CSS基础
CSS概念
CSS是Cascading Style Sheets的简称,中文称为层叠样式表,用来控制网页数据的表现,可以使网页的表现与数据内容分离。属性和属性值用冒号隔开,以分号结尾。
一、CSS的四种引入方式
1.行内式
行内式是在标签的style属性中设定CSS样式。这种方式没有体现出CSS的优势,不推荐使用。
<h1 style="color: red">CSS层叠样式表使用方法1</h1>
2.嵌入式
嵌入式是将CSS样式集中写在网页的<head></head>标签对的<style></style>标签对中。格式如下:
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
p{
background-color: #2b99ff;
}
</style>
</head>
3.链接式
将一个.css文件引入到HTML文件中
<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css" type="text/css"/>
4.导入式
将一个独立的.css文件引入HTML文件中,导入式使用@import 引入外部CSS文件,<style>标记也是写在<head>标记中。
<head>
...
<style type="text/css">
@import "My.css"; 此处注意.css文件的路径
</style>
</head>
注意:
导入式会在整个网页装载完后再装载CSS文件,因此这就导致了一个问题,如果网页比较大则会儿出现先显示无样式的页面,闪烁一下之后,再出现网页的样式。
这是导入式固有的一个缺陷。使用链接式时与导入式不同的是它会以网页文件主体装载前装载CSS文件,因此显示出来的网页从一开始就是带样式的效果的,它
不会象导入式那样先显示无样式的网页,然后再显示有样式的网页,这是链接式的优点。
二、CSS的选择器
1.基本选择器
a.通用选择器 * 表示应用到所有的标签 * {color: yellow} b.标签选择器 匹配所有使用 div 标签的元素(可以匹配所有标签) div {color: yellow} c.类选择器 匹配所有class属性中包含info的元素。 语法:.类名{样式}(类名不能以数字开头,类名要区分大小写。) .Mycolor {color: yellow} <h3 class="Mycolor">nick</h3> d.ID选择器 使用id属性来调用样式,在一个网页中id的值都是唯一的(是W3C规范而不是规则,所以不会报错)。 语法:#ID名{样式}(ID名不能以数字开头) #Mycolor {color: yellow} <h3 id="Mycolor">Nick.</h3>
2.组合选择器
a.多元素选择器 同时匹配h3,h4标签,之间用逗号分隔。 h3,h4 {color: yellow;} <h3>Nick</h3> <h4>Jenny</h4> b.后代元素选择器 匹配所有div标签里嵌套的P标签,之间用空格分隔。 div p {color: yellow;} <div> <p>Nick</p> <div> <p>Nick</p> </div> </div> c.子元素选择器 匹配所有div标签里嵌套的子P标签,之间用>分隔。 div > p {color: yellow;} <div> <p>Nick</p> <p>Nick</p> </div> d.毗邻元素选择器 匹配所有紧随div标签之后的同级标签P,之间用+分隔(只能匹配一个)。 div + p {color: yellow;} <div>Nick</div> <p>Nick</p>
3.属性选择器
(1)[title] & P[title]
设置所有具有title属性的标签元素;设置所有具有title属性的P标签元素。
[title]
{
color: yellow;
}
p[title]
{
color: yellow;
}
<p title="aaa">p标签的title属性选择器</p> <div title="bbb">div标签的title属性选择器</div>
(2)[title="aaa"]
设置所有title属性等于“aaa”的标签元素。
[title="aaa"]
{
color: blue;
}
<p title="aaa">p标签的title属性选择器</p>
(3)[title~="bbb"]
设置所有title属性具有多个空格分隔的值、其中一个值等于“bbb”的标签元素。
[title~="bbb"]
{
color: red;
}
<p title="aaa bbb">Nick</p> <p title="bbb ccc">Nick</p>
(4)[title|="ccc"]
设置所有title属性具有多个连字号分隔(hyphen-separated)的值、其中一个值以"ccc"开头的标签元素。
[title|="ccc"]
{
color: yellow;
}
<p title="ccc-ddd">Nick</p>
(5)[title^="eee"]
设置属性值以指定值开头的每个标签元素。
[title^="eee"]
{
color: green;
}
<p title="eeeFelix">Nick</p>
(6)[title$="fff"]
设置属性值以指定值结尾的每个标签元素。
[title$="fff"]
{
color: red;
}
<p title="Jennyfff">Nick</p>
(7)[title*=""ggg"]
设置属性值中包含指定值的每个元素
[title*="ggg"]
{
color: yellow;
}
<p title="SgggJenny">Nick</p>
4.伪类选择器和伪元素选择器
(1)伪类选择器
在 CSS 定义中,a:hover 必须被置于 a:link 和 a:visited 之后,才是有效的,a:active 必须被置于 a:hover 之后,才是有效的。
由于状态是动态变化的,所以一个元素达到一个特定状态时,它可能得到一个伪类的样式;当状态改变时,它又会失去这个样式。由此可以看出,它的功能和class有些类似,
但它是基于文档之外的抽象,所以叫伪类。
:link、:hover、:active、:visited、:focus
:link(未访问的链接状态),用于定义了常规的链接状态。 :hover(鼠标放在链接上的状态),用于产生视觉效果。 :active(在链接上按下鼠标时的状态)。 :visited(已访问过的链接状态),可以看出已经访问过的链接。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="zh-CN"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>伪类选择器</title> 6 <style> 7 /*没有访问的网站字体颜色为蓝色*/ 8 a:link { 9 color: blue;font-size: 55px; 10 } 11 /*已经访问过的网站字体颜色红色*/ 12 a:visited { 13 color: red;font-size: 38px; 14 } 15 /*鼠标在字体上颜色变为紫色*/ 16 a:hover{ 17 color: darkviolet; 18 } 19 /*鼠标在字体上颜色变为蓝色*/ 20 #d1:hover { 21 color: blue; 22 } 23 24 /*输入框设置背景颜色*/ 25 input:focus { 26 outline: 0; 27 background-color: darkviolet; 28 } 29 30 </style> 31 </head> 32 <body> 33 34 <a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度</a> 35 <a href="http://www.mi.com">小米</a> 36 <div id="d1">我是div标签,鼠标放上了看看我有什么变化?</div> 37 <input type="text" name="" id="">鼠标点我 38 </body> 39 </html>

