tf.gather, tf.gather_nd和tf.slice
在tensorflow和pytorch中,都有一些函数是用于对张量进行索引的,因为pytorch是基于动态图的,它的张量可以动态的进行操作,不需要在对话(session)中进行,因此可能采用这些方法的必要性没有那么足,但是因为tensorflow是基于静态图的,因此如果在构建计算图的过程中需要对张量进行索引,一般是不能进行简单的slice的,因此引入这些函数就很有必要了,我们这里集中介绍下这些函数。
tf.gather
tf.gather(
params, # 需要被索引的张量
indices, # 索引
validate_indices=None,
name=None,
axis=0
)
其作用很简单,就是根据提供的indices在axis这个轴上对params进行索引,拼接成一个新的张量,其示意图如下所示:
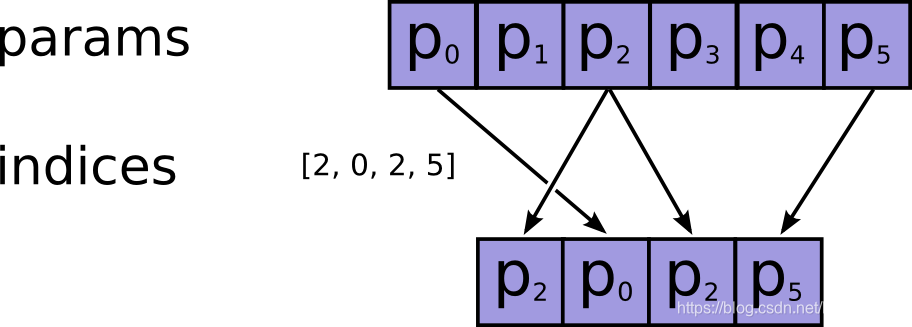
其中的indices可以是标量张量,向量张量或者是更高阶的张量,但是其元素都必须是整数类型,比如int32,int64等,而且注意检查不要越界了,因为如果越界了,如果使用的CPU,则会报错,如果在GPU上进行操作的,那么相应的输出值将会被置为0,而不会报错,因此认真检查是否越界。
(Note that on CPU, if an out of bound index is found, an error is returned. On GPU, if an out of bound index is found, a 0 is stored in the corresponding output value.)
给个代码例子:
params = tf.constant(np.random.normal(size=(5,6)))
index = tf.constant([1,3, 6])
out = tf.gather(params, index)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(out).shape)
print(out.eval())
print('-----------------------------------------')
print(params.eval())
# ------ output
(3, 6)
[[ 0.33662994 -0.33750725 1.5710436 0.78380586 -0.39254751 0.15269514]
[ 0.35278309 0.59719792 -0.86332759 -0.88997637 0.18247123 -1.46388103]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. ]]
-----------------------------------------
[[ 0.98987616 -1.62505873 0.86819471 2.3316706 -1.17362956 0.57264237]
[ 0.33662994 -0.33750725 1.5710436 0.78380586 -0.39254751 0.15269514]
[ 0.62367272 0.83599086 1.60433217 -1.4376806 0.61179675 2.07843436]
[ 0.35278309 0.59719792 -0.86332759 -0.88997637 0.18247123 -1.46388103]
[-1.76421914 0.85159247 0.18397565 0.69460119 -0.0651779 0.14643597]]
可以看到越界的地方全部置为了0。
params = tf.constant(np.random.normal(size=(5,6)))
index = tf.constant([[[0,0],[2,0]]])
out = tf.gather(params, index)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(out).shape)
print(index.eval().shape)
print(out.eval())
print('-----------------------------------------')
print(params.eval())
# ----- output
(1, 2, 2, 6)
(1, 2, 2)
[[[[-1.52187772 -0.86557915 1.15487405 0.94154816 -0.55900061
0.28165203]
[-1.52187772 -0.86557915 1.15487405 0.94154816 -0.55900061
0.28165203]]
[[-0.18865467 -0.00902652 1.03637009 -1.14683883 0.20450098
0.11977745]
[-1.52187772 -0.86557915 1.15487405 0.94154816 -0.55900061
0.28165203]]]]
-----------------------------------------
[[-1.52187772 -0.86557915 1.15487405 0.94154816 -0.55900061 0.28165203]
[-1.55437505 0.1800381 -0.06461522 0.85310958 -1.25240021 -0.64335453]
[-0.18865467 -0.00902652 1.03637009 -1.14683883 0.20450098 0.11977745]
[-0.46992654 -0.07142709 0.35710407 0.24846814 -0.13490197 -1.31201887]
[-0.24019091 0.54458599 0.3623213 -0.10113704 -1.15469468 -0.33837456]]
如果索引indices为矩阵或者更高阶的张量,其索引出来的尺寸就根据索引而定了,如上例子所示。
tf.gather_nd
tf.gather_nd类似于tf.gather,不过后者只能在一个维度上进行索引,而前者可以在多个维度上进行索引,其API为:
tf.gather_nd(
params, # 待索引输入张量
indices, # 索引
name=None
)
例子如:
params = tf.constant(np.random.normal(size=(5,6)))
index = tf.constant([[[0,0],[2,0]]])
out = tf.gather_nd(params, index)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(out).shape)
print(index.eval().shape)
print(out.eval())
print('-----------------------------------------')
print(params.eval())
# -------------- output
(1, 2)
(1, 2, 2)
[[-0.20841454 -0.12850639]]
-----------------------------------------
[[-0.20841454 0.13953242 2.26913464 1.60226729 1.51834021 -0.41044839]
[-1.3215913 -0.15647683 0.17277501 -0.60070571 0.80504465 0.85216738]
[-0.12850639 -0.34113574 0.16567085 -1.61315021 -0.29158798 0.03378417]
[ 0.67928455 0.16899565 1.0065189 -1.05949544 1.87377367 0.71542472]
[-0.2858821 -1.29338336 -0.41112208 -0.21772644 0.17873804 -0.0703971 ]]
tf.slice
用来进行切片操作,实现在python中的a[:,2:3,5:6]类似的操作,例子如:
t = tf.constant([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]],
[[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]],
[[5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6]]])
# shape = (3,2,3)
tf.slice(t, [1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 3]) # [[[3, 3, 3]]], shape (1,1,3)
tf.slice(t, [1, 0, 0], [1, 2, 3]) # [[[3, 3, 3],
# [4, 4, 4]]] shape (1,2,3)
tf.slice(t, [1, 0, 0], [2, 1, 3]) # [[[3, 3, 3]],
# [[5, 5, 5]]] shape (2,1,3)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号