Princeton ELE 475 - 1 ISA issues
Engineering Principle: ABSTRACTION
Abstrcation of real world computers:
↑ Computer Science
-app software
-algorithm
-high-level language
-OS / virtual machine
-instruction set architecture (ISA) ------------------------------------ boundry of hardware and software
-micro-architecture
-digital logic design(RTL) ----------------------------------------------- boundry of "functional" blocks and basic devices
-gates and circuits design
-transistor tech(i.e. CMOS)
-quantum physics
↓ Electrical Engineering & Physics
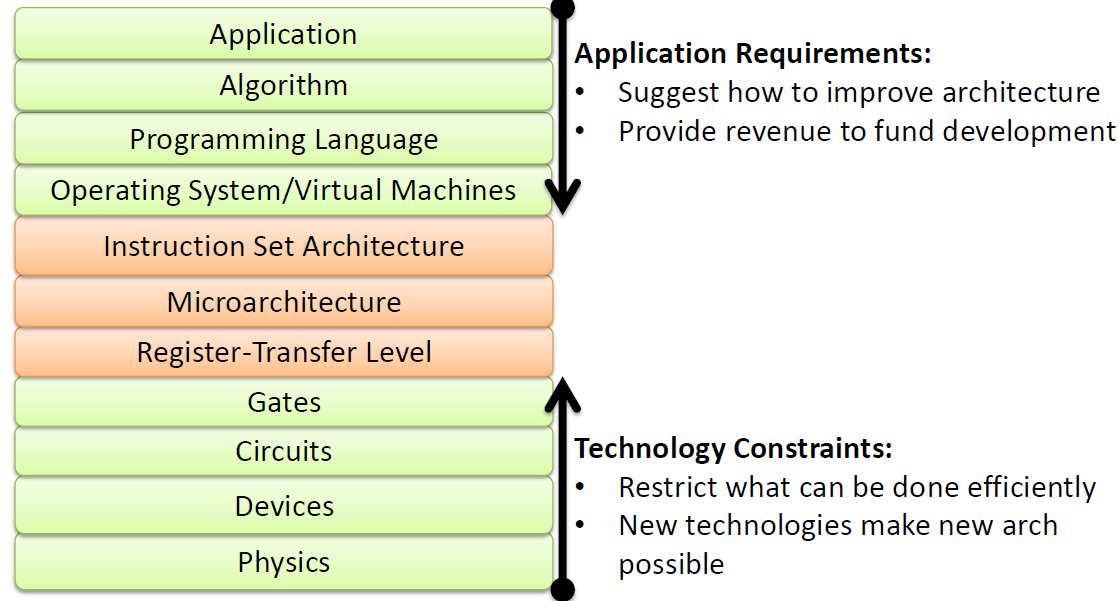
Too much details(too low-level) blur understanding; too few details(too high-level) limits understanding.
Switch your view of abstraction layers to focus on central problems.
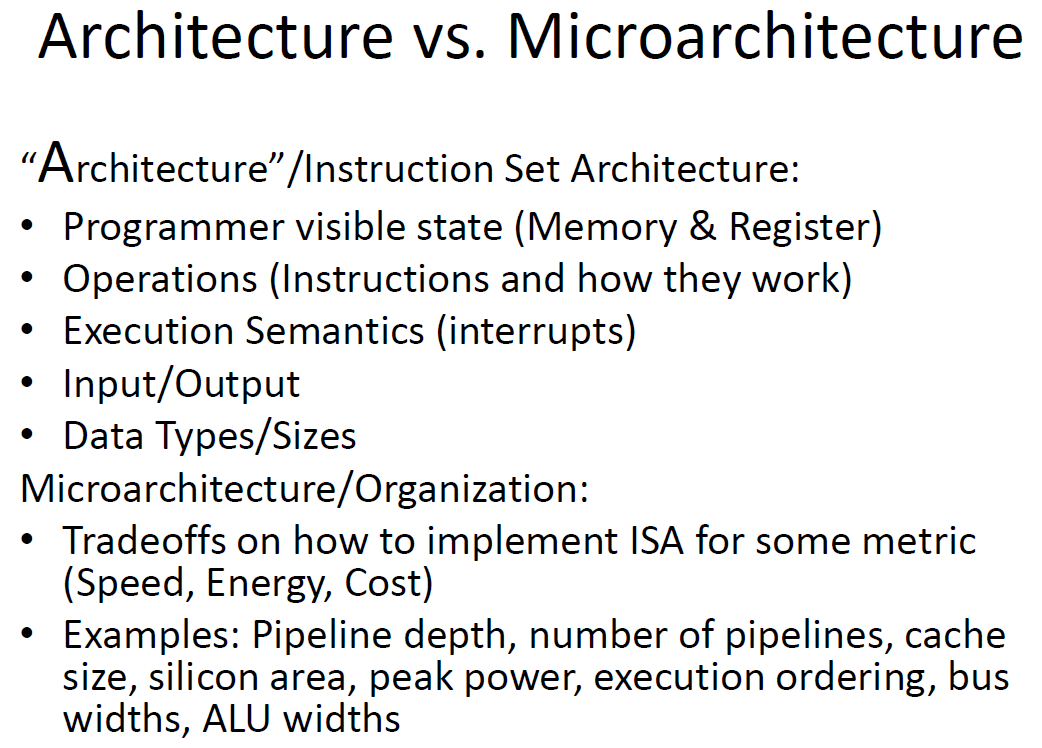
- fundamental machine model
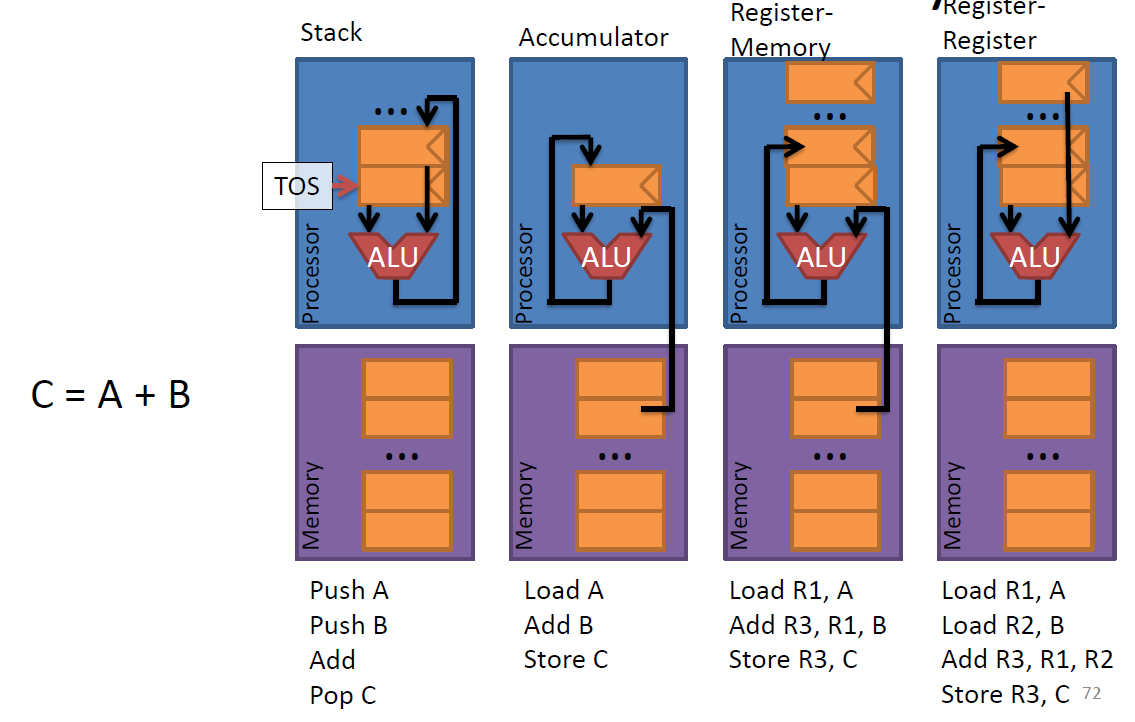
