Java IO
Java 输入流、输出流、字节流、字符流;与处理输入输出相关的系统的类所在的包以及类的继承层次结构。用于获取磁盘中文件或目录信息的File类,标准输入、输出设备的读写方法;顺序文件和随机文件的多种读写方法。
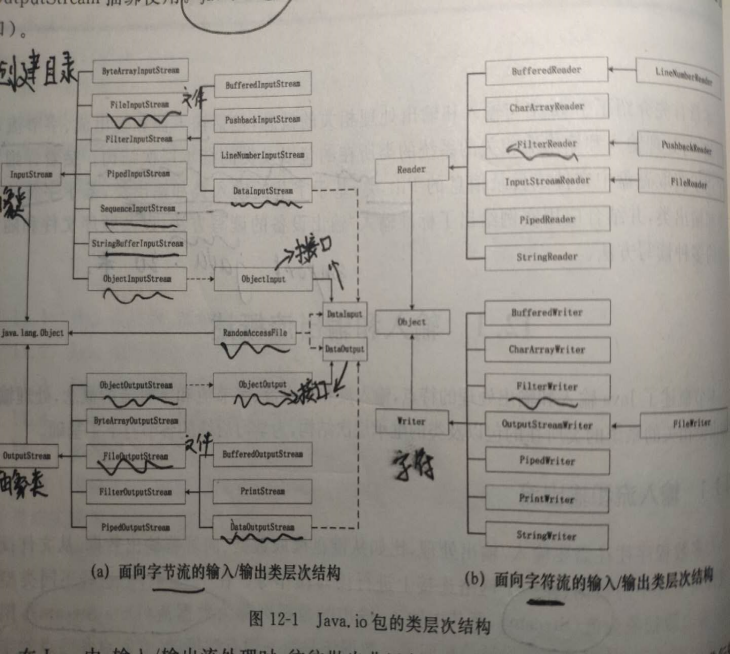
字节流:由InputStream、OutputStream派生的。字符流:Reader和Writer派生的,用于读取双字节的Unicode字符。
1、File类
主要用于获取磁盘中文件或目录的各种信息。File既不打开文件也不处理文件。用于指定奥操作的目录或文件
File f=new File("相对路径\绝对路径")
常见方法:
File file=new File("e:/javaexamples/fileTest.txt"); //构造File类
//File常用方法
String name= file.getName();
String parent= file.getParent();
String path = file.getPath();
String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath();
boolean isExist=file.exists();
boolean canwrite=file.canWrite();
boolean isfile=file.isFile();
boolean isdelete=file.delete(); //删除文件,成功返回true
boolean ismkdir=file.mkdir(); //创建目录
String []list=file.list(); //返回一个目录下所有文件的字符串数组
2、抽象类 InputStream、OutputStream
这两个类不能直接使用,但声明了一些基础的方法:
inputStream:
read()
skip()跳过指定数量不读
available()返回可用的字节数
mark()返回当前标记位置
reset()返回上一个标记过的位置
markSupport()是否支持标记和复位操作
close()关闭流
read(byte b[] ,int off,int set )将数据写入b中,返回-1则结束
OutputStream:
write(byte b[] ,int off,int set)
flush()刷空输出流,强制输出
close()
①FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
打开输入文件,若不存在,产生异常FileNotFoundException
打开输出文件,若不存在,新建一个文件,若文件只读,产生IOException异常
②RandomAccessFile 随机访问文件类
允许同时读写,,可以在文件的任意位置读写。
基本方法:
XXX readXXX():XXX是基本数据类型
void wirteXXX()
String ReadLine()读取下一行
int skipBytes(int n)将指针后移n个字节
long length()返回文件长度
long getFilePointer()返回指针位置
当前字节数*4 =指针位置
void seek(long pos)将指针调到指定位置
3、过滤字节流:
抽象类 FilterInputStream、FilterOutputStream
过滤可以提供更多功能:缓冲、监视行数或将数字字节转成基本数据类型、同步机制。
其中一个常用的是:数据过滤流:DataInputStream、DataOutputStream
提供了基本数据类型的读写方法:readInt()、readByte()、writeBoolean()、write()等
4、标准输入输出流
System提供,程序开始执行时,Java会自动创建3个与设备关联的对象:System.in、System.out、System.err
System,in.read(byte[] b) System.in,read(byte[] b, int off,inf len) 读入数据,遇到回车或填满整个数组
5、对象流、Serializable接口
能够从文件中读写完整的对象。ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
对象持续性:能将对象的状态记录以便将来再生的能力,实现的方式是对象的串行化。
只有可串行化的对象可以通过对象流进行传输。具体就是实现Serializable接口(此接口不包含任何方法,仅表明该类加入了对象串行化协议)
通常将FileInputStream对象封装在类ObjectInputStream中,用readObject()的方法直接从输入流中读取一个对象(与之相对的就是writeObject())
Student stu=new Student();
//Student类已实现Serializable
FileOutpuStream fo= new FileOutputStream("student.dat") //建立对象输出流 ObjectOutputStream so=new ObjectOutputStream(fo) //输出student对象 so.writeObject(stu); FileInpuStream fi= new FileInputStream("student.dat") //建立对象输入流 ObjectInputStream si=new ObjectInputStream(fo) //输入student对象 stu = (Student)so.readObject();
6、管道流、内存读写流、序列输入流
2connect(pis\pos)方法连接:
内存读写流:ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream、StringBufferInputStream
SequenceInputStream:将几个输入流按顺序连接在一起
7、字符流:
主要是两种:InputStreamReader、Writer(最基本的类) 和 BufferedReader、writer(额外提供了readLine()方法读一整行)
基本方法是read()、write()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号