流程,是实现 “设备控制、信息查询、参数配置” 等功能的核心模块。
3.3.6.1 设计目标与核心思路
解决的业务场景:
- 设备信息查询: 如获取产品型号、固件版本、硬件型号等;
- 功能开关控制: 如开启 / 关闭人体存在监测、呼吸监测、心率监测等;
- 参数动态配置: 如设置低缓呼吸阈值、无人计时时长、挣扎灵敏度等;
- 设备状态诊断: 如查询心跳包状态、初始化完成状态、雷达探测范围等。
核心设计思路:
- 状态机模式管理查询生命周期:通过
_query_in_progress、_query_response_received等属性,跟踪 发起查询 → 等待响应 → 处理结果 → 清理状态 的完整流程; - 复用解析逻辑:查询响应帧与主动上报帧的结构完全一致,因此复用
update_properties_from_frame方法进行解析,避免代码冗余; - 硬件 FIFO 保障数据可靠性:树莓派 Pico 的 UART 硬件 FIFO(32 字节)自动缓存响应数据,结合定时器回调的
read_and_parse方法,确保数据无丢失; - 超时重试机制:通过
max_retries和retry_delay参数,应对串口通信的不稳定场景,提升指令执行的可靠性。
3.3.6.2 返回参数设计规范:基于设备响应的 “状态 + 结果” 二元组模式
命令响应逻辑的返回参数设计需严格遵循 “响应成功状态 + 实际结果” 的二元组规范,且 “是否成功”“返回值内容”“属性是否更新” 均需以设备返回的真实响应为唯一判断依据 —— 不得通过 “指令发送成功”“本地逻辑预判” 等非设备响应信息推导结果,确保返回数据与设备真实状态完全一致。
3.3.6.2.1 返回参数的统一格式要求
所有主动指令交互方法(查询、设置、控制类)的返回值必须为二元组 (success: bool, result: Any),各字段定义如下:
- success:布尔值,True 表示收到设备有效响应并完成解析(响应帧格式合法、控制字 / 命令字与指令匹配),False 表示超时、响应不匹配、解析失败等异常场景;
- result:动态类型,根据指令类型返回对应结果:
- 查询类指令(如query_human_distance):返回解析后的设备数据(如距离值、开关状态、产品型号字符串);
- 控制类指令(如enable_human_presence):返回设备响应确认的 “控制是否生效” 布尔值;
- 配置类指令(如set_low_breath_threshold):返回设备响应中确认的配置后参数值;
- 异常场景:result 为 None。
3.3.6.2.2 核心判断依据:设备响应是唯一数据源
无论是 success 的布尔状态、result 的实际值,还是业务属性的更新,均需严格基于设备返回的响应帧数据判断,禁止任何本地逻辑预判:
| 判断维度 | 正确判断依据(基于设备响应) | 错误判断依据(本地预判) |
|---|---|---|
success 是否为真 |
1. 收到完整响应帧;2. 响应帧控制字/命令字与发送指令匹配;3. 响应数据格式合法(长度、CRC校验通过) | 1. 指令发送成功(uart.write返回字节数正常);2. 未收到响应但假设设备已执行;3. 本地逻辑推导“应该成功” |
result 结果值 |
从设备响应数据中直接解析(如距离从响应字节中计算、开关状态从响应位中提取) | 本地预设固定值(如控制类指令直接返回True、查询类指令返回默认值) |
| 属性是否更新 | 响应解析后同步更新属性(如human_distance = 解析后的距离值) |
指令发送成功后直接修改属性(如presence_enabled = True) |
3.3.6.2.3 不同类型指令的返回参数示例
- 查询类指令:返回 “解析后的设备数据”
以 query_human_distance 为例,返回值严格基于设备响应解析,无响应则 success=False、result=None:
def query_human_distance(self, timeout=200):
"""查询人体距离(遵循“状态+结果”二元组规范)"""
return self._execute_operation(R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_DISTANCE, timeout=timeout)
# 实际执行逻辑(_execute_operation内部):
# 1. 发送查询指令后,等待设备响应
# 2. 若收到响应:
# - 校验控制字(0x80)、命令字(0x84)与指令匹配
# - 从响应数据中解析距离值((data[0] << 8) | data[1])
# - 返回 (True, 解析后的距离值),同时更新self.human_distance
# 3. 若超时/响应不匹配:
# - 返回 (False, None),不修改任何属性
- 控制类指令:返回 “设备确认的生效状态”
以 enable_human_presence 为例,result 并非本地预设的 True,而是从设备响应中提取的 “开关是否生效” 状态:
def enable_human_presence(self, timeout=200):
"""打开人体存在功能(遵循“状态+结果”二元组规范)"""
return self._execute_operation(R60ABD1.TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_ON, timeout=timeout)
# 实际执行逻辑:
# 1. 发送控制指令后,等待设备响应
# 2. 若收到响应:
# - 校验控制字(0x80)、命令字(0x00)与指令匹配
# - 从响应数据中解析开关状态(data[0] == 0x01 表示生效)
# - 返回 (True, True),同时更新self.presence_enabled = True
# 3. 若设备响应“未生效”(data[0] == 0x00):
# - 返回 (True, False),self.presence_enabled = False
# 4. 若超时/响应异常:
# - 返回 (False, None),不修改属性
- 配置类指令:返回 “设备确认的配置参数”
以 set_low_breath_threshold 为例,result 是设备响应中确认的配置后阈值,确保配置已实际生效:
def set_low_breath_threshold(self, threshold, timeout=200):
"""设置低缓呼吸阈值(遵循“状态+结果”二元组规范)"""
# 传入自定义配置数据,发送指令
return self._execute_operation(
R60ABD1.TYPE_SET_LOW_BREATH_THRESHOLD,
data=bytes([threshold]),
timeout=timeout
)
# 实际执行逻辑:
# 1. 发送配置指令(携带自定义阈值)后,等待设备响应
# 2. 若收到响应:
# - 校验控制字(0x81)、命令字(0x0B)与指令匹配
# - 从响应数据中解析确认的阈值(data[0])
# - 返回 (True, 确认后的阈值),同时更新self.low_breath_threshold
# 3. 若设备响应的阈值与发送值不一致:
# - 返回 (True, 设备实际配置的阈值),同步更新属性为设备确认值
# 4. 若超时/响应异常:
# - 返回 (False, None),不修改属性
3.3.6.2.4 简要概述
- 一致性:所有命令响应方法返回格式统一,上层调用无需适配不同类型指令的返回逻辑(如统一通过
success判断是否有效,result提取具体结果); - 可靠性:基于设备响应的唯一判断依据,避免 “指令发送成功但设备未执行”“本地状态与设备状态不一致” 等隐蔽问题;
- 可调试性:通过
success状态快速定位 “指令未响应”“响应不匹配” 等问题,通过result直接获取设备真实反馈,便于问题排查; - 兼容性:统一格式为后续功能扩展(如批量指令执行、异常重试机制)提供标准化接口,降低上层系统集成成本。
3.3.6.3 阻塞式查询方法实现:以存在信息查询为例
在 R60ABD1 类中添加以下属性,用于跟踪查询的生命周期:
class R60ABD1:
def __init__(self, data_processor, **kwargs):
# ... 其他属性初始化 ...
# 查询状态管理
self._query_in_progress = False # 是否有查询在进行中
self._query_response_received = False # 是否收到响应
self._query_result = None # 查询结果
self._current_query_type = None # 当前查询类型
self._query_timeout = 200 # 默认查询超时时间(ms)
接下来,我们以存在信息查询为例,说明阻塞式查询方法的设计与实现:
def query_presence_status(self, timeout=200):
"""
查询存在信息状态(阻塞式)
Args:
timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒
Returns:
tuple: (查询状态, 存在状态信息)
- 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败
- 存在状态信息: 0-无人, 1-有人 (查询成功时有效)
"""
if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False # 临时禁用定时器,避免数据竞争
# 初始化查询状态
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO
# 构造查询指令帧
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
control = bytes([0x80])
command = bytes([0x81])
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01])
data = bytes([0x0F])
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + bytes([0x54, 0x43])
# 发送指令
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Presence status query sent: {query_frame.hex()}")
# 等待响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Presence status query timeout")
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100) # 微秒级延迟,避免CPU占用
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Presence status query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
# 清理查询状态并恢复定时器
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
基于相同设计思路,可扩展心跳查询、产品信息查询、初始化状态查询等方法,例如:
def query_heartbeat(self, timeout=200):
"""查询心跳包状态(阻塞式)"""
# 逻辑与query_presence_status一致,仅指令类型和解析逻辑不同
...
def query_product_model(self, timeout=200):
"""查询产品型号(阻塞式)"""
...
3.3.6.4 update_properties_from_frame 的响应帧处理扩展
在原有主动上报解析逻辑中,添加查询响应帧的识别与处理分支,确保属性更新与查询结果同步:
def update_properties_from_frame(self, frame):
control = frame['control_byte']
command = frame['command_byte']
data = frame['data']
# ... 原有主动上报帧处理逻辑(系统、存在、呼吸、心率等)...
# 人体存在检测(查询响应分支)
elif control == 0x80 and command == 0x81:
if data and len(data) > 0:
presence_value = data[0]
self.presence_status = presence_value
# 匹配当前查询类型,更新查询结果
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO and
not self._query_response_received):
self._query_result = presence_value
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Presence status response: {'Someone' if presence_value else 'No one'}")
通过这种方式,查询响应帧会同时更新业务属性和查询结果,实现 “一次解析,双重用途”。
整体流程如下表和图所示:
| 步骤序号 | 操作 / 状态 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 检查查询冲突 | 若已有查询在进行(_query_in_progress=True),返回 None,终止流程 |
| 2 | 临时禁用定时器 | 保存原始运行状态(original_running),设置_is_running=False 避免竞争 |
| 3 | 初始化查询状态 | 设置_query_in_progress=True、_query_response_received=False、_current_query_type="presence",清空_query_result |
| 4 | 构造并发送查询指令 | 组装包含 header、control(0x80)、command(0x81)等的帧,计算 CRC 后通过 UART 发送 |
| 5 | 等待响应(循环) | 记录开始时间,循环等待响应: - 若超时(超过 timeout 毫秒),返回 None - 短暂延迟(100us)避免占用 CPU - 解析数据流,调用 update_properties_from_frame 处理帧 |
| 6 | 处理响应帧 | 当收到 control=0x80、command=0x81 的帧(查询响应): - 若当前是存在查询且未收到响应,更新_query_result 为数据值,设置_query_response_received=True |
| 7 | 返回查询结果 | 响应接收后,退出循环,返回_query_result(0 = 无人,1 = 有人) |
| 8 | 异常处理 | 若过程中发生异常,返回 None |
| 9 | 重置状态(最终步骤) | 无论成功 / 失败 / 超时,重置_query_in_progress=False、_query_response_received=False 等,恢复定时器原始状态 |
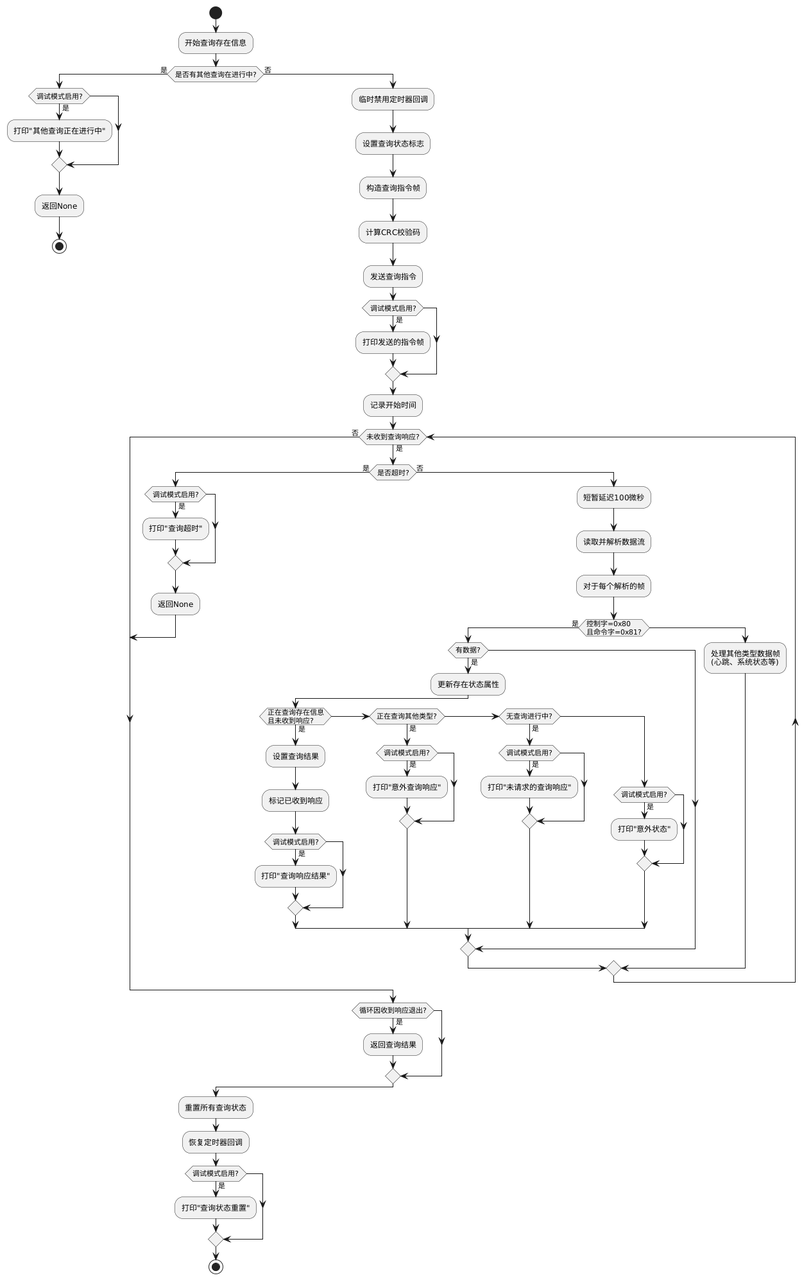
3.3.6.5 测试验证:查询与主动上报的兼容性
接下来,我们首先测试一下该方法能不能在没有任何上报信息时候(除去心跳包外),正常解析:
- 场景 1:关闭主动上报,仅测试查询功能
- 操作:关闭人体存在、心率、呼吸、睡眠的主动上报功能;
- 测试:在 REPL 中调用
query_presence_status,验证返回结果与设备实际状态(有人 / 无人)一致。
- 场景 2:开启主动上报,验证查询与上报的并行性
- 操作:开启所有主动上报功能,同时调用查询方法(如
query_firmware_version); - 测试:观察
main.py输出,确认主动上报数据正常解析的同时,查询指令能返回正确结果(如固件版本字符串)。
- 操作:开启所有主动上报功能,同时调用查询方法(如
首先关闭人体存在主动上报、心率监测、呼吸监测和睡眠监测功能:
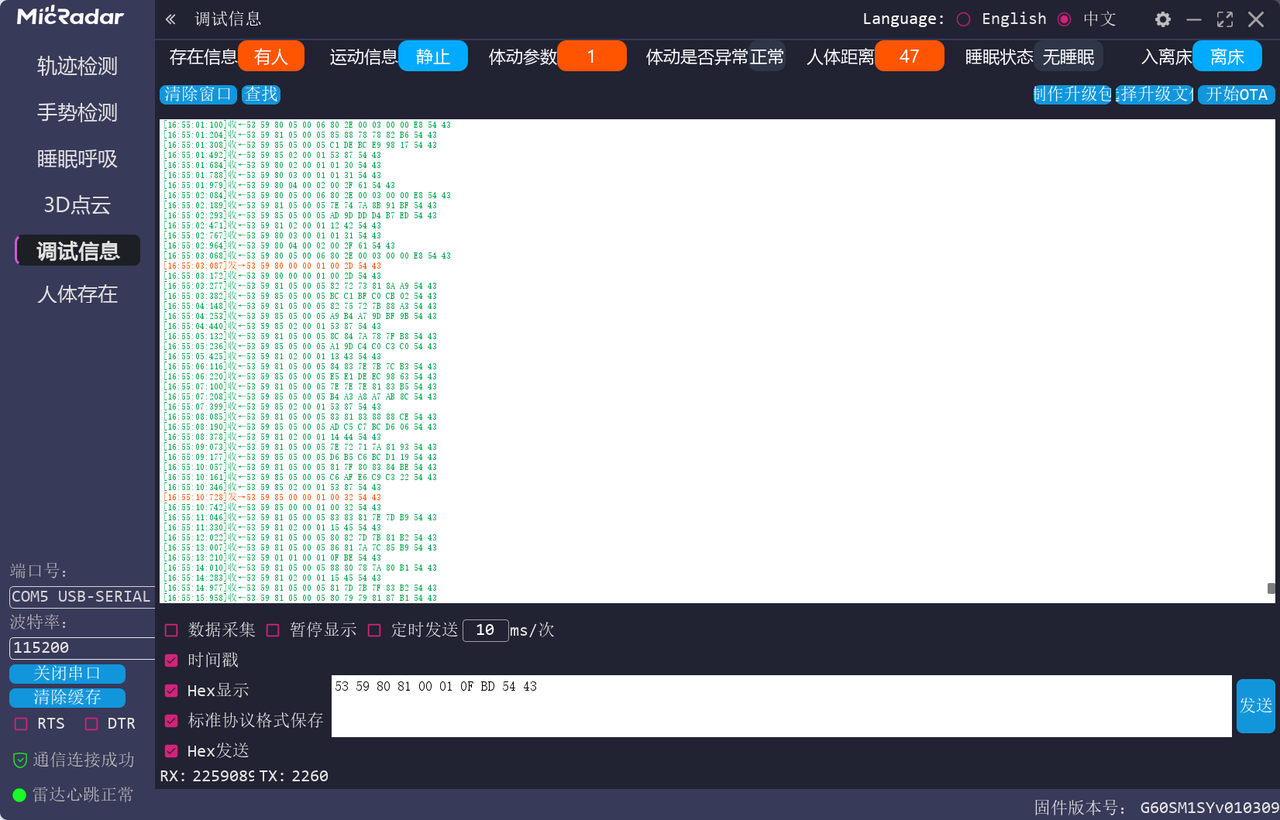
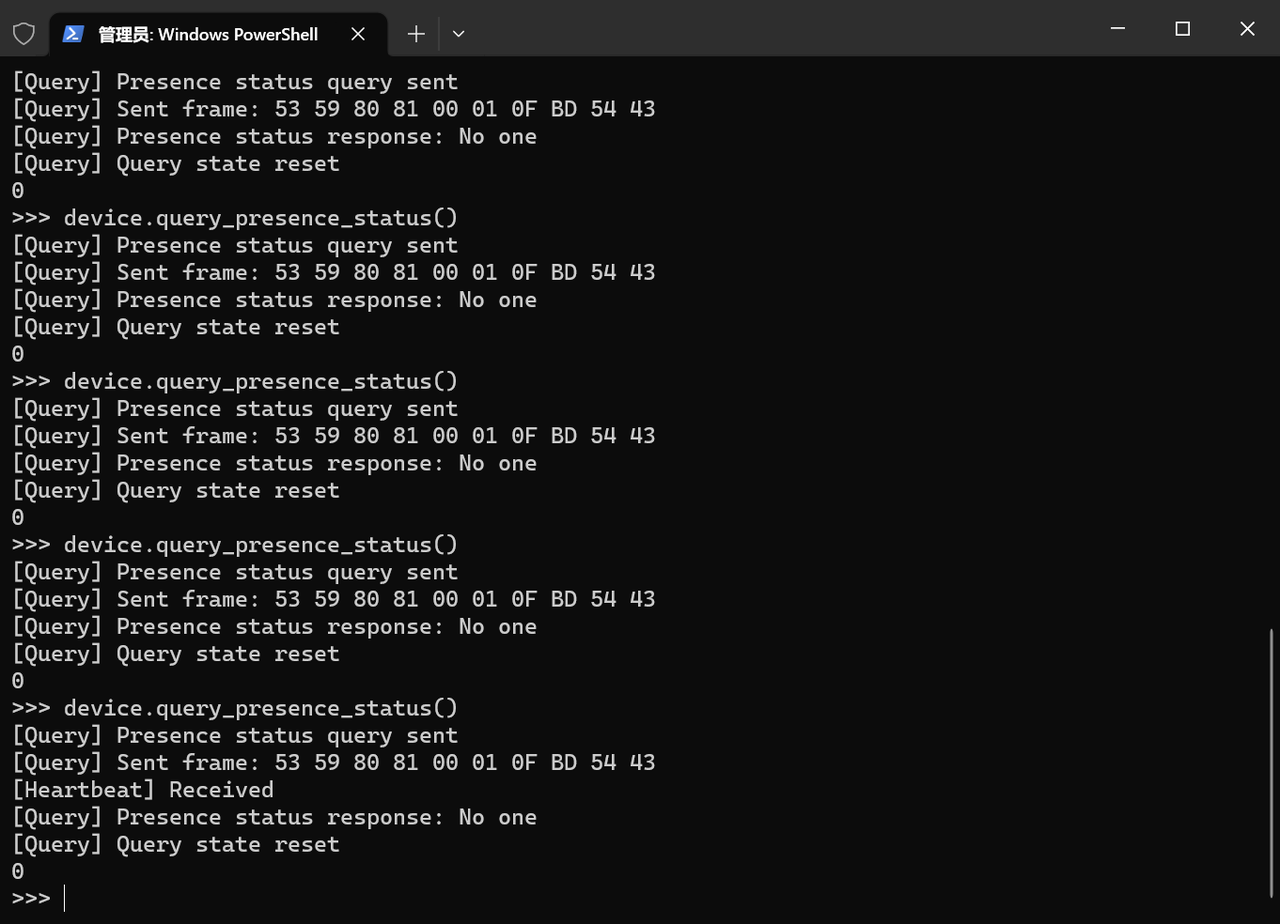
接下来,我们将主动上报数据全部开启,看看能否正常解析(同时修改 main.py):
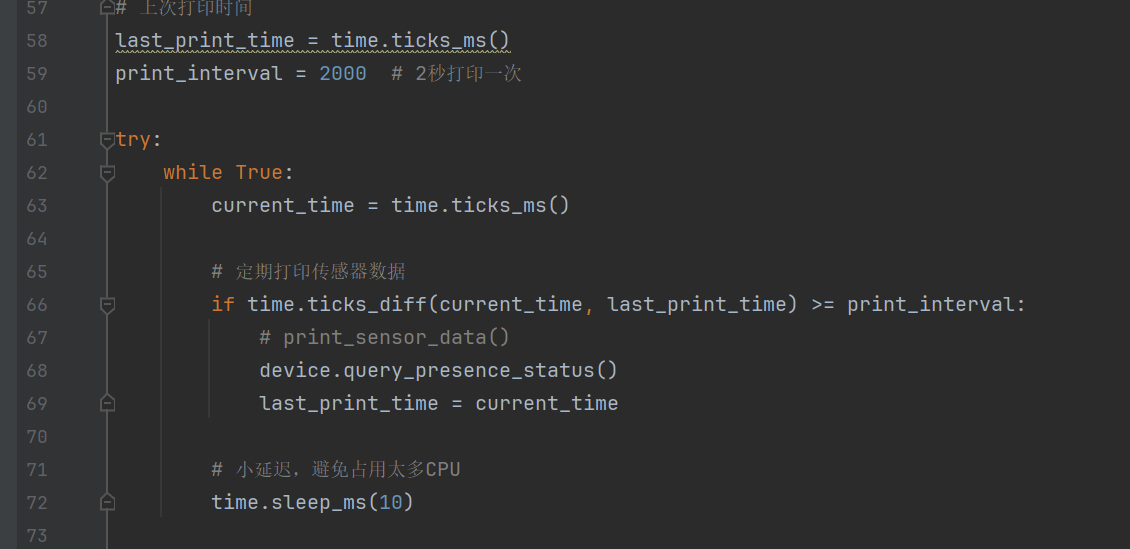
可以看到,正常解析没有问题:
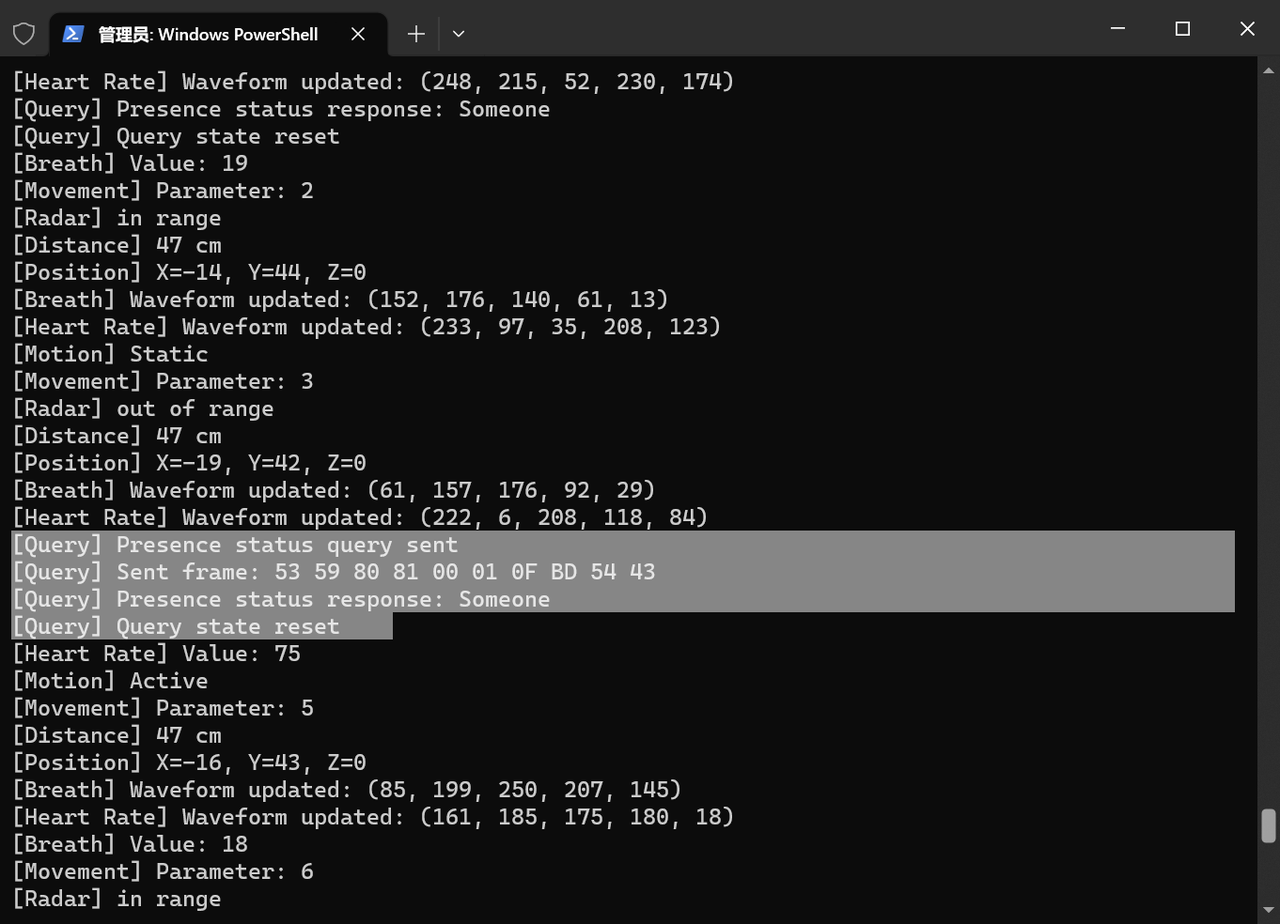
我们取消调试属性,重新烧录代码,并且提前按下 ctrl+c 退出主循环,在 REPL 中测试结果如下:
3.3.6.6 类属性常量的设计:协议与业务的映射桥梁
在 R60ABD1 类中,大量类属性(如 TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT、MOTION_STATIC 等)并非凭空定义,而是对设备通信协议的抽象与封装。这些常量是连接 “底层协议数值” 与 “上层业务逻辑” 的关键桥梁,其设计目的是解决嵌入式设备通信中 “协议数值可读性差、业务逻辑与硬件耦合紧” 的核心问题:
常量的来源:设备协议的 “翻译”
- 毫米波雷达模块的通信协议(如帧结构、状态值、指令类型)通常以十六进制数值定义(如0x01表示 “有人”,0x80表示 “存在信息查询指令”)。直接在代码中使用这些数值会导致:
- 可读性差:if status == 0x01无法直观表达 “有人状态”;
- 可维护性低:协议更新时需全局修改所有硬编码数值;
- 易错性高:数值重复或混淆可能导致逻辑错误。
- 因此,类属性常量的本质是将协议中的数值 “翻译” 为人类可读的标识符。例如:
- 协议中0x00表示 “无运动”,映射为MOTION_NONE;
- 协议中0x81表示 “存在信息查询指令”,映射为TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO。
常量的分类与设计逻辑
根据功能,类属性常量可分为两类,均严格遵循 “与协议一一对应” 的原则:
① 状态值常量:描述设备的业务状态,用于定义设备返回的各类状态(如运动状态、呼吸状态、睡眠状态等)。
# 运动信息状态:对应协议中0x00-0x02的数值
MOTION_NONE, MOTION_STATIC, MOTION_ACTIVE = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
# 呼吸信息状态:对应协议中0x01-0x04的数值
BREATH_NORMAL, BREATH_HIGH, BREATH_LOW, BREATH_NONE = (0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04)
这些常量直接对应协议中定义的状态编码,在update_properties_from_frame方法中用于状态判断与文本转换(如将0x01转换为 MOTION_STATIC)。
② 指令类型常量:标识主动交互的指令,用于定义所有主动查询 / 控制指令的类型(如查询产品型号、开启心率监测等),例如:
# 基础指令类型:对应协议中不同的控制字+命令字组合
TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT = 0 # 心跳包查询指令
TYPE_MODULE_RESET = 1 # 模组复位指令
# 人体存在相关指令:对应协议中0x80控制字下的命令
TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_ON = 8 # 开启人体存在功能
TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO = 11 # 存在信息查询
这些常量与_current_query_type配合,在命令响应逻辑中标识当前查询的类型,确保update_properties_from_frame能准确匹配响应帧并更新_query_result。
常量的核心价值如下:
- 解耦业务与硬件:通过常量隔离协议细节,业务逻辑无需直接处理十六进制数值,降低对硬件协议的依赖;
- 提升代码可维护性:协议更新时,只需修改常量与数值的映射关系,无需调整业务逻辑代码;
- 增强可读性与协作效率:
if status == MOTION_STATIC比if status == 0x01更直观,便于团队协作与后期调试; - 减少错误:避免硬编码数值导致的笔误(如将
0x0F误写为0xF0),通过常量名的唯一性保障逻辑正确性。
3.3.6.7 基础指令类查询方法的扩展与验证
在命令响应逻辑的整体框架下,针对心跳监测、模组复位、产品信息查询、系统初始化检测、雷达范围诊断等基础指令场景,我们扩展了一系列查询方法。这些方法遵循 “状态管理 → 指令构造 → 响应等待 → 属性更新” 的统一流程,并通过 update_properties_from_frame 实现响应帧与业务属性的联动,确保设备交互的完整性与可靠性。
所有基础指令查询方法均基于 query_presence_status 的架构扩展,核心差异体现在指令类型(控制字 + 命令字)、响应解析逻辑、属性更新目标三个维度:
| 方法名 | 指令类型 | 响应解析逻辑 | 属性更新目标 |
|---|---|---|---|
| query_heartbeat | 0x01+0x80 | 心跳包状态直接判断 | heartbeat_last_received |
| reset_module | 0x01+0x02 | 设备原样返回指令作为确认 | module_reset_flag、module_reset_timestamp |
| query_product_model | 0x02+0xA1 | 调用_parse_product_info_data解析字符串 | product_model |
| query_firmware_version | 0x02+0xA4 | 调用_parse_firmware_version_data解析字符串 | firmware_version |
| query_init_complete | 0x05+0x81 | 解析初始化完成标识(0x01为完成) | system_initialized |
| query_radar_range_boundary | 0x07+0x87 | 解析越界标识(0x01为越界) | radar_in_range(越界则为False) |
以 query_heartbeat 为例,其核心逻辑为 “构造心跳查询指令 → 等待响应 → 更新心跳时间戳与查询结果”,通过状态管理避免并发查询,确保指令执行的原子性:
def query_heartbeat(self, timeout=200):
if self._query_in_progress:
return False, None
try:
# 状态初始化与指令构造
self._query_in_progress = True
query_frame = bytes([0x53, 0x59, 0x01, 0x80, 0x00, 0x01, 0x0F, ...]) # 完整帧构造
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
# 响应等待与属性更新(通过update_properties_from_frame实现)
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
return True, self._query_result
finally:
# 状态清理
self._query_in_progress = False
为支持基础指令的查询响应,需在 update_properties_from_frame 中添加指令类型匹配与属性更新分支。以 “心跳查询响应” 和 “产品型号查询响应” 为例,实现 “响应帧 → 属性 → 查询结果” 的联动:
def update_properties_from_frame(self, frame):
control = frame['control_byte']
command = frame['command_byte']
data = frame['data']
# 心跳查询响应:更新心跳时间戳与查询结果
if control == 0x01 and command == 0x80:
self.heartbeat_last_received = time.ticks_ms()
if self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type == self.TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT:
self._query_result = True
self._query_response_received = True
# 产品型号查询响应:解析字符串并更新产品型号属性
elif control == 0x02 and command == 0xA1:
product_info = self._parse_product_info_data(data)[0]
self.product_model = product_info
if self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type == self.TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL:
self._query_result = product_info
self._query_response_received = True
# ... 其他指令响应分支同理扩展 ...
目前 R60ABD1 类的完整代码如下所示:
# Python env :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/11/4 下午5:35
# @Author : 李清水
# @File : r60abd1.py
# @Description :
from machine import Timer
import time
import micropython
def format_time():
_"""格式化当前时间为 [YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.sss] 格式"""_
_ _t = time.localtime()
ms = time.ticks_ms() % 1000
return f"[{t[0]}-{t[1]:02d}-{t[2]:02d} {t[3]:02d}:{t[4]:02d}:{t[5]:02d}.{ms:03d}]"
# 计时装饰器,用于计算函数运行时间
def timed_function(f: callable, *args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> callable:
_"""_
_ 计时装饰器,用于计算并打印函数/方法运行时间。_
_ Args:_
_ f (callable): 需要传入的函数/方法_
_ args (tuple): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的位置参数_
_ kwargs (dict): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的关键字参数_
_ Returns:_
_ callable: 返回计时后的函数_
_ """_
_ _myname = str(f).split(' ')[1]
def new_func(*args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> any:
t: int = time.ticks_us()
result = f(*args, **kwargs)
delta: int = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_us(), t)
print('Function {} Time = {:6.3f}ms'.format(myname, delta / 1000))
return result
return new_func
class R60ABD1:
_"""_
_ R60ABD1雷达设备业务处理类_
_ """_
_ _# 是否启用调试
DEBUG_ENABLED = True
# R60ABD1雷达设备业务处理类中各种状态值和配置选项的常量
# 运动信息状态
MOTION_NONE, MOTION_STATIC, MOTION_ACTIVE = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
# 呼吸信息状态
BREATH_NORMAL, BREATH_HIGH, BREATH_LOW, BREATH_NONE = (0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04)
# 床状态
BED_LEAVE, BED_ENTER, BED_NONE = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
# 睡眠状态
SLEEP_DEEP, SLEEP_LIGHT, SLEEP_AWAKE, SLEEP_NONE = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03)
# 睡眠异常信息
SLEEP_ANOMALY_NONE, SLEEP_ANOMALY_SHORT, SLEEP_ANOMALY_LONG, SLEEP_ANOMALY_NO_PERSON = (0x03, 0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
# 睡眠质量级别
SLEEP_QUALITY_NONE, SLEEP_QUALITY_GOOD, SLEEP_QUALITY_NORMAL, SLEEP_QUALITY_POOR = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03)
# 异常挣扎状态
STRUGGLE_NONE, STRUGGLE_NORMAL, STRUGGLE_ABNORMAL = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
# 无人计时状态
NO_PERSON_TIMING_NONE, NO_PERSON_TIMING_NORMAL, NO_PERSON_TIMING_ABNORMAL = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
# 挣扎状态判读灵敏度
SENSITIVITY_LOW, SENSITIVITY_MEDIUM, SENSITIVITY_HIGH = (0x00, 0x01, 0x02)
# R60ABD1雷达设备指令类型常量,用于标识不同的查询和控制操作
# 基础指令信息查询和设置类型
# 心跳包查询
TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT = 0
# 模组复位指令
TYPE_MODULE_RESET = 1
# 产品型号查询
TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL = 2
# 产品 ID 查询
TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_ID = 3
# 硬件型号查询
TYPE_QUERY_HARDWARE_MODEL = 4
# 固件版本查询
TYPE_QUERY_FIRMWARE_VERSION = 5
# 初始化是否完成查询
TYPE_QUERY_INIT_COMPLETE = 6
# 雷达探测范围越界状态查询
TYPE_QUERY_RADAR_RANGE_BOUNDARY = 7
# 人体存在指令信息查询和设置类型
# 打开人体存在功能
TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_ON = 8
# 关闭人体存在功能
TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_OFF = 9
# 查询人体存在开关状态
TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_PRESENCE_SWITCH = 10
# 存在信息查询
TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO = 11
# 运动信息查询
TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_MOTION_INFO = 12
# 体动参数查询
TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_BODY_MOTION_PARAM = 13
# 人体距离查询
TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_DISTANCE = 14
# 人体方位查询
TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_DIRECTION = 15
# 心率监测指令信息查询和设置类型
# 打开心率监测功能
TYPE_CONTROL_HEART_RATE_MONITOR_ON = 16