(2)伪元素选择器
伪元素选择器,伪元素的效果是需要通过添加一个实际的元素才能达到的。
before、after、first-line、first-letter
/* 为某个元素的第一行文字使用样式。 */ :first-line /* 为某个元素中的文字的首字母或第一个字使用样式。 */ :first-letter /* 在某个元素之前插入一些内容。 */ :before /* 在某个元素之后插入一些内容。 */ :after
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="zh-CN"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>伪元素选择器</title> 6 <style> 7 /*改变段落的第一个字字体和颜色*/ 8 p:first-letter { 9 font-size: 36px; 10 color: red; 11 } 12 13 /*在段落前增加*号*/ 14 .c1:before { 15 content: "***"; 16 color: #ff3ac4; 17 } 18 19 /*在段落后增加[?]号*/ 20 .c1:after { 21 content: "[?]"; 22 color: #7fff35; 23 } 24 </style> 25 </head> 26 <body> 27 <p>春眠不觉晓,处处闻啼鸟。 28 夜来风雨声,花落知多少。</p> 29 <p class="c1">白日依山尽,黄河入海流。 30 欲穷千里目,更上一层楼。</p> 31 32 </body> 33 </html>

三、选择器的继承和优先级
1.选择器的继承
继承是CSS的一个主要特征,它是依赖于祖先-后代的关系的。继承是一种机制,它允许样式不仅可以应用于某个特定的元素,还可以应用于它的后代。例如一个body定义了的字体颜色值也会应用到段落的文本中。
body {
color: red;
}
此时页面上所有标签都会继承body的字体颜色。然而CSS继承性的权重是非常低的,是比普通元素的权重还要低的0。
我们只要给对应的标签设置字体颜色就可覆盖掉它继承的样式。
p {
color: green;
}
此外,继承是CSS重要的一部分,我们甚至不用去考虑它为什么能够这样,但CSS继承也是有限制的。有一些属性不能被继承,如:border, margin, padding, background等。
2.选择器的优先级
浏览器根据什么来决定应该应用哪个样式呢?其实是按照不同选择器的权重来决定的,具体的选择器权重计算方式如下:

