反射
-
Class本身也是一个类
-
-
一个加载的类在JVM中只会有一个Class实例
-
一个Class对象对应的是一个加载到JVM中的一个class文件
-
每个类的实例都会记得自己是由哪个Class实例所生成
-
通过Class可以完整的得到一个类中的所有被加载的结构
2.获取Class类的实例
//测试Class类的创建方法
3.哪些类型可以有Class对象
class、interface、数组、enum、annotation、基本数据类型、void
只要元素类型和维度一样,就是同一个Class对象
4.类的加载
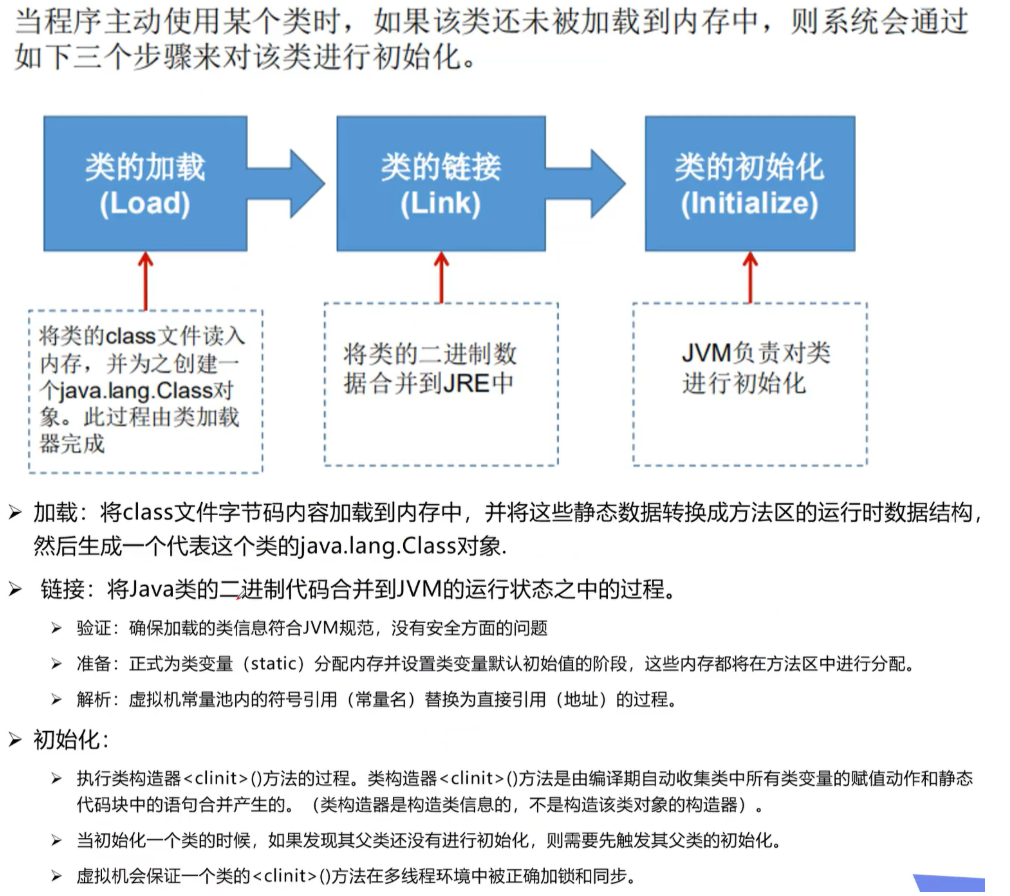
什么时候发生类的初始化:(new一个类和通过反射调用才发生)

5.获取运行时类的完整结构
6.动态创建对象执行方法
7.通过反射获取泛型信息
public void test6(Map<String,User> map, List<User> list){
System.out.println("test6");
}
8.反射操作注解
类注解:
package com.yl.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//类名的注解
//target:作用域,retention:获取级别
属性注解:
package com.yl.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//属性的注解
pojo:
测试:

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号