# 关闭心率监测功能
TYPE_CONTROL_HEART_RATE_MONITOR_OFF = 17
# 查询心率监测开关状态
TYPE_QUERY_HEART_RATE_MONITOR_SWITCH = 18
# 打开心率波形上报开关
TYPE_CONTROL_HEART_RATE_WAVEFORM_REPORT_ON = 19
# 关闭心率波形上报开关
TYPE_CONTROL_HEART_RATE_WAVEFORM_REPORT_OFF = 20
# 查询心率波形上报开关状态
TYPE_QUERY_HEART_RATE_WAVEFORM_REPORT_SWITCH = 21
# 心率数值查询
TYPE_QUERY_HEART_RATE_VALUE = 22
# 心率波形查询
TYPE_QUERY_HEART_RATE_WAVEFORM = 23
# 呼吸监测指令信息查询和设置类型
# 打开呼吸监测功能
TYPE_CONTROL_BREATH_MONITOR_ON = 24
# 关闭呼吸监测功能
TYPE_CONTROL_BREATH_MONITOR_OFF = 25
# 查询呼吸监测开关状态
TYPE_QUERY_BREATH_MONITOR_SWITCH = 26
# 设置低缓呼吸判读阈值
TYPE_SET_LOW_BREATH_THRESHOLD = 27
# 查询低缓呼吸判读阈值
TYPE_QUERY_LOW_BREATH_THRESHOLD = 28
# 呼吸信息查询
TYPE_QUERY_BREATH_INFO = 29
# 呼吸数值查询
TYPE_QUERY_BREATH_VALUE = 30
# 打开呼吸波形上报开关
TYPE_CONTROL_BREATH_WAVEFORM_REPORT_ON = 31
# 关闭呼吸波形上报开关
TYPE_CONTROL_BREATH_WAVEFORM_REPORT_OFF = 32
# 查询呼吸波形上报开关状态
TYPE_QUERY_BREATH_WAVEFORM_REPORT_SWITCH = 33
# 呼吸波形查询
TYPE_QUERY_BREATH_WAVEFORM = 34
# 睡眠监测指令信息查询和设置类型
# 打开睡眠监测功能
TYPE_CONTROL_SLEEP_MONITOR_ON = 35
# 关闭睡眠监测功能
TYPE_CONTROL_SLEEP_MONITOR_OFF = 36
# 查询睡眠监测开关状态
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_MONITOR_SWITCH = 37
# 打开异常挣扎状态监测
TYPE_CONTROL_ABNORMAL_STRUGGLE_ON = 38
# 关闭异常挣扎状态监测
TYPE_CONTROL_ABNORMAL_STRUGGLE_OFF = 39
# 查询异常挣扎状态开关
TYPE_QUERY_ABNORMAL_STRUGGLE_SWITCH = 40
# 查询异常挣扎状态
TYPE_QUERY_ABNORMAL_STRUGGLE_STATUS = 41
# 设置挣扎状态判读灵敏度
TYPE_SET_STRUGGLE_SENSITIVITY = 42
# 查询挣扎状态判读灵敏度
TYPE_QUERY_STRUGGLE_SENSITIVITY = 43
# 打开无人计时功能
TYPE_CONTROL_NO_PERSON_TIMING_ON = 44
# 关闭无人计时功能
TYPE_CONTROL_NO_PERSON_TIMING_OFF = 45
# 查询无人计时功能开关
TYPE_QUERY_NO_PERSON_TIMING_SWITCH = 46
# 设置无人计时时长
TYPE_SET_NO_PERSON_TIMING_DURATION = 47
# 查询无人计时时长
TYPE_QUERY_NO_PERSON_TIMING_DURATION = 48
# 设置睡眠截止时长
TYPE_SET_SLEEP_END_DURATION = 49
# 查询睡眠截止时长
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_END_DURATION = 50
# 入床/离床状态查询
TYPE_QUERY_BED_STATUS = 51
# 睡眠状态查询
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_STATUS = 52
# 清醒时长查询
TYPE_QUERY_AWAKE_DURATION = 53
# 浅睡时长查询
TYPE_QUERY_LIGHT_SLEEP_DURATION = 54
# 深睡时长查询
TYPE_QUERY_DEEP_SLEEP_DURATION = 55
# 睡眠质量评分查询
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_QUALITY_SCORE = 56
# 睡眠综合状态查询
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_COMPREHENSIVE_STATUS = 57
# 睡眠异常查询
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_ANOMALY = 58
# 睡眠统计查询
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_STATISTICS = 59
# 睡眠质量评级查询
TYPE_QUERY_SLEEP_QUALITY_LEVEL = 60
def __init__(self, data_processor, parse_interval=50,presence_enabled=True, heart_rate_enabled=True,
breath_monitoring_enabled=True, sleep_monitoring_enabled=True):
_"""_
_ 初始化R60ABD1实例_
_ Args:_
_ data_processor: DataFlowProcessor实例_
_ presence_enabled: 是否开启人体存在信息监测_
_ heart_rate_enabled: 是否开启心率监测_
_ breath_monitoring_enabled: 是否开启呼吸监测_
_ sleep_monitoring_enabled: 是否开启睡眠监测_
_ """_
_ _if parse_interval > 200:
raise ValueError("parse_interval must be less than 200ms")
self.data_processor = data_processor
self.parse_interval = parse_interval
# 添加运行状态标志
self._is_running = False
# ============================ 1. 系统级属性 ============================
# 心跳包监控
self.heartbeat_last_received = 0 # 最后接收心跳包时间戳(ms)
self.heartbeat_timeout_count = 0 # 心跳超时累计次数
self.heartbeat_interval = 0 # 实际心跳间隔统计(ms)
# 系统状态
self.system_initialized = False # 初始化完成状态(True/False)
self.system_initialized_timestamp = 0 # 初始化完成时间戳(ms)
self.module_reset_flag = False # 模组复位状态标记
self.module_reset_timestamp = 0 # 模组复位时间戳(ms)
# 产品信息
self.product_model = "" # 产品型号(字符串)
self.product_id = "" # 产品ID(字符串)
self.hardware_model = "" # 硬件型号(字符串)
self.firmware_version = "" # 固件版本(字符串)
# ============================ 2. 雷达探测属性 ============================
# 位置状态
self.radar_in_range = False # 是否在探测范围内
# ============================ 3. 人体存在检测属性 ============================
# 基本状态
self.presence_enabled = presence_enabled # 人体存在功能开关
# 存在状态
self.presence_status = 0 # 0:无人, 1:有人
# 运动状态
self.motion_status = 0 # 0:无, 1:静止, 2:活跃
# 量化数据
self.movement_parameter = 0 # 体动参数(0-100)
self.human_distance = 0 # 人体距离(0-65535 cm)
self.human_position_x = 0 # X坐标(有符号)
self.human_position_y = 0 # Y坐标(有符号)
self.human_position_z = 0 # Z坐标(有符号)
# ============================ 4. 呼吸监测属性 ============================
# 功能配置
self.breath_monitoring_enabled = breath_monitoring_enabled # 呼吸监测开关
self.breath_waveform_enabled = False # 呼吸波形上报开关
self.low_breath_threshold = 10 # 低缓呼吸阈值(10-20次/min)
# 监测数据
self.breath_status = 0 # 1:正常, 2:过高, 3:过低, 4:无
self.breath_value = 0 # 呼吸数值(0-35次/分)
self.breath_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 5个字节的波形数据
# ============================ 5. 心率监测属性 ============================
# 功能配置
self.heart_rate_enabled = heart_rate_enabled # 心率监测开关
self.heart_rate_waveform_enabled = False # 心率波形上报开关
# 监测数据
self.heart_rate_value = 0 # 心率数值(60-120)
self.heart_rate_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 5个字节的波形数据
# ============================ 6. 睡眠监测属性 ============================
# 基础状态
self.sleep_monitoring_enabled = sleep_monitoring_enabled # 睡眠监测开关
self.bed_status = 0 # 0:离床, 1:入床, 2:无
self.sleep_status = 0 # 0:深睡, 1:浅睡, 2:清醒, 3:无
# 时长统计
self.awake_duration = 0 # 清醒时长(分钟)
self.light_sleep_duration = 0 # 浅睡时长(分钟)
self.deep_sleep_duration = 0 # 深睡时长(分钟)
# 睡眠质量
self.sleep_quality_score = 0 # 睡眠质量评分(0-100)
self.sleep_quality_rating = 0 # 睡眠质量评级
# 综合状态
self.sleep_comprehensive_status = {} # 包含8个字段的字典
self.sleep_anomaly = 0 # 睡眠异常状态
self.abnormal_struggle_status = 0 # 异常挣扎状态
self.no_person_timing_status = 0 # 无人计时状态
# 配置参数
self.abnormal_struggle_enabled = False # 异常挣扎开关
self.no_person_timing_enabled = False # 无人计时开关
self.no_person_timing_duration = 30 # 无人计时时长
self.sleep_cutoff_duration = 120 # 睡眠截止时长
self.struggle_sensitivity = 1 # 挣扎灵敏度
# 查询状态管理
self._query_in_progress = False # 是否有查询在进行中
self._query_response_received = False # 是否收到查询响应
self._query_result = None # 查询结果
self._current_query_type = None # 当前查询类型
self._query_timeout = 200 # 默认查询超时时间(ms)
self.timer = Timer(-1)
self._start_timer()
def _start_timer(self):
_"""启动定时器"""_
_ _self._is_running = True
self.timer.init(period=self.parse_interval, mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=self._timer_callback)
def _timer_callback(self, timer):
_"""_
_ 定时器回调函数,定期解析数据帧_
_ Args:_
_ timer: 定时器实例_
_ """_
_ _if not self._is_running:
return
# 调用DataFlowProcessor的解析方法
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
# 对每个解析到的帧使用micropython.schedule进行异步处理
for frame in frames:
# 使用micropython.schedule安全地调用属性更新方法
micropython.schedule(self.update_properties_from_frame, frame)
def _calculate_crc(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 计算CRC校验码_
_ 校验码计算:帧头+控制字+命令字+长度标识+数据 求和后,取低八位_
_ Args:_
_ data_bytes: 字节序列或字节数组_
_ Returns:_
_ int: CRC校验码_
_ """_
_ _return sum(data_bytes) & 0xFF
def _parse_human_position_data(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析人体方位数据 (6字节: X(2B), Y(2B), Z(2B))_
_ 位置信息有正负:16位数据,最高位为符号位,剩余15位为数据位_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (x, y, z) 坐标值,单位cm_
_ """_
_ _if len(data_bytes) != 6:
return (0, 0, 0)
x = self._parse_signed_16bit_special(data_bytes[0:2])
y = self._parse_signed_16bit_special(data_bytes[2:4])
z = self._parse_signed_16bit_special(data_bytes[4:6])
return (x, y, z)
def _parse_signed_16bit_special(self, two_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析有符号16位数据(特殊格式:首位符号位 + 后15位数值位)_
_ 最高位为符号位,0=正数,1=负数,剩余15位为数值_
_ Args:_
_ two_bytes: 2字节的字节序列(大端序)_
_ Returns:_
_ int: 有符号16位整数_
_ """_
_ _if len(two_bytes) != 2:
return 0
# 组合成16位无符号整数(大端序)
unsigned_value = (two_bytes[0] << 8) | two_bytes[1]
# 提取符号位和数值
sign_bit = (unsigned_value >> 15) & 0x1 # 最高位为符号位
magnitude = unsigned_value & 0x7FFF # 低15位为数值
# 根据符号位确定正负
if sign_bit == 1: # 负数
return -magnitude
else: # 正数
return magnitude
def _parse_heart_rate_waveform_data(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析心率波形数据 (5字节)_
_ 5个字节代表实时1s内5个数值,波形为正弦波数据,中轴线为128_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: 5个波形数据值 (v1, v2, v3, v4, v5),数值范围0-255_
_ """_
_ _if len(data_bytes) != 5:
return (128, 128, 128, 128, 128)
return (
data_bytes[0],
data_bytes[1],
data_bytes[2],
data_bytes[3],
data_bytes[4]
)
def _parse_sleep_comprehensive_data(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析睡眠综合状态数据 (8字节)_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (存在, 睡眠状态, 平均呼吸, 平均心跳, 翻身次数, 大幅度体动占比, 小幅度体动占比, 呼吸暂停次数)_
_ """_
_ _if len(data_bytes) != 8:
return (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
return (
data_bytes[0], # 存在: 1有人 0无人
data_bytes[1], # 睡眠状态: 3离床 2清醒 1浅睡 0深睡
data_bytes[2], # 平均呼吸: 10分钟内检测的平均值
data_bytes[3], # 平均心跳: 10分钟内检测的平均值
data_bytes[4], # 翻身次数: 处于浅睡或深睡的翻身次数
data_bytes[5], # 大幅度体动占比: 0~100
data_bytes[6], # 小幅度体动占比: 0~100
data_bytes[7] # 呼吸暂停次数: 10分钟呼吸暂停次数
)
def _parse_sleep_statistics_data(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析睡眠统计信息数据 (12字节)_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (睡眠质量评分, 睡眠总时长, 清醒时长占比, 浅睡时长占比, 深睡时长占比,_
_ 离床时长, 离床次数, 翻身次数, 平均呼吸, 平均心跳, 呼吸暂停次数)_
_ """_
_ _if len(data_bytes) != 12:
return (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
# 解析2字节的睡眠总时长
total_sleep_duration = (data_bytes[1] << 8) | data_bytes[2]
return (
data_bytes[0], # 睡眠质量评分: 0~100
total_sleep_duration, # 睡眠总时长: 0~65535分钟
data_bytes[3], # 清醒时长占比: 0~100
data_bytes[4], # 浅睡时长占比: 0~100
data_bytes[5], # 深睡时长占比: 0~100
data_bytes[6], # 离床时长: 0~255
data_bytes[7], # 离床次数: 0~255
data_bytes[8], # 翻身次数: 0~255
data_bytes[9], # 平均呼吸: 0~25
data_bytes[10], # 平均心跳: 0~100
data_bytes[11] # 呼吸暂停次数: 0~10
)
def _parse_breath_waveform_data(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析呼吸波形数据 (5字节)_
_ 5个字节代表实时1s内5个数值,波形为正弦波数据,中轴线为128_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: 5个波形数据值 (v1, v2, v3, v4, v5),数值范围0-255_
_ """_
_ _if len(data_bytes) != 5:
return (128, 128, 128, 128, 128)
return (
data_bytes[0],
data_bytes[1],
data_bytes[2],
data_bytes[3],
data_bytes[4]
)
def _parse_product_info_data(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析产品信息数据 (可变长度字符串)_
_ 正确处理包含空字节的字符串_
_ """_
_ _try:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Raw product data: {data_bytes}, hex: {data_bytes.hex()}")
# 找到第一个空字节的位置,截取有效部分
if b'\x00' in data_bytes:
# 找到第一个空字节,截取之前的部分
null_index = data_bytes.index(b'\x00')
valid_data = data_bytes[:null_index]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] After null removal: {valid_data}, hex: {valid_data.hex()}")
else:
valid_data = data_bytes
# 解码为字符串 - 移除关键字参数
# MicroPython 的 decode 方法不支持 errors='ignore' 关键字参数
product_info = valid_data.decode('utf-8').strip()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Decoded product info: '{product_info}'")
return (product_info,)
except Exception as e:
# 如果解码失败,尝试其他方式
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Product info parse error: {e}, data: {data_bytes}")
# 尝试使用 ascii 解码作为备选方案
try:
product_info = valid_data.decode('ascii').strip()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] ASCII decoded product info: '{product_info}'")
return (product_info,)
except:
return ("",)
def _parse_firmware_version_data(self, data_bytes):
_"""_
_ 解析固件版本数据 (可变长度字符串)_
_ 正确处理包含空字节的字符串_
_ """_
_ _try:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Raw firmware data: {data_bytes}, hex: {data_bytes.hex()}")
# 找到第一个空字节的位置,截取有效部分
if b'\x00' in data_bytes:
# 找到第一个空字节,截取之前的部分
null_index = data_bytes.index(b'\x00')
valid_data = data_bytes[:null_index]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] After null removal: {valid_data}, hex: {valid_data.hex()}")
else:
valid_data = data_bytes
# 解码为字符串 - 移除关键字参数
version = valid_data.decode('utf-8').strip()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Decoded firmware version: '{version}'")
return (version,)
except Exception as e:
# 如果解码失败,尝试其他方式
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] Firmware version parse error: {e}, data: {data_bytes}")
# 尝试使用 ascii 解码作为备选方案
try:
version = valid_data.decode('ascii').strip()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Parse] ASCII decoded firmware version: '{version}'")
return (version,)
except:
return ("",)
def query_heartbeat(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询心跳包(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 心跳状态)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 心跳状态: True-心跳正常, False-心跳异常 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _# 检查查询状态,避免多个查询同时进行
if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
# 保存原始定时器状态并临时禁用定时器,避免数据竞争
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
# 设置查询状态标志
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT
# 构造心跳包查询指令帧
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59]) # 帧头
control = bytes([0x01]) # 控制字:系统指令
command = bytes([0x80]) # 命令字:心跳包查询
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01]) # 数据长度:1字节
data = bytes([0x0F]) # 固定数据
# 计算CRC校验码
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43]) # 帧尾
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
# 发送查询指令
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Heartbeat query sent")
# 打印发送的指令帧用于调试
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待设备响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
# 检查是否超时
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Heartbeat query timeout")
return False, None
# 短暂延迟避免过度占用CPU
time.sleep_us(100)
# 继续处理数据流,确保响应能被解析
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
# 返回查询结果:成功状态和心跳状态
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
# 异常处理:打印错误信息并返回失败状态
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Heartbeat query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
# 清理查询状态,确保资源正确释放
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
# 恢复定时器状态
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass # 如果original_running未定义,保持当前状态
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Heartbeat query state reset")
def reset_module(self, timeout=500):
_"""_
_ 模组复位(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒(复位需要较长时间,默认500ms)_
_ Returns:_
_ bool: True-复位成功, False-复位失败_
_ """_
_ _if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False
try:
# 保存原始定时器状态并临时禁用定时器
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
# 设置复位查询状态
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_MODULE_RESET
# 构造模组复位指令帧
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59]) # 帧头
control = bytes([0x01]) # 控制字:系统指令
command = bytes([0x02]) # 命令字:模组复位
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01]) # 数据长度:1字节
data = bytes([0x0F]) # 固定数据
# 计算CRC校验码
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43]) # 帧尾
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
# 发送复位指令
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Module reset command sent")
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待复位响应(设备会原样返回指令作为确认)
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Module reset timeout")
return False
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
# 返回复位结果
return self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Module reset error: {e}")
return False
finally:
# 清理查询状态
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
# 恢复定时器状态
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Module reset state reset")