内联样式表的权值最高 style=""-------------------------1000; 统计选择符中的ID属性个数。 #id -------------100 统计选择符中的CLASS属性个数。 .class -------------10 统计选择符中的HTML标签名个数。 p ------------- -1
四、CSS的常用属性
1.颜色属性
color
- HEX(十六进制色:color: #FFFF00 --> 缩写:#FF0)
- RGB(红绿蓝,使用方式:color:rgb(255,255,0)或者color:rgb(100%,100%,0%))
- RGBA(红绿蓝透明度,A是透明度在0~1之间取值。使用方式:color:rgba(255,255,0,0.5))
- HSL(CSS3有效,H表示色调,S表示饱和度,L表示亮度,使用方式:color:hsl(360,100%,50%))
- HSLA(和HSL相似,A表示Alpha透明度,取值0~1之间。)
<div style="color:blueviolet">CSS颜色属性</div> <div style="color:#ffee33">CSS颜色属性</div> <div style="color:rgb(255,0,0)">CSS颜色属性</div> <div style="color:rgba(255,0,0,0.5)">CSS颜色属性</div>
transparent
全透明,使用方式:color: transparent;
opacity
元素的透明度,语法:opacity: 0.5; 属性值在0.0到1.0范围内,0表示透明,1表示不透明。 filter滤镜属性(只适用于早期的IE浏览器,语法:filter:alpha(opacity:20);)。
2.字体属性
font-style: 用于规定斜体文本
normal 文本正常显示 italic 文本斜体显示 oblique 文本倾斜显示
font-weight: 设置文本的粗细
normal(默认) bold(加粗) bolder(相当于<strong>和<b>标签) lighter (常规) 100 ~ 900 整百(400=normal,700=bold)
font-size: 设置字体的大小
默认值:medium <absolute-size>可选参数值:xx-small、 x-small、 small、 medium、 large、 x-large、 xx-large <relative-size>相对于父标签中字体的尺寸进行调节。可选参数值:smaller、 larger <percentage>百分比指定文字大小。 <length>用长度值指定文字大小,不允许负值。
font-family:字体名称
使用逗号隔开多种字体(优先级从前向后,如果系统中没有找到当前字体,则往后面寻找)
body {
font-family: "Microsoft Yahei", "微软雅黑", "Arial", sans-serif
}
font:简写属性
语法:font:字体大小/行高 字体;(字体要在最后)
3. 文本属性
white-space: 设置元素中空白的处理方式
normal:默认处理方式。 pre:保留空格,当文字超出边界时不换行 nowrap:不保留空格,强制在同一行内显示所有文本,直到文本结束或者碰到br标签 pre-wrap:保留空格,当文字碰到边界时换行 pre-line:不保留空格,保留文字的换行,当文字碰到边界时换行
direction: 规定文本的方向
ltr 默认,文本方向从左到右。 rtl 文本方向从右到左。
text-align: 文本的水平对齐方式
left center right
line-height: 文本行高
normal 默认
vertical-align: 文本所在行高的垂直对齐方式
baseline 默认 sub 垂直对齐文本的下标,和<sub>标签一样的效果 super 垂直对齐文本的上标,和<sup>标签一样的效果 top 对象的顶端与所在容器的顶端对齐 text-top 对象的顶端与所在行文字顶端对齐 middle 元素对象基于基线垂直对齐 bottom 对象的底端与所在行的文字底部对齐 text-bottom 对象的底端与所在行文字的底端对齐
text-indent: 文本缩进
letter-spacing: 添加字母之间的空白
word-spacing: 添加每个单词之间的空白
text-transform: 属性控制文本的大小写
capitalize 文本中的每个单词以大写字母开头。 uppercase 定义仅有大写字母。 lowercase 定义仅有小写字母。
text-overflow: 文本溢出样式
clip 修剪文本。 ellipsis 显示省略符号...来代表被修剪的文本。 string 使用给定的字符串来代表被修剪的文本。
text-decoration: 文本的装饰(去除a标签的下划线 text-decoration:none)
none 默认。 underline 下划线。 overline 上划线。 line-through 中线。
text-shadow:文本阴影
第一个参数是左右位置 第二个参数是上下位置 第三个参数是虚化效果 第四个参数是颜色 text-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #888;
word-wrap:自动换行
word-wrap: break-word;
4. 背景属性
background-color: 背景颜色
background-image 设置图像为背景
url("http://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/suoning/845162/o_ns.png"); 图片地址
background-image:linear-gradient(green,blue,yellow,red,black); 颜色渐变效果
background-position 设置背景图像的位置坐标
background-position: center center; 图片置中,x轴center,y轴center
1px -195px 截取图片某部分,分别代表坐标x,y轴
background-repeat 设置背景图像不重复平铺
no-repeat 设置图像不重复,常用
round 自动缩放直到适应并填充满整个容器
space 以相同的间距平铺且填充满整个容器
background-attachment 背景图像是否固定或者随着页面的其余部分滚动
background 简写
background: url("o_ns.png") no-repeat 0 -196px;
background: url("o_ns.png") no-repeat center bottom 15px;
background: url("o_ns.png") no-repeat left 30px bottom 15px;

