vLLM源码之分离式架构
1,背景
本文主要分析vLLM分离式架构原理。
关于大模型推理分离式架构,一直是今年讨论的一个热点,笔者之前针对该技术也做了一些总结。
作为大模型推理最流行的框架之一,vLLM功能迭代非常的快。关于vLLM的一些个人理解,笔者之前也做了一些总结。
当前,vLLM社区已经有分离式架构的pr,分别是如下2个。本文以第一个为基础介绍一下vLLM分离式架构简单实现。
2,vLLM分离式架构
本章主要介绍vLLM社区版分离式架构实现,目前该实现功能较为简单,代码简洁,没有复杂的调度、kv cache pool等功能,适合初学者学习。
2.1,整体架构
quick start
按照要求安装好vLLM,执行benchmarks/disagg_benchmarks/visualize_benchmark_results.py即可完成一个测试。我们进行简单的拆解,看一下到底怎么使用的。

我们看到首先启动了3个进程,然后curl即可,第一个进程是一个叫proxy的进行,后面2个进程分别是vLLM的producer和consumer进程。
接着介绍一下vLLM分离式整体架构,如下图所示,是原pr的设计图。
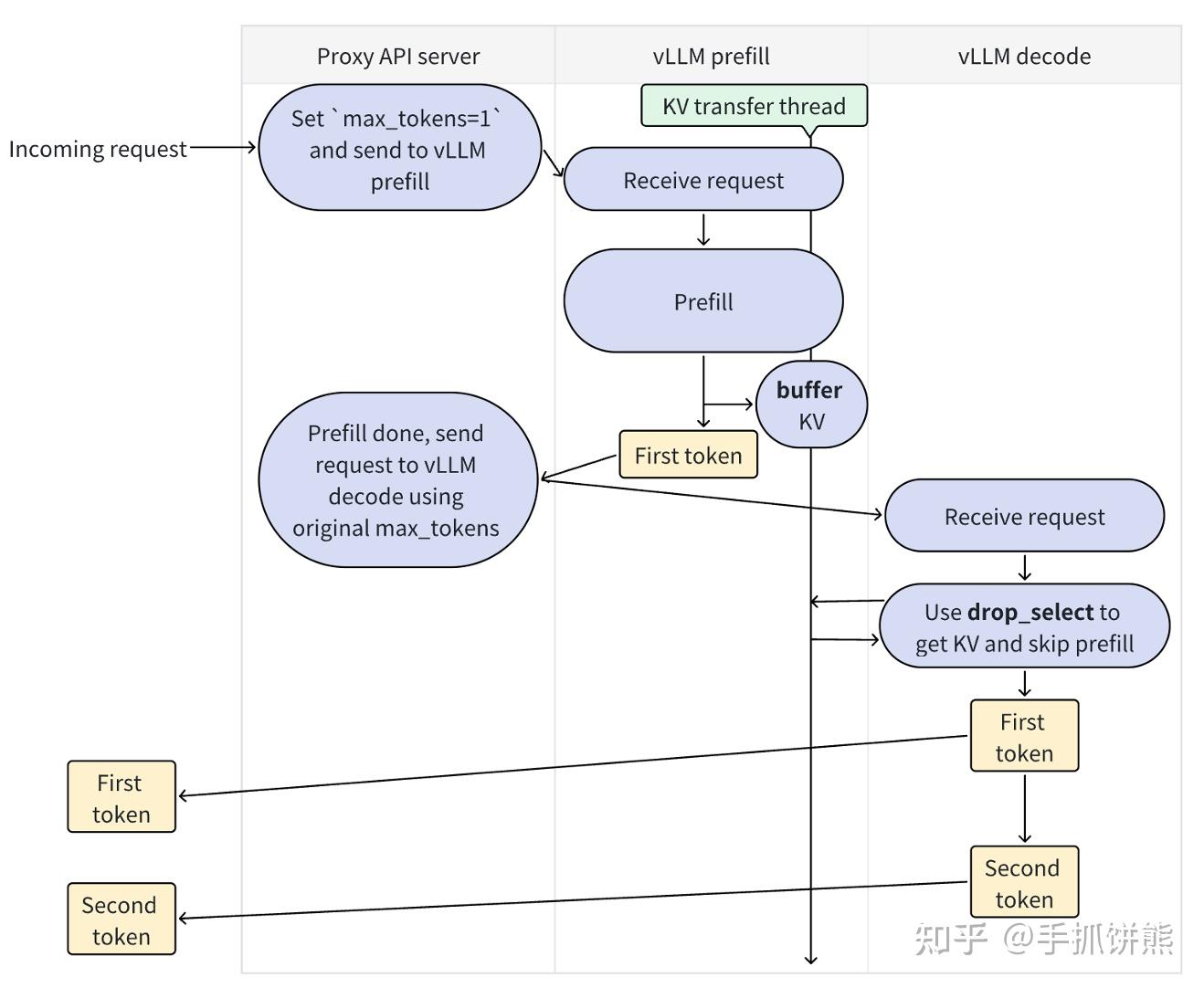
对上述架构解释如下:
- 该系统有Proxy API server、vLLM prefill、vLLM decode三个角色;
- 请求到来时,先进入Proxy API server,Proxy API server将请求发送给vLLM prefill,vLLM prefill进行prefill,产生kv cache,并转发,将First token返回给Proxy API server;
- Proxy API server继续将请求发送给vLLM decode,vLLM decode进行drop_select操作,我们可以看出注释,该功能主要是获取kv和跳过prefill,drop_select之后再产生First token;