def query_product_model(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询产品型号(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 产品型号)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 产品型号: 字符串 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
# 保存原始定时器状态并临时禁用定时器
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
# 设置产品型号查询状态
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL
# 构造产品型号查询指令帧
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59]) # 帧头
control = bytes([0x02]) # 控制字:产品信息
command = bytes([0xA1]) # 命令字:产品型号查询
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01]) # 数据长度:1字节
data = bytes([0x0F]) # 固定数据
# 计算CRC校验码
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43]) # 帧尾
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
# 发送查询指令
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Product model query sent")
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待产品型号响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Product model query timeout")
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
# 返回查询结果:成功状态和产品型号字符串
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Product model query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
# 清理查询状态
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
# 恢复定时器状态
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Product model query state reset")
def query_product_id(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询产品ID(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 产品ID)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 产品ID: 字符串 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_ID
# 构造产品ID查询指令
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
control = bytes([0x02])
command = bytes([0xA2])
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01])
data = bytes([0x0F])
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Product ID query sent")
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Product ID query timeout")
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Product ID query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Product ID query state reset")
def query_hardware_model(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询硬件型号(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 硬件型号)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 硬件型号: 字符串 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HARDWARE_MODEL
# 构造硬件型号查询指令
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
control = bytes([0x02])
command = bytes([0xA3])
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01])
data = bytes([0x0F])
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Hardware model query sent")
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Hardware model query timeout")
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Hardware model query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Hardware model query state reset")
def query_firmware_version(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询固件版本(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 固件版本)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 固件版本: 字符串 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_FIRMWARE_VERSION
# 构造固件版本查询指令
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
control = bytes([0x02])
command = bytes([0xA4])
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01])
data = bytes([0x0F])
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Firmware version query sent")
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Firmware version query timeout")
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Firmware version query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Firmware version query state reset")
def query_init_complete(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询初始化是否完成(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 初始化状态)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 初始化状态: True-已完成, False-未完成 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_INIT_COMPLETE
# 构造初始化完成查询指令
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
control = bytes([0x05])
command = bytes([0x81])
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01])
data = bytes([0x0F])
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Init complete query sent")
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Init complete query timeout")
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Init complete query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Init complete query state reset")
def query_radar_range_boundary(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询雷达探测范围越界状态(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 越界状态)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 越界状态: True-越界, False-正常范围内 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_RADAR_RANGE_BOUNDARY
# 构造雷达探测范围查询指令
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
control = bytes([0x07])
command = bytes([0x87])
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01])
data = bytes([0x0F])
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Radar range boundary query sent")
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Radar range boundary query timeout")
return False, None
time.sleep_us(100)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Radar range boundary query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Radar range boundary query state reset")
def query_presence_status(self, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 查询存在信息状态(阻塞式)_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ tuple: (查询状态, 存在状态信息)_
_ - 查询状态: True-查询成功, False-查询失败_
_ - 存在状态信息: 0-无人, 1-有人 (查询成功时有效)_
_ """_
_ _# 检查是否已有查询在进行中
if self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Another query in progress, aborting")
return False, None
try:
# 临时禁用定时器回调,避免竞争
original_running = self._is_running
self._is_running = False
# 设置查询状态
self._query_in_progress = True
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO
# 构造并发送查询指令
header = bytes([0x53, 0x59])
control = bytes([0x80])
command = bytes([0x81])
length = bytes([0x00, 0x01])
data = bytes([0x0F])
crc_data = header + control + command + length + data
crc = self._calculate_crc(crc_data)
trailer = bytes([0x54, 0x43])
query_frame = crc_data + bytes([crc]) + trailer
self.data_processor.uart.write(query_frame)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Presence status query sent")
# 调试信息:打印发送的指令
frame_hex = ' '.join(['{:02X}'.format(b) for b in query_frame])
print(f"[Query] Sent frame: {frame_hex}")
# 等待响应
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while not self._query_response_received:
# 检查超时
if time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) >= timeout:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Presence status query timeout")
return False, None
# 短暂延迟,避免完全占用CPU
time.sleep_us(100)
# 继续处理数据流(确保响应能被解析)
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
# 返回查询结果
return True, self._query_result
except Exception as e:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Presence status query error: {e}")
return False, None
finally:
# 重置所有查询状态
self._query_in_progress = False
self._query_response_received = False
self._query_result = None
self._current_query_type = None
# 安全地恢复定时器状态
try:
self._is_running = original_running
except NameError:
# 如果 original_running 未定义,保持定时器运行状态不变
pass
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Query state reset")
def update_properties_from_frame(self, frame):
_"""_
_ 根据解析的帧更新属性值_
_ Args:_
_ frame: DataFlowProcessor解析后的帧数据字典_
_ """_
_ _control = frame['control_byte']
command = frame['command_byte']
data = frame['data']
# 心跳包 (0x01)
if control == 0x01:
# 心跳包上报
if command == 0x01:
self.heartbeat_last_received = time.ticks_ms()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Heartbeat] Received")
# 心跳包查询响应
elif command == 0x80:
# 更新心跳包最后接收时间
self.heartbeat_last_received = time.ticks_ms()
# 处理心跳包查询响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT and
not self._query_response_received):
# 设置查询结果为心跳正常
self._query_result = True
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Heartbeat response received")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了心跳包响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Heartbeat] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Heartbeat] Unsolicited query response")
# 模组复位响应
elif command == 0x02:
# 模组复位成功,设备原样返回指令作为确认
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_MODULE_RESET and
not self._query_response_received):
# 更新模组复位状态和时间戳
self.module_reset_flag = True
self.module_reset_timestamp = time.ticks_ms()
self._query_result = True # 复位成功
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Query] Module reset response received")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了模组复位响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_MODULE_RESET:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Reset] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Reset] Unsolicited query response")
# 产品信息指令 (0x02)
elif control == 0x02:
# 产品型号查询响应
if command == 0xA1:
if data:
# 解析产品型号数据
product_info = self._parse_product_info_data(data)[0]
# 更新产品型号属性
self.product_model = product_info
# 处理产品型号查询响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL and
not self._query_response_received):
# 设置查询结果为产品型号字符串
self._query_result = product_info
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Product model response: {product_info}")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了产品型号响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(
f"[Product Model] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query: {product_info}")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Product Model] Unsolicited query response: {product_info}")
# 产品ID查询响应
elif command == 0xA2:
if data:
# 解析产品ID数据
product_id = self._parse_product_info_data(data)[0]
# 更新产品ID属性
self.product_id = product_id
print(product_id)
# 处理产品ID查询响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_ID and
not self._query_response_received):
# 设置查询结果为产品ID字符串
self._query_result = product_id
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Product ID response: {product_id}")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了产品ID响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_ID:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(
f"[Product ID] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query: {product_id}")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Product ID] Unsolicited query response: {product_id}")
# 硬件型号查询响应
elif command == 0xA3:
if data:
# 解析硬件型号数据
hardware_model = self._parse_product_info_data(data)[0]
# 更新硬件型号属性
self.hardware_model = hardware_model
print(hardware_model)
# 处理硬件型号查询响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HARDWARE_MODEL and
not self._query_response_received):
# 设置查询结果为硬件型号字符串
self._query_result = hardware_model
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Hardware model response: {hardware_model}")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了硬件型号响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HARDWARE_MODEL:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(
f"[Hardware Model] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query: {hardware_model}")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Hardware Model] Unsolicited query response: {hardware_model}")
# 固件版本查询响应
elif command == 0xA4:
if data:
# 解析固件版本数据
firmware_version = self._parse_firmware_version_data(data)[0]
# 更新固件版本属性
self.firmware_version = firmware_version
print(firmware_version)
# 处理固件版本查询响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_FIRMWARE_VERSION and
not self._query_response_received):
# 设置查询结果为固件版本字符串
self._query_result = firmware_version
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Firmware version response: {firmware_version}")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了固件版本响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_FIRMWARE_VERSION:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(
f"[Firmware] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query: {firmware_version}")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Firmware] Unsolicited query response: {firmware_version}")
# 系统初始化状态 (0x05)
elif control == 0x05:
# 初始化完成信息
if command == 0x01:
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.system_initialized = (data[0] == 0x01)
self.system_initialized_timestamp = time.ticks_ms()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status = "completed" if self.system_initialized else "not completed"
print(f"[System] Initialization {status}")
# 初始化完成查询响应
elif command == 0x81:
if data and len(data) > 0:
# 解析初始化状态:0x01表示已完成
init_status = (data[0] == 0x01)
# 更新系统初始化状态
self.system_initialized = init_status
# 处理初始化完成查询响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_INIT_COMPLETE and
not self._query_response_received):
# 设置查询结果为初始化状态
self._query_result = init_status
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "completed" if init_status else "not completed"
print(f"[Query] Init complete response: {status_text}")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了初始化完成响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_INIT_COMPLETE:
status_text = "completed" if init_status else "not completed"
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(
f"[Init Complete] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query: {status_text}")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "completed" if init_status else "not completed"
print(f"[Init Complete] Unsolicited query response: {status_text}")
# 雷达探测范围 (0x07)
elif control == 0x07:
# 位置越界状态上报
if command == 0x07:
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.radar_in_range = (data[0] == 0x01)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status = "in range" if self.radar_in_range else "out of range"
print(f"[Radar] {status}")
# 位置越界状态查询响应
elif command == 0x87:
if data and len(data) > 0:
# 解析越界状态:0x01表示越界
boundary_status = (data[0] == 0x01)
# 更新雷达探测范围状态(越界表示不在范围内)
self.radar_in_range = not boundary_status
# 处理雷达探测范围查询响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_RADAR_RANGE_BOUNDARY and
not self._query_response_received):
# 设置查询结果为越界状态(True表示越界)
self._query_result = boundary_status
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "out of range" if boundary_status else "in range"
print(f"[Query] Radar range boundary response: {status_text}")
# 当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了雷达范围响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_RADAR_RANGE_BOUNDARY:
status_text = "out of range" if boundary_status else "in range"
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(
f"[Radar Range] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query: {status_text}")
# 没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "out of range" if boundary_status else "in range"
print(f"[Radar Range] Unsolicited query response: {status_text}")
# 人体存在检测 (0x80)
elif control == 0x80:
if command == 0x01: # 存在信息
