JAVA基础--String、ArrayList--2022年8月24日
第一节 String
1、String是什么,可以做什么
字符串类型,可以定义字符串变量指向字符串对象
2、String是不可变字符串的原因
String变量每次的修改都是重新指向一个新的字符串对象
原来的字符串对象都是没有改变的,多以称不可以变字符串
3、字符串对象的特点有哪些
双引号创建的字符串对象,在字符串常量池中存储同一个
通过new构造器创建的字符串对象,在堆内存中分开存储
4、java关于String的面试题
看视频吧~
5、如果是字符串比较应该使用什么方式进行比较,为什么
使用String提供的equals方法
只关心内容一样就返回true
字符串里面真正存贮的是地址,不是值
6、开发中什么时候使用==比较数据
基本数据类型的比较使用==
7、String常用API

8、String常用案例
验证码功能
public static void main(String[] args){ String st = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; String code = ""; //随机5个字符 Random r = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { int num = r.nextInt(st.length()); char c = st.charAt(num); code += c; } System.out.println(code); }
模拟用户登录功能,最多只给三次机会
package Strings; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args){ //模拟用户登录功能 //1、定义正确的登录名称和密码 String okName = "毛飞红"; String okPassword = "123456"; //用户输入名称和密码 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.println("请输入用户名称:"); String name = sc.next(); System.out.println("请输入用户密码:"); String password = sc.next(); //输入正确的情况 if(name.equals(okName) && password.equals(okPassword)) { System.out.println("欢迎进入"); break; }else { if(i == 2) System.out.println("用户名称或密码错误,请等待10分钟后再次输入"); else { System.out.println("用户名称或密码错误,您还有"+(2-i)+"次机会"); } } } } }
手机号码屏蔽
public static void main(String[] args){ //手机号码屏蔽 //1、键盘输入一个手机号码 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入您的手机号码:"); String number = sc.next(); //2、截取前三位和后四位 String before = number.substring(0,3); String after = number.substring(7); String phoneNum = before + "****" + after; System.out.println(phoneNum); }
第二节 ArrayList
1、数组和集合的元素存储的个数问题?
数组定义后类型确定,长度确定
集合类型可以不固定,长度可变
2、数组和集合适合的场景
数组适合类型和长度确定的场景
集合适合做数据个数不确定的场景,且要做增删元素的场景
3、ArrayList类如何创建集合对象的,如何添加元素
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
public boolean add();
public boolean add(int index,E element);
4、怎么去统一ArrayList集合操作的元素类型
使用泛型<数据类型>
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList();
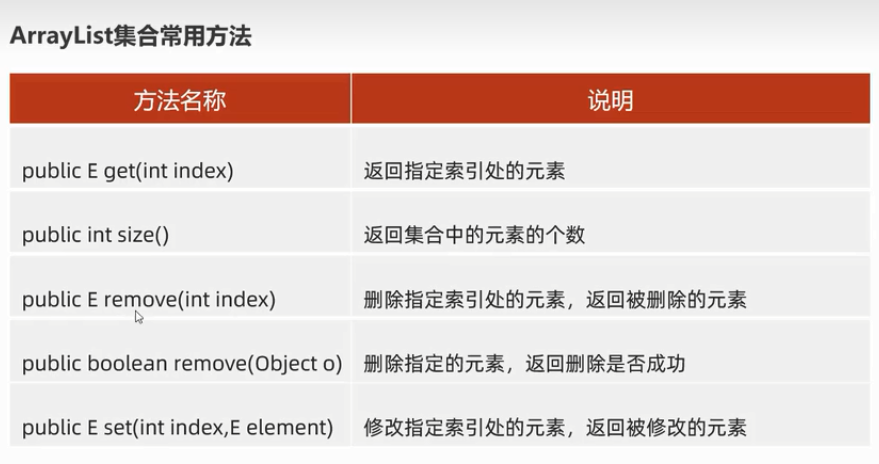
5、ArrayList常用方法
6、集合案例
集合遍历元素,然后删除它

package com.flowerDance.arrayList; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<Integer> scores = new ArrayList<>(); scores.add(98); scores.add(77); scores.add(66); scores.add(89); scores.add(79); scores.add(50); scores.add(100); //错误代码 /*for (int i = 0; i < scores.size(); i++) { if(scores.get(i) < 80){ scores.remove(i); } } System.out.println(scores);*/ //完美解决方法一 /*for (int i = 0; i < scores.size(); i++) { if(scores.get(i) < 80){ scores.remove(i); i--; } } System.out.println(scores);*/ //完美解决方法二 for (int i = scores.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) { if(scores.get(i) < 80){ scores.remove(i); } } System.out.println(scores); } }
存储自定义类型的对象(集合存储的元素并不是对象本身,而是对象的地址)
