JSP(Java Server Pages),Java服务器页面。JSP是一种基于文本的程序,其特点就是HTML和Java代码共同存在。JSP是为了简化Servlet的工作出现的替代品,Servlet输出HTML是非常困难的,JSP就是替代Servlet输出HTML的。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
String s="hello world";
out.println(s);
%>
</body>
</html>
JSP的工作原理:Tomcat访问任何的资源都是在访问Servlet。而JSP本身就是一种Servlet。其实JSP在第一次被访问的时候会被编译为HttpJspPage类(该类是HttpServlet的一个子类)。
package org.apache.jsp; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import javax.servlet.jsp.*; import java.util.Date; public final class _1_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent { private static final JspFactory _jspxFactory = JspFactory.getDefaultFactory(); private static java.util.List<String> _jspx_dependants; private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory; private org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_instancemanager; public java.util.List<String> getDependants() { return _jspx_dependants; } public void _jspInit() { _el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory(); _jsp_instancemanager = org.apache.jasper.runtime.InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(getServletConfig()); } public void _jspDestroy() { } public void _jspService(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) throws java.io.IOException, ServletException { final PageContext pageContext; HttpSession session = null; final ServletContext application; final ServletConfig config; JspWriter out = null; final Object page = this; JspWriter _jspx_out = null; PageContext _jspx_page_context = null; try { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, true, 8192, true); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); session = pageContext.getSession(); out = pageContext.getOut(); _jspx_out = out; out.write("\r\n"); out.write("\r\n"); out.write("<html>\r\n"); out.write("<head>\r\n"); out.write(" <title>简单使用JSP</title>\r\n"); out.write("</head>\r\n"); out.write("<body>\r\n"); String s = "HelloWorld"; out.println(s); out.write("\r\n"); out.write("</body>\r\n"); out.write("</html>\r\n"); } catch (Throwable t) { if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)){ out = _jspx_out; if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0) try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {} if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t); } } finally { _jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context); } } }
- 编译过程:浏览器第一次请求1.jsp时,Tomcat会将1.jsp转化成1_jsp.java这么一个类,并将该文件编译成class文件。编译完毕后再运行class文件来响应浏览器的请求。
- 以后访问1.jsp就不再重新编译jsp文件了,直接调用class文件来响应浏览器。如果Tomcat检测到JSP页面改动了,会重新编译的。
- 既然JSP是一个Servlet,那JSP页面中HTML排版标签是out.write()出去的。其实,JSP就是封装了Servlet的Java程序罢了。
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write("<head>\r\n");
out.write(" <title>简单使用JSP</title>\r\n");
out.write("</head>\r\n");
out.write("<body>\r\n");
jsp页面中的代码是怎么执行的?java代码就直接在类中的service()中。
String s = "HelloWorld";
out.println(s);
JSP比Servlet更方便的一个重要原因就是:内置了9个对象。内置对象有:out、session、response、request、config、page、application、pageContext、exception。
JSP生命周期
JSP也是Servlet,运行时只有一个实例,JSP初始化和销毁时也会调用Servlet的init()和destroy()方法。另外,JSP还有自己的初始化和销毁的方法。
JSP的语法
JSP代码可以分为两部分:
- 模板数据:就是HTML代码
- 元素:JSP页面中的java代码、JSP指令、JSP标签
JSP脚本
JSP的脚本就是JSP页面中的java代码,也叫做scriptlet。JSP的脚本必须使用<%%>括起来,不然会被当成模板数据。
JSP脚本有三种方式:
- <%%> 【定义局部变量,编写语句】
- <%!%> 【定义类或方法,但是没人这样用】
- <%=%>【也称之为表达式输出,输出各种类型的变量,int、double、String、Object等】
如果过多地使用<%%>会导致代码混乱,JSP还提供了一种scriptlet标签,使用此标签和<%%>有相同的功能,只不过它更美观了。
<jsp:scriptlet> String s="hello world"; out.println(s); </jsp:scriptlet>
JSP注释
<%--jsp注释--%> //java单行注释 // /*java多行注释*/ /**/
JSP指令
JSP指令用来表明JSP页面的相关属性,如编码方式,文档类型等等
JSP指令的语法:
<%@指令 属性名="值" %>
page指令
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
page指令常见属性:
- language="java"
- extends="package.class"
- import="{package.class | package.*}, ..."
