python数据分析--matplotlib
axis轴指的是x轴或者是y轴的坐标。
例:假设一天中每隔两个小时(range(2,26,2))的气温(℃)分别是[15,16,17,5,17,20,26,17,28,26,25,24,18]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = [i for i in range(2,26,2)] y = [16,17,5,17,20,26,17,28,26,25,24,18] plt.plot(x,y,'r') plt.title('Temperature') plt.show()

图片进行优化:
matplotlib默认不支持中文字符,因为默认的英文字体无法显示汉字,那如何修改matplotlib的默认字体?通过matplotlib.rc可以修改,通过matplotlib下的font_manager可以解决。
linux下查看支持的字体:fc-list
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import random x = [i for i in range(0,60)] y_city1 = [random.randint(20,35) for i in range(60)] y_city2 = [random.randint(10,25) for i in range(60)] #设置图片大小 plt.figure(figsize=(30,10),dpi=120) #保存图片 plt.savefig('./plot_fig.png') #调整x,y轴的刻度 xTicks = ['10 h {} min'.format(i) for i in range(60)] plt.xticks(x[::3],xTicks[::3],rotation=90) #设置x,y的标签 plt.xlabel('hour') plt.ylabel('temperature') #绘制网格 plt.grid(alpha=0.4) #绘制 plt.plot(x,y_city1,'r',label='city1') plt.plot(x,y_city2,'b',label='city2') plt.title('Temperature Change') #添加图例 plt.legend() plt.show()
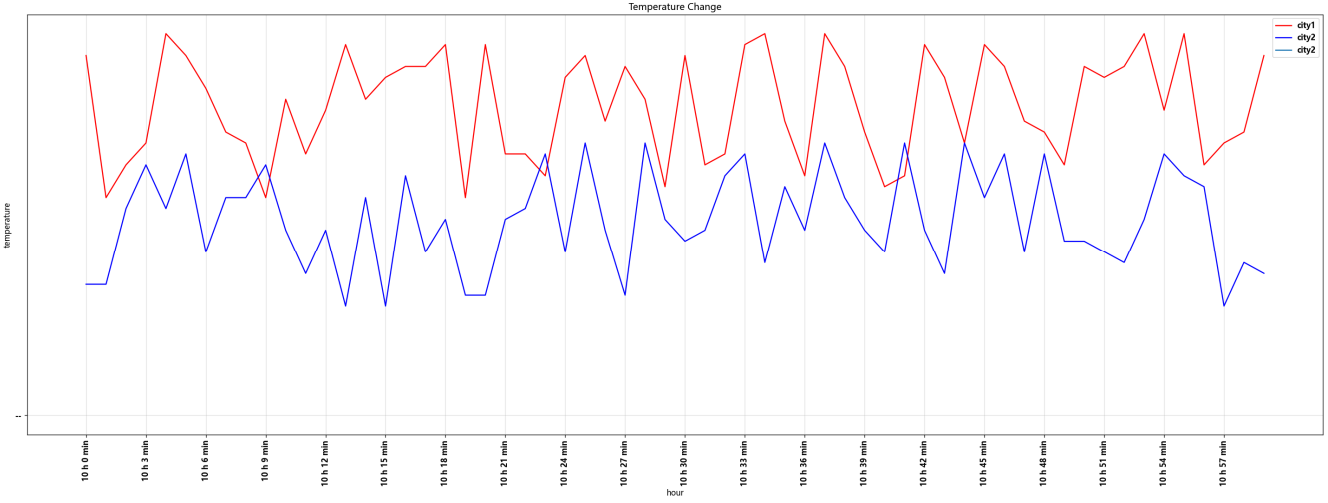
常用统计图:
①折线图:以折线的上升或下降表示统计数量的增减变化的统计图。
特点:能够显示数据的变化趋势,反应事物的变化情况。
②直方图:由一系列高度不等的纵向条纹或线段表示数据分布的情况。一般用横轴表示数据范围,纵轴表示分布情况。
特点:绘制连连续性的数据,展示一组或多组数据的分布状况。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import random movie_times = [random.randint(80,130) for times in range(10)] #组数=极差/组距=(max(a)-min(a))/bin_width plt.figure(figsize=(20,10)) bin_width = 5 num_bins = int((max(movie_times)-min(movie_times))/bin_width) plt.hist(movie_times,num_bins) plt.xticks(range(min(movie_times),max(movie_times)+bin_width,bin_width)) plt.grid(0.5) plt.show()