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.presence_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "No one" if self.presence_status == 0 else "Someone"
print(f"[Presence] {status_text}")
elif command == 0x81: # 存在信息(查询响应)
if data and len(data) > 0:
presence_value = data[0]
# 更新属性
self.presence_status = presence_value
# 处理查询响应
# 情况1:当前正在进行存在信息查询,且尚未收到响应
if (self._query_in_progress and
self._current_query_type == R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO and
not self._query_response_received):
self._query_result = presence_value
self._query_response_received = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "No one" if presence_value == 0 else "Someone"
print(f"[Query] Presence status response: {status_text}")
# 情况2:当前正在进行其他类型的查询,但收到了存在信息响应
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_EXISTENCE_INFO:
status_text = "No one" if presence_value == 0 else "Someone"
print(f"[Presence] Unexpected query response during {self._current_query_type} query: {status_text}")
# 情况3:没有查询在进行,但收到了查询响应
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "No one" if presence_value == 0 else "Someone"
print(f"[Presence] Unsolicited query response: {status_text}")
# 情况4:其他情况(理论上不应该到达这里)
else:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = "No one" if presence_value == 0 else "Someone"
print(f"[Presence] Unexpected state in query response handling, query response: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x02: # 运动信息
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.motion_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][
self.motion_status] if self.motion_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Motion] {status_text}")
elif command == 0x03: # 体动参数
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.movement_parameter = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Movement] Parameter: {self.movement_parameter}")
elif command == 0x04: # 人体距离
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.human_distance = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Distance] {self.human_distance} cm")
elif command == 0x05: # 人体方位
if data and len(data) == 6:
x, y, z = self._parse_human_position_data(data)
self.human_position_x = x
self.human_position_y = y
self.human_position_z = z
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Position] X={x}, Y={y}, Z={z}")
# 呼吸监测 (0x81)
elif control == 0x81:
if command == 0x01: # 呼吸状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.breath_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Normal", "High", "Low", "None"][
self.breath_status - 1] if 1 <= self.breath_status <= 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Breath] Status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x02: # 呼吸数值
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.breath_value = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Breath] Value: {self.breath_value}")
elif command == 0x05: # 呼吸波形
if data and len(data) == 5:
waveform = self._parse_breath_waveform_data(data)
self.breath_waveform = list(waveform)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Breath] Waveform updated: {waveform}")
# 心率监测 (0x85)
elif control == 0x85:
if command == 0x02: # 心率数值
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.heart_rate_value = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Heart Rate] Value: {self.heart_rate_value}")
elif command == 0x05: # 心率波形
if data and len(data) == 5:
waveform = self._parse_heart_rate_waveform_data(data)
self.heart_rate_waveform = list(waveform)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Heart Rate] Waveform updated: {waveform}")
# 睡眠监测 (0x84)
elif control == 0x84:
if command == 0x01: # 入床/离床状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.bed_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Leave bed", "Enter bed", "None"][
self.bed_status] if self.bed_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Bed] Status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x02: # 睡眠状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Deep sleep", "Light sleep", "Awake", "None"][
self.sleep_status] if self.sleep_status < 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x03: # 清醒时长
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.awake_duration = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Awake duration: {self.awake_duration} min")
elif command == 0x04: # 浅睡时长
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.light_sleep_duration = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Light sleep duration: {self.light_sleep_duration} min")
elif command == 0x05: # 深睡时长
if data and len(data) >= 2:
self.deep_sleep_duration = (data[0] << 8) | data[1]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Deep sleep duration: {self.deep_sleep_duration} min")
elif command == 0x06: # 睡眠质量评分
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_quality_score = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Quality score: {self.sleep_quality_score}")
elif command == 0x0C: # 睡眠综合状态
if data and len(data) == 8:
comprehensive_data = self._parse_sleep_comprehensive_data(data)
# 更新到字典属性
self.sleep_comprehensive_status = {
'presence': comprehensive_data[0],
'sleep_status': comprehensive_data[1],
'avg_breath': comprehensive_data[2],
'avg_heart_rate': comprehensive_data[3],
'turnover_count': comprehensive_data[4],
'large_movement_ratio': comprehensive_data[5],
'small_movement_ratio': comprehensive_data[6],
'apnea_count': comprehensive_data[7]
}
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Sleep] Comprehensive status updated")
elif command == 0x0D: # 睡眠质量分析/统计信息
if data and len(data) == 12:
stats_data = self._parse_sleep_statistics_data(data)
# 更新对应的睡眠统计属性
self.sleep_quality_score = stats_data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
# 注意:stats_data[1]是总睡眠时长,需要根据实际情况决定如何分配
print(f"[Sleep] Statistics updated")
elif command == 0x0E: # 睡眠异常
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_anomaly = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["Short sleep (<4h)", "Long sleep (>12h)", "No person anomaly", "Normal"][
self.sleep_anomaly] if self.sleep_anomaly < 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Anomaly: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x10: # 睡眠质量评级
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.sleep_quality_rating = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["None", "Good", "Normal", "Poor"][
self.sleep_quality_rating] if self.sleep_quality_rating < 4 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Quality rating: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x11: # 异常挣扎状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.abnormal_struggle_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["None", "Normal", "Abnormal"][
self.abnormal_struggle_status] if self.abnormal_struggle_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] Struggle status: {status_text}")
elif command == 0x12: # 无人计时状态
if data and len(data) > 0:
self.no_person_timing_status = data[0]
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
status_text = ["None", "Normal", "Abnormal"][
self.no_person_timing_status] if self.no_person_timing_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print(f"[Sleep] No person timing: {status_text}")
def close(self):
_"""_
_ 停止定时器,解析剩余数据帧,输出统计信息_
_ """_
_ _# 停止定时器
self._is_running = False
self.timer.deinit()
# 是否有查询在进行中
self._query_in_progress = False
# 是否收到查询响应
self._query_response_received = False
# 查询结果
self._query_result = None
# 当前查询类型
self._current_query_type = None
# 解析剩余数据帧
try:
frames = self.data_processor.read_and_parse()
for frame in frames:
self.update_properties_from_frame(frame)
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"Failed to deinitialize timer: {str(e)}")
# 获取并输出统计信息
try:
stats = self.data_processor.get_stats()
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(" [R60ABD1] Final statistics: %s" % format_time())
print(" Total bytes received: %d" % stats['total_bytes_received'])
print(" Total frames parsed: %d" % stats['total_frames_parsed'])
print(" CRC errors: %d" % stats['crc_errors'])
print(" Frame errors: %d" % stats['frame_errors'])
print(" Invalid frames: %d" % stats['invalid_frames'])
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"Failed to get statistics: {str(e)}")
# 清空缓冲区
try:
self.data_processor.clear_buffer()
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"Failed to clear buffer: {str(e)}")
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("%s [R60ABD1] Resources fully released" % format_time())
对应相关测试的 main.py 文件代码如下所示:
# Python env :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/11/4 下午5:33
# @Author : 李清水
# @File : main.py
# @Description :
from machine import UART, Pin, Timer
import time
from data_flow_processor import DataFlowProcessor
from r60abd1 import R60ABD1, format_time
time.sleep(3)
# 初始化UART0:TX=16, RX=17,波特率115200
uart = UART(0, baudrate=115200, tx=Pin(16), rx=Pin(17), timeout=0)
# 创建DataFlowProcessor实例
processor = DataFlowProcessor(uart)
# 创建R60ABD1实例
device = R60ABD1(processor, parse_interval=50)
# ======================================== 功能函数 ============================================
def print_sensor_data():
_"""打印传感器数据到Thonny控制台"""_
_ _print("=" * 50)
print("%s Sensor Data" % format_time())
print("=" * 50)
# 心率数据
print("Heart Rate: %d bpm" % device.heart_rate_value)
print("Heart Rate Waveform: %s" % str(device.heart_rate_waveform))
# 呼吸数据
print("Breath Rate: %d bpm" % device.breath_value)
print("Breath Status: %d" % device.breath_status)
print("Breath Waveform: %s" % str(device.breath_waveform))
# 人体存在数据
print("Movement Parameter: %d" % device.movement_parameter)
print("Presence Status: %s" % ("Someone" if device.presence_status == 1 else "No one"))
print("Motion Status: %s" % ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][
device.motion_status] if device.motion_status < 3 else "Unknown")
# 距离和位置
print("Human Distance: %d cm" % device.human_distance)
print("Human Position: X=%d, Y=%d, Z=%d" % (
device.human_position_x, device.human_position_y, device.human_position_z))
# 雷达状态
print("Radar in Range: %s" % ("Yes" if device.radar_in_range else "No"))
print("=" * 50)
# ======================================== 主程序 ============================================
# 上次打印时间
last_print_time = time.ticks_ms()
print_interval = 2000 # 2秒打印一次
success, product_model = device.query_product_model()
if success:
print("Product Model: %s" % product_model)
else:
print("Query Product Model failed")
success, product_id = device.query_product_id()
if success:
print("Product ID: %s" % product_id)
else:
print("Query Product ID failed")
success, hardware_model = device.query_hardware_model()
if success:
print("Hardware Model: %s" % hardware_model)
else:
print("Query Hardware Model failed")
success, firmware_version = device.query_firmware_version()
if success:
print("Hardware Version: %s" % firmware_version)
else:
print("Query Hardware Version failed")
success, init_status = device.query_init_complete()
if success:
print("Init Status: %s" % init_status)
else:
print("Query Init Status failed")
success, boundary_status = device.query_radar_range_boundary()
if success:
status_text = "out of range" if boundary_status else "in range"
print("Boundary Status: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Boundary Status failed")
try:
while True:
current_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 定期打印传感器数据
if time.ticks_diff(current_time, last_print_time) >= print_interval:
# print_sensor_data()
success, presence_status = device.query_presence_status()
if success:
print("Presence Status: %s" % ("Someone" if presence_status == 1 else "No one"))
else:
print("Query Presence Status failed")
last_print_time = current_time
success, heartbeat_status = device.query_heartbeat()
if success:
print("Heartbeat Status: %s" % ("Normal" if heartbeat_status == 1 else "Abnormal"))
else:
print("Query Heartbeat failed")
# 小延迟,避免占用太多CPU
time.sleep_ms(10)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("%s Program interrupted by user" % format_time())
finally:
# 清理资源
print("%s Cleaning up resources..." % format_time())
# 停止实例运行
device.close()
# 销毁实例
del device
print("%s Program exited" % format_time())
为验证功能的可用性,在测试前我们先关闭人体存在、心率、呼吸、睡眠的主动上报功能。
在 REPL 中依次调用 query_product_model、query_heartbeat、query_radar_range_boundary 等方法,验证返回结果与设备实际状态一致(如 query_product_model 返回 R60ASM1,query_heartbeat 返回 (True, True))。
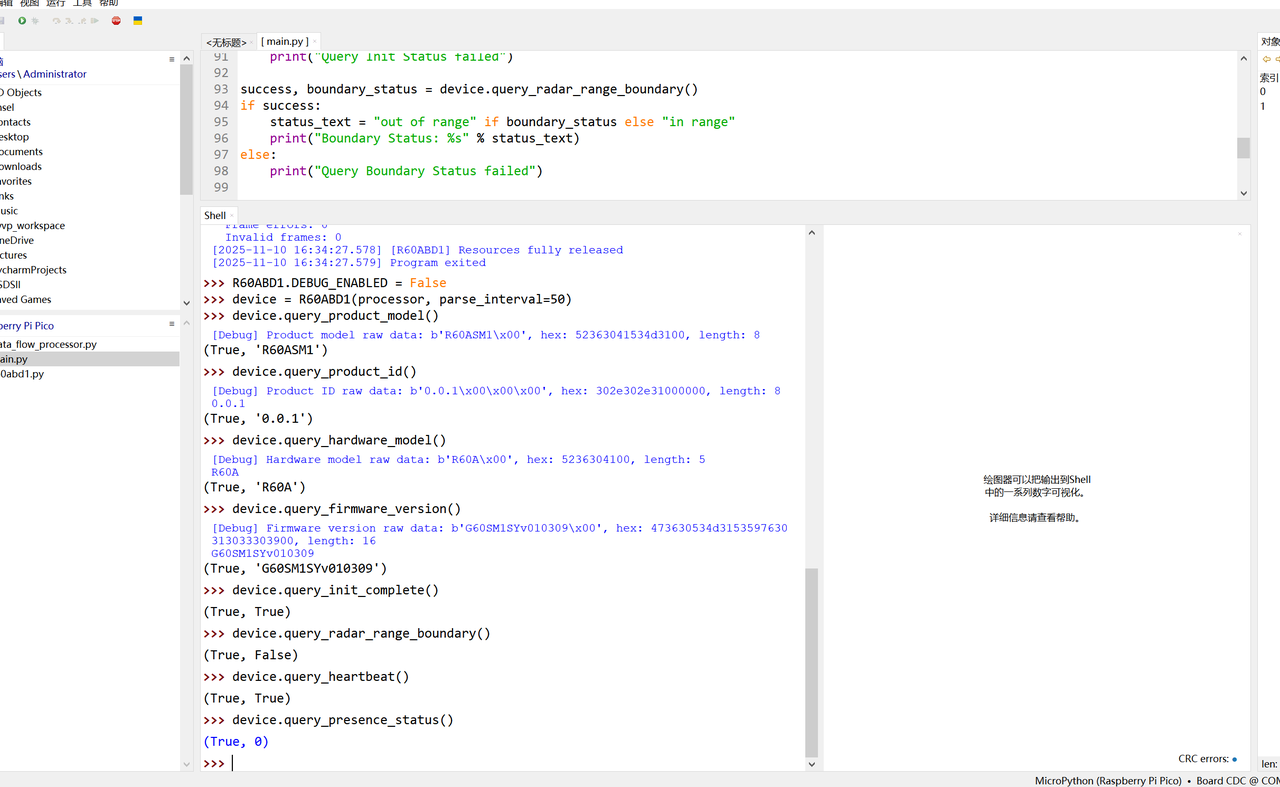
然后再将所有主动上报功能都打开,同时调用 query_firmware_version 等查询方法,验证在有多个主动上报数据情况下,能不能正确处理被动响应的数据帧:
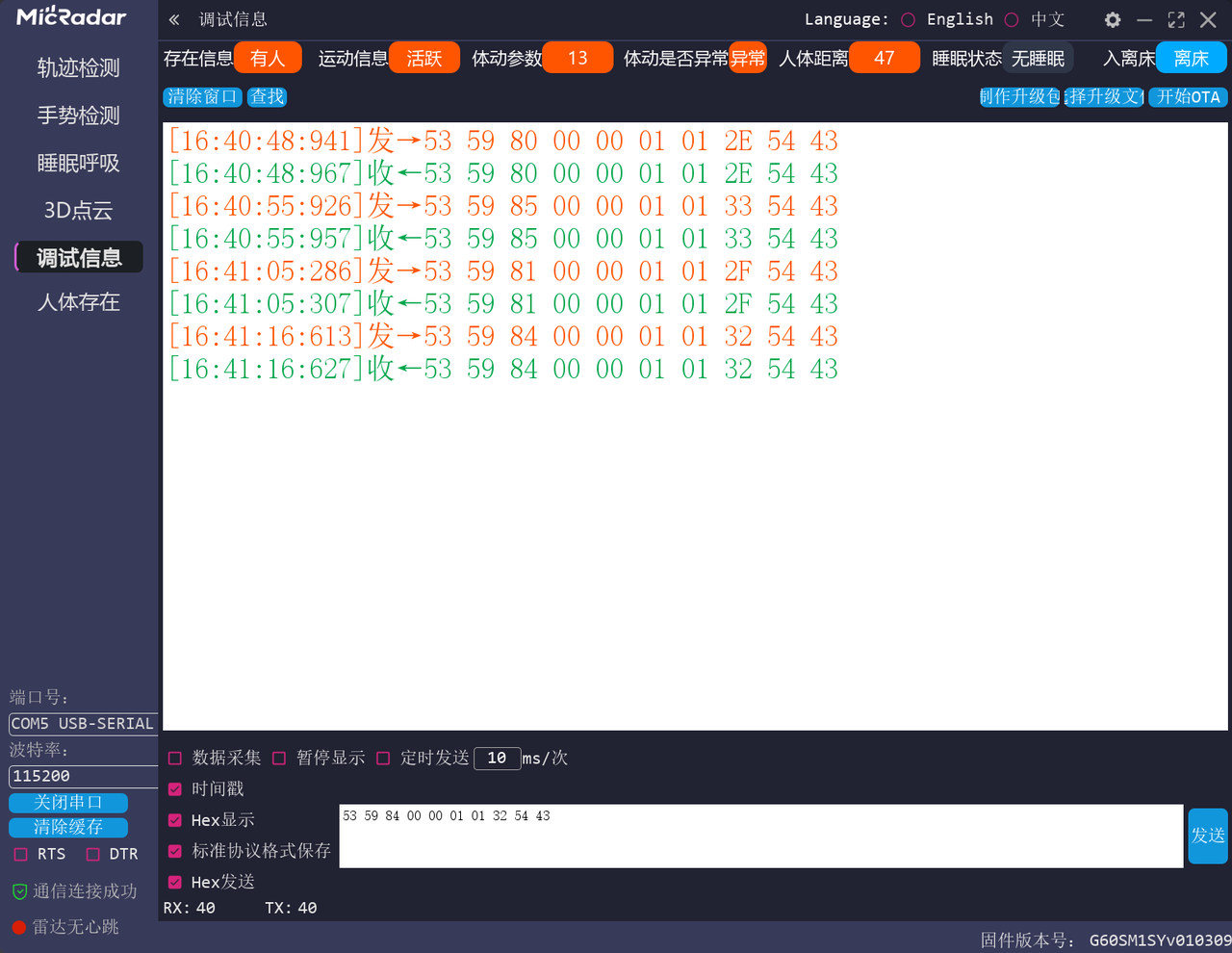
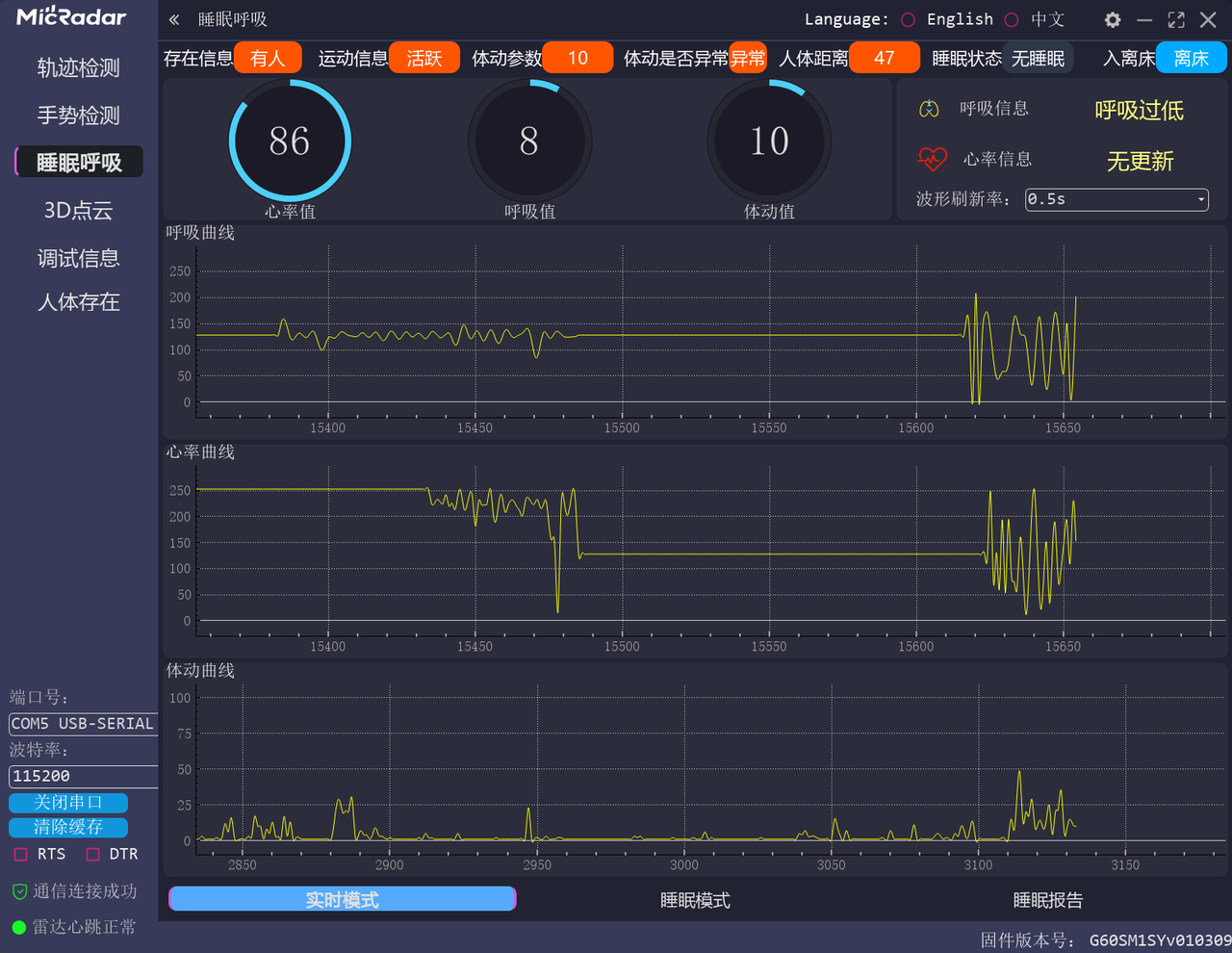
观察 main.py 输出,确认主动上报数据(如心率波形、呼吸状态)正常解析的同时,查询指令能返回正确结果(如固件版本 G60SM1SYv010309)。
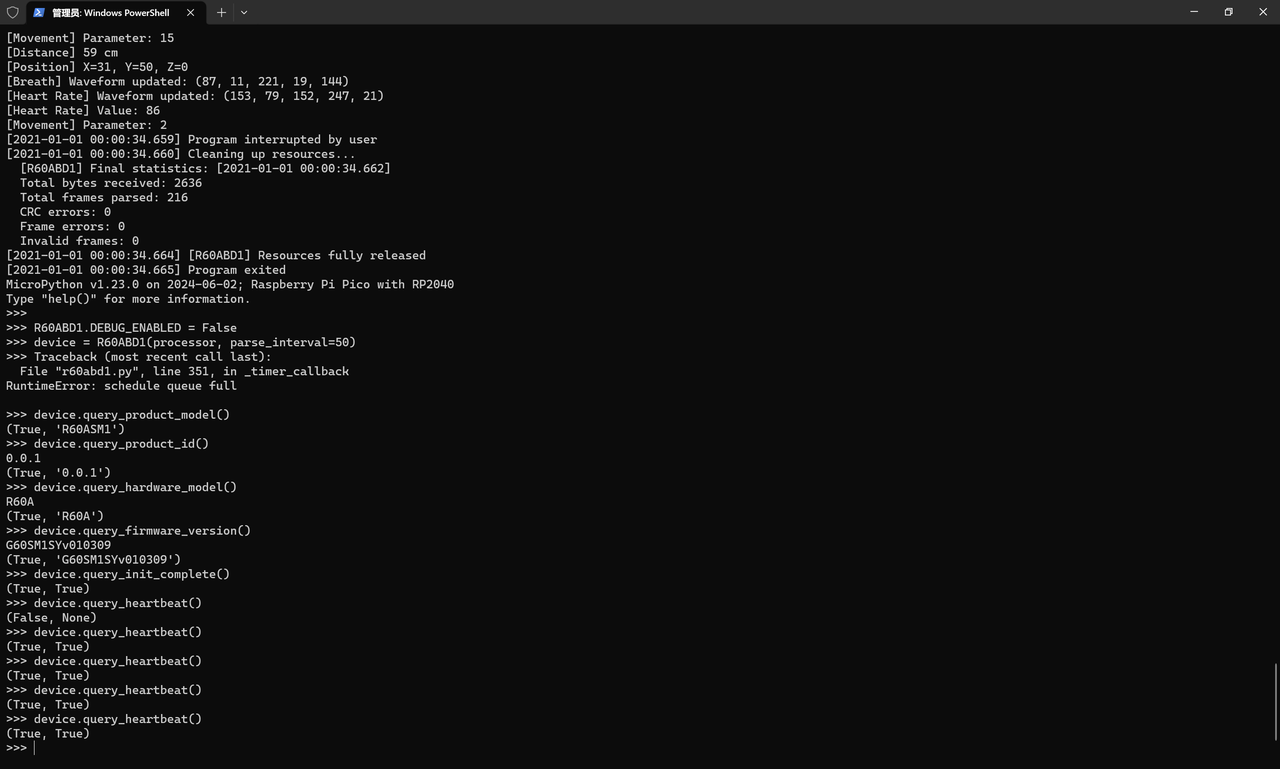
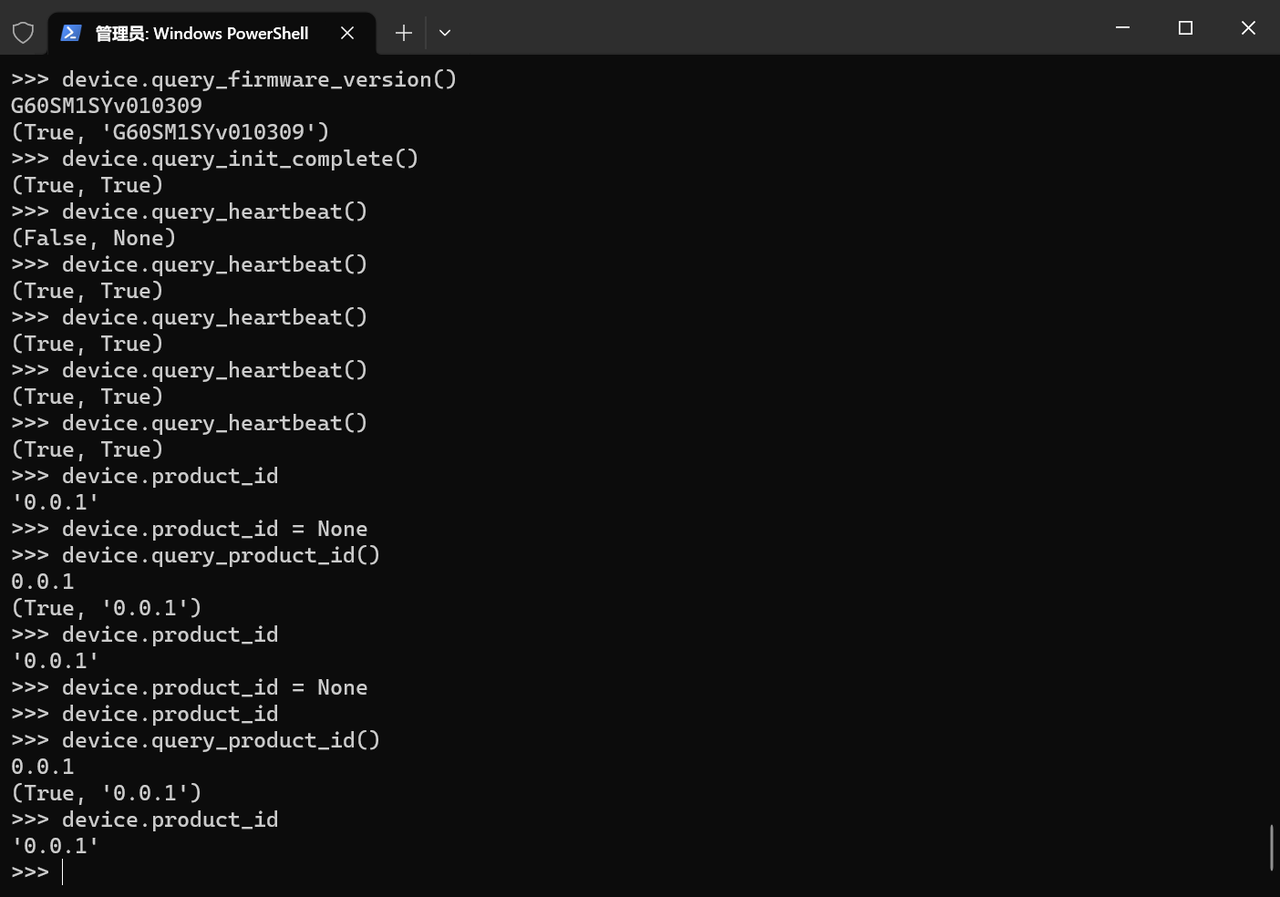
3.3.7 业务驱动层的重构:帧封装、指令解耦与响应统一化
随着雷达功能的逐步丰富(从基础心跳监测到人体存在、心率、呼吸、睡眠等多维度监测),原有业务驱动类的代码结构逐渐暴露短板:帧构建逻辑在数十个查询 / 设置方法中重复出现,指令类型与底层协议数值(控制字、命令字)强耦合,不同指令的响应处理逻辑存在大量冗余。这些问题导致代码维护成本陡增 —— 新增一个指令需重复编写帧构建与响应处理代码,修改协议参数需全局搜索硬编码的十六进制数值,极易引发遗漏或错误。
为解决上述问题,我们采用 “统一帧封装 + 指令映射解耦 + 响应逻辑归一化” 的三层重构策略,将业务驱动层从 “过程式堆砌” 升级为 “模块化设计”,显著提升了代码的可维护性、可扩展性与可靠性。
3.3.7.1 帧发送的统一封装
在重构前,每个查询 / 设置方法(如 query_heartbeat、reset_module)都需独立构建数据帧,包含帧头拼接、长度计算、CRC 校验、帧尾添加等重复逻辑。这种分散式实现不仅导致代码冗余(重复代码占比超 40%),还因手工计算长度、CRC 等操作易引发协议错误(如长度字节与实际数据长度不匹配、CRC 校验失败导致设备拒收)。
将帧构建的全流程封装到 DataFlowProcessor 类的 build_and_send_frame 方法中,实现从 “参数输入” 到 “帧发送” 的自动化处理。该方法的核心逻辑如下:
def build_and_send_frame(self, control_byte, command_byte, data=b''):
# 帧头(协议固定为0x53 0x59)
header = self.HEADER # 类常量,如b'\x53\x59'
# 控制字、命令字转换为单字节
control = bytes([control_byte])
command = bytes([command_byte])
# 数据长度(按协议要求采用大端格式,2字节)
data_len = len(data)
length_bytes = bytes([(data_len >> 8) & 0xFF, data_len & 0xFF]) # 高位在前,低位在后
# 组装帧主体(帧头+控制字+命令字+长度+数据)
frame_without_crc = header + control + command + length_bytes + data
# 计算CRC校验(协议规定为帧主体所有字节之和的低8位)
crc = self._calculate_crc(frame_without_crc) # 内部调用sum(frame_without_crc) & 0xFF
# 帧尾(协议固定为0x54 0x43)
trailer = self.TRAILER # 类常量,如b'\x54\x43'
# 完整帧拼接并发送
complete_frame = frame_without_crc + bytes([crc]) + trailer
self.uart.write(complete_frame) # 通过串口发送
return complete_frame # 返回完整帧用于调试
3.3.7.2 指令映射表:COMMAND_MAP 的解耦设计
重构前,指令类型(如 “查询产品型号”“打开心率监测”)与底层协议数值(控制字、命令字)直接耦合。例如,“查询产品型号” 的控制字 0x02、命令字 0xA1 直接硬编码在 query_product_model 方法中。这种设计导致:
- 新增指令需重复编写帧参数;
- 协议更新时(如命令字变更)需全局修改所有关联方法,极易遗漏;
- 代码可读性差(十六进制数值难以直观理解其含义)。
设计 COMMAND_MAP 字典,将 “指令类型常量” 与 “帧参数(控制字、命令字、默认数据)” 建立映射关系,实现逻辑与数值的解耦。其核心结构如下:
# 指令类型常量(直观描述操作含义)
TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT = 0 # 心跳包查询
TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL = 2 # 产品型号查询
TYPE_CONTROL_HEART_RATE_MONITOR_ON = 16 # 打开心率监测
# 指令映射表(关联常量与协议参数)
COMMAND_MAP = {
TYPE_QUERY_HEARTBEAT: {
'control_byte': 0x01, # 控制字(系统指令)
'command_byte': 0x80, # 命令字(心跳查询)
'data': bytes([0x0F]) # 默认数据(协议固定)
},
TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL: {
'control_byte': 0x02, # 控制字(产品信息)
'command_byte': 0xA1, # 命令字(型号查询)
'data': bytes([0x0F]) # 默认数据
},
TYPE_CONTROL_HEART_RATE_MONITOR_ON: {
'control_byte': 0x85, # 控制字(心率监测)
'command_byte': 0x00, # 命令字(功能开关)
'data': bytes([0x01]) # 数据(1表示打开)
