Linux-Shell脚本编程-学习-1-Linux基本命令
在学习Linux-Shell脚本编程之前,我们需要学习一定的Linux基本命令,不然在后面学习Shell脚本编程的的时候,我们就呵呵了。
我学习所用的系统是Ubuntu 16.04版本
也没有什么规则,就是记录一下我所用到的基Linux命令,也没有什么大纲,就是想到什么写什么了,剩下的后面子在补充了。呵呵哒
1. 用户切换 su:当我们从普通用户切换到root用户是,需要输入root用户的密码,当我们从root用户切换到普通用户是,不需要输入密码
2.重置密码 password命令:可以重置当前用户的密码,如果要重置其他用户密码,那需要切换到其他用户,或者使用管理员用户,或者使用管理员权限 sudo
3. 使用管理员权限:sudo,使普通用户的本次操作拥有管理员权限,需要输入管理员密码
4. 切换目录 cd: 切换目录,例如:“$ cd /home/dreamlife/temp/切换到dreamlife用户的temp目录下。
5. 相对文件路劲:”.“和”..“单点符号表示当前目录,双点符号表示当前目录的父目录
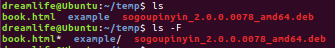
6. 查看当前目录下文字:ls,最基本的ls命令会显示当前文件下的文件和目录。为了区分文件和目录,我们可以使用"ls -F" 来区分,”ls“与”ls -F“区别如下图
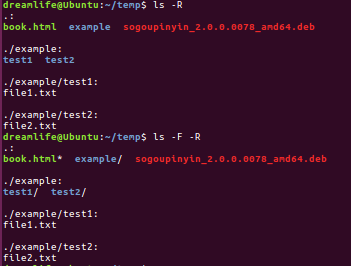
显示隐藏文件,需要用到”ls -a“命令如下图
还有一个命令就是 ”ls -R“,这个命令的用途就是让你快速了解一个目录下的结构,效果自己对比,如果对于大型项目,那么这个文件可能会很长了。
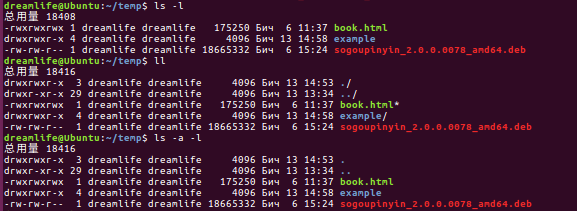
另一个常用的命令”ls-l“和“ls -a -l”(也 可以写作“ll“)这几个命令可以更详细的显示每个文件的相信信息,上效果图
详细信息大致有一下几种
1. 文件类型(d:目录,-:文件,C:字符型文件,b:块文件)等
2. 文件的权限:读写执行,分为单个组合,文件属主权限,属组成员权限,其他用户权限
3. 文件的硬链接总数。
4. 文件属主用户名
5. 文件属组组名
6.文件的大小
7. 文件上次修改时间
8. 文件名或目录名
如果向了解ls其他的命令,可以世界使用 ls --help来查看ls的其他命令
$ ls --help
用法:ls [选项]... [文件]...
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default).
Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified.
必选参数对长短选项同时适用。
-a, --all 不隐藏任何以. 开始的项目
-A, --almost-all 列出除. 及.. 以外的任何项目
--author 与-l 同时使用时列出每个文件的作者
-b, --escape 以八进制溢出序列表示不可打印的字符
--block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g.,
'--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of
1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below
-B, --ignore-backups do not list implied entries ending with ~
-c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last
modification of file status information);
with -l: show ctime and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first
-C list entries by columns
--color[=WHEN] colorize the output; WHEN can be 'always' (default
if omitted), 'auto', or 'never'; more info below
-d, --directory list directories themselves, not their contents
-D, --dired generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode
-f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color
-F, --classify append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
--file-type likewise, except do not append '*'
--format=WORD across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l,
single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C
--full-time like -l --time-style=full-iso
-g 类似-l,但不列出所有者
--group-directories-first