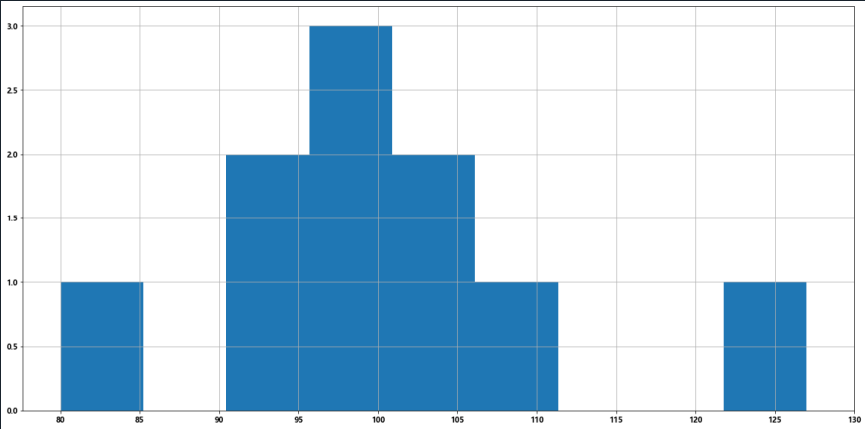
③条形图:排列在工作表的列或者行中的数据可以绘制到条形图中。
特点:绘制离散的数据,能够一眼看出各个数据的大小,比较数据之间的差别。
例1:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import random film_names = ['Avengers: Endgame','Avatar','Titanic','Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens','Avengers: Infinity War', 'Jurassic World','The Lion King','The Avengers','Furious 7','Frozen II'] gross = [27.9,27.9,21.9,20.6,20.4,16.7,16.5,15.1,15.1,14.5] plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.bar(range(len(film_names)),gross,width=0.5,color='orange') plt.xticks(range(len(film_names)),film_names,rotation=90) plt.xlabel('film name') plt.ylabel('gross') plt.title('Movie box office ranking') plt.show()
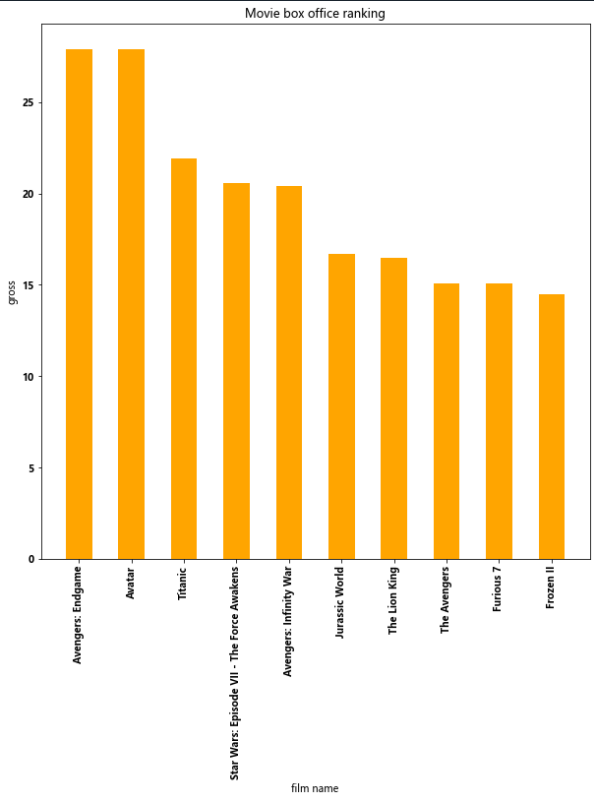
例2:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt film_names = ['Avengers: Endgame','Avatar','Titanic','Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens','Avengers: Infinity War', 'Jurassic World','The Lion King','The Avengers','Furious 7','Frozen II'] gross = [27.9,27.9,21.9,20.6,20.4,16.7,16.5,15.1,15.1,14.5] plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.barh(range(len(film_names)),gross,height=0.3,color='orange') plt.grid(0.7) plt.yticks(range(len(film_names)),film_names,rotation=0) plt.ylabel('movie name') plt.xlabel('gross') plt.title('Movie box office ranking') plt.show()
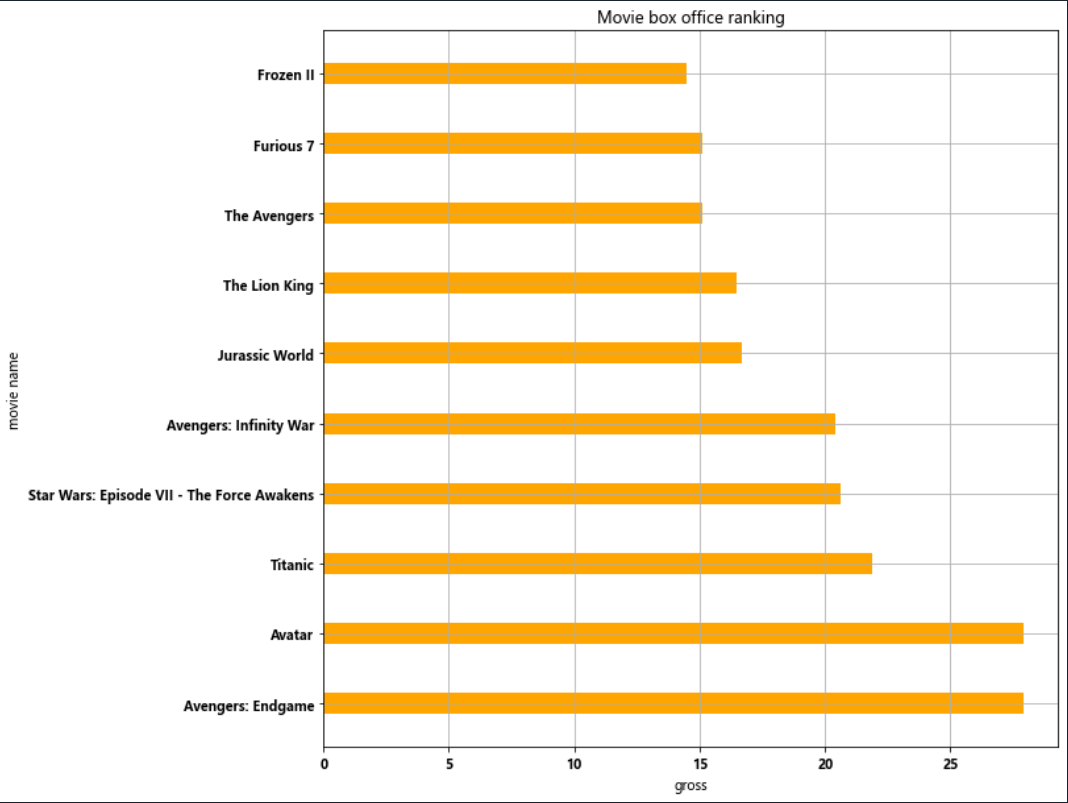