},
# ... 其他指令映射 ...
}
3.3.7.3 查询响应逻辑的统一化:_handle_query_response 方法
重构前,update_properties_from_frame 方法中,不同指令的响应处理逻辑高度重复。例如,“心跳查询响应”“产品型号查询响应” 均需判断三种场景:
- 响应与当前查询匹配;
- 响应与当前查询不匹配(并发冲突);
- 无查询时收到响应(主动上报)。
这种重复导致代码冗长(单方法超 1000 行),且不同指令的场景判断逻辑可能存在差异(如部分指令遗漏异常响应处理),隐藏潜在 Bug。
提取 _handle_query_response 方法,将三种响应场景的处理逻辑抽象为通用逻辑,通过参数化适配不同指令。其核心实现如下:
def _handle_query_response(self, expected_type, response_data, response_name):
# 场景1:响应与当前查询类型匹配(正常流程)
if (self._query_in_progress and # 存在正在进行的查询
self._current_query_type == expected_type and # 响应类型匹配
not self._query_response_received): # 尚未收到响应
self._query_result = response_data # 记录结果
self._query_response_received = True # 标记响应已收到
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
query_name = self.QUERY_NAME_MAP.get(expected_type, f"Unknown({expected_type})")
print(f"[Query] {query_name} response received: {response_data}")
# 场景2:响应与当前查询类型不匹配(并发冲突)
elif self._query_in_progress and self._current_query_type != expected_type:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
current_query = self.QUERY_NAME_MAP.get(self._current_query_type, f"Unknown({self._current_query_type})")
print(f"[Query] Unexpected {response_name} response during {current_query} query: {response_data}")
# 场景3:无查询时收到响应(设备主动上报)
elif not self._query_in_progress:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Query] Unsolicited {response_name} response: {response_data}")
在 update_properties_from_frame 中,只需通过一行代码调用该方法即可完成响应处理,例如:
# 产品型号查询响应处理(重构后)
if control == 0x02 and command == 0xA1 and data:
product_model = self._parse_product_info_data(data)[0]
self.product_model = product_model # 更新属性
self._handle_query_response(
expected_type=TYPE_QUERY_PRODUCT_MODEL,
response_data=product_model,
response_name="Product Model"
)
3.3.7.4 重构后的测试验证
这里,我们需要验证重构后的代码在设备主动上报数据时,能否同时正常处理查询指令。
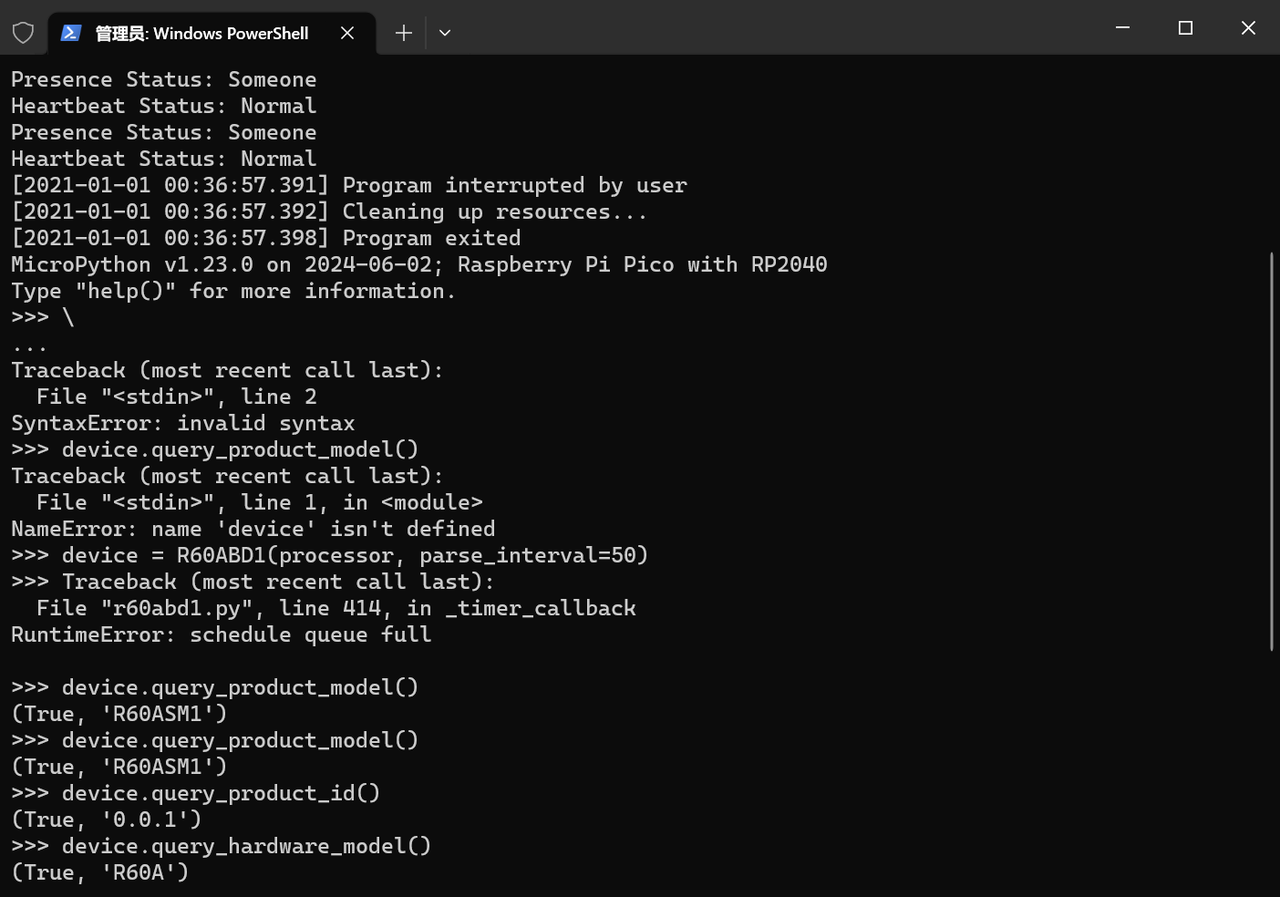
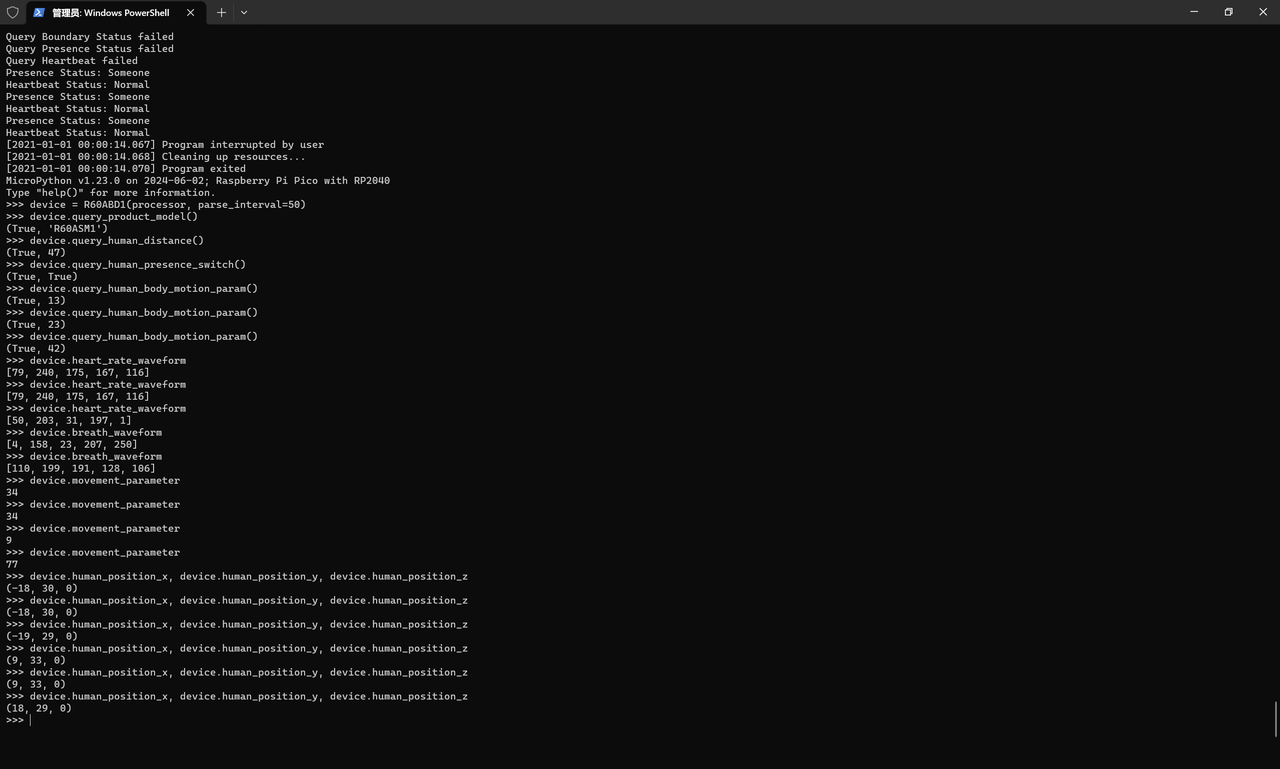
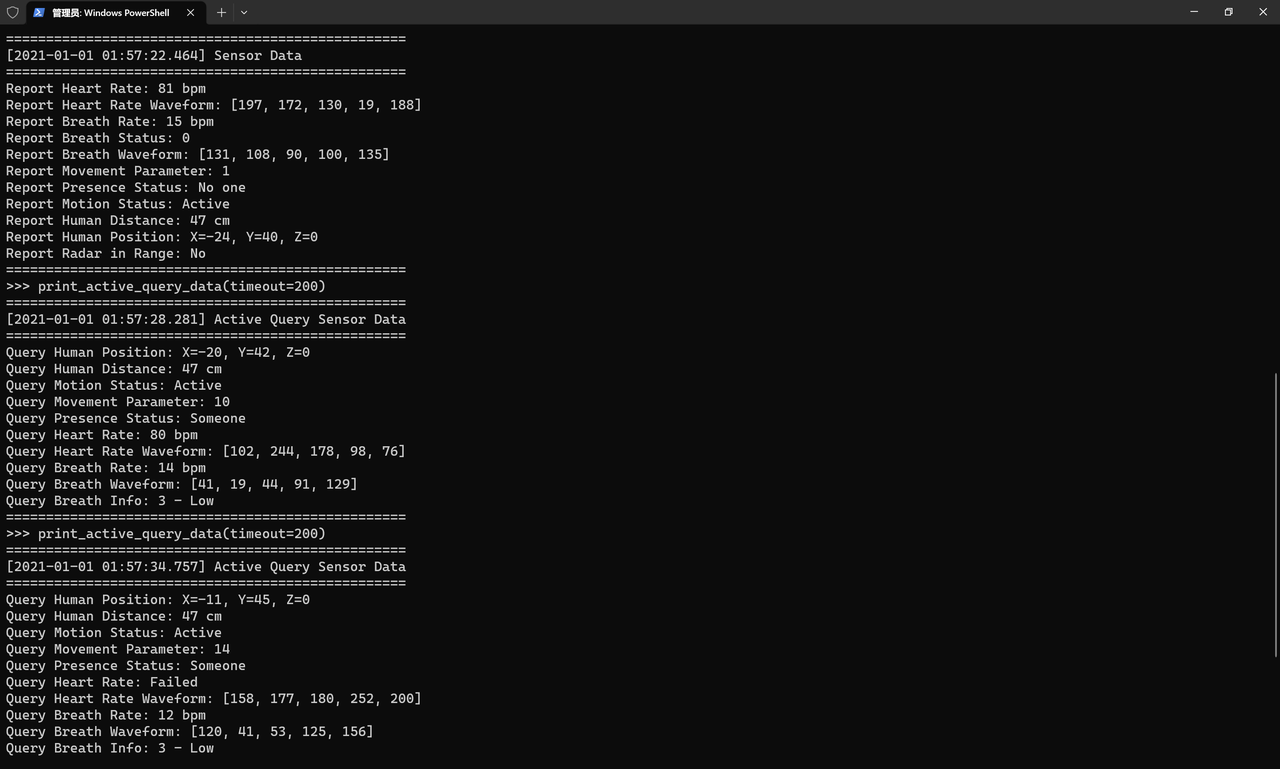
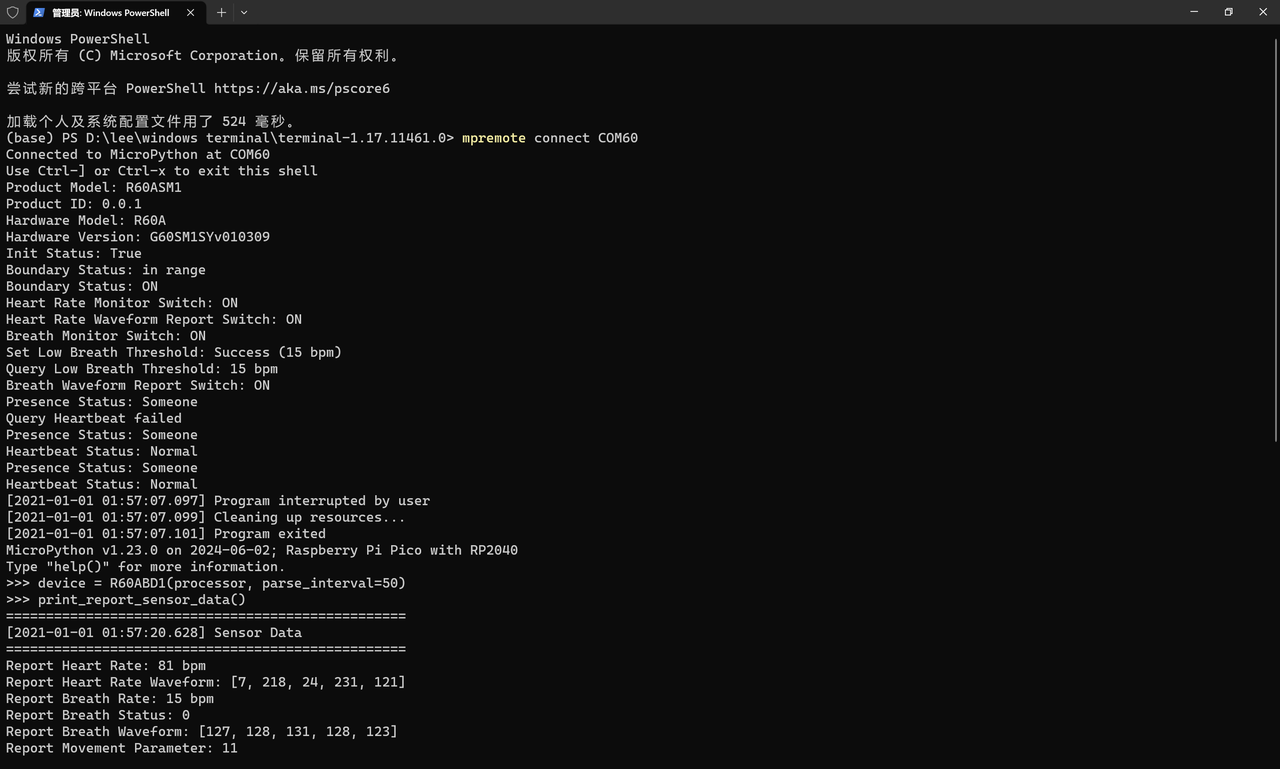
可以看到测试无误。
3.3.7.5 业务驱动层的属性更新严格遵循 “单一数据源 + 响应驱动” 原则
业务驱动层的属性更新必须坚守 “单一数据源” 与 “响应驱动” 双重核心:单一数据源限定为雷达设备返回的真实响应数据,响应驱动要求所有属性修改仅在update_properties_from_frame方法解析设备响应时执行,上层查询 / 控制方法(如 enable_human_presence、query_human_distance)仅负责发送指令,不得基于 “指令发送成功” 等本地逻辑预判结果或修改属性,从根源避免状态不一致问题。
错误示例如下,上层控制方法会在指令发送成功后,未经设备响应确认就主动修改属性,例如:
def enable_human_presence(self, timeout=200):
success, result = self._execute_operation(R60ABD1.TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_ON, timeout=timeout)
if success: # 仅判断指令发送成功,未等设备响应确认
self.presence_enabled = True # 预判修改属性,存在风险
return success, result
这种设计的问题在于:“指令发送成功” 不代表设备已实际执行(如设备硬件故障、指令接收成功但执行失败),此时 presence_enabled=True 的本地状态与设备真实状态可能不一致,且会与 update_properties_from_frame 中基于设备响应的属性修改形成冲突,破坏数据唯一性。
对于控制类方法而言,上层控制方法彻底剥离属性修改逻辑,仅专注于指令发送,所有状态更新依赖设备响应:
def enable_human_presence(self, timeout=200):
# 仅发送“打开人体存在”指令,不修改任何属性
return self._execute_operation(R60ABD1.TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_ON, timeout=timeout)
def disable_human_presence(self, timeout=200):
# 仅发送“关闭人体存在”指令,不预判执行结果
return self._execute_operation(R60ABD1.TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_OFF, timeout=timeout)
属性更新的唯一入口在 update_properties_from_frame 解析设备响应时:
# 人体存在开关控制响应解析(唯一属性修改点)
if control == 0x80 and command == 0x00 and data:
switch_status = (data[0] == 0x01) # 以设备响应数据为唯一依据
self.presence_enabled = switch_status # 仅在此处修改属性
# 匹配响应与操作类型,更新查询结果
if data[0] == 0x01:
self._handle_query_response(R60ABD1.TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_ON, True, "Human Presence ON")
else:
self._handle_query_response(R60ABD1.TYPE_CONTROL_HUMAN_PRESENCE_OFF, True, "Human Presence OFF")
查询类方法同样遵循 “不修改属性” 原则,仅通过 _execute_operation 发送查询指令,属性更新由设备响应解析驱动,例如:
def query_human_distance(self, timeout=200):
# 仅发送“人体距离查询”指令,不处理属性更新
return self._execute_operation(R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_DISTANCE, timeout=timeout)
当设备返回距离查询响应时,update_properties_from_frame 解析数据并更新属性,同时通过 _handle_query_response 同步查询结果:
# 人体距离查询响应解析(唯一属性修改点)
if control == 0x80 and command == 0x84 and data and len(data) >= 2:
distance = (data[0] << 8) | data[1] # 解析设备响应的真实距离数据
self.human_distance = distance # 仅在此处修改属性
self._handle_query_response(
R60ABD1.TYPE_QUERY_HUMAN_DISTANCE,
distance,
"Human Distance"
)
该原则的核心价值在于:确保本地属性状态与雷达设备真实状态完全同步,避免 “本地预判” 与 “设备实际” 的偏差;同时通过属性修改的唯一入口,让状态变化可追溯(每一次属性更新都对应明确的设备响应),为后续状态监控、异常告警等功能提供可靠的数据基础。
四、驱动代码整合优化与相关测试
驱动代码的整合核心是实现 “配置化初始化、全流程容错、可追溯测试”,通过优化初始化方法的参数设计、强化异常处理机制、完善测试脚本覆盖,确保驱动类的可靠性、易用性与低资源占用特性。以下从初始化优化、测试脚本实现、性能分析三方面展开说明。
4.1 初始化方法的优化设计:配置化、容错性与可追溯性
原初始化方法存在 “功能配置固化、异常处理薄弱、状态追溯困难” 等问题,优化后的初始化方法以 “参数化配置、全流程重试、错误可追溯” 为核心,支持雷达所有功能的灵活配置,并通过异常机制与重试逻辑提升初始化成功率。
4.1.1 核心优化点与设计原则
这里,我们首先需要在初始化方法中增加一些可配置参数,覆盖雷达所有核心功能,支持开发者根据业务需求灵活开关功能、调整参数,无需修改底层代码:
- 功能开关类:心率波形上报、呼吸波形上报、异常挣扎监测、无人计时等;
- 参数配置类:挣扎灵敏度(低 / 中 / 高)、无人计时时长(30-180 分钟)、睡眠截止时长(5-120 分钟)等;
- 容错控制类:最大重试次数(0-10 次)、重试延迟(0-1000ms)、初始化超时(1-30 秒)等。
常见示例如下:
# 全功能开启,高实时性配置
device = R60ABD1(
processor,
parse_interval=50, # 高实时性,50ms解析一次
presence_enabled=True,
heart_rate_enabled=True,
heart_rate_waveform_enabled=True, # 开启心率波形上报
breath_monitoring_enabled=True,
breath_waveform_enabled=True, # 开启呼吸波形上报
sleep_monitoring_enabled=True,
abnormal_struggle_enabled=True, # 开启异常挣扎监测
struggle_sensitivity=1, # 中等灵敏度
no_person_timing_enabled=True, # 开启无人计时
no_person_timing_duration=60, # 无人计时60分钟
sleep_cutoff_duration=120, # 睡眠截止时长120分钟
max_retries=3, # 最大重试3次
retry_delay=200, # 重试延迟200ms
init_timeout=10000 # 初始化超时10秒
)
# 低功耗配置,关闭非必要功能
device = R60ABD1(
processor,
parse_interval=200, # 低频率解析,降低功耗
presence_enabled=True,
heart_rate_enabled=True,
heart_rate_waveform_enabled=False, # 关闭心率波形(减少数据传输)
breath_monitoring_enabled=True,
breath_waveform_enabled=False, # 关闭呼吸波形
sleep_monitoring_enabled=True,
abnormal_struggle_enabled=False, # 关闭异常挣扎监测
no_person_timing_enabled=False, # 关闭无人计时
max_retries=2,
retry_delay=100,
init_timeout=5000
)
所有参数均添加严格的合法性校验(通过 _validate_init_parameters 方法),例如:
- 解析间隔限制在 10-500ms,避免过短导致 CPU 占用过高;
- 无人计时时长需为 30-180 分钟且步长为 10 分钟,符合设备协议要求;
- 灵敏度仅支持 0(低)、1(中)、2(高)三个枚举值,避免非法配置。
示例代码如下:
# 错误示例:挣扎灵敏度传入3(仅支持0/1/2)
try:
device = R60ABD1(processor, struggle_sensitivity=3)
except ValueError as e:
print(e) # 输出:struggle_sensitivity must be 0 (low), 1 (medium), or 2 (high)
同时进行异常机制与容错设计:
- 自定义异常DeviceInitializationError:统一捕获初始化失败场景;
- 配置错误记录:通过_configuration_errors列表追溯失败项;
- 自动重试:关键操作(如设备复位、功能配置)支持自动重试。
# 自定义异常类
class DeviceInitializationError(Exception):
_"""设备初始化错误异常"""_
_ _pass
# 应用代码示例
try:
device = R60ABD1(processor, parse_interval=300)
# 获取初始化状态与错误信息
init_status = device.get_configuration_status()
if init_status['initialization_complete']:
print("初始化成功!")
print(f"设备型号:{init_status['device_info']['product_model']}")
else:
print(f"初始化部分失败,错误项:{init_status['configuration_errors']}")
except DeviceInitializationError as e:
print(f"初始化失败:{e}")
# 输出:Device initialization failed: Failed to load Product Model
优化后的初始化流程分为 5 个步骤,形成 “参数验证 → 设备信息读取 → 初始化等待 → 自动配置 → 配置验证” 的闭环,示例流程如下:
def _complete_initialization(self):
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 步骤1:读取设备信息(产品型号、ID等)
self._load_device_information()
# 步骤2:等待设备初始化,未完成则复位
if not self._wait_for_device_initialization():
self._reset_and_wait_for_initialization()
# 步骤3:自动配置功能(基于__init__参数)
self._auto_configure_device()
# 步骤4:验证关键配置(如功能开关状态)
self._verify_critical_configuration()
print(f"初始化耗时:{time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time)}ms")
4.1.2 关键功能代码解析
4.1.2.1 设备复位与初始化等待
当设备未完成初始化时,自动触发复位流程,确保驱动恢复正常:
def _reset_and_wait_for_initialization(self):
# 发送复位指令(带重试)
reset_success = self._execute_with_retry(self.reset_module, "Reset Device", timeout=1000)
if not reset_success:
return False
time.sleep(3) # 等待设备重启
return self._wait_for_device_initialization(timeout=10000)
# 调用示例:在初始化中自动触发
if not self._wait_for_device_initialization():
print("设备未初始化,尝试复位...")