group directories before files;
can be augmented with a --sort option, but any
use of --sort=none (-U) disables grouping
-G, --no-group in a long listing, don't print group names
-h, --human-readable with -l and/or -s, print human readable sizes
(e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
--si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-H, --dereference-command-line
follow symbolic links listed on the command line
--dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir
follow each command line symbolic link
that points to a directory
--hide=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
(overridden by -a or -A)
--indicator-style=WORD append indicator with style WORD to entry names:
none (default), slash (-p),
file-type (--file-type), classify (-F)
-i, --inode print the index number of each file
-I, --ignore=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
-k, --kibibytes default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage
-l 使用较长格式列出信息
-L, --dereference 当显示符号链接的文件信息时,显示符号链接所指示
的对象而并非符号链接本身的信息
-m 所有项目以逗号分隔,并填满整行行宽
-n, --numeric-uid-gid 类似 -l,但列出UID 及GID 号
-N, --literal 输出未经处理的项目名称 (如不特别处理控制字符)
-o 类似 -l,但不列出有关组的信息
-p, --indicator-style=slash 对目录加上表示符号"/"
-q, --hide-control-chars print ? instead of nongraphic characters
--show-control-chars show nongraphic characters as-is (the default,
unless program is 'ls' and output is a terminal)
-Q, --quote-name enclose entry names in double quotes
--quoting-style=WORD use quoting style WORD for entry names:
literal, locale, shell, shell-always,
shell-escape, shell-escape-always, c, escape
-r, --reverse 逆序排列
-R, --recursive 递归显示子目录
-s, --size 以块数形式显示每个文件分配的尺寸
-S sort by file size, largest first
--sort=WORD sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S),
time (-t), version (-v), extension (-X)
--time=WORD with -l, show time as WORD instead of default
modification time: atime or access or use (-u);
ctime or status (-c); also use specified time
as sort key if --sort=time (newest first)
--time-style=STYLE with -l, show times using style STYLE:
full-iso, long-iso, iso, locale, or +FORMAT;
FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date'; if FORMAT
is FORMAT1<newline>FORMAT2, then FORMAT1 applies
to non-recent files and FORMAT2 to recent files;
if STYLE is prefixed with 'posix-', STYLE
takes effect only outside the POSIX locale
-t sort by modification time, newest first
-T, --tabsize=COLS assume tab stops at each COLS instead of 8