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="zh-CN"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>背景属性</title> 6 <!--背景颜色--> 7 <style> 8 .c1 { 9 background-color: grey; 10 } 11 /*背景图片*/ 12 .c2 { 13 width: 800px; 14 height: 600px; 15 /*background-image: url("snow.PNG");*/ 16 /*background-repeat: no-repeat;*/ 17 /*background-repeat: repeat-x;*/ 18 /*background-repeat: repeat-y;*/ 19 /*background-position: 50% 50%;*/ 20 /*background-position: center;*/ 21 /*background-position: 331px 328px;*/ 22 background: url("IMG_1390.JPG") no-repeat 50% 50%; 23 } 24 </style> 25 </head> 26 <body> 27 28 <div>今天下雪了</div> 29 30 <div class="c1">一起去看雪</div> 31 32 <div class="c2"> 33 <div>告诉大家一个好消息,今天下雪了</div> 34 35 </div> 36 </body> 37 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="zh-CN"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>背景图片固定</title> 6 <style> 7 .c1 { 8 height: 300px; 9 background-color: blue; 10 } 11 .c2 { 12 height: 300px; 13 background: url("IMG_1390.JPG"); 14 background-attachment: fixed; 15 } 16 .c3 { 17 height: 300px; 18 background-color: red; 19 } 20 21 </style> 22 </head> 23 <body> 24 <div class="c1"></div> 25 <div class="c2"></div> 26 <div class="c3"></div> 27 </body> 28 </html>
5.列表属性
list-style-type: 列表项标志的类型
none 去除标志
decimal-leading-zero; 02.
square; 方框
circle; 空心圆
upper-alph; & disc; 实心圆
list-style-image:将图象设置为列表项标志
list-style-position:列表项标志的位置
inside
outside
list-style:缩写
五、页面布局
1.border 边框
border-style:边框样式
solid 默认,实线
double 双线
dotted 点状线条
dashed 虚线
border-color:边框颜色
border-width:边框宽度
border-radius:圆角
1个参数:四个角都应用
2个参数:第一个参数应用于 左上、右下;第二个参数应用于 左下、右上
3个参数:第一个参数应用于 左上;第二个参数应用于 左下、右上;第三个参数应用于右下
4个参数:左上、右上、右下、左下(顺时针)
border: 简写
border: 2px solid red;
box-shadow:边框阴影
第一个参数是左右位置
第二个参数是上下位置
第三个参数是虚化效果
第四个参数是颜色
box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px #888;
第一个参数是左右位置
第二个参数是上下位置
第三个参数是虚化效果
第四个参数是颜色
box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px #888;