- session="true | false"
- buffer="none | 8kb | sizekb"
- autoFlush="true | false"
- isThreadSafe="true | false"
- info="text"
- errorPage="relative_url"
- isErrorPage="true | false"
- contentType="mimeType ;charset=characterSet " | "text/html ; charset=ISO-8859-1"
- pageEncoding="characterSet | ISO-8859-1"
- isELIgnored="true | false"
一般,只需要在page指令中指定contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8",就不会出现中文乱码问题。
当然ContentType不仅仅可以指定以text/html的方式显示,还可以使用其他的形式显示出来。在conf/web.xml文件中可以查询出来。
<%@ page contentType="application/msword;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
String s="hello world";
out.println(s);
%>
</body>
</html>
当操作不当,或者服务器出错了,页面都是会出现友好提示的。这个也能通过page指令来实现跳转到友好提示页面上。
page指令errorPage=""和isErrorPage这两个属性。
page.jsp 出现了错误,通过page指令的errorPage属性跳转到error.jsp页面上
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" errorPage="error.jsp" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<jsp:scriptlet>
int i=2/0;
</jsp:scriptlet>
</body>
</html>
error.jsp 页面要通过page指令的isErrorPage属性设置页面就是错误页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" isErrorPage="true" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
String s="出现错误了,跳转过来的";
out.println(s);
%>
</body>
</html>
地址栏没有变化,属于服务器跳转。以上的做法是单个页面设置的,如果会有很多错误(JSP多的情况下,错误就会多),单个设置太麻烦了。
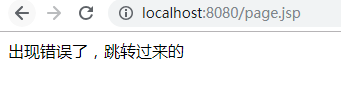
可以在web.xml文件中全局设置错误页,只要发生了404错误或者空指针异常的错误都会跳转到error.jsp页面上
<error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/error.jsp</location> </error-page> <error-page> <exception-type>java.lang.NullPointerException</exception-type> <location>/error.jsp</location> </error-page>
include指令
之前可以使用request.getRequestDispatcher(String url).include(request,response)来对页头和页尾进行包含。
现在使用include指令包含页头页尾。
head.jsp
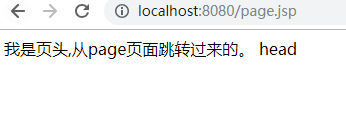
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>页头</title> </head> <body> 我是页头 <br/> <br/> </body> </html>
foot.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>页尾</title> </head> <body> 我是页尾 <br/> <br/> </body> </html>
page.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" errorPage="error.jsp" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <%@include file="head.jsp"%> <%@include file="foot.jsp"%> </body> </html>
访问page.jsp
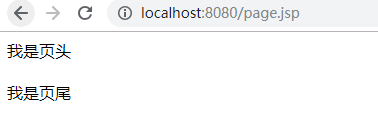
include指令是静态包含。静态包含的意思就是:把文件的代码内容都包含进来,再编译。
jsp还提供另一种包含文件的方式:jsp行为--动态包含。
taglib指令
jsp支持标签技术,要使用标签技术就先得声明标签库和标签前缀。taglib指令就是用来指明jsp页面内使用标签库技术。