- 我们可以看到,vLLM decode阶段其实也会产生First token,Proxy API server最终的token其实全部都是从vLLM decode拿到的,vLLM prefill只负责产生kv cache。
这里第4点的实现看起来确实有点奇怪,比如为什么vLLM decode为什么还要进行First token计算,既然vLLM decode的First token计算vLLM prefill计算有啥区别。这些后面分析代码的时候会解释,再分析代码之前,我们再看一下Proxy API server的代码如下,我们可以看到代码和架构图一样的简单,就是分别发送一个请求给vLLM prefill和vLLM decode。
2.2,核心组件
总结一下上述的vLLM分离式架构请求流程,有Proxy API server、vLLM prefill、vLLM decode三个实例(这里可以理解为进程,但是实际一个实例可能是多个进程),请求首先在vLLM prefill进行prefill计算,计算完之后将kv cache发送vLLM decode,vLLM decode进行后续的decode阶段。我们对照pr看看需要实现这个功能,大概要进行哪些修改。
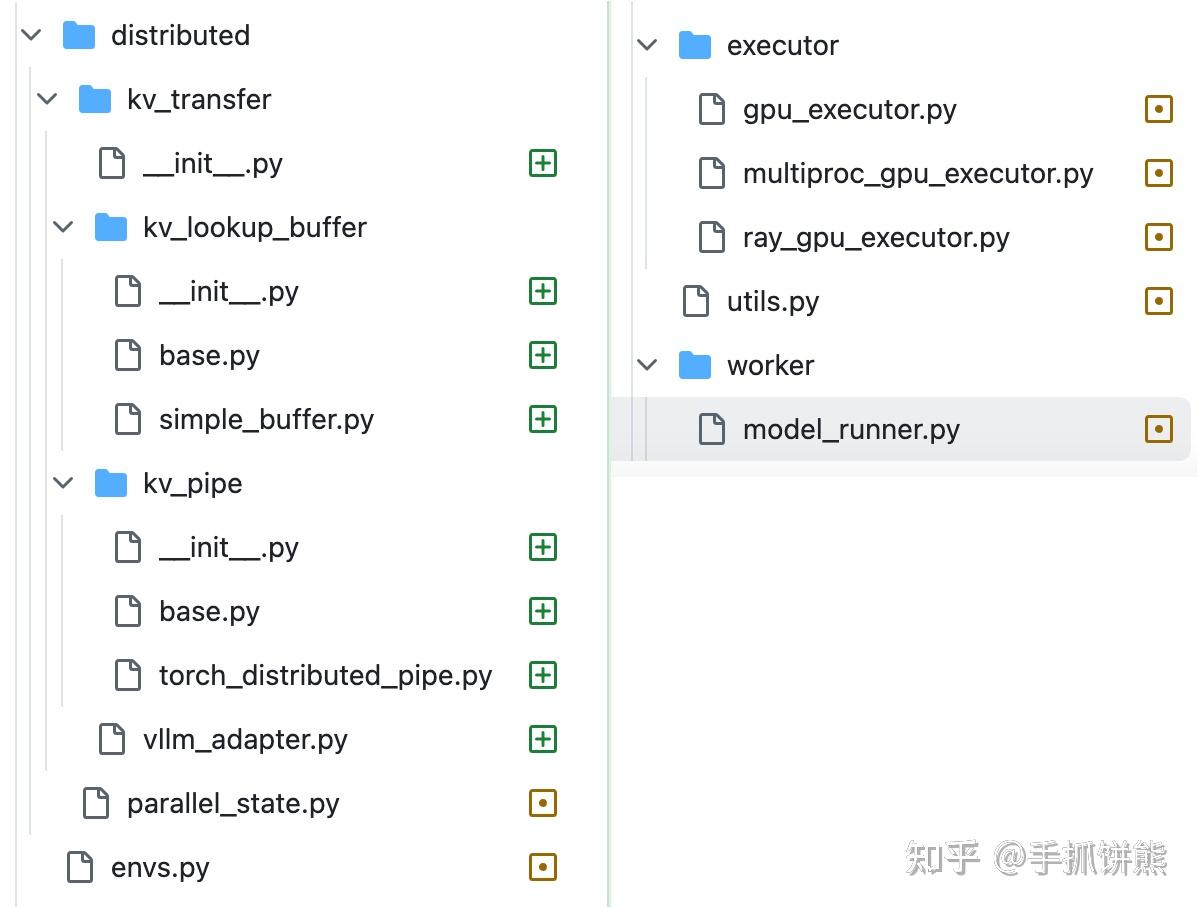
我们看到pr主要添加和修改了上述文件,说明如下:
kv_pipe:从名字我们可以看出,这是一个通信通道,vLLM prefill借助这个类发送消息给vLLM decode、vLLM decode通过这个类接受消息。这里的消息特指torch的Tensor,底层也是使用torch的分布式api如send recv。
class KVPipeBase(ABC):
"""
This class provides an interface for sending and receiving tensors, or
None, by distributed communications.
