前三次作业总结
其实到这个学期才正式接触java。对于一门陌生的语言来说,它的语法规则、它的功能特性、它的擅长邻域自然是十分重要的,第一天一开始连输入、输出也确实让我个人不知所措、摸不着头脑(现在当然还是会输入输出的哈)。但我们这门课其实叫“面向对象程序设计”而不是叫“java语言程序设计”,老师强调的和教学核心里讲的也是要求我们核心掌握的是面向对象的程序设计思想。我们之前课程安排已经学习了C语言,后面我自己也了解了一点点C++、Python等等,但对于什么是面向对象、什么程序才算面向对象、面向对象有什么用……还是云里雾里。同时上个学期,我们课程学的单片机原理,以及这个学期的感知层编程和传感器应用,又是另一个不同的聚焦于硬件开发的专业课方向。所以不同的邻域聚焦在一起也是很有“特色”呢。
一、前言
第一次作业
第一次作业的题目分别是:
7-1 计算两个数的和
7-2 电话键盘字母数字转换
7-3 成绩分级管理
7-4 计算税率
7-5 计算钱币
7-6 使用一维数组求平均值
7-7 对多个整数进行排序
7-8 判断三角形类型
运用知识点
如果按现在的“眼光”来看这道题,这八道题目应该算是仅次于输出“Hello world”的最简单的java练习题目了吧。但是在做的时候并不是这样的。这几道题目在最初C语言的程序设计的课程中也有类似的题。因为这次是在用java编程,所以这次主要是在考察java的基本语法。考察的语法主要包括:
1、创建的类名要与.java文件名一致。
在PTA中包含main函数的核心类都是Main,因此我们上传的代码文件都必须是以Main位核心类名,如果使用其它名字,都将会无法被接收端接受。
2、main函数的声明格式为public static void main(String[] args)。
其中static作用为使类中的属性或方法在无对象引用的时候仍然可以用类名直接调用,同时该类的所有对象都将共用static声明的属性。
3、应用Scanner类完成输入。
java输入和其它部分操作可以引入Scanner类,而引入Scanner类需要 import java.util.Scanner; 引入相关库。同时当输入的内容为整数、小数、字符串等等不同内容时,需要运用Scanner类中不同方法。如String str = scan.nextLine(); int num = scan.nextInt(); 等等
4、应用System.out.println(); 等完成输出。
5、判断语句(与c语言基本一致)
6、循环语句(与c语言基本一致)
7、对象的建立
具体在第二次作业主要使用到
难度
像前面说到的那样,这次作业算是最基本的基本语法内容,而且还会发现题目和c语言以前的题目十分类似,语法也大体相同。但是对于几个星期前第一次真正接触java编程来说,做这几道题目比第二次作业所花的时间和精力要多的多。一个小时的时间都在熟悉工具、解决各种报错,甚至是输入输出。但是也正是输入输出解决了以后,其它内容也确实可以比较快的通过已经拥有的基本的语法知识完成出来。
第二次作业
第二次作业的题目分别是:
7-1 IP地址转换
7-2 合并两个有序数组为新的有序数组
7-3 判断闰年及星期几
7-4 求下一天
7-5 求前N天
运用知识点
在第二次作业中,我们才算正式使用对象中方法和属性的概念来分解工作完成需求,具体包括:
1、方法的声明格式
2、方法的调用
3、属性的设置与运用
(其实这些与c语言函数的使用基本相同)
对于属性,伴随课程的学习,变量属性类似int、fioat等等都存在了对象中,而类如String,则是将地址存入对象中,再用此地址找到对应的String对象。
难度
因为这些内容——方法和属性的使用与“全局变量”和函数的使用非常相似,再加上对java的适应,完成的难度并不是非常大。
第三次作业
第三次作业的题目分别是:
7-1 创建账户类Account
7-2 定义日期类
7-3 一元多项式求导(类设计)
运用知识点
在这一期作业中,我们可能才算正式开始使用面向对象的方法来为任务进行分工简化。在这期的三题中,我们按照题目给的格式指导设计额外的类来处理相关的工作。
1、对象的创建
2、对象属性与方法的调用
难度