-stack: 2 implicit operands
-accumulator: 1implicit & 1 explicit
-GPR: 2 explicit operands
-reg-reg model is also known as load/store
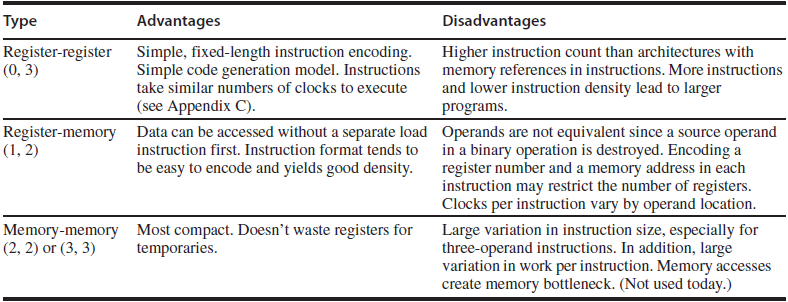
- classes of instructions

- addressing modes
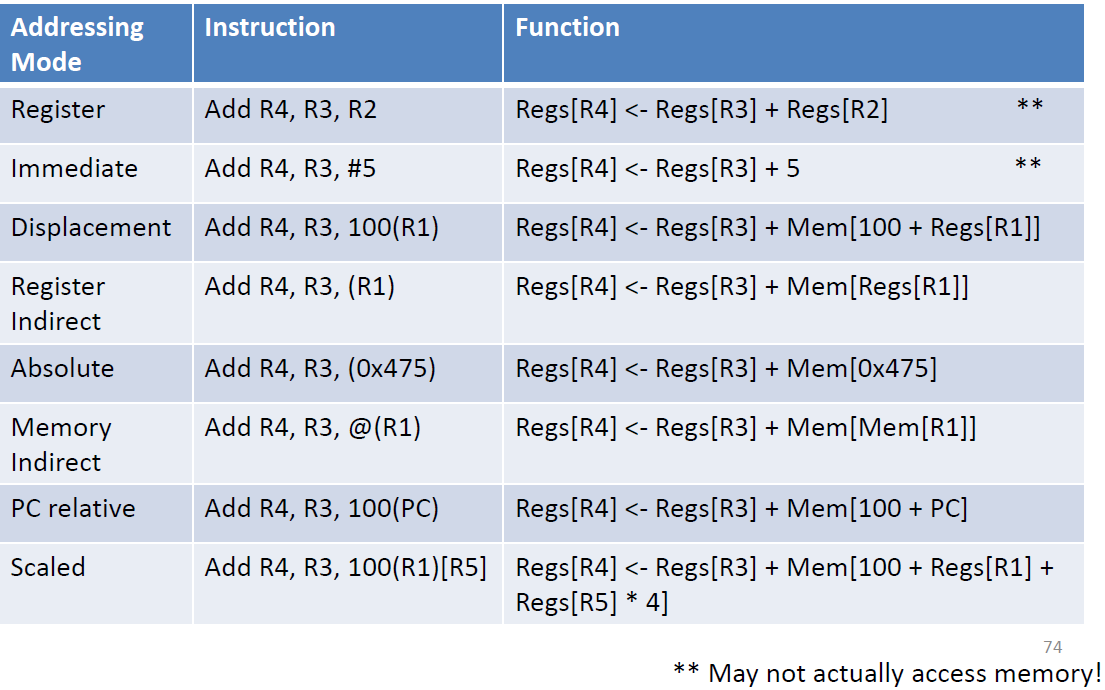
- data types and sizes
-integer, floating points
-8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit
- ISA encoding (format)
-fixed length
-variable length
-VLIW(Very Long Instruction Word)
for purely SEQUENTIAL computers, clock freq↑, it goes faster, but it also produces more heat, so much heat that a expensive cooling system is demanded
power wall = clock frequency wall = processing speed wall
must employ PARALLELISM ! ! !
- instruction level parallelism
- data level parallelism
- thread level parallelism
Michal Flynn [1966] taxonomy [Today's computers are HYBRID]
- SISD: single instrcution stream & single data stream
-uniprocessor
-can exploit ILP such as superscalar and speculation execution
- SIMD: single ins. stream & multiple data stream
-the same instruction executed by multiple processors using different data streams
-exploit data-level parallelism by applying the same operations to multiple items of data in parallel
-multiple data memory & single ins. memory and control unit
- MISD: multiple ins. stream & single data stream
- MIMD: multiple ins. stream & multiple data stream
other useful resources:
CS-224 from Bilkent University (youtube podcast series)
ELE-475 from Princeton University (coursera)
Computer Organization and Design - The Hardware Software Interface(5th edition)
Computer Architecture - A Quantitative Approach(5th edition)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号