reset_success = self._reset_and_wait_for_initialization()
print(f"复位后初始化:{'成功' if reset_success else '失败'}")
4.1.2.2 配置错误追溯
通过 get_configuration_status 方法获取完整初始化状态,便于问题定位:
# 调用示例:初始化后查询状态
init_status = device.get_configuration_status()
print(f"初始化完成:{init_status['initialization_complete']}")
print(f"错误列表:{init_status['configuration_errors']}")
# 输出示例:
# 初始化完成:True
# 错误列表:["Failed to load Hardware Model", "Enable Abnormal Struggle Monitor failed"]
4.1.2.3 带重试的操作执行
_execute_with_retry 方法为关键操作提供重试机制,提升成功率:
def _execute_with_retry(self, operation, operation_name, timeout=200):
for attempt in range(self.max_retries + 1):
try:
success, result = operation(timeout=timeout)
if success:
return True
if attempt < self.max_retries:
time.sleep_ms(self.retry_delay)
except Exception as e:
if attempt < self.max_retries:
time.sleep_ms(self.retry_delay)
else:
print(f"{operation_name}重试{self.max_retries+1}次失败:{e}")
return False
# 调用示例:读取产品型号(失败自动重试3次)
success = self._execute_with_retry(self.query_product_model, "Load Product Model")
4.1.2 初始化部分完整代码示例
完整代码如下:
# 自定义异常类
class DeviceInitializationError(Exception):
_"""设备初始化错误异常"""_
_ _pass
def __init__(self, data_processor, parse_interval=200,
presence_enabled=True,
heart_rate_enabled=True, heart_rate_waveform_enabled=False,
breath_monitoring_enabled=True, breath_waveform_enabled=False,
sleep_monitoring_enabled=True,
abnormal_struggle_enabled=False, struggle_sensitivity=1,
no_person_timing_enabled=False, no_person_timing_duration=30,
sleep_cutoff_duration=120,
max_retries=3, retry_delay=100, init_timeout=5000):
_"""_
_ 初始化R60ABD1实例_
_ Args:_
_ data_processor: DataFlowProcessor实例_
_ parse_interval: 数据解析间隔,单位毫秒 (建议50-200ms)_
_ presence_enabled: 是否开启人体存在信息监测_
_ heart_rate_enabled: 是否开启心率监测_
_ heart_rate_waveform_enabled: 是否开启心率波形主动上报_
_ breath_monitoring_enabled: 是否开启呼吸监测_
_ breath_waveform_enabled: 是否开启呼吸波形主动上报_
_ sleep_monitoring_enabled: 是否开启睡眠监测_
_ abnormal_struggle_enabled: 是否开启异常挣扎监测_
_ struggle_sensitivity: 挣扎灵敏度 (0=低, 1=中, 2=高)_
_ no_person_timing_enabled: 是否开启无人计时功能_
_ no_person_timing_duration: 无人计时时长 (30-180分钟)_
_ sleep_cutoff_duration: 睡眠截止时长 (5-120分钟)_
_ max_retries: 最大重试次数_
_ retry_delay: 重试延迟时间,单位毫秒_
_ init_timeout: 初始化超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Raises:_
_ ValueError: 参数验证失败_
_ DeviceInitializationError: 设备初始化失败_
_ """_
_ _# 参数验证
self._validate_init_parameters(
parse_interval, struggle_sensitivity, no_person_timing_duration,
sleep_cutoff_duration, max_retries, retry_delay, init_timeout
)
if parse_interval > 500:
raise ValueError("parse_interval must be less than 500ms")
self.data_processor = data_processor
self.parse_interval = parse_interval
self.max_retries = max_retries
self.retry_delay = retry_delay
self.init_timeout = init_timeout
# 添加运行状态标志
self._is_running = False
self._initialization_complete = False
self._configuration_errors = []
# ============================= 系统级属性 ============================
# 心跳包监控
# 最后接收心跳包时间戳(ms)
self.heartbeat_last_received = 0
# 心跳超时累计次数
self.heartbeat_timeout_count = 0
# 实际心跳间隔统计(ms)
self.heartbeat_interval = 0
# 系统状态
# 初始化完成状态(True/False)
self.system_initialized = False
# 初始化完成时间戳(ms)
self.system_initialized_timestamp = 0
# 模组复位状态标记
self.module_reset_flag = False
# 模组复位时间戳(ms)
self.module_reset_timestamp = 0
# 产品信息
# 产品型号(字符串)
self.product_model = ""
# 产品ID(字符串)
self.product_id = ""
# 硬件型号(字符串)
self.hardware_model = ""
# 固件版本(字符串)
self.firmware_version = ""
# ============================ 雷达探测属性 ============================
# 位置状态
# 是否在探测范围内
self.radar_in_range = False
# =========================== 人体存在检测属性 ==========================
# 基本状态
# 人体存在功能开关
self.presence_enabled = presence_enabled
# 存在状态
# 0:无人, 1:有人
self.presence_status = 0
# 运动状态
# 0:无, 1:静止, 2:活跃
self.motion_status = 0
# 量化数据
# 体动参数(0-100)
self.movement_parameter = 0
# 人体距离(0-65535 cm)
self.human_distance = 0
# X坐标(有符号)
self.human_position_x = 0
# Y坐标(有符号)
self.human_position_y = 0
# Z坐标(有符号)
self.human_position_z = 0
# ============================= 呼吸监测属性 ===========================
# 功能配置
# 呼吸监测开关
self.breath_monitoring_enabled = breath_monitoring_enabled
# 呼吸波形上报开关
self.breath_waveform_enabled = False
# 低缓呼吸阈值(10-20次/min)
self.low_breath_threshold = 10
# 监测数据
# 1:正常, 2:过高, 3:过低, 4:无
self.breath_status = 0
# 呼吸数值(0-35次/分)
self.breath_value = 0
# 5个字节的波形数据
self.breath_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
# ============================= 心率监测属性 ============================
# 功能配置
# 心率监测开关
self.heart_rate_enabled = heart_rate_enabled
# 心率波形上报开关
self.heart_rate_waveform_enabled = False
# 监测数据
# 心率数值(60-120)
self.heart_rate_value = 0
# 5个字节的波形数据
self.heart_rate_waveform = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
# ============================ 睡眠监测属性 ============================
# 基础状态
# 睡眠监测开关
self.sleep_monitoring_enabled = sleep_monitoring_enabled
# 入床/离床状态
# 0:离床, 1:入床, 2:无
self.bed_status = 0
# 睡眠状态
# 0:深睡, 1:浅睡, 2:清醒, 3:无
self.sleep_status = 0
# 时长统计
# 清醒时长(分钟)
self.awake_duration = 0
# 浅睡时长(分钟)
self.light_sleep_duration = 0
# 深睡时长(分钟)
self.deep_sleep_duration = 0
# 睡眠质量
# 睡眠质量评分(0-100)
self.sleep_quality_score = 0
# 睡眠质量评级
self.sleep_quality_rating = 0
# 综合状态
# 包含8个字段的字典
self.sleep_comprehensive_status = {}
# 睡眠异常状态
self.sleep_anomaly = 0
# 异常挣扎状态
self.abnormal_struggle_status = 0
# 无人计时状态
self.no_person_timing_status = 0
# 配置参数
# 异常挣扎开关
self.abnormal_struggle_enabled = abnormal_struggle_enabled
# 无人计时开关
self.no_person_timing_enabled = no_person_timing_enabled
# 无人计时时长
self.no_person_timing_duration = no_person_timing_duration
# 睡眠截止时长
self.sleep_cutoff_duration = sleep_cutoff_duration
# 挣扎灵敏度
self.struggle_sensitivity = struggle_sensitivity
# 查询状态管理
# 是否有查询在进行中
self._query_in_progress = False
# 是否收到查询响应
self._query_response_received = False
# 查询结果
self._query_result = None
# 当前查询类型
self._current_query_type = None
# 默认查询超时时间(ms)
self._query_timeout = 200
# 内部使用的定时器
self._timer = Timer(-1)
try:
# 启动定时器
self._start_timer()
# 执行完整的初始化流程
self._complete_initialization()
self._initialization_complete = True
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Init] R60ABD1 initialized successfully")
status = self.get_configuration_status()
print(f"[Init] Configuration errors: {len(status['configuration_errors'])}")
print(f"[Init] Product: {self.product_model} v{self.firmware_version}")
except Exception as e:
# 初始化失败,停止定时器
self._is_running = False
if hasattr(self, '_timer'):
self._timer.deinit()
raise DeviceInitializationError(f"Device initialization failed: {str(e)}")
def _validate_init_parameters(self, parse_interval, struggle_sensitivity,
no_person_timing_duration, sleep_cutoff_duration,
max_retries, retry_delay, init_timeout):
_"""验证初始化参数"""_
_ _if parse_interval > 500 or parse_interval < 10:
raise ValueError("parse_interval must be between 10ms and 500ms")
if struggle_sensitivity not in [self.SENSITIVITY_LOW, self.SENSITIVITY_MEDIUM, self.SENSITIVITY_HIGH]:
raise ValueError("struggle_sensitivity must be 0 (low), 1 (medium), or 2 (high)")
if no_person_timing_duration < 30 or no_person_timing_duration > 180 or no_person_timing_duration % 10 != 0:
raise ValueError("no_person_timing_duration must be between 30-180 minutes in steps of 10")
if sleep_cutoff_duration < 5 or sleep_cutoff_duration > 120:
raise ValueError("sleep_cutoff_duration must be between 5-120 minutes")
if max_retries < 0 or max_retries > 10:
raise ValueError("max_retries must be between 0 and 10")
if retry_delay < 0 or retry_delay > 1000:
raise ValueError("retry_delay must be between 0ms and 1000ms")
if init_timeout < 1000 or init_timeout > 30000:
raise ValueError("init_timeout must be between 1000ms and 30000ms")
def _complete_initialization(self):
_"""_
_ 完整的初始化流程_
_ Raises:_
_ DeviceInitializationError: 初始化失败_
_ """_
_ _start_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 步骤1: 读取设备基本信息
device_info_loaded = self._load_device_information()
if not device_info_loaded:
raise DeviceInitializationError("Failed to load device information")
# 步骤2: 检查并等待设备初始化完成
init_success = self._wait_for_device_initialization()
if not init_success:
# 尝试重启设备
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Init] Device not initialized, attempting reset...")
reset_success = self._reset_and_wait_for_initialization()
if not reset_success:
raise DeviceInitializationError("Device initialization failed even after reset")
# 步骤3: 配置设备功能
self._auto_configure_device()
# 步骤4: 验证关键功能配置
self._verify_critical_configuration()
elapsed_time = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Init] Initialization completed in {elapsed_time}ms")
def _load_device_information(self):
_"""_
_ 加载设备基本信息_
_ Returns:_
_ bool: 是否成功加载所有设备信息_
_ """_
_ _info_queries = [
("Product Model", self.query_product_model),
("Product ID", self.query_product_id),
("Hardware Model", self.query_hardware_model),
("Firmware Version", self.query_firmware_version)
]
all_success = True
for info_name, query_func in info_queries:
success = self._execute_with_retry(query_func, f"Load {info_name}")
if not success:
all_success = False
self._configuration_errors.append(f"Failed to load {info_name}")
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Init] Warning: Failed to load {info_name}")
return all_success
def _wait_for_device_initialization(self, timeout=None):
_"""_
_ 等待设备初始化完成_
_ Args:_
_ timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒_
_ Returns:_
_ bool: 设备是否初始化完成_
_ """_
_ _if timeout is None:
timeout = self.init_timeout
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
while time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start_time) < timeout:
success, init_status = self.query_init_complete(timeout=500)
if success and init_status:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Init] Device initialization confirmed")
return True
# 短暂延迟后重试
time.sleep_ms(200)
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Init] Device initialization timeout")
return False
def _reset_and_wait_for_initialization(self):
_"""_
_ 重置设备并等待初始化完成_
_ Returns:_
_ bool: 重置和初始化是否成功_
_ """_
_ _# 发送复位指令
reset_success = self._execute_with_retry(
self.reset_module,
"Reset Device",
timeout=1000
)
if not reset_success:
return False
# 等待3秒让设备重启
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print("[Init] Waiting 3 seconds for device reset...")
time.sleep(3)
# 重新等待初始化完成
return self._wait_for_device_initialization(timeout=10000) # 10秒超时
def _auto_configure_device(self):
_"""_
_ 自动配置设备功能_
_ """_
_ _configuration_steps = []
# 基础功能配置
if self.presence_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(("Enable Human Presence", self.enable_human_presence))
else:
configuration_steps.append(("Disable Human Presence", self.disable_human_presence))
# 心率监测配置
if self.heart_rate_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(("Enable Heart Rate Monitor", self.enable_heart_rate_monitor))
if self.heart_rate_waveform_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(
("Enable Heart Rate Waveform Report", self.enable_heart_rate_waveform_report))
else:
configuration_steps.append(
("Disable Heart Rate Waveform Report", self.disable_heart_rate_waveform_report))
else:
configuration_steps.append(("Disable Heart Rate Monitor", self.disable_heart_rate_monitor))
# 呼吸监测配置
if self.breath_monitoring_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(("Enable Breath Monitor", self.enable_breath_monitor))
if self.breath_waveform_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(("Enable Breath Waveform Report", self.enable_breath_waveform_report))
else:
configuration_steps.append(("Disable Breath Waveform Report", self.disable_breath_waveform_report))
else:
configuration_steps.append(("Disable Breath Monitor", self.disable_breath_monitor))
# 睡眠监测配置
if self.sleep_monitoring_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(("Enable Sleep Monitor", self.enable_sleep_monitor))
# 异常挣扎配置
if self.abnormal_struggle_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(("Enable Abnormal Struggle Monitor", self.enable_abnormal_struggle_monitor))
# 设置挣扎灵敏度
configuration_steps.append(("Set Struggle Sensitivity",
lambda: self.set_struggle_sensitivity(self.struggle_sensitivity)))
else:
configuration_steps.append(
("Disable Abnormal Struggle Monitor", self.disable_abnormal_struggle_monitor))
# 无人计时配置
if self.no_person_timing_enabled:
configuration_steps.append(("Enable No Person Timing", self.enable_no_person_timing))
# 设置无人计时时长
configuration_steps.append(("Set No Person Timing Duration",
lambda: self.set_no_person_timing_duration(self.no_person_timing_duration)))
else:
configuration_steps.append(("Disable No Person Timing", self.disable_no_person_timing))
# 设置睡眠截止时长
configuration_steps.append(("Set Sleep End Duration",
lambda: self.set_sleep_end_duration(self.sleep_cutoff_duration)))
else:
configuration_steps.append(("Disable Sleep Monitor", self.disable_sleep_monitor))
# 执行配置步骤
for step_name, step_function in configuration_steps:
success = self._execute_with_retry(step_function, step_name)
if not success:
self._configuration_errors.append(f"Failed to {step_name}")
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Init] Warning: {step_name} failed")
def _verify_critical_configuration(self):
_"""_
_ 验证关键配置是否成功_
_ """_
_ _critical_verifications = []
# 验证设备初始化状态
critical_verifications.append(("Device Initialization", self.query_init_complete))
# 验证雷达范围状态
critical_verifications.append(("Radar Range", self.query_radar_range_boundary))
# 根据启用的功能添加验证
if self.presence_enabled:
critical_verifications.append(("Presence Detection", self.query_human_presence_switch))
if self.heart_rate_enabled:
critical_verifications.append(("Heart Rate Monitor", self.query_heart_rate_monitor_switch))
if self.breath_monitoring_enabled:
critical_verifications.append(("Breath Monitor", self.query_breath_monitor_switch))
if self.sleep_monitoring_enabled:
critical_verifications.append(("Sleep Monitor", self.query_sleep_monitor_switch))
# 执行验证
for verify_name, verify_func in critical_verifications:
success, result = verify_func(timeout=500)
if not success:
self._configuration_errors.append(f"Verification failed: {verify_name}")
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Init] Warning: {verify_name} verification failed")
def _execute_with_retry(self, operation, operation_name, timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 带重试的执行操作_
_ """_
_ _for attempt in range(self.max_retries + 1):
try:
success, result = operation(timeout=timeout)
if success:
return True
if attempt < self.max_retries:
time.sleep_ms(self.retry_delay)
except Exception as e:
if attempt < self.max_retries:
time.sleep_ms(self.retry_delay)
else:
if R60ABD1.DEBUG_ENABLED:
print(f"[Init] {operation_name} failed after {self.max_retries + 1} attempts: {e}")
return False
def get_configuration_status(self):
_"""_
_ 获取设备配置状态_
_ """_
_ _return {
'initialization_complete': self._initialization_complete,
'configuration_errors': self._configuration_errors.copy(),
'device_info': {
'product_model': self.product_model,
'product_id': self.product_id,
'hardware_model': self.hardware_model,
'firmware_version': self.firmware_version
},
'current_settings': {
'presence_enabled': self.presence_enabled,
'heart_rate_enabled': self.heart_rate_enabled,
'heart_rate_waveform_enabled': self.heart_rate_waveform_enabled,
'breath_monitoring_enabled': self.breath_monitoring_enabled,
'breath_waveform_enabled': self.breath_waveform_enabled,
'sleep_monitoring_enabled': self.sleep_monitoring_enabled,
'abnormal_struggle_enabled': self.abnormal_struggle_enabled,
'struggle_sensitivity': self.struggle_sensitivity,
'no_person_timing_enabled': self.no_person_timing_enabled,
'no_person_timing_duration': self.no_person_timing_duration,
'sleep_cutoff_duration': self.sleep_cutoff_duration
}
}
完整步骤如下:
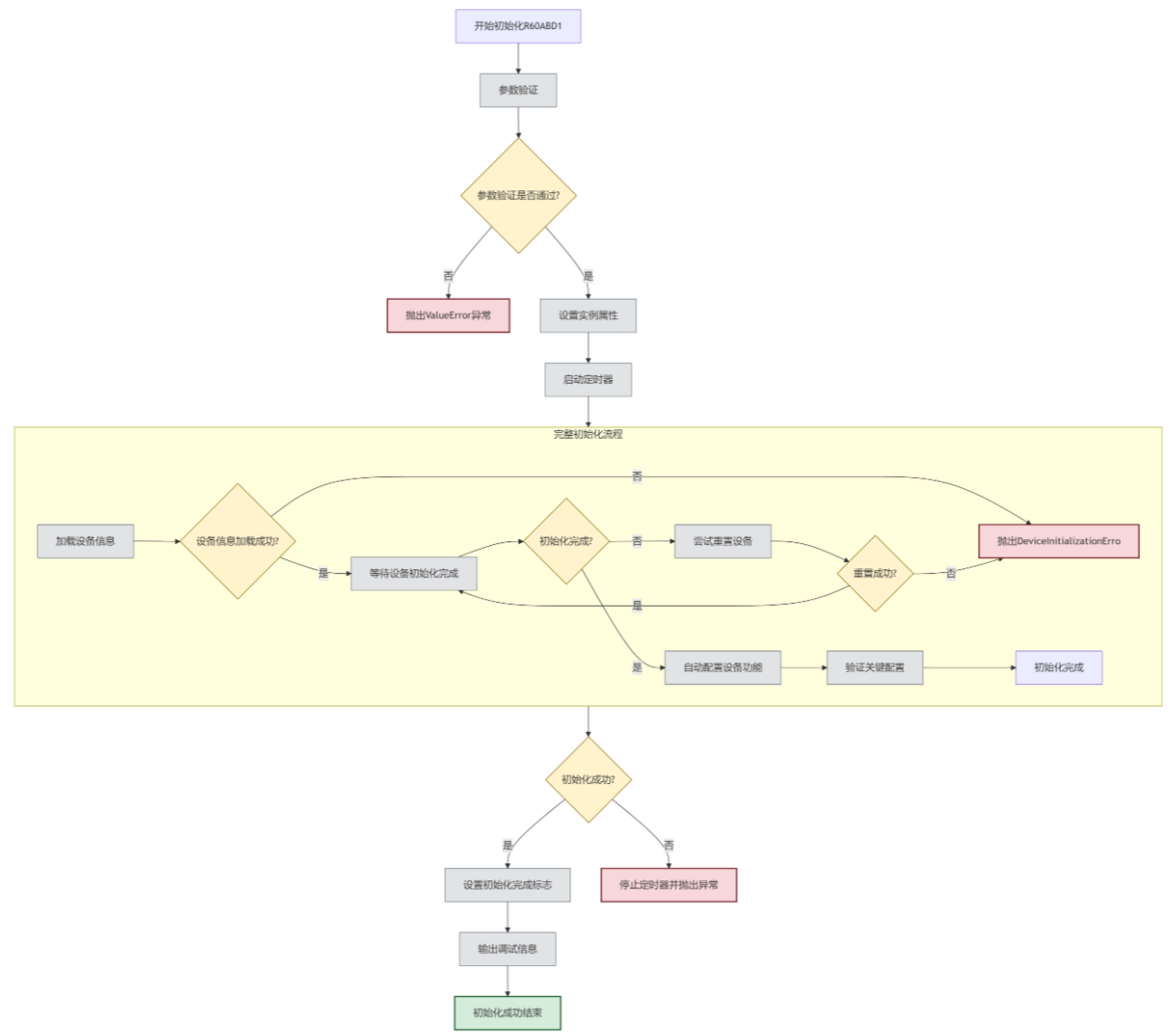
4.2 测试脚本:全功能覆盖与快速验证
main.py 作为配套测试脚本,实现 “初始化验证、功能测试、数据监控” 三大核心功能,示例代码覆盖关键测试场景,便于开发者快速验证驱动可靠性。
4.2.1 测试驱动库的核心维度与实现方式
驱动库的测试需覆盖 “初始化 → 功能调用 → 数据交互 → 资源释放” 全生命周期,结合 main.py 代码,具体测试维度与实现如下:
4.2.2.1 设备复位与初始化等待
初始化是驱动库运行的基础,需验证 “参数合法性校验、设备通信正常性、配置项生效性”。
# 初始化配置代码片段(来自main.py)
uart = UART(0, baudrate=115200, tx=Pin(16), rx=Pin(17), timeout=0)
processor = DataFlowProcessor(uart)
# 尝试创建驱动实例(触发参数校验与初始化流程)
try:
device = R60ABD1(processor, parse_interval=200)
print("驱动实例创建成功")
except ValueError as e:
print(f"参数校验失败:{e}") # 验证参数合法性(如parse_interval超限)
except DeviceInitializationError as e:
print(f"初始化失败:{e}") # 验证设备通信/配置异常处理
# 验证设备基础信息读取(初始化关键步骤)
success, product_model = device.query_product_model()
assert success, "产品型号查询失败,初始化异常"
print(f"产品型号:{product_model}") # 验证设备信息读取正确
4.2.2.2 功能接口测试:覆盖查询、控制、配置全类型接口
驱动库的核心价值在于提供可靠的功能接口,需按 “查询类 → 控制类 → 配置类” 分类测试,确保每个接口的输入输出符合预期。
- 查询类接口测试(获取设备状态 / 数据)
查询类接口(如 query_human_distance、query_heart_rate_value)需验证 “是否能正确返回设备数据”,失败时是否返回 (False, None)。
# 主动查询数据测试(来自main.py的print_active_query_data函数核心逻辑)
def test_query_interfaces():
# 测试人体距离查询
success, distance = device.query_human_distance(timeout=200)
if success:
assert isinstance(distance, int) and 0 <= distance <= 65535, "距离值范围异常"
print(f"人体距离查询成功:{distance}cm")
else:
print("人体距离查询失败(可能设备未检测到目标)")
# 测试心率查询
success, heart_rate = device.query_heart_rate_value(timeout=200)
if success:
assert isinstance(heart_rate, int) and 0 <= heart_rate <= 200, "心率值范围异常"
print(f"心率查询成功:{heart_rate}bpm")
else:
print("心率查询失败(可能未开启心率监测)")
test_query_interfaces()
测试要点如下:
- 成功时返回值类型与范围是否符合文档(如距离为 0-65535cm 的整数);
- 失败时
success是否为False,result是否为None; - 接口是否兼容超时参数(如
timeout=200时超过 200ms 未响应则返回失败)。
- 控制类接口测试(开关功能)
控制类接口(如 enable_human_presence、enable_sleep_monitor)需验证 “是否能正确控制设备功能”,且状态变更能通过查询接口确认。
def test_control_interfaces():
# 测试开启人体存在监测
success, _ = device.enable_human_presence()
assert success, "开启人体存在监测失败"
# 验证功能是否生效(通过查询接口确认)
success, status = device.query_human_presence_switch()
assert success and status is True, "人体存在监测未实际开启"
print("人体存在监测开启成功并验证通过")
# 测试关闭人体存在监测
success, _ = device.disable_human_presence()
assert success, "关闭人体存在监测失败"
success, status = device.query_human_presence_switch()
assert success and status is False, "人体存在监测未实际关闭"
print("人体存在监测关闭成功并验证通过")
test_control_interfaces()
测试要点如下:
- 控制指令发送成功后,通过对应查询接口(例如
query_human_presence_switch)验证状态是否实际变更; - 控制失败时(如设备不支持该功能),
success是否为False。
- 配置类接口测试(调整参数)
配置类接口(如 set_struggle_sensitivity、set_no_person_timing_duration)需验证 “参数是否能正确写入设备”,且查询时返回配置值。
def test_config_interfaces():
# 测试设置挣扎灵敏度为中等(1)
target_sensitivity = 1
success, _ = device.set_struggle_sensitivity(target_sensitivity)
assert success, "设置挣扎灵敏度失败"
# 验证配置是否生效
success, sensitivity = device.query_struggle_sensitivity()
assert success and sensitivity == target_sensitivity, "挣扎灵敏度配置未生效"
print(f"挣扎灵敏度设置为{target_sensitivity}(中等)并验证通过")
# 测试设置无人计时时长为60分钟
target_duration = 60
success, _ = device.set_no_person_timing_duration(target_duration)
assert success, "设置无人计时时长失败"
success, duration = device.query_no_person_timing_duration()
assert success and duration == target_duration, "无人计时时长配置未生效"
print(f"无人计时时长设置为{target_duration}分钟并验证通过")
test_config_interfaces()
测试要点如下:
- 配置参数需在合法范围内(如挣扎灵敏度仅支持 0/1/2),超出范围时是否返回失败;
- 配置成功后,通过查询接口验证返回值与配置值一致。
4.2.2.3 实时数据监控测试:验证主动上报与属性同步
设备会主动上报实时数据(如心率波形、呼吸状态),需验证驱动库的 update_properties_from_frame 方法是否能正确解析并更新属性。
# 实时上报数据监控(来自main.py的核心逻辑)
def test_realtime_data():
last_print = time.ticks_ms()
print_interval = 2000 # 每2秒打印一次实时属性
try:
while time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), last_print) < 10000: # 监控10秒
current = time.ticks_ms()
if time.ticks_diff(current, last_print) >= print_interval:
# 打印驱动类属性(验证主动上报数据是否同步)
print(f"\n实时属性({time.strftime('%H:%M:%S')}):")
print(f"存在状态:{'有人' if device.presence_status == 1 else '无人'}")
print(f"呼吸频率:{device.breath_value}bpm")
print(f"心率波形:{device.heart_rate_waveform}")
last_print = current
time.sleep_ms(10)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
test_realtime_data()
测试要点如下:
- 驱动类属性(如
presence_status、breath_value)是否随设备上报数据实时更新; - 波形数据(如
heart_rate_waveform)的长度与格式是否符合协议(如 5 字节列表)。
4.2.2 测试脚本完整代码示例
# Python env : MicroPython v1.23.0
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/11/4 下午5:33