前面两道题的内容相对简单,而且由于题目给的面向对象方式的类的属性与方法的设计特别清晰、详细,因此在实际操作的时候格外轻松。但第三题多项式求导,其需考虑的内容就异常多了,各种输入格式的判断、分割、处理、输出,相对来说比较难完成。而且最后一个测试点还存在bug,对指数为1的x的单项式求导后的正数结果前面本来应该输出+号与其它单项式连接但测试例子却不会将其输出造成问题。
二、设计与分析
第一次作业7-8
源代码
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 6 double a[] = new double[3]; 7 int i; 8 for(i = 0; i < 3; i++){ 9 a[i] = in.nextDouble(); 10 } 11 for(i = 0; i < 3; i++){ 12 if(a[i] < 1 || a[i] > 200){ 13 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 14 return; 15 } 16 } 17 Arrays.sort(a); 18 if(a[0] + a[1] > a[2]){ 19 if(a[0] == a[2]){ 20 System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); 21 } 22 else if(a[0] == a[1] && a[0] * a[0] + a[1] * a[1] - a[2] * a[2] < 0.000001) 23 System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); 24 else if(a[0] == a[1] || a[1]==a[2] || a[0]==a[2]) 25 System.out.println("Isosceles triangle"); 26 else if(a[0] * a[0] + a[1] * a[1] == a[2] * a[2]) 27 System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); 28 else{ 29 System.out.println("General triangle"); 30 } 31 32 } 33 else 34 System.out.println("Not a triangle"); 35 } 36 37 }
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
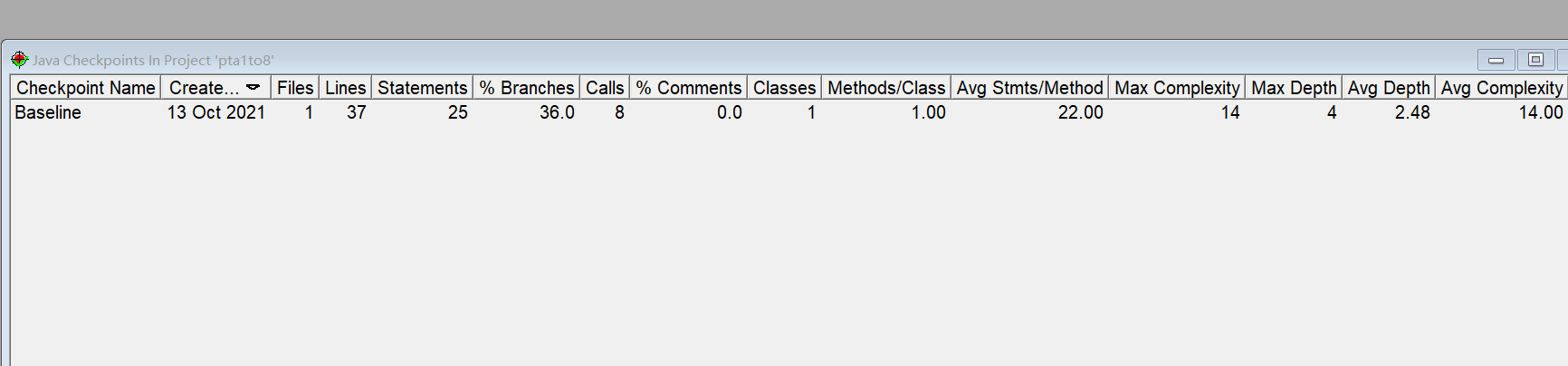
分析
这道题要求根据输入的三角形的三条边判断所能构成的三角形的类型,数据非法输出“Wrong Format”; 不能构成三角形输出“Not a triangle”;够成等边三角形输出“Equilateral triangle”;能够成等腰直角三角形输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”;能够成等腰三角形输出“Isosceles triangle”; 能够成直角三角形输出“Right-angled triangle”;够成一般三角形输出“General triangle”。这7种输出分别代表了7种分析判断的情况,且这7种情况有优先的先后顺序,即同时满足多种情况的时候,顺序越靠前输出优先度越高。因此越靠前的条件越先判断,一旦输出即可结束。
首先判断输入的合法性,一旦判断非法即可直接完成输出然后结束
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++){
if(a[i] < 1 || a[i] > 200){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
}
通过合法检验后再Arrays.sort(a);控制输入的三条边按从小到大的顺序排序。用它们的大小关系如(最短)两边之和大于第三边等等具体条件完成各种条件的判断和输出。
