2019.10.18
1、调试教材P335【例18.4】进度条线程的插入(join)。(20分)
代码:
package MyThread;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JProgressBar;
public class JoinText extends JFrame{
private Thread threadA;
private Thread threadB;
final JProgressBar progressBar=new JProgressBar();
final JProgressBar progressBar2=new JProgressBar();
int count=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
init(new JoinText(),100,100);
}
public JoinText() {
super();
getContentPane().add(progressBar,BorderLayout.NORTH);
getContentPane().add(progressBar2,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
progressBar.setStringPainted(true);
progressBar2.setStringPainted(true);
threadA=new Thread(new Runnable() {
int count=0;
public void run() {
while(true) {
progressBar.setValue(++count);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
threadB.join();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB=new Thread(new Runnable() {
int count=0;
public void run() {
while(true) {
progressBar2.setValue(++count);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(count==100) {
break;
}
}
}
});
threadB.start();
}
public static void init(JFrame frame,int width,int height) {
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(width, height);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
运行截图:
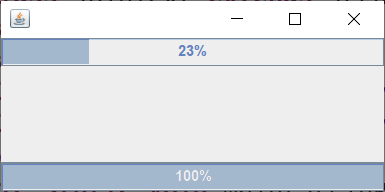
2、仿照教材P335【例18.4】,将教材P330【例18.2】改造成两个线程(定义匿名内部类的方式),效果是上下两个图标分别按照不同的速度滚动。(20分)
package MyThread;
import javax.swing.*;
public class MySnow {
JFrame f;
JLabel l1,l2,l3,l4;
Icon i1,i2,i3,i4;
public MySnow() {
f=new JFrame("下雪");
l1=new JLabel();
l2=new JLabel();
l3=new JLabel();
l4=new JLabel();
f.setVisible(true);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setBounds(200, 200, 500, 400);
f.add(l1);
f.add(l2);
f.add(l3);
f.add(l4);
l1.setBounds(40, 1, 45, 45);
l2.setBounds(150, 1, 45, 45);
l3.setBounds(280, 1, 45, 45);
l4.setBounds(400, 1, 45, 45);
i1=new ImageIcon("d:/图片/1.gif");
i2=new ImageIcon("d:/图片/1.gif");
i3=new ImageIcon("d:/图片/1.gif");
i4=new ImageIcon("d:/图片/1.gif");
l1.setIcon(i1);
l2.setIcon(i2);
l3.setIcon(i3);
l4.setIcon(i4);
Thread t1=new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(true) {
l1.setBounds(40, i, 45, 45);
i=i+5;
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i==360) {
i=-45;
}
}
}
});t1.start();
Thread t2=new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(true) {
l2.setBounds(150, i, 45, 45);
i=i+8;
try {
Thread.sleep(150);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i==360) {
i=-48;
}
}
}
});t2.start();
Thread t3=new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(true) {
l3.setBounds(280, i, 45, 45);
i=i+3;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i==360) {
i=-45;
}
}
}
});t3.start();
Thread t4=new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(true) {
l4.setBounds(400, i, 45, 45);
i=i+10;
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i==360) {
i=-50;
}
}
}
});t4.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MySnow();
}
}
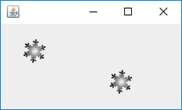
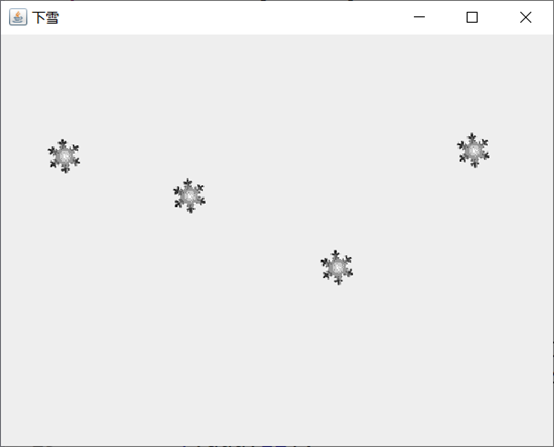
运行截图:
3、调试教材P341【例18.8】火车站售票系统,体会多线程同时访问资源带来的冲突问题。并分别采用“同步块”和“同步方法”两种线程同步机制,改进原来的代码,即实现【例18.9】和【例18.10】。(30分)
代码:
package MyThread;
public class MyTrainSale implements Runnable{
int num=10;
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized(""){
if(num>0){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("tickets"+--num);
}else {
break;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
MyTrainSale t=new MyTrainSale();
Thread tA=new Thread(t);
Thread tB=new Thread(t);
Thread tC=new Thread(t);
Thread tD=new Thread(t);
tA.start();
tB.start();
tC.start();
tD.start();
}
}
运行截图:

代码2:
package MyThread;
public class MyTrainSales implements Runnable{
int num=10;
public synchronized void doit(){
if(num>0){
try{
Thread.sleep(10);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("tickers"+--num);
}
}
public void run(){
while(true){
doit();
}
}
public static void main(String[]args){
MyTrainSales t=new MyTrainSales();
Thread tA=new Thread(t);
Thread tB=new Thread(t);
Thread tC=new Thread(t);
Thread tD=new Thread(t);
tA.start();
tB.start();
tC.start();
tD.start();
}
}
运行截图:

