SQL 基础知识总结(2)
昨天记录了一下简单的检索数据和过滤数据以及聚合函数处理,今天继续~
九、分组数据
关于分组数据最主要的就是 select 的子句的 group by 子句和 having 子句;
1、group by 子句
group by 子句必须出现在 where 子句之后,order by 子句之前;
group by 子句中列出的每一列都必须是检索列或有效的表达式,不能是聚集函数
select vend_id, count(*) as num_prods from Products group by vend_id --group by 对每个组进行聚集,根据vend_id字段进行分组
2、having 子句
having 子句与 where 子句非常类似,所有类型的 where 子句都可以用 having 来替代,但 where 是过滤行,having 是过滤分组,即 where 是在分组前进行过滤,having 是在分组后进行过滤;
使用 having 子句时应该结合使用 group by 子句
select vend_id, count(*) as num_prods from Products where prod_price >=4 group by vend_id --按 vend_id 字段进行分组 having count(*) >=2 --分组后过滤计数为2或2以上的分组
注:
(1)、group by 和 order by 的区别
一般在使用 group by 子句时,应该也给出 order by 子句,以确保数据正确排序
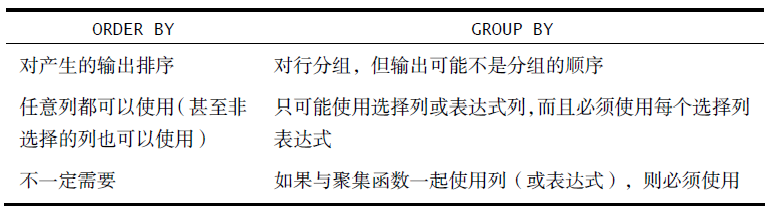
select order_num, count(*) as items from OrderItems group by order_num --按订单号分组 having count(*) >=3 --对分组后的数据进行过滤 order by items,order_num --排序输出
(2)、select 子句
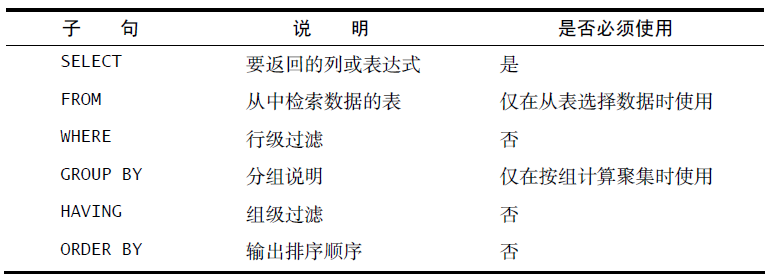
十、使用子查询
作为子查询的 select 语句只能查询单个列,如果搜索多个列会返回错误
select cust_name, cust_contact from Customers --返回所需的顾客信息 where cust_id in (select cust_id from Orders --返回顾客ID where order_num in (select order_num from OrderItems --返回订单号列表 where prod_id = 'RGAN01'))
计算字段使用子查询
select cust_name, cust_state, (select count(*) from Orders where Orders.cust_id = Customers.cust_id) as orders --完全限定列名,用一个句点表名分隔表名和列名,在有可能混淆列名(即在不同表中列名相同)时需使用 from Customers order by cust_name
十一、联结表
SQL最强大的功能之一就是能在数据查询的执行中联结(join)表,在说联结之前,有必要说一下关系表以及关系数据库
关系表就是把信息分解成多个表,一类数据一个表,各表通过某些共同的值互相联结,也称关系数据库
好处:
信息不会重复,不会浪费时间和空间
如果某项信息有变动,只更新此表中的单个记录即可,相关表中的数据不用改动;
可伸缩行好(可伸缩性可理解为能够适应不断增加的工作量而不失败)
1、内联结
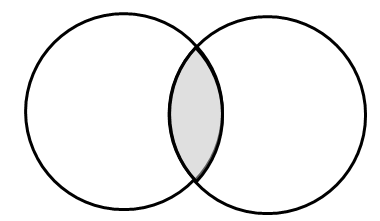
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from Vendors inner join Products on Vendors.vend_id = Products.vend_id 等价于 select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from Vendors,Products where Vendors.vend_id = Products.vend_id --此类形式必须要有 where 子句,否则返回的结果就是笛卡尔积,即检索出的行数为第一个表中行数乘以第二个表中
子查询可以用联结表示
select cust_name, cust_contact from Customers --返回所需的顾客信息 where cust_id in (select cust_id from Orders --返回顾客ID where order_num in (select order_num from OrderItems --返回订单号列表 where prod_id = 'RGAN01')) 等价于 select cust_name, cust_contact from Customers, Orders, OrderItems where Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id and OrderItems.order_num = Orders.order_num and prod_id = 'RGAN01'
2、外联结:左外联结和右外联结
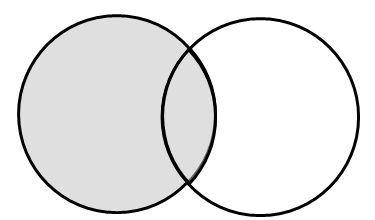
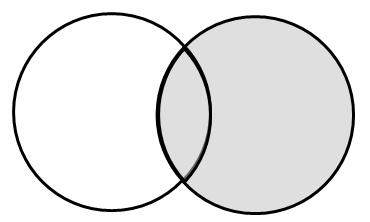
select Customers.cust_id, Orders.order_num from Customers left outer join Orders --left outer join 左外联结 on Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id select Customers.cust_id, Orders.order_num from Customers right outer join Orders --right outer join 右外联结 on Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id
十二、补充部分
1、控制流函数
(1)
case when then when then when then else end
(2)
if(条件,结果1,结果2)
select a.issue_no 单号, case when a.type=1 then '国内' when a.type=2 then '国际' else '其他' end 类型,a.create_time 时间 from complaint a,complaint_problem b where a.config_no=b.config_no select sum(passenger_count*(if(type =4 ,2,1))) as ct,date_format(p.time, '%Y-%m-%') v_date --if(条件,结果1,结果2),date_format(时间,'格式') from info o,record p where p.id=o.id group by v_date
常用时间格式:
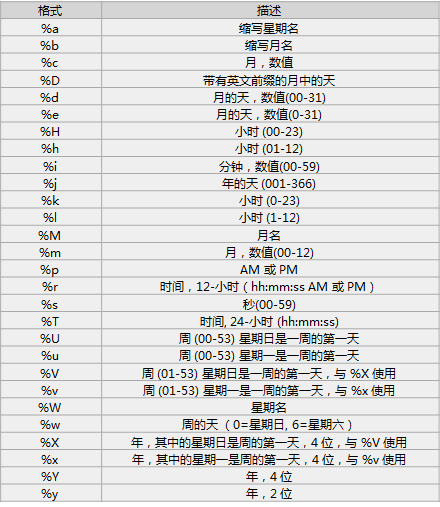
SQL基础查询总结部分暂时到这,下一个hive sql~~



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号