"""
@abstractmethod
def send_tensor(self, tensor: Optional[torch.Tensor]) -> None:
"""Send a tensor, or None, via the pipe.
Need to support sending None -- important for error handling.
TODO: add a `key` argument so that we can use traditional
key-value database as the distributed communication mechanism behind
the pipe.
Args:
tensor (Optional[torch.Tensor]): The tensor to be sent. Can be None.
Raises:
NotImplementedError: This method must be implemented in subclasses.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
@abstractmethod
def recv_tensor(self) -> Optional[torch.Tensor]:
"""Receive a tensor (can be None) from the pipeline.
Returns:
Optional[torch.Tensor]: The tensor received from the pipeline. Can
be None.
Raises:
NotImplementedError: This method must be implemented in subclasses.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
kv_buffer:我们可以看到kv_pipe发送是基础的torch的Tensor,这个比较底层,不是很好用,需要进一步抽象才能给上层用,即kv buffer,我们可以看到,这个kv_buffer有insert和drop_select 2个函数,vLLM prefill使用insert发送kv数据, vLLM decode接受kv数据,交换的消息是 input_tokens, roi, key, value, hidden这些数据,数据的粒度是attention一层的。
class KVLookupBufferBase(ABC):
"""
Abstract base class for a lookup buffer.
This class provides an abstraction for a key-value (KV) cache lookup buffer.
The key of the lookup buffer:
- input_tokens: token IDs of the request
- roi: a binary mask on top of input_tokens.
- Purpose of roi: Since KV cache may only be available for a subset of
tokens in the input (for example, when vLLM is connected to an external
KV cache service), roi specifies the subset of tokens that the KV cache
is associated with.
- NOTE: roi can be further extended to describe which part of KV the
current process is holding (each process may only hold a part of KV
due to TP and PP). This is not implemented for now.
The value of the lookup buffer:
- key: the key tensor in the KV cache
- value: the value tensor in the KV cache
- hidden: the final hidden state generated by model forwarding. This allows
vLLM to bypass further model forwarding by transmitting the hidden state.
"""
@abstractmethod
def insert(self, input_tokens: torch.Tensor, roi: torch.Tensor,
key: torch.Tensor, value: torch.Tensor,
hidden: torch.Tensor) -> None:
"""Insert into the lookup buffer.
The functionality is similar to the following python statement
```
buffer[input_tokens, roi] = [key, value, hidden]
```
FIXME: in the future, we should only have two arguments, key and value,
where key is a tensor dict and value is a tensor dict.
FIXME: we should transmit both sampler outputs and the hidden states.
Args:
input_tokens (torch.Tensor): token IDs.
roi (torch.Tensor): A binary mask on top of the input tokens
key (torch.Tensor): The key tensor in the KV cache.
value (torch.Tensor): The value tensor in the KV cache.
hidden (torch.Tensor): The final hidden state tensor generated
during model forwarding to bypass model
forwarding.
Raises:
NotImplementedError: This method must be implemented in subclasses.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
@abstractmethod
def drop_select(
self, input_tokens: Optional[torch.Tensor],
roi: Optional[torch.Tensor]) -> List[Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
"""Select and *drop* KV cache entries from the lookup buffer.
The functionality is similar to the following python statements
```
ret = buffer.pop(input_tokens, roi)
return ret
```
If `input_tokens` and `roi` is `None`, it means selecting any of the
KV caches in the buffer, return, and remove it from the buffer, useful
when offloading KV cache to KV cache storage service.
Args:
input_tokens (torch.Tensor): token IDs.
roi (torch.Tensor): A binary mask on top of the input tokens
Returns:
List[Optional[torch.Tensor]]: A list of tensors. Can be None.