因为这次代码写的时间较早,因此大量使用了if else语句判断,没有将判断内容方法化所以如 SourceMonitor所示的这样圈复杂度较高。
第二次作业7-4
源代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static int[] a= new int[] {0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year=input.nextInt(); int month=input.nextInt(); int day=input.nextInt(); if(isLeapYear(year)) { a[2] = 29; } else a[2] = 28; if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)==true) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else{ nextDate(year, month, day); } } public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { boolean check; check = (year<1820 || year>2020 || month<1 || month>12 || day>a[month] || day<1); return check; } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { boolean isLeap; isLeap = year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 ); return isLeap; } public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) { day = day + 1; if(day>a[month]) { day=day-a[month]; month++; } if(month>12) { year++; month=month-12; } System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); } }
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
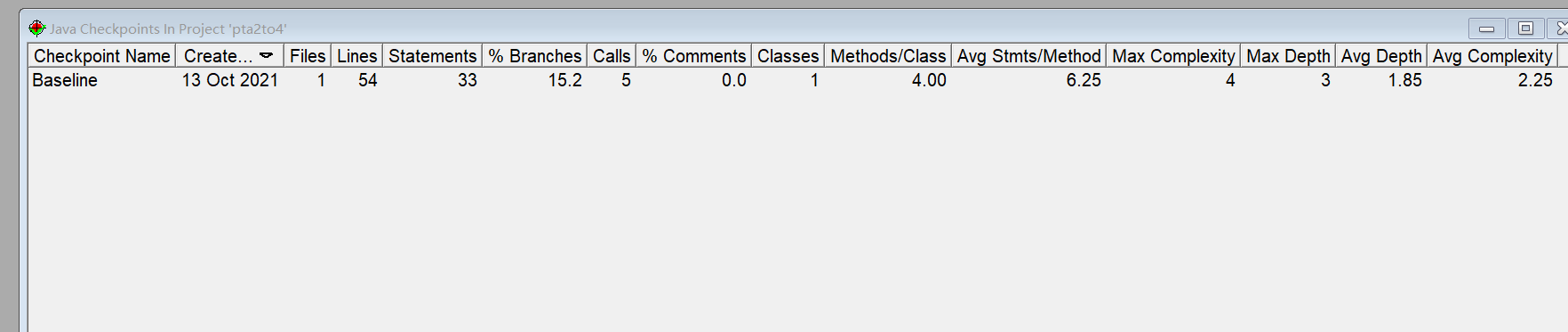
分析
题目要求输入年月日的值,输出该日期的下一天。
如上题一样,首先也是合法性的判断。年份的合法性比较简单,如题目要求在一定范围内即可,月份也是1-12为要求。而日期的判断,可以通过率先建立天数表
public static int[] allmon= new int[] {0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};可以建在方法外作为对象的属性共同使用。
在判断时先判断输入的年份是否为闰年。如果是allmon[2]的值调为29,对应闰年2月29天,反之为28。然后将输入月份作为索引值用来与allmon数组比较。越界即判断日期非法。
判断合法性之后即对下一天求解。先让日期+1,如果超过了表中该月最大天数,即日期为差,月份+1,此时如果月份大于12,则年份+1,月份为差。都合法后输出年月日。
在这道题中,因为题目要求了相关方法
public static void main(String[] args);//主方法
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) ;//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day);//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) ; //求输入日期的下一天