-u with -lt: sort by, and show, access time;
with -l: show access time and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by access time, newest first
-U do not sort; list entries in directory order
-v natural sort of (version) numbers within text
-w, --width=COLS set output width to COLS. 0 means no limit
-x list entries by lines instead of by columns
-X sort alphabetically by entry extension
-Z, --context print any security context of each file
-1 list one file per line. Avoid '\n' with -q or -b
--help 显示此帮助信息并退出
--version 显示版本信息并退出
The SIZE argument is an integer and optional unit (example: 10K is 10*1024).
Units are K,M,G,T,P,E,Z,Y (powers of 1024) or KB,MB,... (powers of 1000).
使用色彩来区分文件类型的功能已被禁用,默认设置和 --color=never 同时禁用了它。
使用 --color=auto 选项,ls 只在标准输出被连至终端时才生成颜色代码。
LS_COLORS 环境变量可改变此设置,可使用 dircolors 命令来设置。
退出状态:
0 正常
1 一般问题 (例如:无法访问子文件夹)
2 严重问题 (例如:无法使用命令行参数)
GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
请向<http://translationproject.org/team/zh_CN.html> 报告ls 的翻译错误
Full documentation at: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/ls>
or available locally via: info '(coreutils) ls invocation'
7. 查看当前目录位置命令:pwd
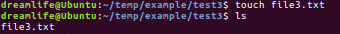
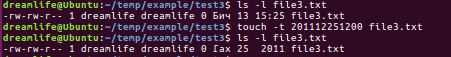
8.创建空文件 touch <文件名>
touch创建出来的文件都是空文件,当这个文件存在是,那么touch将改变时间文件的访问时间
9. 复制文件:CP
cp命令将源文件复至一个新文件,他们有不同的索引节点号,有不同的创建日期和修改时间
如果文件名字冲突,则会提示是否覆盖,需要自己确定。
在实际使用中 ,我们很多时候需要讲一个目录完成的复制到另一个目录,那么现在需要执行 “cp -R”来执行,它可以递归的复制整个目录到目的目录。
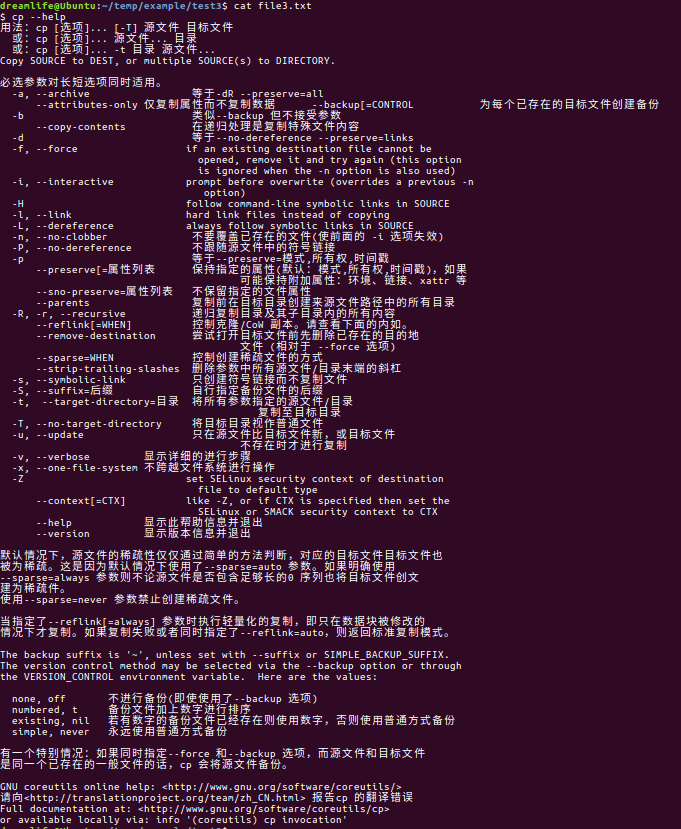
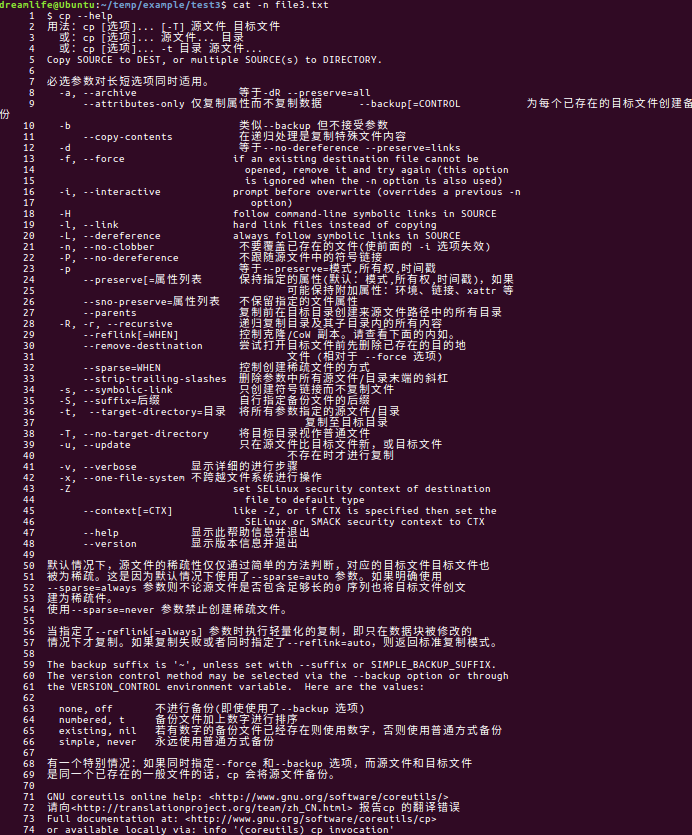
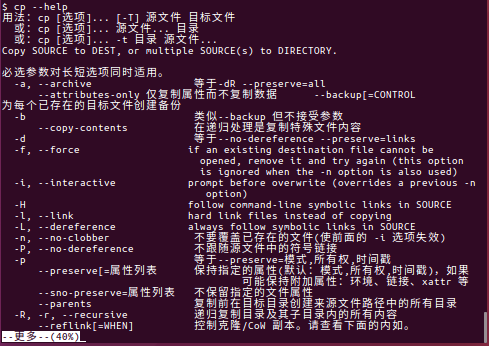
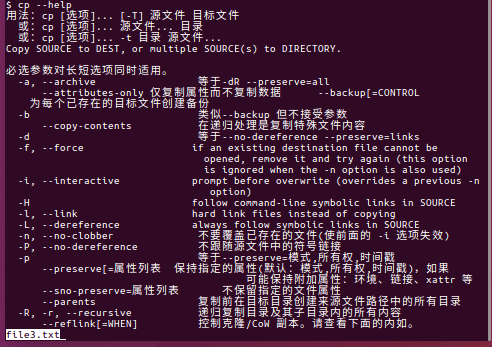
其他的CP暂时还用不到,如果需要了解,可以执行“ $ cp --help ”
$ cp --help 用法:cp [选项]... [-T] 源文件 目标文件 或:cp [选项]... 源文件... 目录 或:cp [选项]... -t 目录 源文件... Copy SOURCE to DEST, or multiple SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY. 必选参数对长短选项同时适用。 -a, --archive 等于-dR --preserve=all --attributes-only 仅复制属性而不复制数据 --backup[=CONTROL 为每个已存在的目标文件创建备份 -b 类似--backup 但不接受参数 --copy-contents 在递归处理是复制特殊文件内容 -d 等于--no-dereference --preserve=links -f, --force if an existing destination file cannot be opened, remove it and try again (this option is ignored when the -n option is also used) -i, --interactive prompt before overwrite (overrides a previous -n option) -H follow command-line symbolic links in SOURCE -l, --link hard link files instead of copying -L, --dereference always follow symbolic links in SOURCE -n, --no-clobber 不要覆盖已存在的文件(使前面的 -i 选项失效) -P, --no-dereference 不跟随源文件中的符号链接 -p 等于--preserve=模式,所有权,时间戳 --preserve[=属性列表 保持指定的属性(默认:模式,所有权,时间戳),如果 可能保持附加属性:环境、链接、xattr 等 --sno-preserve=属性列表 不保留指定的文件属性 --parents 复制前在目标目录创建来源文件路径中的所有目录 -R, -r, --recursive 递归复制目录及其子目录内的所有内容 --reflink[=WHEN] 控制克隆/CoW 副本。