Raises:
NotImplementedError: This method must be implemented in subclasses.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
vllm_adapter和model_runner是串整个流程的,驱动vLLM prefill前向之后发送kv cache、vLLM decode前向之前获取kv cache。
最终组件的整体流程如下图。
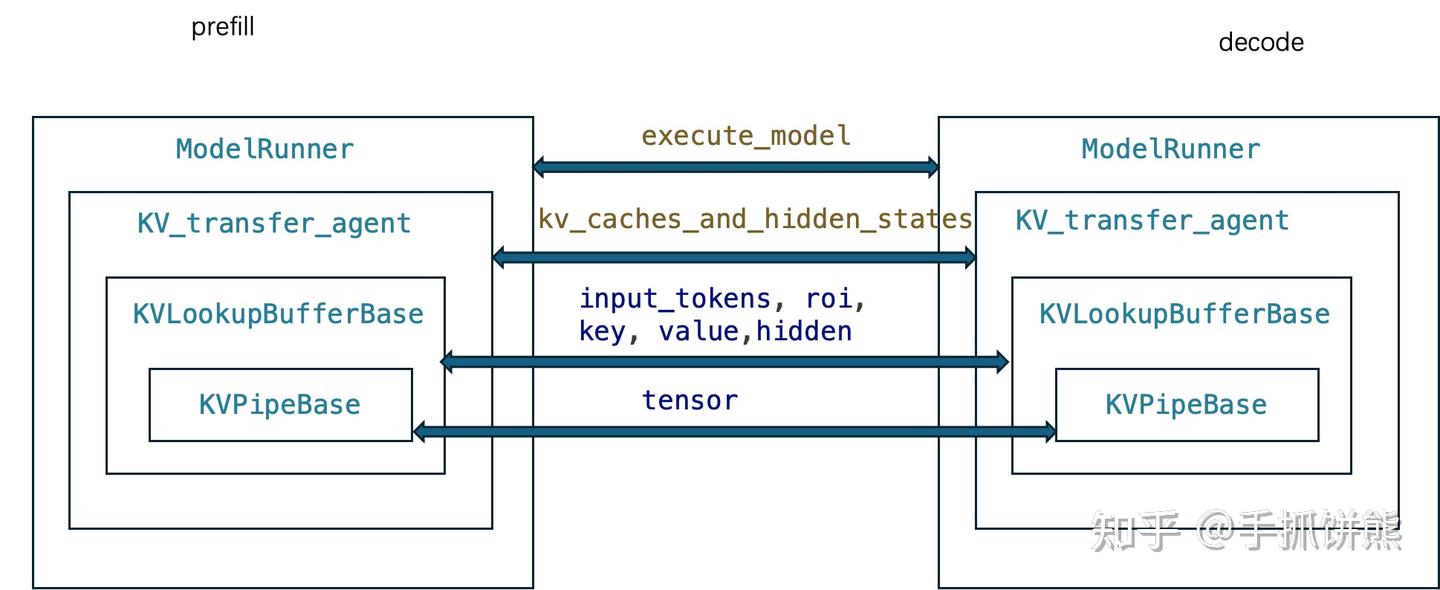
对上图的说明如下:
vLLM prefill和vLLM decode在接受到请求后都会执行ModelRunner的execute_model,依赖KV_transfer_agent类执行发送和接收所有attention layer的kv cache,KV_transfer_agent依赖KVLookupBufferBase执行单层attention layer的kv cache的发送和接收。