第五周动手动脑1
结果:


1 package second;
2
3 public class Test {
4 /*
5 * 类的初始化块
6 */
7 {
8 value=100;
9 }
10 public int value=200;//字段的初始值
11
12 public Test(){
13 }
14 /*
15 * 构造函数初始化
16 */
17 public Test(int value){
18 this.value=value;
19 }
20 public static void main(String[] args){
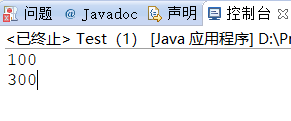
21 Test obj=new Test();
22 System.out.println(obj.value);//结果 100
23
24 obj=new Test(300);
25 System.out.println(obj.value);//结果 300
26 }
27 }
总结:在执行类成员定义时,指定的默认值或类的初始化块,执行哪个? 看哪个“排在后面”
注:类的初始化块不接受任何参数,而且,只要创建类的对象,它们就会被执行。
所以,类的初始化块适合于封装那些“对象创建时,必须执行的代码”
二、类的静态字段
1.例如:


1 class Employee{
2 String name;
3 long salary;
4 static int total;
5 }
2.访问类的静态字段:通过对象名或类名作为前缀访问静态数据
2.1类名直接访问(推荐使用):Employee.total=1;
2.2对象名访问:
Employee newhire=new Employee();
newhire.total=1;
三、类的静态初始化块
1.例子


1 package first;
2
3
4 class Root//父类
5 {
6 static{
7 System.out.println("Root的静态初始化块");
8 }
9 {
10 System.out.println("Root的普通初始化块");
11 }
12 public Root()
13 {
14 System.out.println("Root的无参数的构造器");
15 }
16 }
17 class Mid extends Root
18 {
19 static{
20 System.out.println("Mid的静态初始化块");
21 }
22 {
23 System.out.println("Mid的普通初始化块");
24 }
25 public Mid()
26 {
27 System.out.println("Mid的无参数的构造器");
28 }
29 public Mid(String msg)
30 {
31 //通过this调用同一类中重载的构造器
32 this();
33 System.out.println("Mid的带参数构造器,其参数值:" + msg);
34 }
35 }
36 class Leaf extends Mid//子类
37 {
38 static{
39 System.out.println("Leaf的静态初始化块");
40 }
41 {
42 System.out.println("Leaf的普通初始化块");
43 }
44 public Leaf()
45 {
46 //通过super调用父类中有一个字符串参数的构造器
47 super("Java初始化顺序演示");
48 System.out.println("执行Leaf的构造器");
49 }
50
51 }
52
53 public class TestStaticInitializeBlock
54 {
55 public static void main(String[] args)
56 {
57 new Leaf();
58
59 }
60 }
结果:
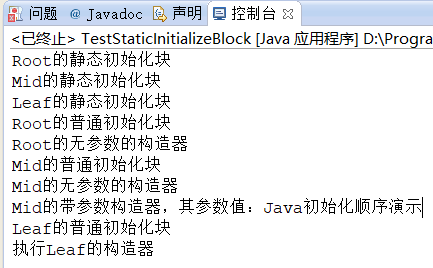
2.总结:
2.1静态初始化块只执行一次。
2.2创建子类型的对象时,会导致父类型的静态初始化块的执行
四、类的静态方法(类的静态方法只能访问类的静态成员!!!)
1.例如


1 class Employee{
2 String name;
3 long salary;
4 short employee_id;
5 static int total;
6 static void clear(){
7 total=0;
8 }
9 }
2.如何在静态方法中访问类的实例成员(即没有附加static关键字的字段或方法)?


public class Example
{
int x = 3;//类的实例变量,初始化值为3
static int y = 4;//类的静态变量,初始化值为4
public static void method()//静态方法
{
System.out.println("实例变量x = " + new Example().x);//在静态方法中访问类的实例变量需首先进行类的实例化
System.out.println("静态变量y = " + y);//在静态方法中可直接访问类的静态变量
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Example.method();
Example ex = new Example();
System.out.println("x = " + ex.x);
}
}
解决方案:在静态方法中访问类的实例变量需首先进行类的实例化
类中静态的方法或者属性,本质上来讲并不是该类的成员,在java虚拟机装在类的时候,这些静态的东西已经有了对象,它只是在这个类中"寄居",不需要通过类的构造器(构造函数)类实现实例化;而非静态
的属性或者方法,在类的装载是并没有存在,需在执行了该类的构造函数后才可依赖该类的实例对象存在。
在外部调用静态方法时,可以使用"类名.方法名"的方式,也可以使用"对象名.方法名"的方式。而实例方法只有后面这种方式。也就是说,调用静态方法可以无需创建对象。
五、Integer的诡异性
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer i1=100;
Integer j1=100;
System.out.println(i1=j1);//true
Integer i2=129;
Integer j2=129;
System.out.println(i2=j2);//false
}
原因:查看源码可知,在通过valueOf方法创建Integer对象的时候,如果数值在[-128,127]之间,便返回指向IntegerCache.cache中已经存在的对象的引用;否则创建一个新的Integer对象。
1 * This method will always cache values in the range -128 to 127,
2 * inclusive, and may cache other values outside of this range.
3 *
4 * @param i an {@code int} value.
5 * @return an {@code Integer} instance representing {@code i}.
6 * @since 1.5
7 */
8 public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
9 if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
10 return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
11 return new Integer(i);
12 }
/**
* Cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between
* -128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by JLS.
*
* The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache
* may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>} option.
* During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property
* may be set and saved in the private system properties in the
* sun.misc.VM class.
*/
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号