请查看下面的内如。 --remove-destination 尝试打开目标文件前先删除已存在的目的地 文件 (相对于 --force 选项) --sparse=WHEN 控制创建稀疏文件的方式 --strip-trailing-slashes 删除参数中所有源文件/目录末端的斜杠 -s, --symbolic-link 只创建符号链接而不复制文件 -S, --suffix=后缀 自行指定备份文件的后缀 -t, --target-directory=目录 将所有参数指定的源文件/目录 复制至目标目录 -T, --no-target-directory 将目标目录视作普通文件 -u, --update 只在源文件比目标文件新,或目标文件 不存在时才进行复制 -v, --verbose 显示详细的进行步骤 -x, --one-file-system 不跨越文件系统进行操作 -Z set SELinux security context of destination file to default type --context[=CTX] like -Z, or if CTX is specified then set the SELinux or SMACK security context to CTX --help 显示此帮助信息并退出 --version 显示版本信息并退出 默认情况下,源文件的稀疏性仅仅通过简单的方法判断,对应的目标文件目标文件也 被为稀疏。这是因为默认情况下使用了--sparse=auto 参数。如果明确使用 --sparse=always 参数则不论源文件是否包含足够长的0 序列也将目标文件创文 建为稀疏件。 使用--sparse=never 参数禁止创建稀疏文件。 当指定了--reflink[=always] 参数时执行轻量化的复制,即只在数据块被修改的 情况下才复制。如果复制失败或者同时指定了--reflink=auto,则返回标准复制模式。 The backup suffix is '~', unless set with --suffix or SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX. The version control method may be selected via the --backup option or through the VERSION_CONTROL environment variable. Here are the values: none, off 不进行备份(即使使用了--backup 选项) numbered, t 备份文件加上数字进行排序 existing, nil 若有数字的备份文件已经存在则使用数字,否则使用普通方式备份 simple, never 永远使用普通方式备份 有一个特别情况:如果同时指定--force 和--backup 选项,而源文件和目标文件 是同一个已存在的一般文件的话,cp 会将源文件备份。 GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/> 请向<http://translationproject.org/team/zh_CN.html> 报告cp 的翻译错误 Full documentation at: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/cp> or available locally via: info '(coreutils) cp invocation'
10.重命名文件和移动文件:mv
11.删除文件rm
最常用 rm -i 文件名 删除文件并提示
rm -rf 删除文件整个目录
删除目录还有一个命令也是可以使用的 rmdir 文件名
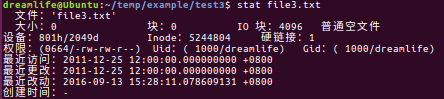
12 查看文件统计信息:stat
13.查看文件类型 file
14.查看文件内容cat
cat命令将提供最基本的查看文本内容功能
cat -n会在文本前面加上行号
-n会给所有行加上行号,包括空白行,如果是希望给文本行加行号,那就需要使用-b命令
另外,如果要压缩多个空白行,可以使用-s参数
15.查看文本升级版神器 more
16.查看文本升级版的升级版神器 less
17 对付长文件神器 tail,默认显示文本尾10行,对于查看log文件有帮助,与之对应的还有head是显示文件头10行
19 关机重启 shutdown -h now 关机 shutdown -r now 重启 后面的now可以换成时间。
20 ubuntu(GNOME桌面)下的文本编辑器 gedit 文件名
21 软件安装 apt install等等其他命令可以自行百度。
好了,目前我所需要的命令差不多都整理在这里了。未完待续中。。。。。。。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号