package com.flowerDance.arrayList; public class Movie { private String name; private double score; private String actor; public Movie() { } public Movie(String name, double score, String actor) { this.name = name; this.score = score; this.actor = actor; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getScore() { return score; } public void setScore(double score) { this.score = score; } public String getActor() { return actor; } public void setActor(String actor) { this.actor = actor; } }
package com.flowerDance.arrayList; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<Movie> movies = new ArrayList<>(); movies.add(new Movie("《肖申克的救赎》",9.7,"罗宾斯")); movies.add(new Movie("《霸王别姬》",9.6,"张国荣、张丰毅")); movies.add(new Movie("《阿甘正传》",9.5,"汤姆 汉克斯")); System.out.println(movies); for (int i = 0; i < movies.size(); i++) { Movie movie = movies.get(i); System.out.println("电影名称"+movie.getName()); System.out.println("评分"+movie.getScore()); System.out.println("主演"+movie.getActor()); } } }
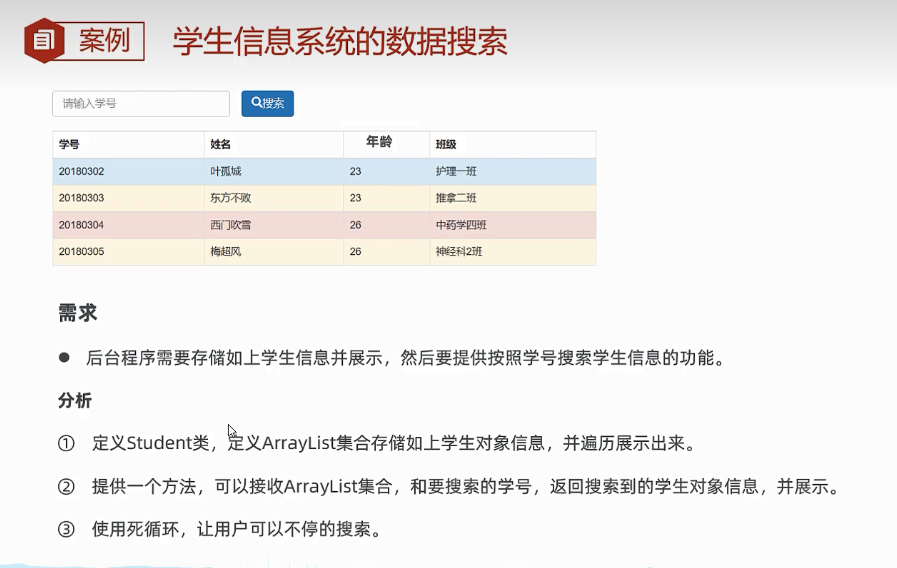
元素搜索
package com.flowerDance.arrayList; public class Student { private String id; private String name; private int age; private String className; public Student() { } public Student(String id, String name, int age, String className) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.className = className; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getClassName() { return className; } public void setClassName(String className) { this.className = className; } }
package com.flowerDance.arrayList; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args){ //1、创建arraylist存储student ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>(); students.add(new Student("20180302","叶孤城",23,"护理一班")); students.add(new Student("20180303","东方不败",23,"推拿二班")); students.add(new Student("20180304","西门吹雪",26,"中药学四班")); students.add(new Student("20180305","梅超风",26,"神经科二班")); //2、展示学生信息 System.out.println("学号\t\t姓名\t\t年龄\t班级"); for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) { Student s = students.get(i); System.out.println(s.getId()+"\t"+s.getName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getClassName()); } //3、搜索学生 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); while (true){ System.out.println("请输入学生学号:"); String id = sc.next(); //查无此人 Student s = getStudentById(students,id); if(s == null){ System.out.println("查无此人"); }else{ System.out.println(s.getId()+"\t\t"+s.getName()+"\t\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getClassName()); } } } public static Student getStudentById( ArrayList<Student> students,String id){ //查找学生 for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) { if(students.get(i).getId().equals(id)){ return students.get(i); } } //查无此人 return null; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号