因此按照这种分解格式复杂度如 SourceMonitor所示较低。
第二次作业7-5
源代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static int[] allmon= new int[] {0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year=input.nextInt(); int month=input.nextInt(); int day=input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); if(isLeapYear(year)) { allmon[2] = 29; } else allmon[2] = 28; if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)==true) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else{ nextDate(year, month, day, n); } } public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { boolean check; check = (year<1820 || year>2020 || month<1 || month>12 || day>allmon[month] || day<1); return check; } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { boolean isLeap; isLeap = year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 ); return isLeap; } public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day,int n) { int c=day; if(n>0) { day=day-n; if(day<1) { month--; if(month<1) { month = month+12; year--; } day=allmon[month]-n+c; } } else { day=day-n; if(day>allmon[month]) { day=day-allmon[month]; month++; } if(month>12) { year++; month=month-12; } } System.out.println(n+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); } }
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
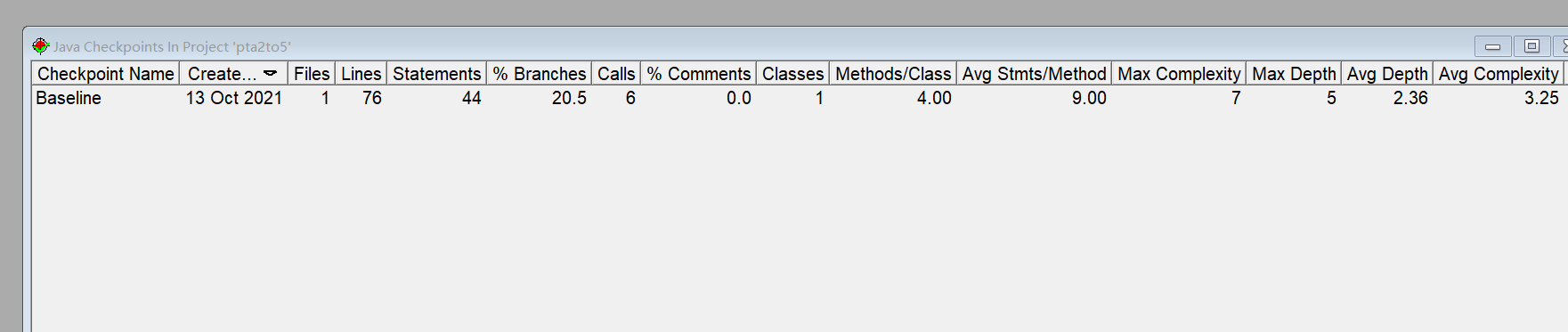
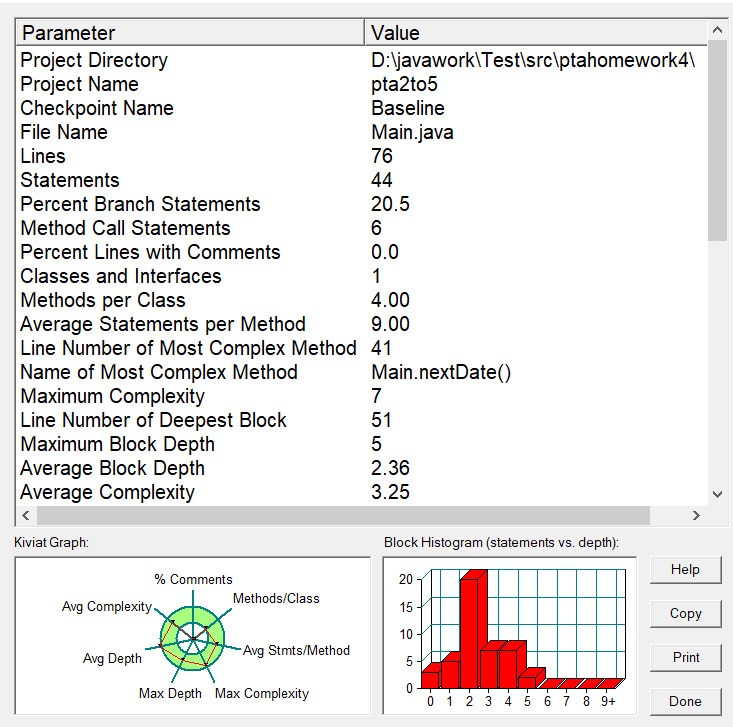
分析
这道题基本与上题一致,同样先合法性的判断。年份如题目要求的范围,月份1-12为要求,日期的判断建立天数表public static int[] allmon= new int[] {0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
再判断时先判断输入的年份是否为闰年。是allmon[2]的值调为29,反之为28。然后将输入月份作为索引值用来与allmon数组比较,天数越界即判断日期非法。
同样判断完后,让天数减n天,如果超过了表中该月最大天数或小于1,即日期为差,月份+1-1,直到天数合适,如果月份大于12小于1,则年份+1-1,月份为差,直到全部合法。最后将合法内容结果输出即可完成。
这道题中同样可以参照上题的相关方法,
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day)