# @Author : 李清水
# @File : main.py
# @Description : 测试R60ABD1雷达设备驱动类的代码
# @License : CC BY-NC 4.0
# ======================================== 导入相关模块 =========================================
from machine import UART, Pin, Timer
import time
from data_flow_processor import DataFlowProcessor
from r60abd1 import R60ABD1, format_time
# ======================================== 全局变量 ============================================
# 上次打印时间
last_print_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 定时打印间隔:2秒打印一次
print_interval = 2000
# ======================================== 功能函数 ============================================
def print_report_sensor_data():
_"""打印传感器数据到Thonny控制台"""_
_ _# 声明全局变量
global device
print("=" * 50)
print("%s Sensor Data" % format_time())
print("=" * 50)
# 心率数据
print("Report Heart Rate: %d bpm" % device.heart_rate_value)
print("Report Heart Rate Waveform: %s" % str(device.heart_rate_waveform))
# 呼吸数据
print("Report Breath Rate: %d bpm" % device.breath_value)
print("Report Breath Status: %d" % device.breath_status)
print("Report Breath Waveform: %s" % str(device.breath_waveform))
# 人体存在数据
print("Report Movement Parameter: %d" % device.movement_parameter)
print("Report Presence Status: %s" % ("Someone" if device.presence_status == 1 else "No one"))
print("Report Motion Status: %s" % ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][
device.motion_status] if device.motion_status < 3 else "Unknown")
# 距离和位置
print("Report Human Distance: %d cm" % device.human_distance)
print("Report Human Position: X=%d, Y=%d, Z=%d" % (
device.human_position_x, device.human_position_y, device.human_position_z))
# 雷达状态
print("Report Radar in Range: %s" % ("Yes" if device.radar_in_range else "No"))
print("=" * 50)
def print_active_query_data(timeout=200):
_"""_
_ 主动查询并打印传感器数据(阻塞式查询)_
_ """_
_ _# 声明全局变量
global device
print("=" * 50)
print("%s Active Query Sensor Data" % format_time())
print("=" * 50)
# 查询人体方位
success, direction_data = device.query_human_direction(timeout)
if success:
x, y, z = direction_data
print("Query Human Position: X=%d, Y=%d, Z=%d" % (x, y, z))
else:
print("Query Human Position: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询人体距离
success, distance = device.query_human_distance(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Human Distance: %d cm" % distance)
else:
print("Query Human Distance: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询运动信息
success, motion_status = device.query_human_motion_info(timeout)
if success:
motion_text = ["No motion", "Static", "Active"][motion_status] if motion_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print("Query Motion Status: %s" % motion_text)
else:
print("Query Motion Status: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询体动参数
success, motion_param = device.query_human_body_motion_param(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Movement Parameter: %d" % motion_param)
else:
print("Query Movement Parameter: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询存在状态
success, presence_status = device.query_presence_status(timeout)
if success:
status_text = "Someone" if presence_status == 1 else "No one"
print("Query Presence Status: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Presence Status: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询心率数值
success, heart_rate = device.query_heart_rate_value(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Heart Rate: %d bpm" % heart_rate)
else:
print("Query Heart Rate: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询心率波形
success, heart_rate_waveform = device.query_heart_rate_waveform(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Heart Rate Waveform: %s" % str(heart_rate_waveform))
else:
print("Query Heart Rate Waveform: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询呼吸数值
success, breath_rate = device.query_breath_value(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Breath Rate: %d bpm" % breath_rate)
else:
print("Query Breath Rate: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询呼吸波形
success, breath_waveform = device.query_breath_waveform(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Breath Waveform: %s" % str(breath_waveform))
else:
print("Query Breath Waveform: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询呼吸信息
success, breath_info = device.query_breath_info(timeout)
if success:
status_text = ["Normal", "High", "Low", "None"][breath_info - 1] if 1 <= breath_info <= 4 else "Unknown"
print("Query Breath Info: %d - %s" % (breath_info, status_text))
else:
print("Query Breath Info: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询床状态
success, bed_status = device.query_bed_status(timeout)
if success:
status_text = ["Leave bed", "Enter bed", "None"][bed_status] if bed_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print("Query Bed Status: %d - %s" % (bed_status, status_text))
else:
print("Query Bed Status: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询无人计时状态
success, no_person_timing_status = device.query_no_person_timing_status(timeout)
if success:
status_text = ["None", "Normal", "Abnormal"][
no_person_timing_status] if no_person_timing_status < 3 else "Unknown"
print("Query No Person Timing Status: %d - %s" % (no_person_timing_status, status_text))
else:
print("Query No Person Timing Status: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询睡眠状态
success, sleep_status = device.query_sleep_status(timeout)
if success:
status_text = ["Deep sleep", "Light sleep", "Awake", "None"][sleep_status] if sleep_status < 4 else "Unknown"
print("Query Sleep Status: %d - %s" % (sleep_status, status_text))
else:
print("Query Sleep Status: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询清醒时长
success, awake_duration = device.query_awake_duration(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Awake Duration: %d min" % awake_duration)
else:
print("Query Awake Duration: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询浅睡时长
success, light_sleep_duration = device.query_light_sleep_duration(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Light Sleep Duration: %d min" % light_sleep_duration)
else:
print("Query Light Sleep Duration: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询深睡时长
success, deep_sleep_duration = device.query_deep_sleep_duration(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Deep Sleep Duration: %d min" % deep_sleep_duration)
else:
print("Query Deep Sleep Duration: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询睡眠质量评分
success, sleep_quality_score = device.query_sleep_quality_score(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Sleep Quality Score: %d/100" % sleep_quality_score)
else:
print("Query Sleep Quality Score: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询睡眠综合状态
success, sleep_comprehensive_status = device.query_sleep_comprehensive_status(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Sleep Comprehensive Status: Success")
# 可以进一步解析和显示详细数据
if len(sleep_comprehensive_status) >= 8:
print(" - Presence: %s" % ("Someone" if sleep_comprehensive_status[0] == 1 else "No one"))
print(" - Sleep Status: %s" % ["Deep sleep", "Light sleep", "Awake", "None"][sleep_comprehensive_status[1]] if sleep_comprehensive_status[1] < 4 else "Unknown")
print(" - Avg Breath: %d bpm" % sleep_comprehensive_status[2])
print(" - Avg Heart Rate: %d bpm" % sleep_comprehensive_status[3])
print(" - Turnover Count: %d" % sleep_comprehensive_status[4])
print(" - Large Movement Ratio: %d%%" % sleep_comprehensive_status[5])
print(" - Small Movement Ratio: %d%%" % sleep_comprehensive_status[6])
print(" - Apnea Count: %d" % sleep_comprehensive_status[7])
else:
print("Query Sleep Comprehensive Status: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询睡眠异常
success, sleep_anomaly = device.query_sleep_anomaly(timeout)
if success:
status_text = ["Short sleep (<4h)", "Long sleep (>12h)", "No person anomaly", "Normal"][sleep_anomaly] if sleep_anomaly < 4 else "Unknown"
print("Query Sleep Anomaly: %d - %s" % (sleep_anomaly, status_text))
else:
print("Query Sleep Anomaly: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询睡眠统计
success, sleep_statistics = device.query_sleep_statistics(timeout)
if success:
print("Query Sleep Statistics: Success")
# 可以进一步解析和显示详细数据
if len(sleep_statistics) >= 11:
print(" - Quality Score: %d/100" % sleep_statistics[0])
print(" - Total Sleep Duration: %d min" % sleep_statistics[1])
print(" - Awake Ratio: %d%%" % sleep_statistics[2])
print(" - Light Sleep Ratio: %d%%" % sleep_statistics[3])
print(" - Deep Sleep Ratio: %d%%" % sleep_statistics[4])
print(" - Leave Bed Duration: %d min" % sleep_statistics[5])
print(" - Leave Bed Count: %d" % sleep_statistics[6])
print(" - Turnover Count: %d" % sleep_statistics[7])
print(" - Avg Breath: %d bpm" % sleep_statistics[8])
print(" - Avg Heart Rate: %d bpm" % sleep_statistics[9])
print(" - Apnea Count: %d" % sleep_statistics[10])
else:
print("Query Sleep Statistics: Failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询睡眠质量评级
success, sleep_quality_level = device.query_sleep_quality_level(timeout)
if success:
status_text = ["None", "Good", "Normal", "Poor"][sleep_quality_level] if sleep_quality_level < 4 else "Unknown"
print("Query Sleep Quality Level: %d - %s" % (sleep_quality_level, status_text))
else:
print("Query Sleep Quality Level: Failed")
print("=" * 50)
# ======================================== 自定义类 ============================================
# ======================================== 初始化配置 ==========================================
# 上电延时
time.sleep(3)
# 打印调试信息
print("FreakStudio: Using R60ABD1 millimeter wave information collection")
# 初始化UART0:TX=16, RX=17,波特率115200
uart = UART(0, baudrate=115200, tx=Pin(16), rx=Pin(17), timeout=0)
# 创建DataFlowProcessor实例
processor = DataFlowProcessor(uart)
# 创建R60ABD1实例
device = R60ABD1(processor, parse_interval=200)
success, product_model = device.query_product_model()
if success:
print("Product Model: %s" % product_model)
else:
print("Query Product Model failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, product_id = device.query_product_id()
if success:
print("Product ID: %s" % product_id)
else:
print("Query Product ID failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, hardware_model = device.query_hardware_model()
if success:
print("Hardware Model: %s" % hardware_model)
else:
print("Query Hardware Model failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, firmware_version = device.query_firmware_version()
if success:
print("Hardware Version: %s" % firmware_version)
else:
print("Query Hardware Version failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, init_status = device.query_init_complete()
if success:
print("Init Status: %s" % init_status)
else:
print("Query Init Status failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, boundary_status = device.query_radar_range_boundary()
if success:
status_text = "out of range" if boundary_status else "in range"
print("Boundary Status: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Boundary Status failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, presence_switch_status = device.query_human_presence_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if presence_switch_status else "OFF"
print("Boundary Status: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Boundary Status failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, heart_rate_monitor_switch_status = device.query_heart_rate_monitor_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if heart_rate_monitor_switch_status else "OFF"
print("Heart Rate Monitor Switch: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Heart Rate Monitor Switch failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
success, heart_rate_waveform_report_switch_status = device.query_heart_rate_waveform_report_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if heart_rate_waveform_report_switch_status else "OFF"
print("Heart Rate Waveform Report Switch: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Heart Rate Waveform Report Switch failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询呼吸监测开关状态
success, breath_monitor_switch_status = device.query_breath_monitor_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if breath_monitor_switch_status else "OFF"
print("Breath Monitor Switch: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Breath Monitor Switch failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 设置低缓呼吸阈值为15次/分
success, set_result = device.set_low_breath_threshold(15)
if success:
print("Set Low Breath Threshold: Success (15 bpm)")
else:
print("Set Low Breath Threshold failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询当前低缓呼吸阈值
success, low_breath_threshold = device.query_low_breath_threshold()
if success:
print("Query Low Breath Threshold: %d bpm" % low_breath_threshold)
else:
print("Query Low Breath Threshold failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询呼吸波形上报开关状态
success, breath_waveform_report_switch_status = device.query_breath_waveform_report_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if breath_waveform_report_switch_status else "OFF"
print("Breath Waveform Report Switch: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Breath Waveform Report Switch failed")
# 查询睡眠监测开关状态
success, sleep_monitor_switch_status = device.query_sleep_monitor_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if sleep_monitor_switch_status else "OFF"
print("Sleep Monitor Switch: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Sleep Monitor Switch failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 打开睡眠监测功能
success, result = device.enable_sleep_monitor()
if success:
print("Enable Sleep Monitor: Success")
else:
print("Enable Sleep Monitor failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询异常挣扎监测开关状态
success, abnormal_struggle_switch_status = device.query_abnormal_struggle_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if abnormal_struggle_switch_status else "OFF"
print("Abnormal Struggle Monitor Switch: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query Abnormal Struggle Monitor Switch failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 打开异常挣扎监测功能
success, result = device.enable_abnormal_struggle_monitor()
if success:
print("Enable Abnormal Struggle Monitor: Success")
else:
print("Enable Abnormal Struggle Monitor failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询挣扎灵敏度
success, struggle_sensitivity = device.query_struggle_sensitivity()
if success:
sensitivity_text = ["Low", "Medium", "High"][struggle_sensitivity] if struggle_sensitivity < 3 else "Unknown"
print("Struggle Sensitivity: %d - %s" % (struggle_sensitivity, sensitivity_text))
else:
print("Query Struggle Sensitivity failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 设置挣扎灵敏度为中等
success, result = device.set_struggle_sensitivity(1) # 1 = 中等灵敏度
if success:
print("Set Struggle Sensitivity: Success (Medium)")
else:
print("Set Struggle Sensitivity failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询无人计时功能开关状态
success, no_person_timing_switch_status = device.query_no_person_timing_switch()
if success:
status_text = "ON" if no_person_timing_switch_status else "OFF"
print("No Person Timing Switch: %s" % status_text)
else:
print("Query No Person Timing Switch failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 打开无人计时功能
success, result = device.enable_no_person_timing()
if success:
print("Enable No Person Timing: Success")
else:
print("Enable No Person Timing failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询无人计时时长
success, no_person_timing_duration = device.query_no_person_timing_duration()
if success:
print("No Person Timing Duration: %d minutes" % no_person_timing_duration)
else:
print("Query No Person Timing Duration failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 设置无人计时时长为30分钟
success, result = device.set_no_person_timing_duration(30)
if success:
print("Set No Person Timing Duration: Success (30 minutes)")
else:
print("Set No Person Timing Duration failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 查询睡眠截止时长
success, sleep_end_duration = device.query_sleep_end_duration()
if success:
print("Sleep End Duration: %d minutes" % sleep_end_duration)
else:
print("Query Sleep End Duration failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# 设置睡眠截止时长为10分钟
success, result = device.set_sleep_end_duration(10)
if success:
print("Set Sleep End Duration: Success (10 minutes)")
else:
print("Set Sleep End Duration failed")
time.sleep(0.5)
# ======================================== 主程序 ===========================================
try:
while True:
current_time = time.ticks_ms()
# 定期打印传感器数据
if time.ticks_diff(current_time, last_print_time) >= print_interval:
# print_report_sensor_data()
success, presence_status = device.query_presence_status()
if success:
print("Presence Status: %s" % ("Someone" if presence_status == 1 else "No one"))
else:
print("Query Presence Status failed")
last_print_time = current_time
time.sleep(0.2)
success, heartbeat_status = device.query_heartbeat()
if success:
print("Heartbeat Status: %s" % ("Normal" if heartbeat_status == 1 else "Abnormal"))
else:
print("Query Heartbeat failed")
# 小延迟,避免占用太多CPU
time.sleep_ms(10)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("%s Program interrupted by user" % format_time())
finally:
# 清理资源
print("%s Cleaning up resources..." % format_time())
# 停止实例运行
device.close()
# 销毁实例
del device
print("%s Program exited" % format_time())
4.3 性能测试与系统资源分析
性能测试的核心目标是验证驱动库在嵌入式环境(如树莓派 Pico)中的资源占用合理性、实时性与稳定性,确保其能长期可靠运行且不影响系统其他功能。
嵌入式系统(如树莓派 Pico)的 CPU、内存资源有限,驱动库的性能缺陷可能导致:
- 系统卡顿:CPU占用过高,导致其他任务(如网络通信、用户交互)响应延迟;
- 数据丢失:解析间隔不合理或处理时间过长,导致设备上报数据未及时处理;
- 稳定性下降:长时间高负载运行可能引发内存泄漏、定时器异常等问题;
- 实时性不足:健康监测、异常告警等场景对数据更新延迟敏感,性能不达标会影响功能有效性。
基于驱动库的特性,需重点关注以下指标:
- 核心方法执行时间:
update_properties_from_frame是驱动库解析设备数据的核心方法,其执行时间直接影响CPU占用。- 指标定义:单次解析设备数据帧的耗时(单位:ms);
- 关键值:
- 平均值:反映长期运行的平均负载;
- 最大值:反映最坏情况下的负载峰值;
- 分布范围:是否存在频繁的长尾延迟(如偶尔超过 1ms)。
- 实时性:设备数据的更新延迟需满足业务场景需求。
- 指标定义:从设备上报数据到驱动库属性更新的时间差;
- 影响因素:解析间隔(
parse_interval)和update_properties_from_frame执行时间。
- 稳定性(长时间运行表现):驱动库需能稳定运行至少 24 小时,无内存泄漏、功能退化等问题。
- 指标定义:
- 内存占用变化:是否随时间持续增长;
- 功能有效性:长时间运行后,查询 / 控制接口是否仍能正常工作;
- 异常重启次数:是否因性能问题导致系统重启。
- 指标定义:
这里,我们主要测试不同数据解析周期情况下 update_properties_from_frame 方法的解析时间,这里调节不同数据解析周期,就是调节“定时器间隔” 即 parse_interval 参数(单位:毫秒):驱动库会通过定时器,每隔 parse_interval 毫秒自动调用 update_properties_from_frame 方法,从设备读取最新的传感器数据(如心率、呼吸波形、人体存在状态等)并解析更新到属性中。
例如:
parse_interval=50表示每 50 毫秒解析一次数据;parse_interval=200表示每 200 毫秒解析一次数据。
传感器数据(如心率波动、人体运动状态)是动态变化的,定时器间隔决定了驱动库采集这些变化的灵敏度:
- 间隔过短(如 50ms):每 50ms 更新一次数据,能快速捕捉微小变化(如心率瞬间升高、人体轻微移动),适合对实时性要求高的场景(如异常挣扎监测);
- 间隔过长(如 200ms):数据更新延迟增加,可能错过短时间内的关键变化(如突发的呼吸暂停),但能降低资源消耗。
同时,设备会持续向驱动库发送数据帧,这些数据会先暂存在缓冲区中:
- 间隔过短(如 50ms):缓冲区数据尚未积累就被处理,单次处理的数据量少(可能仅 1-2 帧),但频繁调用可能导致 “处理 - 等待” 的低效循环;
- 间隔过长(如 200ms):缓冲区可能积累多帧数据(如 4-5 帧),单次处理的数据量增加,可能导致单次执行时间延长(如从 0.2ms 增至 0.6ms),但调用频率降低,总体资源占用更优。
为精准量化 update_properties_from_frame 方法的执行耗时,我们在该方法上应用了计时装饰器:
# 计时装饰器,用于计算函数运行时间
def timed_function(f: callable, *args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> callable:
_"""_
_ 计时装饰器,用于计算并打印函数/方法运行时间。_
_ Args:_
_ f (callable): 需要传入的函数/方法_
_ args (tuple): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的位置参数_
_ kwargs (dict): 函数/方法 f 传入的任意数量的关键字参数_
_ Returns:_
_ callable: 返回计时后的函数_
_ """_
_ _myname = str(f).split(' ')[1]
def new_func(*args: tuple, **kwargs: dict) -> any:
t: int = time.ticks_us()
result = f(*args, **kwargs)
delta: int = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_us(), t)
print('Function {} Time = {:6.3f}ms'.format(myname, delta / 1000))
return result
return new_func
timed_function 装饰器的核心逻辑是在方法调用前后记录时间戳,计算差值并转换为毫秒单位打印。将其应用于 update_properties_from_frame 后,每次解析设备数据帧时,都会输出类似如下的耗时日志:
Function update_properties_from_frame Time = 0.287ms
Function update_properties_from_frame Time = 0.164ms
Function update_properties_from_frame Time = 0.625ms
...