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="zh-CN"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>边框</title> 6 <style> 7 div{ 8 height: 200px; 9 width: 300px; 10 background-color: blue; 11 /*border-width: 5px;*/ 12 /*border-color: black;*/ 13 /*border-style: solid;*/ 14 /*border-right: 5px solid black;*/ 15 border: 5px solid black; 16 } 17 </style> 18 </head> 19 <body> 20 <div></div> 21 </body> 22 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 div { 8 border:2px solid; 9 border-radius:25px; 10 width: 140px; 11 } 12 </style> 13 </head> 14 <body> 15 <div> 16 CSS边框变椭圆形 17 </div> 18 </body> 19 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="zh-CN"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>11overflow溢出</title> 6 <style> 7 .header-img { 8 width: 100px; 9 height: 100px; 10 border: 2px solid red; 11 12 /*图片显示为圆形*/ 13 border-radius: 100%; 14 /*图片超出部分隐藏*/ 15 overflow: hidden; 16 } 17 img { 18 max-width: 100%; 19 } 20 21 </style> 22 </head> 23 <body> 24 <div class="header-img"> 25 <img src="https://timgsa.baidu.com/timg?image&quality=80&size=b9999_10000&sec=1546078190241&di=77051d899864eb770228d764b73592c9&imgtype=0&src=http%3A%2F%2Fb-ssl.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201707%2F18%2F20170718102720_nurX5.jpeg" alt=""> 26 </div> 27 28 </body> 29 </html>