KVPipeBase则提供最底层的tensor发送和接收(这里还有数据协议封装和进程控制,做过rpc的都了解,没做过rpc的可以从后面代码看到)。
2.3,kv_pipe
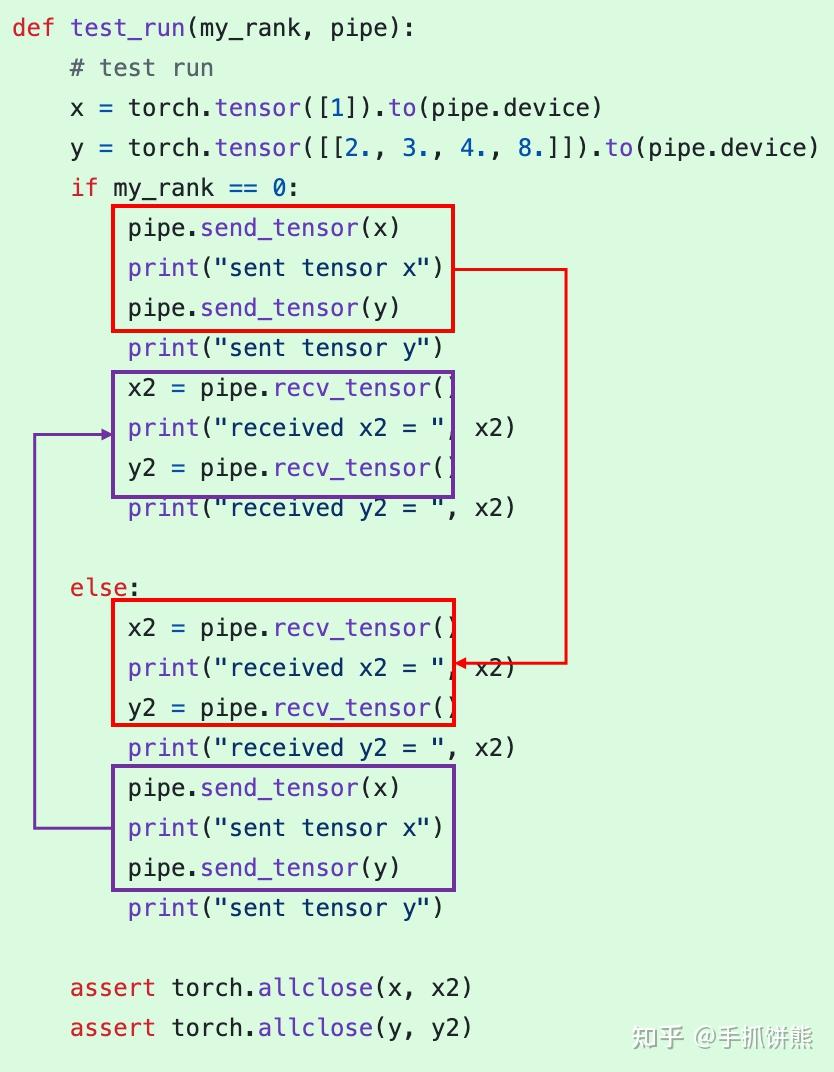
上图代码是kv pipe的单元测试,有2个进程,分别是rank 0 和rank 1,我们可以看到,rank 0 的发送必有rank 1的接收,卧龙凤雏一定是成对出现的。

上述代码是kv_pipe的send_tensor方法的实现,我们可以看到2个点:
- 这个prefill阶段发送是异步的;
- send_metadata主要记录数据类型、数据维度,以及需要发送tensor的shape,这个很好理解,prefill作为发送端是知道这些信息的,但是decode作为接受端你怎么知道这些信息呢?那就是先接受一些metadata数据,以确定接下来接收什么样的shape的数据。

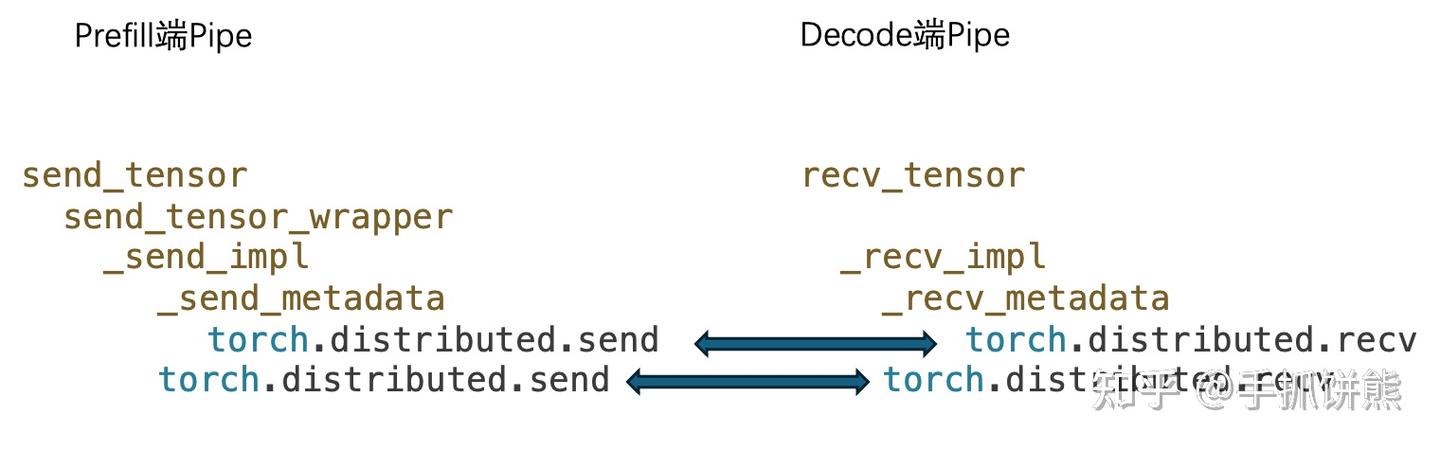
