步梯 abc 367
Tasks - AtCoder Beginner Contest 367
A - Shout Everyday (atcoder.jp)
签到
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2;
void solve()
{
int a,b,c;
std::cin >> a >> b >> c;
bool ok = true;
if(b > c) {
if(a >= b && a <= 24) ok = false;
if(a < c) ok = false;
}
else {
if(a >= b && a <= c) ok = false;
}
if(ok) std::cout << "Yes\n";
else std::cout << "No\n";
return;
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
//std::cin >> _ ;
while(_ --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
反转去除前导零
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e6 +50;
void solve()
{
std::string s;
std::cin >> s;
std::reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
int n = s.size();
int cnt = 0;
//std::cout << s << '\n';
while(s.size())
{
if(s[0] != '0') break;
if(s[0] == '.') {
s.erase(0,1);
break;
}
if(s[0] == '0') s.erase(0,1);
}
if(s[0] == '.') s.erase(0,1);
std::reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
std::cout << s << '\n';
return;
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
//std::cin >> _ ;
while(_ --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C - Enumerate Sequences (atcoder.jp)
爆搜
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e5 + 50;
int a[N],R[N];
int n,k;
void dfs (int m, int s) {
if(m > n) {
if(s % k == 0) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
std::cout << a[i] << " ";
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= R[m-1]; i++) {
a[m] = i;
dfs(m+1,s + i);
}
}
void solve() {
std::cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) std::cin >> R[i];
dfs(1,0);
return;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
//std::cin >> _;
while(_ --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
考虑到\(s,t\) 在环上的大小关系分为两类
\(s < t\) 断环为链 \(Sum_{t-1} - Sum_{s-1}\) % m = 0
\((a-b) \mod m = 0\) , \(a,b\) 对 \(m\) 同余
枚举 \(t\) ,令 \(s = t - 1\) ,\(cnt\) 统计相同余数
最巧妙的地方
for(int t = 2 ; t <= n; t++) {
cnt[sum[t-2]] ++;// s -> t - 1 , s - 1 -> t - 2
res += cnt[sum[t-1]]; // 保证 与t配对的s 均是小于t的
}
\(s > t\)
\(Sum_n - Sum_{s-1} + Sum_{t-1}\) = \(suf_s + Sum_{t-1}\)
($a + b $ ) % m = 0, \(a \mod m + b \mod m = m\)
同理枚举 \(s\)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e6 + 50;
void solve()
{
int n,m;
std::cin >> n >> m;
std::vector<int> a(n);
std::vector<ll> sum(n+1),suf(n+2);
std::map<int,int> cnt;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++) {
std::cin >> a[i];
sum[i+1] = (sum[i] + a[i]) % m;
//std::cout << sum[i+1] << " ";
}
//std::cout << '\n';
for(int i = n ;i >= 1;i --) {
suf[i] = (suf[i+1] + a[i-1]) % m;
//std::cout << suf[i] << " ";
}
//std::cout << '\n';
ll res = 0;
for(int t = 2 ; t <= n; t++) {
cnt[sum[t-2]] ++;// s -> t - 1
res += cnt[sum[t-1]];
}
cnt.clear();
for(int s = 2; s <= n; s++) {
cnt[sum[s-2]] ++; // t -> s - 1
res += cnt[(m - suf[s]) % m];// 防止后缀和取模等于0 产生cnt[m]
}
std::cout << res << '\n';
return;
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
//std::cin >> _ ;
while(_ --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E - Permute K times (atcoder.jp)
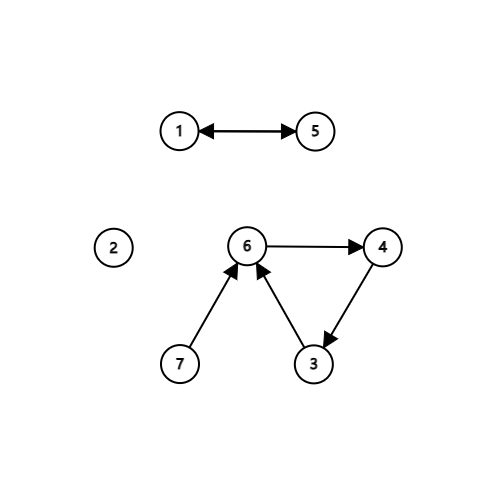
问\(A_7\)经过次变换值为\(A_x\)
经过一次 \(A_6\),经过两次\(A_4\) ,经过三次\(A_3\) , 经过四次\(A_6\)
可以构建\(i \quad x[i]\)基环树森林
每次转移就是在转移边
用倍增 \(st[i][0] = x[i]\) 表示\(i\) 的 \(2^{i}\) 转移后点是多少
\(k \le 10^{18}\)
\(st[i][j] = st[st[i][j-1]][j-1]\)
\(2^{j} = 2^{j-1} + 2^{j-1}\)
经过\(2^{j-1}\) 次转移的点,再转移\(2^{j-1}\) 次
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e5 + 50;
int st[N][63];
void solve() {
int n;
ll k;
std::cin >> n >> k;
std::vector<int> X(n),A(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) std::cin >> X[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) std::cin >> A[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
st[i][0] = X[i-1];
}
for(int j = 1; j <= 62; j ++) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
st[i][j] = st[st[i][j-1]][j-1];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x = i;
ll y = k;
for(int j = 62; j >= 0; j --) {
if(y >= (1ll << j)) {
x = st[x][j];
y -= (1ll << j);
}
}
std::cout << A[x-1] << " ";
}
return;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
//std::cin >> _;
while(_ --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
F - Rearrange Query (atcoder.jp)
-
Problem Statement
You are given sequences of positive integers of length \(N\): \(A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N)\) and \(B=(B_1,B_2,\ldots,B_N)\).
You are given \(Q\) queries to process in order. The \(i\)-th query is explained below.
- You are given positive integers \(l_i,r_i,L_i,R_i\). Print
Yesif it is possible to rearrange the subsequence \((A_{l_i},A_{l_i+1},\ldots,A_{r_i})\) to match the subsequence \((B_{L_i},B_{L_i+1},\ldots,B_{R_i})\), andNootherwise.
哈希
将每个\(i\) 映射到更大的范围,利用前缀和查询是否相等
#include <bits/stdc++.h> typedef long long ll; const int N = 2e6 + 50; const ll base = 1145141; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; void solve() { int n,q; std::cin >> n >> q; std::vector<int> a(n),b(n); std::vector<ll> p(n+1),ha(n+1,0),hb(n+1,0); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { std::cin >> a[i]; } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { std::cin >> b[i]; } p[0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { p[i] = p[i-1] * base % mod; } for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { ha[i+1] = (ha[i] + p[a[i]]) % mod; } for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { hb[i+1] = (hb[i] + p[b[i]]) % mod; } while(q--) { int l,r,L,R; std::cin >> l >> r >> L >> R; l--; L--; if((ha[r] - ha[l] + mod) % mod == (hb[R] - hb[L] + mod) % mod) { std::cout << "Yes\n"; } else { std::cout << "No\n"; } } return; } int main() { std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); std::cin.tie(nullptr); int _ = 1; //std::cin >> _ ; while(_ --) { solve(); } return 0; } - You are given positive integers \(l_i,r_i,L_i,R_i\). Print


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号