LeetCode 863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/all-nodes-distance-k-in-binary-tree/
题目:
We are given a binary tree (with root node root), a target node, and an integer value K.
Return a list of the values of all nodes that have a distance K from the target node. The answer can be returned in any order.
Example 1:
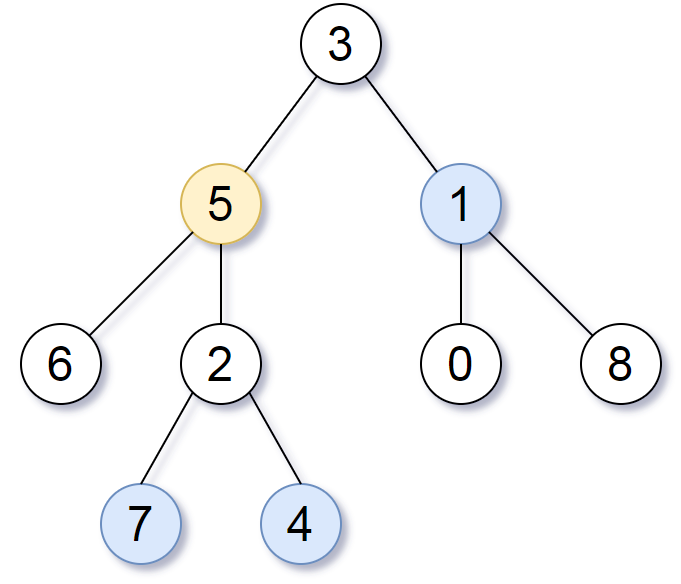
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation:
The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5)
have values 7, 4, and 1.
![]() Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note:
- The given tree is non-empty.
- Each node in the tree has unique values
0 <= node.val <= 500. - The
targetnode is a node in the tree. 0 <= K <= 1000.
题解:
Clone this tree with new type of Node containing a pointer to parent.
Find the cloned target node and do BFS from it.
Time Complexity: O(n). Deep clone takes O(n). BFS takes O(n).
Time Complexity: O(n). Regardless res.
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 Node clonedTargetNode; 12 public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) { 13 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 14 if(root == null){ 15 return res; 16 } 17 18 deepClone(root, null, target); 19 LinkedList<Node> que = new LinkedList<Node>(); 20 que.add(clonedTargetNode); 21 22 HashSet<Node> used = new HashSet<Node>(); 23 used.add(clonedTargetNode); 24 while(!que.isEmpty()){ 25 int size = que.size(); 26 if(K==0){ 27 for(int i = 0; i<size; i++){ 28 res.add(que.poll().val); 29 } 30 31 return res; 32 } 33 34 for(int i = 0; i<size; i++){ 35 Node cur = que.poll(); 36 if(cur.parent != null && !used.contains(cur.parent)){ 37 que.add(cur.parent); 38 used.add(cur.parent); 39 } 40 41 if(cur.left != null && !used.contains(cur.left)){ 42 que.add(cur.left); 43 used.add(cur.left); 44 } 45 46 if(cur.right != null && !used.contains(cur.right)){ 47 que.add(cur.right); 48 used.add(cur.right); 49 } 50 } 51 52 K--; 53 } 54 55 return res; 56 } 57 58 private Node deepClone(TreeNode root, Node parent, TreeNode target){ 59 if(root == null){ 60 return null; 61 } 62 63 Node clonedRoot = new Node(root.val); 64 if(root == target){ 65 clonedTargetNode = clonedRoot; 66 } 67 68 clonedRoot.parent = parent; 69 clonedRoot.left = deepClone(root.left, clonedRoot, target); 70 clonedRoot.right = deepClone(root.right, clonedRoot, target); 71 return clonedRoot; 72 } 73 } 74 75 class Node{ 76 int val; 77 Node parent; 78 Node left; 79 Node right; 80 Node(int x){ 81 this.val = x; 82 } 83 }
First find the path and distance from root to the target node.
Have a map to record this path, each node and its distance to taget node.
Then do another DFS to find all the results.
DFS returns void. DFS state includes current root, target distance k, current distance and res.
When map contains current root, then it is on the path to the target. Update current distance to map.get(root).
if current distance == k, then add the node.
Otherwise, continue on left and right children.
Time Complexity: O(n).
Space: O(logn).
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 Map<TreeNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 12 public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int k) { 13 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); 14 find(root, target); 15 dfs(root, k, 0, res); 16 return res; 17 } 18 19 private void find(TreeNode root, TreeNode target){ 20 if(root == null){ 21 return; 22 } 23 24 if(root == target){ 25 map.put(root, 0); 26 return; 27 } 28 29 find(root.left, target); 30 if(map.containsKey(root.left)){ 31 map.put(root, map.get(root.left) + 1); 32 return; 33 } 34 35 find(root.right, target); 36 if(map.containsKey(root.right)){ 37 map.put(root, map.get(root.right) + 1); 38 return; 39 } 40 41 return; 42 } 43 44 private void dfs(TreeNode root, int k, int dis, List<Integer> res){ 45 if(root == null){ 46 return; 47 } 48 49 if(map.containsKey(root)){ 50 dis = map.get(root); 51 } 52 53 if(dis == k){ 54 res.add(root.val); 55 } 56 57 dfs(root.left, k, dis + 1, res); 58 dfs(root.right, k, dis + 1, res); 59 } 60 }
 Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号