上述代码是recv_tensor的实现,我们看到它确实实现recv一个metadata,然后再recv真正的tensor。下图是prefill和decode的pipe类的发送和接收线程栈图。
2.4,kv_buffer
看一下kv_buffer的单元测试。
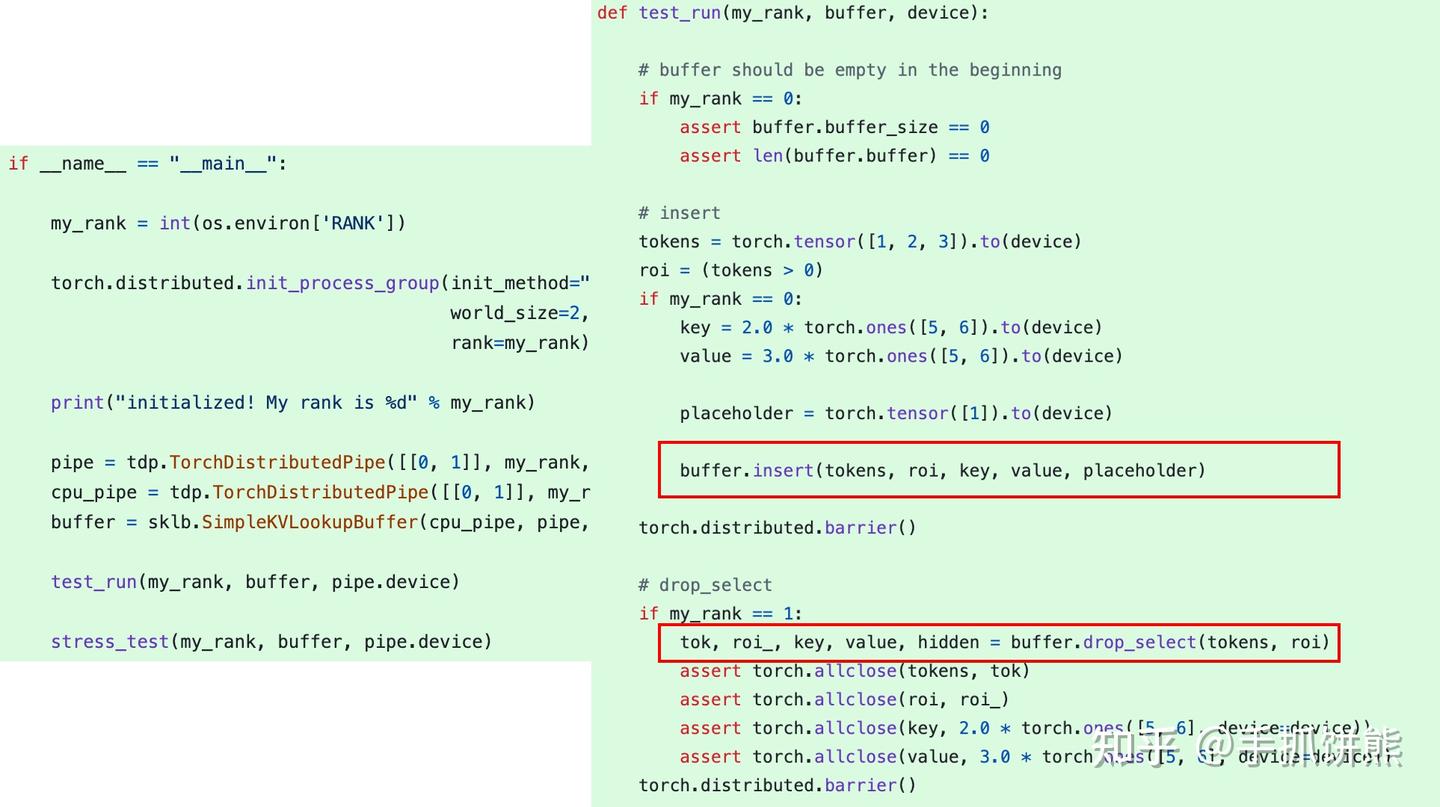
也是一个prefill和一个decode,分为2个进程,不过发送的数据已经抽象成tokens、roi、key、value、hidden了。
prefill端的insert的code如下图。
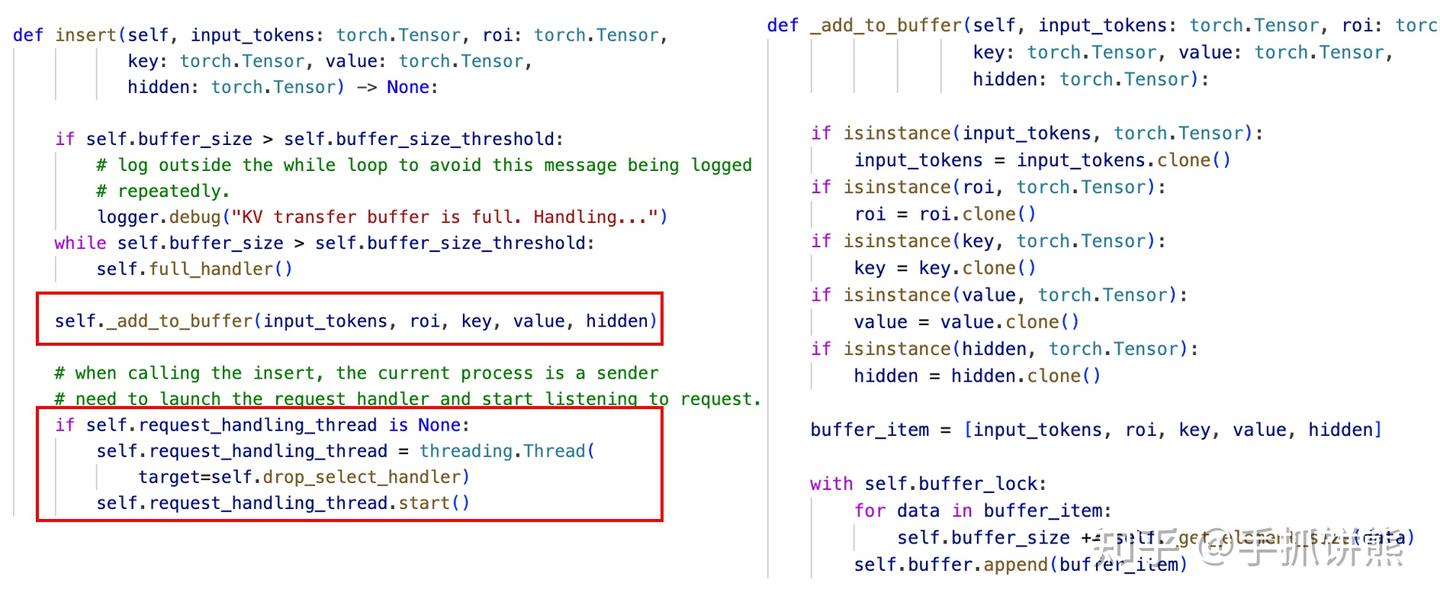
我们可以看到insert主要执行_add_to_buffer,这个容易理解,先将数据加入到本地buffer里;下面的和thread相关的只掉用一次,即如果没有创建过线程,就创建一个线程后台执行drop_select_handler。这个本质上也是一个生产者消费者模型。