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .radius1 { 8 display: inline-block; 9 width: 100px; 10 height: 100px; 11 background-color: yellow; 12 border-radius: 20px; 13 } 14 .radius2 { 15 display: inline-block; 16 width: 100px; 17 height: 100px; 18 background-color: red; 19 border-radius: 20px 35px; 20 } 21 .radius3 { 22 display: inline-block; 23 width: 100px; 24 height: 100px; 25 background-color: blue; 26 border-radius: 20px 35px 50px; 27 } 28 .radius4 { 29 display: inline-block; 30 width: 100px; 31 height: 100px; 32 background-color: green; 33 border-radius: 20px 35px 50px 60px; 34 } 35 </style> 36 </head> 37 <body> 38 <div> 39 <span class="radius1"></span> 40 <span class="radius2"></span> 41 <span class="radius3"></span> 42 <span class="radius4"></span> 43 </div> 44 </body> 45 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .triangle-one { 8 display: inline-block; 9 border-top: 50px red solid; 10 border-right: 50px green solid; 11 border-bottom: 50px yellow solid; 12 border-left: 50px blue solid; 13 } 14 .triangle-two { 15 display: inline-block; 16 border-top: 0 red solid; 17 border-right: 50px green solid; 18 border-bottom: 50px yellow solid; 19 border-left: 50px blue solid; 20 } 21 .triangle-stree { 22 display: inline-block; 23 border-top: 50px red solid; 24 border-right: 0 green solid; 25 border-bottom: 50px yellow solid; 26 border-left: 50px blue solid; 27 } 28 .triangle-four { 29 display: inline-block; 30 border-top: 50px red solid; 31 border-right: 0 green solid; 32 border-bottom: 0 yellow solid; 33 border-left: 50px blue solid; 34 } 35 36 .triangle-five { 37 display: inline-block; 38 border: 50px transparent solid; 39 border-top: 50px red solid; 40 } 41 .triangle-six { 42 display: inline-block; 43 border: 50px transparent solid; 44 border-bottom: 50px yellow solid; 45 } 46 .triangle-seven { 47 display: inline-block; 48 border: 50px transparent solid; 49 border-top: 60px red solid; 50 border-right: 0; 51 } 52 .triangle-eight { 53 display: inline-block; 54 border: 50px transparent solid; 55 border-left: 30px yellow solid; 56 border-bottom: 0; 57 } 58 </style> 59 </head> 60 <body> 61 <div class="triangle-one"></div> 62 <div class="triangle-two"></div> 63 <div class="triangle-stree"></div> 64 <div class="triangle-four"></div> 65 <div class="triangle-five"></div> 66 <div class="triangle-six"></div> 67 <div class="triangle-seven"></div> 68 <div class="triangle-eight"></div> 69 </body> 70 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .back { 8 width: 1000px; 9 height: 1000px; 10 margin: 0 auto; 11 background-color: #ddd; 12 position: relative; 13 } 14 .back-in { 15 position: absolute; 16 width: 1020px; 17 height: 45px; 18 left: -20px; 19 top: 50px; 20 background-color: #2F4F4F; 21 } 22 .back-img { 23 border: 20px solid transparent; 24 border-top: 10px solid dimgrey; 25 border-right: 0; 26 display: inline-block; 27 position: absolute; 28 top: 95px; 29 left: -20px; 30 } 31 .back-font { 32 line-height: 9px; 33 margin-left: 30px; 34 color: white; 35 } 36 </style> 37 </head> 38 <body> 39 <div class="back"> 40 <div class="back-in"><h3 class="back-font">CSS边框 ^.^</h3></div> 41 <div class="back-img"></div> 42 </div> 43 </body> 44 </html>
2.display
none 不显示。 block 显示为块级元素。 inline 显示为内联元素。 inline-block 行内块元素(会保持块元素的高宽)。 list-item 显示为列表元素。
3. visibility
visible 元素可见 hidden 元素不可见 collapse 当在表格元素中使用时,此值可删除一行或一列,不会影响表格的布局。
display:"none"与visibility:hidden的区别: visibility:hidden: 可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。 display:none: 可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失。
4.盒子模型
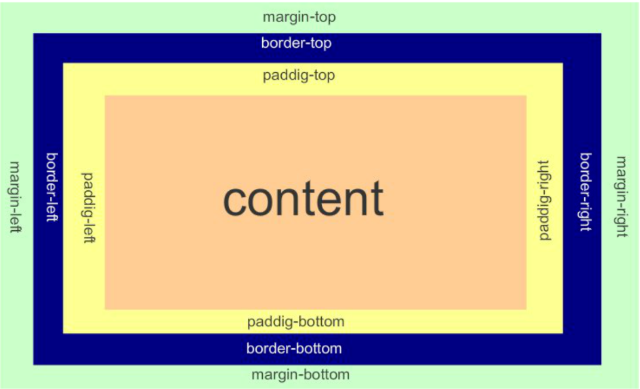
- margin(外边框): 用于控制元素与元素之间的距离;margin的最基本用途就是控制元素周围空间的间隔,从视觉角度上达到相互隔开的目的。
- padding(内填充): 用于控制内容与边框之间的距离;
- Border(边框): 围绕在内边距和内容外的边框。
- Content(内容): 盒子的内容,显示文本和图像。
margin外边距
.margin-test {
margin-top:5px;
margin-right:10px;
margin-bottom:15px;
margin-left:20px;
}
推荐使用简写:
.margin-test {
margin: 5px 10px 15px 20px;
}
顺序:上右下左
.mycenter {
margin: 0 auto;
}
padding内填充
.padding-test {
padding-top: 5px;
padding-right: 10px;
padding-bottom: 15px;
padding-left: 20px;
}
推荐使用简写:
.padding-test {
padding: 5px 10px 15px 20px;
}
顺序:上右下左
补充padding的常用简写方式:
提供一个,用于四边;
提供两个,第一个用于上-下,第二个用于左-右;
如果提供三个,第一个用于上,第二个用于左-右,第三个用于下;
提供四个参数值,将按上-右-下-左的顺序作用于四边;
边框在默认情况下会定位于浏览器窗口的左上角,但是并没有紧贴着浏览器的窗口的边框,这是因为body本身也是一个盒子,外层还有html,
在默认情况下,body距离html会有若干像素的margin,所以body中的盒子不会紧贴浏览器窗口的边框了。
解决方法:
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>8盒子模型</title> <style> /*body下chrom浏览器自动有8像素的距离,需要自定义设置成0*/ * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .c1 { height: 200px; width: 300px; border: 5px solid green; /*padding: 5px;*/ /*margin-top: 5px;*/ /*margin-right: 10px;*/ /*margin-bottom: 15px;*/ /*margin-left: 20px;*/ /*margin: 5px 10px 15px 20px;*/ /*margin: 20px 30px;*/ /*margin: 10px 20px 30px;*/ margin: 0 auto; } .c2 { height: 100px; width: 100%; background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> <div class="c2"></div> </body> </html>
5.float浮动
在 CSS 中,任何元素都可以浮动。
浮动元素会生成一个块级框,而不论它本身是何种元素。
关于浮动的两个特点:
浮动的框可以向左或向右移动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止。
由于浮动框不在文档的普通流中,所以文档的普通流中的块框表现得就像浮动框不存在一样。
float属性:
none
left 左浮动
right 右浮动