例3:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np film_names = ['Avengers: Endgame','Avatar','Titanic','Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens','Avengers: Infinity War', 'Jurassic World','The Lion King','The Avengers','Furious 7','Frozen II'] gross_1 = [27.9,27.9,21.9,20.6,20.4,16.7,16.5,15.1,15.1,14.5] gross_2 = [26.4,26.7,20.8,19.6,19.6,15.4,13.2,14.0,14.9,13.9] gross_3 = [26.0,25.5,19.0,18.6,17.9,13.0,13.1,13.5,12.9,10.2] height = 0.25 plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.barh(np.arange(len(film_names))-height/3,gross_1,height=0.2,color='orange') plt.barh(np.arange(len(film_names))+height/3,gross_2,height=0.2,color='blue') plt.barh(np.arange(len(film_names))-3.2*height/3,gross_3,height=0.2,color='red') plt.grid(0.7) plt.yticks(range(len(film_names)),film_names,rotation=0) plt.ylabel('movie name') plt.xlabel('gross') plt.title('Movie box office ranking') plt.show()

④散点图:用两组数据构成多个坐标点,考察坐标点的分布,判断两变量之间是否存在某种关联或总结坐标的分布模式。
特点:判断变量之间是否存在数量关联趋势,展示离群点。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import random data_1 = [random.randint(0,100) for i in range(30)] data_2 = [random.randint(0,100) for i in range(30)] num_1 = [i for i in range(30)] num_2 = [i for i in range(30,60)] plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80) plt.scatter(num_1,data_1,label='class 1') plt.scatter(num_2,data_2,label='class 2') plt.xticks(list(num_1+num_2)[::3],rotation=45) plt.yticks([score for score in range(0,110,10)],rotation=45) plt.xlabel('student numbers') plt.ylabel('score') plt.title('Figure') plt.legend() plt.show()

关于其他:
1.seaborn:https://seaborn.pydata.org/
2.plotly:https://plotly.com/python/
3.echarts:https://echarts.apache.org/zh/index.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号