4、(30分)编写10个线程,第一个线程从1加到10,第二个线程从11加到20,…第十个线程从91加到100,最后把10个线程的结果相加。提示:
(1)定义类继承Thread;
(2)类成员变量:
①start:表示累加的起始值;
②summary:表示10个线程的累加和;
③run()方法:完成起始值开始的10个数累加;并将累加和计入总和。注意:中间和计入总和summary操作需要用同步块synchronized同步;
(3) main()中创建10个线程并启动,在显示10个线程和之前需要利用线程插队机制(join())保证所有线程全部工作完成。
package MyMenu;
public class MyThreadjoins extends Thread{
private int start;
static int summary;
public MyThreadjoins(int start) {
this.start=start;
}
public synchronized void add(int num) {
summary=summary+num;
}
public void run() {
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
sum=i+start+sum;
}
add(sum);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread t[]=new Thread[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
t[i]=new MyThreadjoins(i*10+1);
t[i].start();
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
t[i].join();
}
System.out.println(summary);
}
}
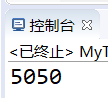
运行截图:
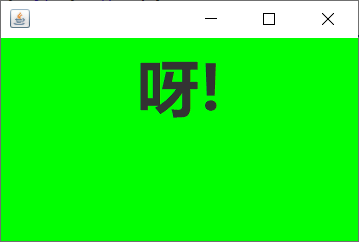
5、利用线程编写一个可以变换颜色的框架的程序。(附加题:20分)
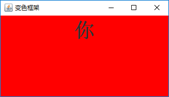
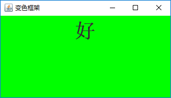
代码:
package MyThread;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import javax.swing.*;
public class MyColor {
JFrame f;
JPanel p;
JLabel l;
String[]str= {"你","好","呀!"};
Color[]color= {Color.RED,Color.YELLOW,Color.GREEN};
public MyColor() {
f=new JFrame();
p=new JPanel();
l=new JLabel();
f.setVisible(true);
f.setBounds(500, 300, 300, 200);
f.add(p);
p.add(l);
l.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑",Font.BOLD,50));
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Thread t=new Thread(new Runnable() {
int i=0;
public void run() {
while(true) {
p.setBackground(color[i]);
l.setText(str[i]);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
i++;
if(i==3) {
i=0;
}
}
}
});t.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyColor();
}
}
运行截图:


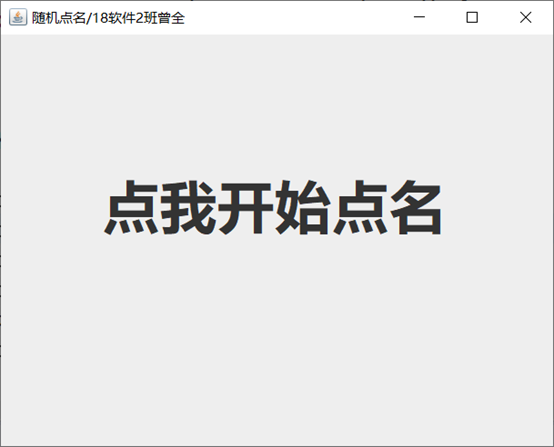
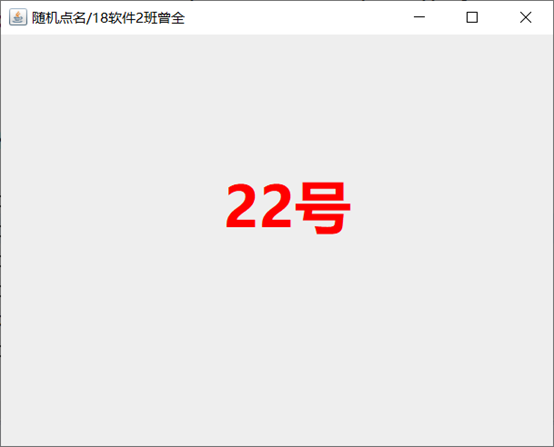
6、利用线程实现一个随机点名程序(附加题:30分)

代码:
package MyThread;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.util.Random;
import javax.swing.*;
public class RandomNames {
Random r=new Random();
int temp,time,count;
JFrame f;
JLabel l;
public RandomNames() {
f=new JFrame("随机点名/18软件2班曾全");
l=new JLabel("点我开始点名");
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
l.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
if(e.getButton()==MouseEvent.BUTTON1) {
new Thread(t).start();
}
}
});
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
l.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑",Font.BOLD,50));
f.setBounds(400, 200, 500, 400);
f.add(l);
l.setBounds(90, -50, 500, 400);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new RandomNames();
}
Thread t=new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
temp=r.nextInt(60)+1;
time=(3+r.nextInt(4))*10;
while(true) {
l.setForeground(Color.BLACK);
l.setText(" "+temp+"号");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
count++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
temp=r.nextInt(60)+1;
if(time==count) {
l.setForeground(Color.RED);
count=0;
break;
}
}
}
});
}
运行截图:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号