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>9float页面布局</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .c1 { height: 1000px; width: 20%; background-color: deepskyblue; float: left; } .c2 { height: 1000px; width: 80%; background-color: #ff3ac4; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> <div class="c2"></div> </body> </html>
6.clear清除浮动
clear属性规定元素的哪一侧不允许其他浮动元素。
none : 默认值。允许两边都可以有浮动对象 left : 不允许左边有浮动对象 right : 不允许右边有浮动对象 both : 不允许两边有浮动对象 inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 clear 属性的值。 注意:clear属性只会对自身起作用,而不会影响其他元素。
清除浮动的副作用(父标签塌陷问题)
主要有三种方式:
- 固定高度
- 伪元素清除法
- overflow:hidden
伪元素清除法(使用较多):
.clearfix:after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>10清除浮动</title> <style> #d1 { border: 1px solid black; } .c1, .c2{ float: left; height: 100px; width: 100px; } /*.c3 {*/ /*height: 100px;*/ /*}*/ /*解决父标签塌陷,浮动的元素脱离了父级的div标签*/ #d1:after { content: ""; clear:left; display: block; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1"> <div class="c1">div c1</div> <div class="c2">div c2</div> <!--<div class="c3"></div>--> </div> </body> </html>
7.overflow 溢出
- visible 默认值。内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外。
- hidden 内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的。
- scroll 内容会被修剪,但是浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。
- auto 如果内容被修剪,则浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。
- inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 overflow 属性的值。
overflow(水平和垂直均设置)
overflow-x(设置水平方向)
overflow-y(设置垂直方向)

<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>圆形的头像示例</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; background-color: #eeeeee; } .header-img { width: 150px; height: 150px; border: 3px solid white; border-radius: 50%; overflow: hidden; } .header-img>img { max-width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="header-img"> <img src="https://q1mi.github.io/Blog/asset/img/head_img.jpg" alt=""> </div> </body> </html>
8.position 定位
static 默认值,无定位,不能当作绝对定位的参照物,并且设置标签对象的left、top等值是不起作用的的。 relative 相对定位是相对于该元素在文档流中的原始位置,即以自己原始位置为参照物。有趣的是,即使设定了元素的相对定位以及偏移值,元素还占有着原来的位置,即占据文档流空间。 对象遵循正常文档流,但将依据top,right,bottom,left等属性在正常文档流中偏移位置。而其层叠通过z-index属性定义。 注意:position:relative的一个主要用法:方便绝对定位元素找到参照物。 absolute 定义:设置为绝对定位的元素框从文档流完全删除,并相对于最近的已定位祖先元素定位,如果元素没有已定位的祖先元素,那么它的位置相对于最初的包含块(即body元素)。 元素原先在正常文档流中所占的空间会关闭,就好像该元素原来不存在一样。元素定位后生成一个块级框,而不论原来它在正常流中生成何种类型的框。 重点:如果父级设置了position属性,例如position:relative;,那么子元素就会以父级的左上角为原始点进行定位。这样能很好的解决自适应网站的标签偏离问题,即父级为自适应的, 那我子元素就设置position:absolute;父元素设置position:relative;,然后Top、Right、Bottom、Left用百分比宽度表示。 另外,对象脱离正常文档流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性进行绝对定位。而其层叠通过z-index属性定义。 fixed 对象脱离正常文档流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性以窗口为参考点进行定位,当出现滚动条时,对象不会随着滚动。而其层叠通过z-index属性 定义。 注意点: 一个元素若设置了 position:absolute | fixed; 则该元素就不能设置float。这 是一个常识性的知识点,因为这是两个不同的流,一个是浮动流,另一个是“定位流”。 但是 relative 却可以。因为它原本所占的空间仍然占据文档流。 在理论上,被设置为fixed的元素会被定位于浏览器窗口的一个指定坐标,不论窗口是否滚动,它都会固定在这个位置。
通过以下四种属性进行定位: left top right bottom z-index