JSP行为
JSP行为(JSP Actions)是一组JSP内置的标签,只书写少量的标记代码就能够使用JSP提供丰富的功能,JSP行为是对常用的JSP功能的抽象和封装。
把这些JSP内置的标签称之为JSP行为,能够和JSTL标签区分开来。
include行为
include指令时静态包含,include行为时动态包含。其实include行为就是封装了request.getRequestDispatcher(String url).include(request,response)。
<jsp:include page=""/>
page.jsp页面中也将页头和页尾包含进来。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" errorPage="error.jsp" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <jsp:include page="head.jsp"></jsp:include> <jsp:include page="foot.jsp"></jsp:include> </body> </html>
page.jsp效果
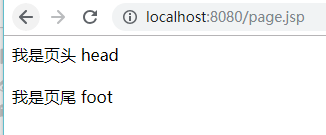
jsp行为来包含文件,jsp源文件
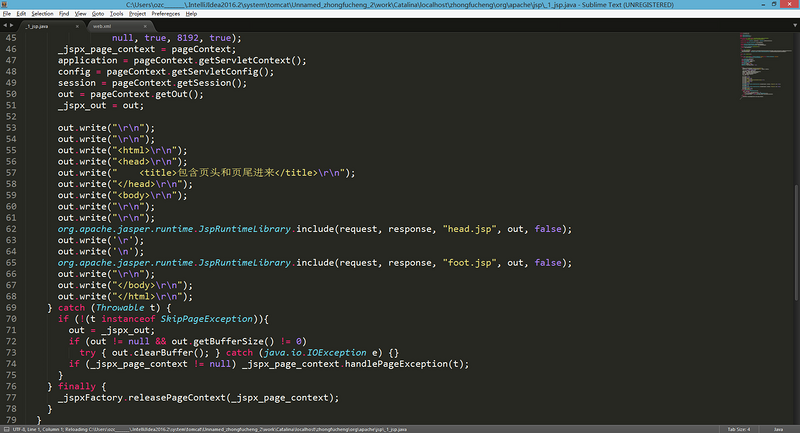
jsp行为包含文件就是先编译被包含的页面,再将页面的结果写入到包含的页面中。
动态包含可以向被包含的页面传递参数(用处不大),并且是分别处理包含页面的(将被包含页面编译后得出的结果再写进包含页面)【如果有相同名称的参数,使用静态包含就会报错】。
head.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>页头</title> </head> <body> 我是页头 <% String s="head"; out.println(s); %> <br/> <br/> </body> </html>
foot.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>页尾</title> </head> <body> 我是页尾 <% String s="foot"; out.println(s); %> <br/> <br/> </body> </html>
这时,使用静态包含就出现异常。
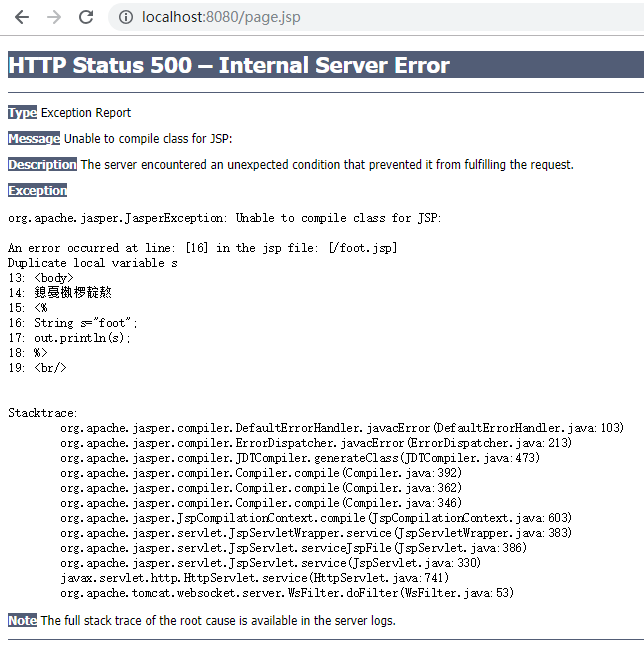
出现异常的原因很简单,就是同一个文件中有两个相同的变量s。使用动态包含就可以避免这种情况。
param行为
当使用<jsp:include>和<jsp:forward>行为引入或将请求转发给其它资源时,可以使用<jsp:param>行为向这个资源传递参数。
forward行为
之前使用request.getRequestDispatcher(String url).forward(request,response)进行跳转,其实forward行为就是对其封装。
<jsp:forward page=""/>
访问page.jsp页面就跳转到head.jsp页面中
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" errorPage="error.jsp" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <jsp:forward page="head.jsp"/> </body> </html>
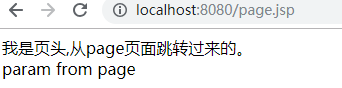
传递参数,就在forward行为嵌套param行为
page.jsp页面设置参数
<jsp:forward page="head.jsp"> <jsp:param name="headStr" value="从page页面传递的参数"/> </jsp:forward>
head.jsp页面获取传递过来的参数
<% String s=request.getParameter("headStr"); out.println(s); %>
directive行为
directive行为就是替代指令<%@%>的语法的
- <jsp:directive.include file=""/>相当于<%@include file=""%>
- <jsp:directive.page/>相当于<%@page%>
- <jsp:directive.taglib/>相当于<%@taglib%>
<jsp:directive.include file="head.jsp"></jsp:directive.include> <jsp:directive.include file="foot.jsp"></jsp:directive.include>

javaBean行为
JSP还提供了操作javaBean对象的行为
- <jsp:useBean id=""/>
- <jsp:setProperty name="" property=""/>
- <jsp:getProperty name="" property=""/>

 posted on
posted on

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号