前言
在应用程序开发的过程中,常常需要用到批量提交到数据库的功能。而常用的批量提交有几种方式,下面分别就几种方式在批量提交中的性能表现进行对比,并作为知识碎片记录一下,方便以后的查找。这边暂时不比较Sql Server 2005和Sql Server 2008 分别提供的SqlBulkCopy和表变量参数的方式导入数据,只关注SQL的批量提交和执行。
- 第一种:单条提交SQL语句;
- 第二种:SqlCommandSet;
- 第三中:把多条SQL语句拼凑在一起提交;
测试环境
操作系统:Win7
开发工具:vs2008
数据库:Sql Server 2008(虚拟机:内存-764MB)
处理器:Pentium(R) Dual-Core T4300 @ 2.10GHz
内存:2GB
测试步骤
-
创建测试表
/****** Object: Table [dbo].[Product] Script Date: 04/09/2010 15:47:53 ******/ IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[Product]') AND type in (N'U')) DROP TABLE [dbo].[Product] GO USE [testing] GO /****** Object: Table [dbo].[Product] Script Date: 04/09/2010 15:47:53 ******/ SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Product]( [Id] [uniqueidentifier] NOT NULL, [Name] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Category] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Discontinued] [bit] NULL, PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ( [Id] ASC )WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY] ) ON [PRIMARY] GO
-
测试用例编写及测试
1、逐条提交
static void ExecuteBatchOneByOne() { string sqlString = @"insert into product(name, category, discontinued, id) values(@p1, @p2, @p3, @p4) "; totalEffected = 0; using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString)) { conn.Open(); SqlTransaction trans = conn.BeginTransaction(System.Data.IsolationLevel.ReadUncommitted); try { CCodeTimer.Time("execute insert one by one", iterations * batchSize, () => { SqlCommand cmd = conn.CreateCommand(); cmd.Transaction = trans; cmd.CommandText = sqlString; cmd.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.Text; cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p1", "test1"); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p2", "test1"); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p3", 0); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p4", Guid.NewGuid()); totalEffected += cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); }); trans.Commit(); } catch (Exception e) { trans.Rollback(); Console.WriteLine(e.ToString()); } } }
2、使用SqlClient.SqlCommandSet批量提交
static void ExecuteBatchByCommandSet() { string sqlString = @"insert into product(name, category, discontinued, id) values(@p1, @p2, @p3, @p4)"; totalEffected = 0; using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString)) { conn.Open(); SqlTransaction trans = conn.BeginTransaction(System.Data.IsolationLevel.ReadUncommitted); try { CCodeTimer.Time("execute insert by SqlClient.SqlCommandSet", iterations, () => { SqlCommandSet commandSet = new SqlCommandSet(); commandSet.Connection = conn; commandSet.Transaction = trans; for (int i = 0; i < batchSize; i++) { SqlCommand cmd = conn.CreateCommand(); cmd.CommandText = sqlString; cmd.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.Text; cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p1", "test2"); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p2", "test2"); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p3", 0); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@p4", Guid.NewGuid()); commandSet.Append(cmd); } totalEffected += commandSet.ExecuteNonQuery(); }); trans.Commit(); } catch (Exception e) { trans.Rollback(); Console.WriteLine(e.ToString()); } } }
