【SimpleFOC】 各种编码器
Magnetic sensor
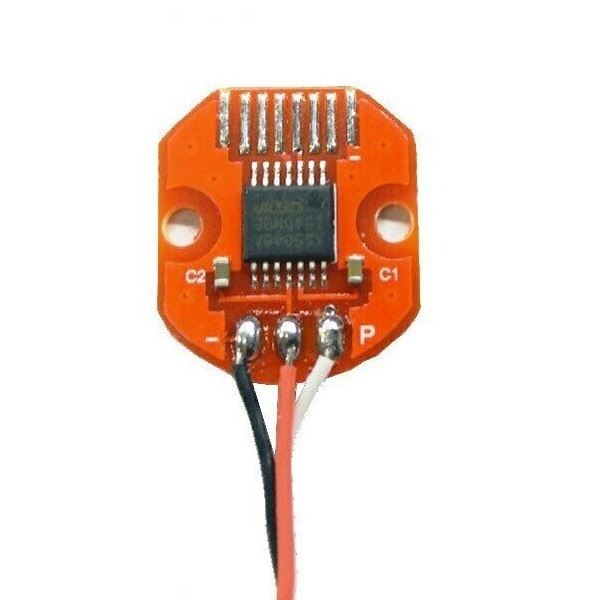


Magnetic sensors implementation in this library (current version ) support communications:
- SPI - MagneticSensorSPI
- I2C - MagneticSensorI2C
- Analog - MagneticSensorAnalog
- PWM - MagneticSensorPWM
- ABI - equivalent to encoder sensors - encoder docs
- UVW - equivalent to hall sensors - hall sensors docs .
Analog方式(模拟方式)
Standalone sensor
To get the magnetic sensor angle and velocity at any given time you can use the public methods:
class MagneticSensorAnalog{
public:
// shaft velocity getter
float getVelocity();
// shaft angle getter
float getAngle();
}Calling
getVelocitymultiple timesWhen calling
getVelocityit will only calculate the velocity if the elapsed time from the previous call is longer than the time specified in teh variablemin_elapsed_time(default 100us). If the elapsed time from the last call is shorter thanmin_elapsed_timethe function will return previously calculated value. Variablemin_elapsed_timecan be changed easily if necessary:sensor.min_elapsed_time = 0.0001; // 100us by default
Example code
Here is a quick example for AS5600 magnetic sensor using it’s analog output:
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
// MagneticSensorAnalog(uint8_t _pinAnalog, int _min, int _max)
// pinAnalog - the pin that is reading the analog output from magnetic sensor
// min_raw_count - the smallest expected reading.
// max_raw_count - the largest value read.
MagneticSensorAnalog sensor = MagneticSensorAnalog(A1, 14, 1020);
void setup() {
// monitoring port
Serial.begin(115200);
// initialise magnetic sensor hardware
sensor.init();
Serial.println("Sensor ready");
_delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
// IMPORTANT - call as frequently as possible
// update the sensor values
sensor.update();
// display the angle and the angular velocity to the terminal
Serial.print(sensor.getAngle());
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(sensor.getVelocity());
}
Position sensor for FOC algorithm
To use the ensor with the FOC algorithm implemented in this library, once when you have initialized sensor.init() you just need to link it to the BLDC motor by executing:
motor.linkSensor(&sensor);And you will be able to access the angle and velocity of the motor using the motor instance:
motor.shaft_angle; // motor angle
motor.shaft_velocity; // motor velocity
Example code
Here is a quick example for analog output magnetic sensor with a BLDC motor and driver:
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
// motor and driver
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor(7);
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(9, 5, 6, 8);
// MagneticSensorAnalog(uint8_t _pinAnalog, int _min, int _max)
// pinAnalog - the pin that is reading the analog output from magnetic sensor
// min_raw_count - the smallest expected reading.
// max_raw_count - the largest value read.
MagneticSensorAnalog sensor = MagneticSensorAnalog(A1, 14, 1020);
void setup() {
// driver
driver.init()
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// init magnetic sensor hardware
sensor.init();
motor.linkSensor(&sensor);
// init motor hardware
motor.init();
motor.initFOC();
Serial.println("Motor ready");
_delay(1000);
}
void loop(){
motor.loopFOC();
motor.move();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号