insert不停的_add_to_buffer。drop_select_handler后台则不停的处理这些buffer,至于如何处理,我们看代码。

prefill阶段drop_select_handler是一个while循环,不同的处理buffer数据,但是会阻塞在self.sinnal_pipe.recv_tensor()上,本质上drop_select_handler里的很多通信操作会和decode阶段drop_select里的通信操作成对出现,成对出现的线已经拉好。
2.5,模型集成
vLLM进程会根据自己是prefill还是decode掉用KV_transfer_agent的不同方法,如果是prefill,则在模型执行后执行send_kv_caches_and_hidden_states,如果是decode阶段,则在模型执行前调用recv_kv_caches_and_hidden_states。
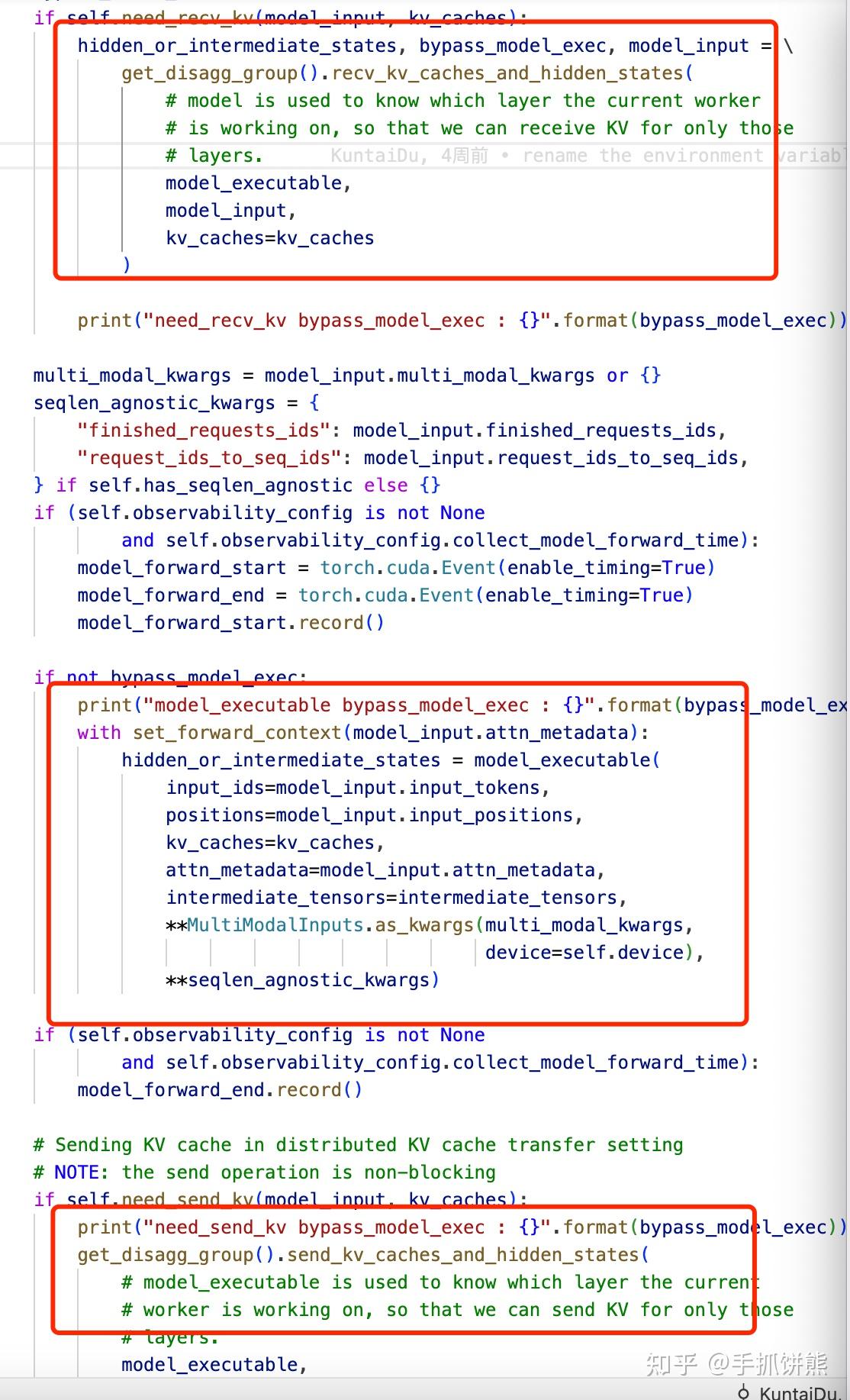