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>定位</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .c1, .c2, .c3, .c4, .c4-father{ height: 150px; width: 150px; } .c1 { background-color: red; } /*相对定位*/ .c2 { background-color: green; position: relative; left: 400px; top: 150px; } .c3 { background-color: blue; } .c4-father { background-color: lawngreen; position: relative; left: 150px; } /*绝对定位*/ .c4 { background-color: deeppink; position: absolute; top: 150px; left: 400px; } .fix-position { position: fixed; right: 30px; bottom: 30px; background-color: grey; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> <div class="c2"></div> <div class="c3"></div> <div class="c4-father"> <div class="c4"></div> </div> <div class="fix-position"><a href="">返回顶部</a></div> </body> </html>
9. z-index 元素层叠顺序
设置对象的层叠顺序。
z-index 值表示谁压着谁,数值大的压盖住数值小的, 只有定位了的元素,才能有z-index,也就是说,不管相对定位,绝对定位,固定定位,都可以使用z-index,而浮动元素不能使用z-index z-index值没有单位,就是一个正整数,默认的z-index值为0如果大家都没有z-index值,或者z-index值一样,那么谁写在HTML后面,谁在上面压着别人,定位了元素,永远压住没有定位的元素。 从父现象:父亲怂了,儿子再牛逼也没用

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Z-index元素层叠顺序</title> <style> .z-index1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: yellow; position: absolute; z-index: -1; } .z-index2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; position: absolute; top: 20px; left: 20px; z-index: 5; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="z-index1"></div> <div class="z-index2"></div> </body> </html>


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>3青春版模块示例</title> <style> .cover { position: absolute; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0; background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.5); z-index: 999; } .modal { width: 600px; height: 400px; background-color: white; position: fixed; top: 50%; left: 50%; margin-top: -200px; margin-left: -300px; z-index: 1000; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cover"></div> <div class="modal"></div> </body> </html>
10. outline 边框轮廓
- outline-width 轮廓宽度
- outline-color 轮廓颜色
- outline-style 轮廓样式

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>15边框轮廓</title> <style> .c1 { width: 120px; height: 120px; background-color: red; outline-color: blue; outline-style:dashed; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> </body> </html>
11.zoom缩放比例
.zoom1 {
zoom: 100%;
}
.zoom2 {
zoom: 150%;
}
.zoom3 {
zoom: 200%;
}

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>自定义模态框</title> <style> .cover { background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.65); position: fixed; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0; z-index: 998; } .modal { background-color: white; position: fixed; width: 600px; height: 400px; left: 50%; top: 50%; margin: -200px 0 0 -300px; z-index: 1000; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cover"></div> <div class="modal"></div> </body> </html>
12.opacity不透明度
取值 0~1
和rgba的区别:
- opacity改变元素、子元素的透明度效果
- rgba只改变背景颜色透明度效果

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="zh-CN"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>透明度</title> 6 <style> 7 .c1 { 8 width: 150px; 9 height: 150px; 10 border: 2px solid blue; 11 background-color: black; 12 opacity: 0.5; 13 color: red; 14 } 15 .c2 { 16 width: 150px; 17 height: 150px; 18 border: 2px solid blue; 19 background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.5); 20 color: red; 21 } 22 </style> 23 </head> 24 <body> 25 <div class="c1">我是C1,测试opacity透明度</div> 26 <div class="c2">我是C2,测试rgba透明度</div> 27 </body> 28 </html>






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号