3、使用多条SQL拼凑后批量提交
static void ExecuteBatchByCommandStrings() { totalEffected = 0; using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString)) { conn.Open(); SqlTransaction trans = conn.BeginTransaction(System.Data.IsolationLevel.ReadUncommitted); try { CCodeTimer.Time("execute insert by Command String", iterations, () => { SqlCommand cmd = conn.CreateCommand(); cmd.Transaction = trans; cmd.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.Text; StringBuilder sqlBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < batchSize; i++) { sqlBuilder.Append("insert into product(name, category, discontinued, id) ") .Append("values(") .AppendFormat("@p{0}_0, @p{0}_1, @p{0}_2, @p{0}_3", i) .Append(");"); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(string.Format("@p{0}_0", i), "test3"); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(string.Format("@p{0}_1", i), "test3"); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(string.Format("@p{0}_2", i), 0); cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue(string.Format("@p{0}_3", i), Guid.NewGuid()); } cmd.CommandText = sqlBuilder.ToString(); totalEffected += cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); }); trans.Commit(); } catch (Exception e) { trans.Rollback(); Console.WriteLine(e.ToString()); } } }
4、执行测试
static void ExecuteBatchPerformanceTests() { CTestUtil.TestName(); Console.WriteLine("Iterations: {0}", iterations); Console.WriteLine("Batch Size: {0}\r\n", batchSize); ExecuteBatchOneByOne(); Console.WriteLine("Total effected rows: {0}\r\n", totalEffected); ExecuteBatchByCommandSet(); Console.WriteLine("Total effected rows: {0}\r\n", totalEffected); ExecuteBatchByCommandStrings(); Console.WriteLine("Total effected rows: {0}\r\n", totalEffected); }
-
测试结果
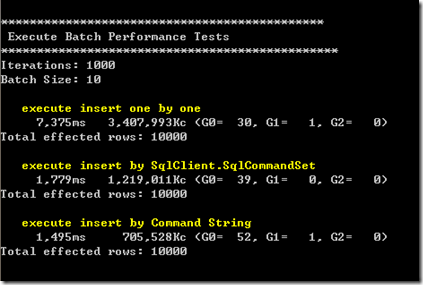
1、BatchSize为10的情况:
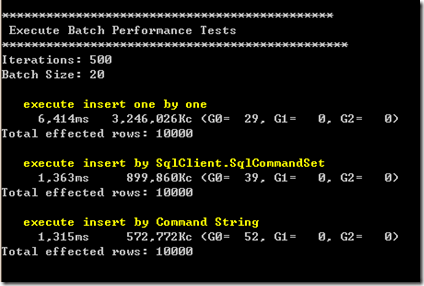
2、BatchSize为20的情况:
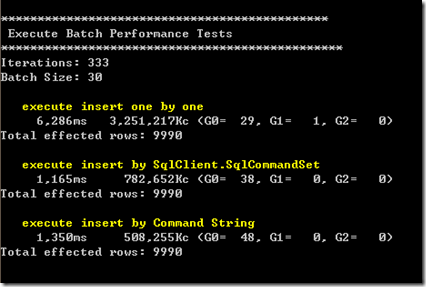
3、BatchSize为30的情况:
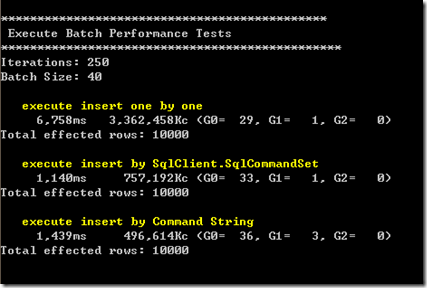
4、BatchSize为40的情况:
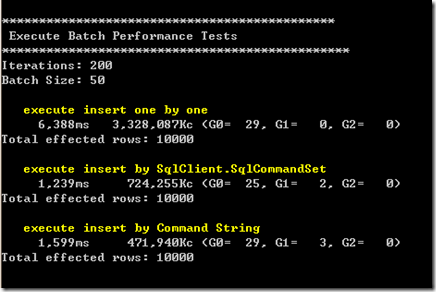
5、BatchSize为50的情况:
-
结论
- 使用ADO.NET 2.0提供的SqlCommandSet(这个类没有对外发布,可以通过反射自己封装)在执行性能上表现优越,在新增1万条数据的情况下提升了70%~80%;
- 使用拼凑SQL语句后批量提交的性能表现与SqlCommandSet相当,但随着Batch Size 的增大(大于25,这个值和SQL 语句的长度和参数个数有关),性能相较于SqlCommandSet呈下降趋势,同时这种方式有个缺点,当命令参数达到一定数量的时候会执行失败,我测试的结果有的4000个参数以上就无法成功执行,有的3000个参数就无法执行,怀疑和SQL SERVER的硬件环境和某些配置有关,具体还有待查阅,如果有知道的人可以直接告诉我:)
- 最近在研究NHibernate的时候发现它采用的是SqlCommandSet的方式进行批处理的,很多地方可以借鉴一下。
Technorati 标签: 性能;批处理;Performance




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号