send_kv_caches_and_hidden_states的代码如下图。

recv_kv_caches_and_hidden_states的代码如下图。
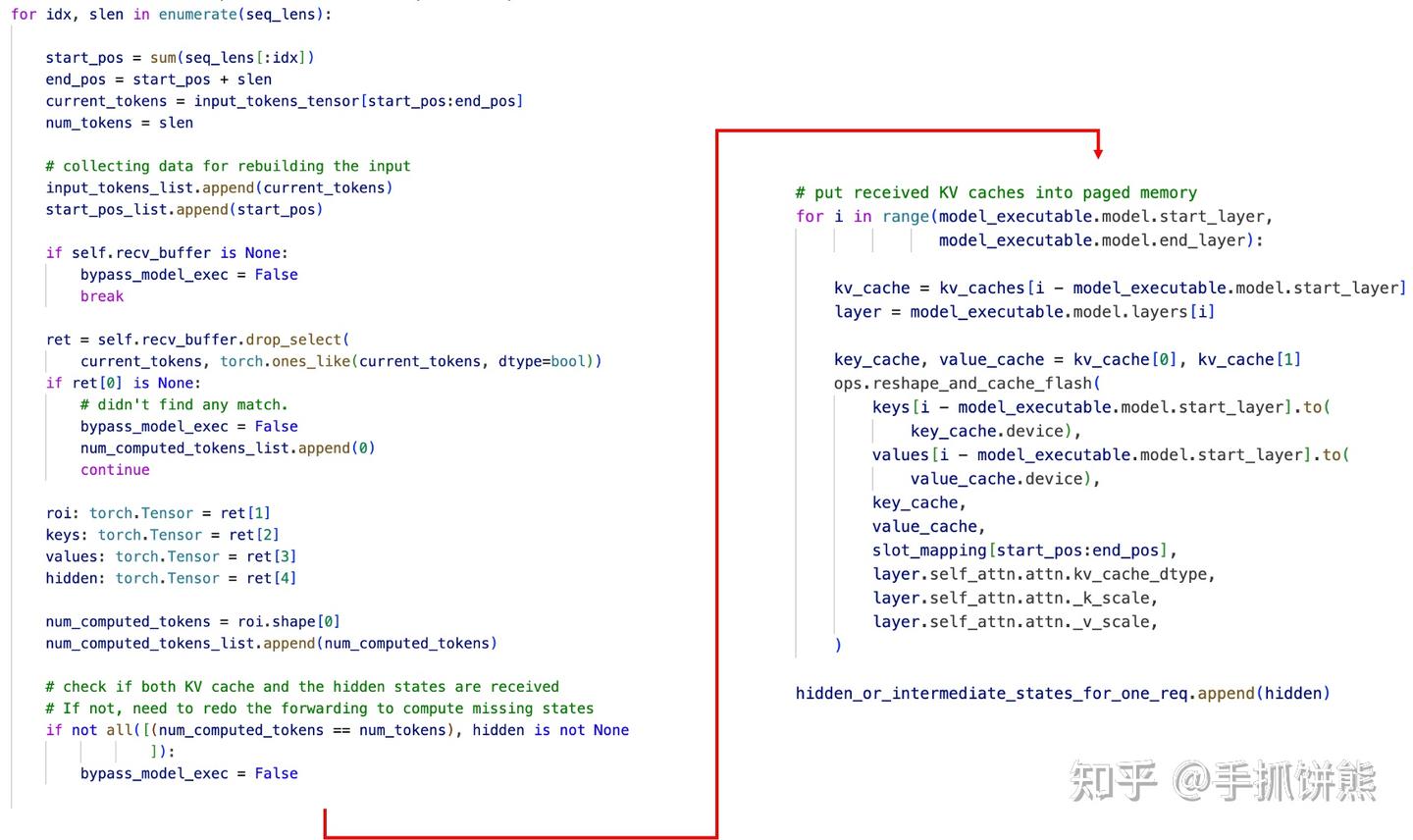
左边是接收kv cache、右边是保存kv cache,以便后续pageattention使用。
这里还有一个hidden,我们前面分析了,其实decode阶段也是需要计算first token的,decode拿到了hidden即可执行。
3,整体总结
本文只分析了主流程,还有一些细节没有写,读者可以根据自己需要debug。本pr的实现目前也是一个base版本的,如layer wise通信、prefix cache等均没体现。
posted on 2025-02-25 22:56 ExplorerMan 阅读(1079) 评论(0) 收藏 举报




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号