通过采集大量日志数据,我们对 50ms、100ms、200ms 三种典型解析间隔下的性能指标进行了统计分析。
定时器间隔为:50 ms 时测试结果如下:

定时器间隔为:100 ms 时测试结果如下:
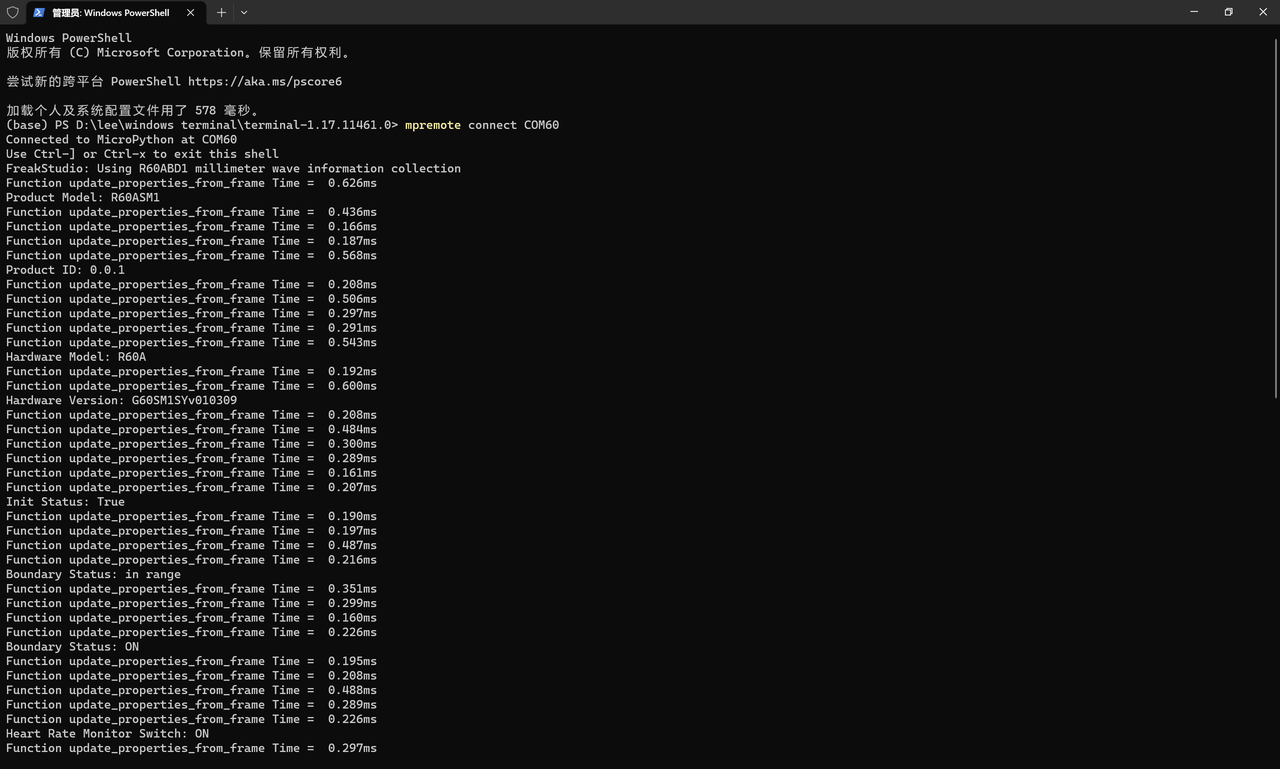
定时器间隔为:200 ms 时测试结果如下:
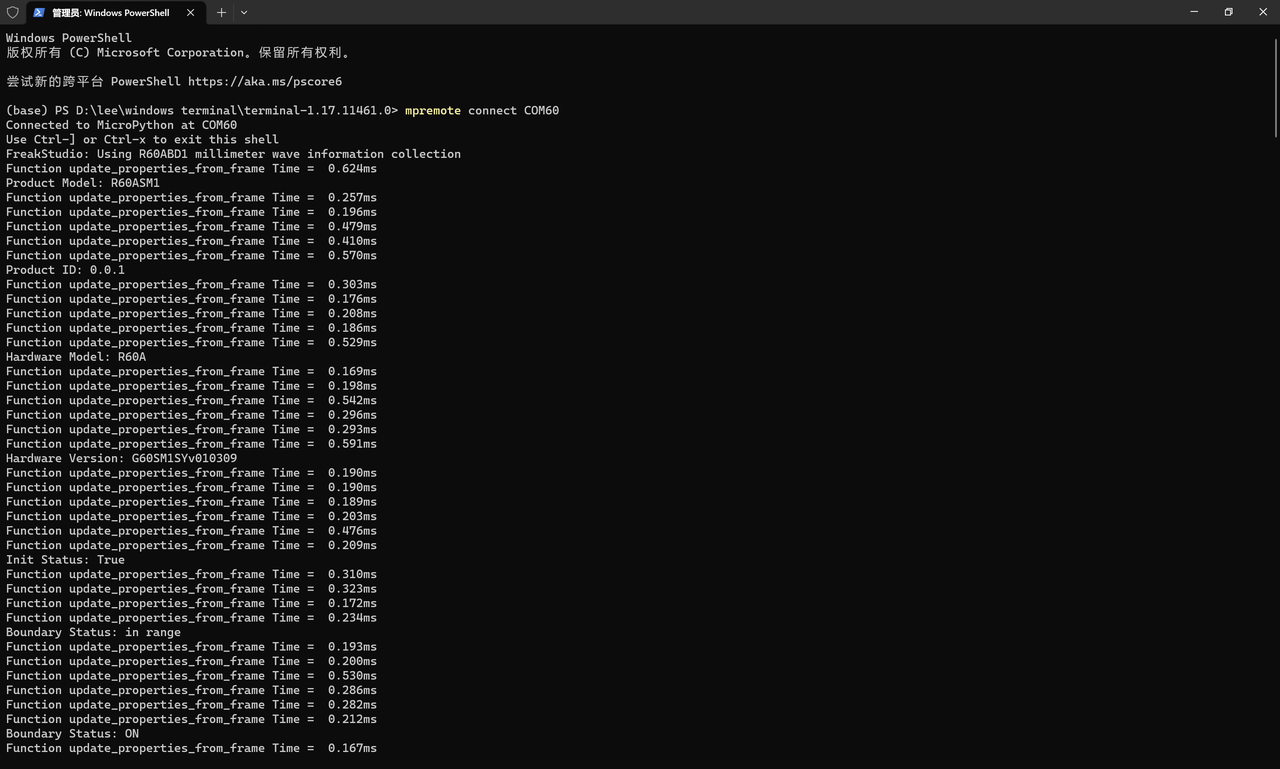
不同数据解析测试结果如下所示:
五、附件资料与源码链接
内部固件可看:
https://f1829ryac0m.feishu.cn/docx/O1trdIGMEocKh2xRX7QcGTLxnNd?from=from_copylink
源码链接:
关于我们更多介绍可以查看云文档:Freak 嵌入式工作室云文档,或者访问我们的 wiki:https://github.com/leezisheng/Doc/wik

 本文以 R60ABD1 雷达为实战案例,详解 MicroPython 环境下自定义串口通信协议架构的设计与分析方法,聚焦数据解析与业务逻辑分离核心,拆解协议封装、指令交互等关键环节,提供可复用的嵌入式串口驱动开发思路。
本文以 R60ABD1 雷达为实战案例,详解 MicroPython 环境下自定义串口通信协议架构的设计与分析方法,聚焦数据解析与业务逻辑分离核心,拆解协议封装、指令交互等关键环节,提供可复用的嵌入式串口驱动开发思路。
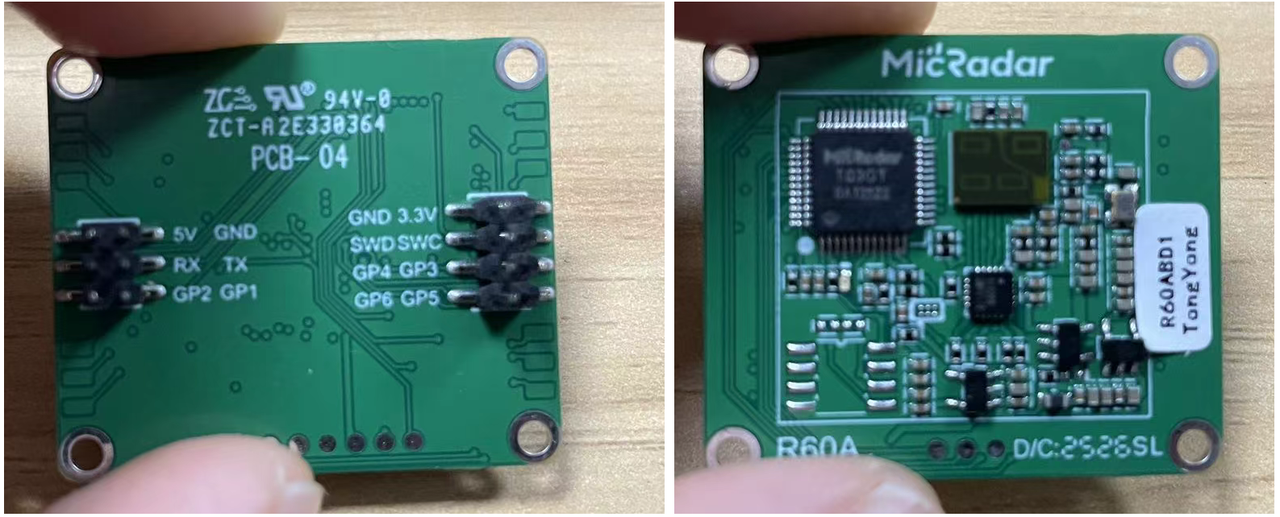
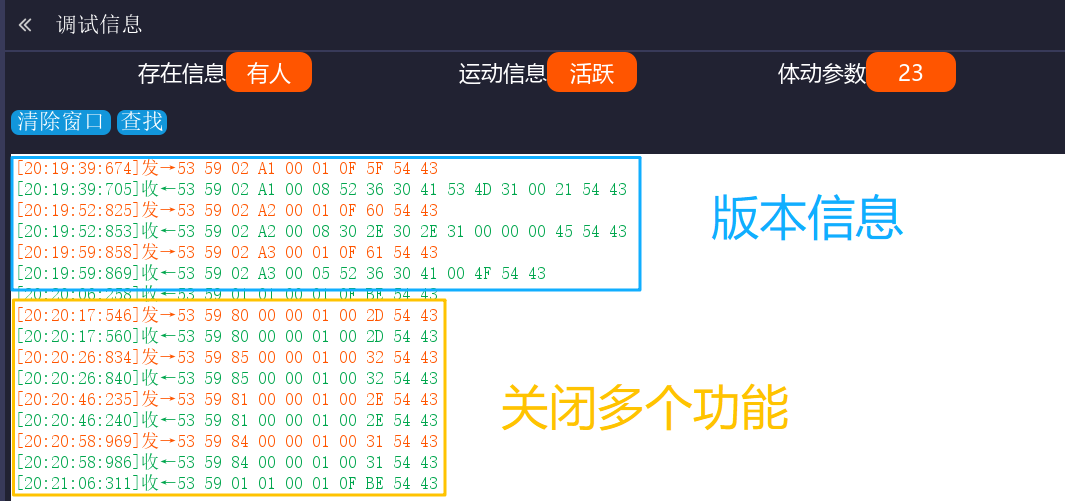
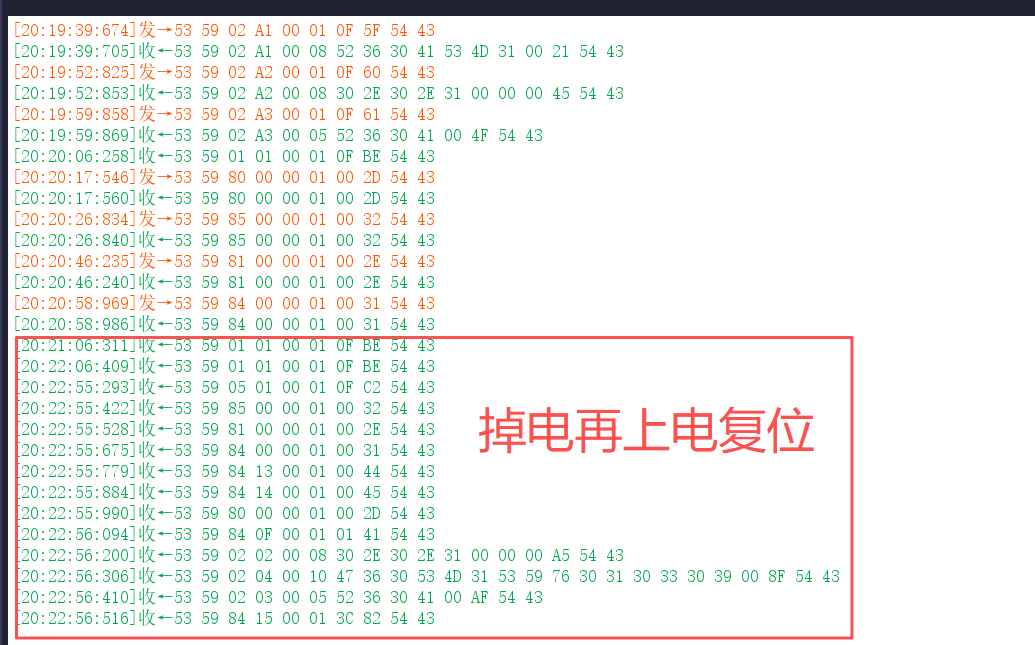
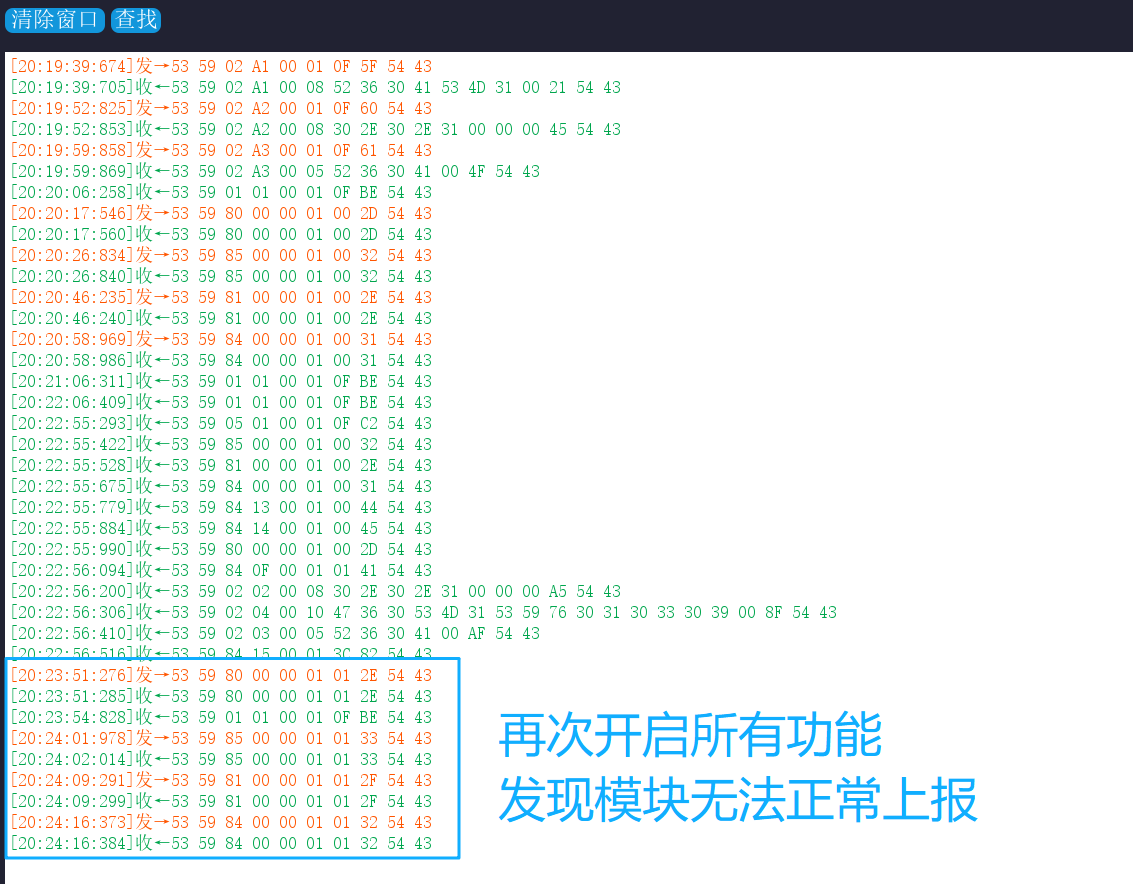
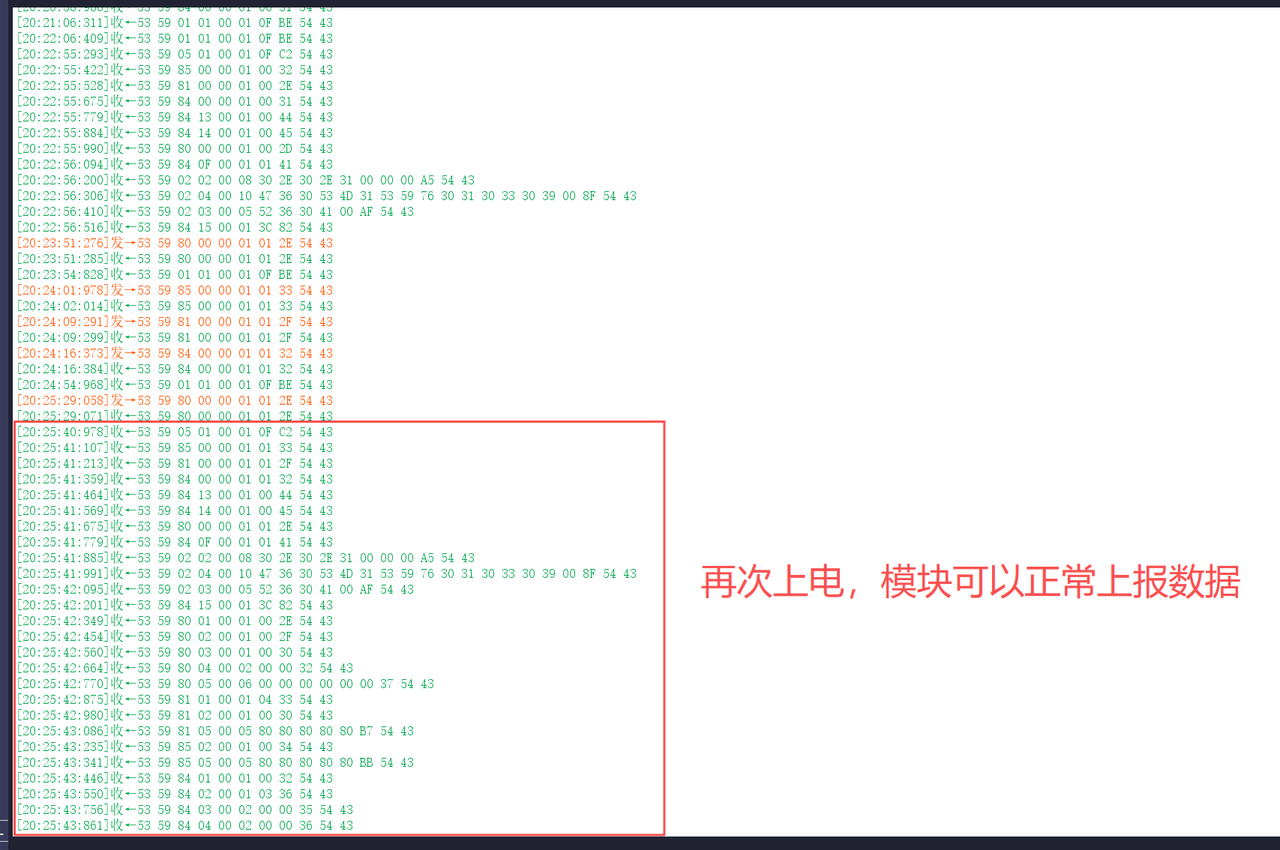
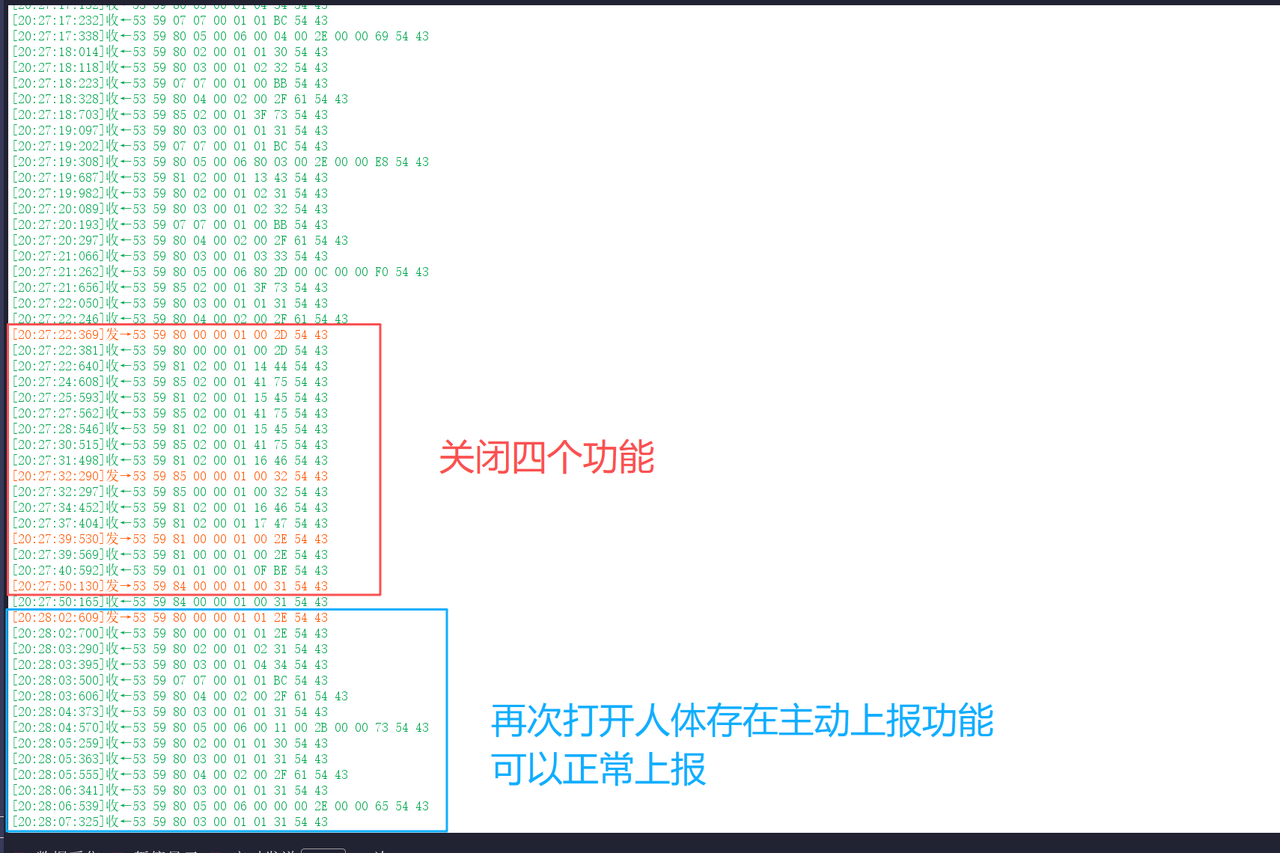

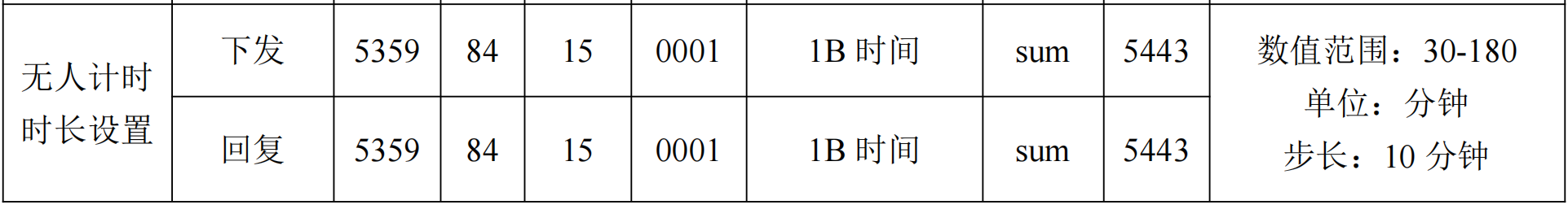

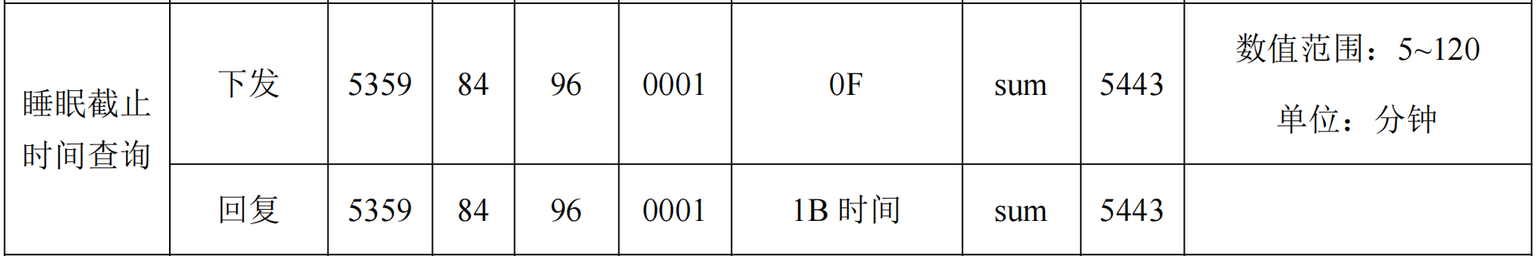


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号