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year)
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day,int n)
因此复杂度同样如SourceMonitor所示较低。
第三次作业7-2
源代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); Date rq=new Date(); rq.year=scan.nextInt(); rq.month=scan.nextInt(); rq.day=scan.nextInt(); if(rq.checkInputValidity()==false) System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong"); else { rq.getnextDate(); System.out.println("Next day is:"+rq.year+"-"+rq.month+"-"+rq.day); } } } class Date{ int year; int month; int day; int[] maxnum=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; Date() { } Date(int year,int month,int day){ this.year=year; this.month=month; this.day=day; } public int getYear(){ return year; } public void setYear(int year) { this.year = year; } public int getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(int month) { this.month = month; } public int getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(int day) { this.day = day; } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { boolean isLeap = false; if( year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )) isLeap = true; return isLeap; } public boolean checkInputValidity() { boolean check = true; if(isLeapYear(year)==false) maxnum[2] = 28; if(year<1900 || year>2000 || month<1 || month>12 || day>maxnum[month] || day<1) check = false; return check; } public void getnextDate() { int c=day; int n=-1; if(n>0) { day=day-n; if(day<1) { month--; if(month<1) { month = month+12; year--; } day=maxnum[month]-n+c; } } else { day=day-n; if(day>maxnum[month]) { day=day-maxnum[month]; month++; } if(month>12) { year++; month=month-12; } } } }
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
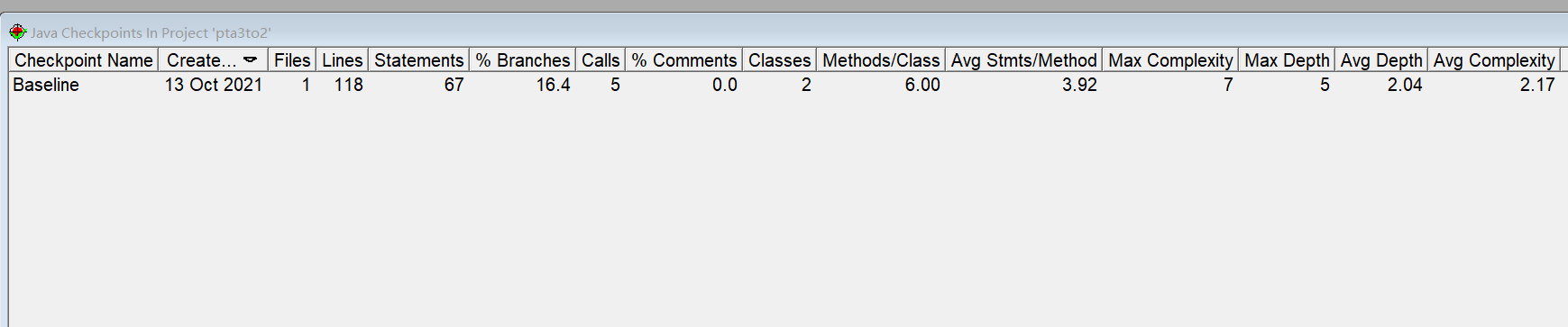
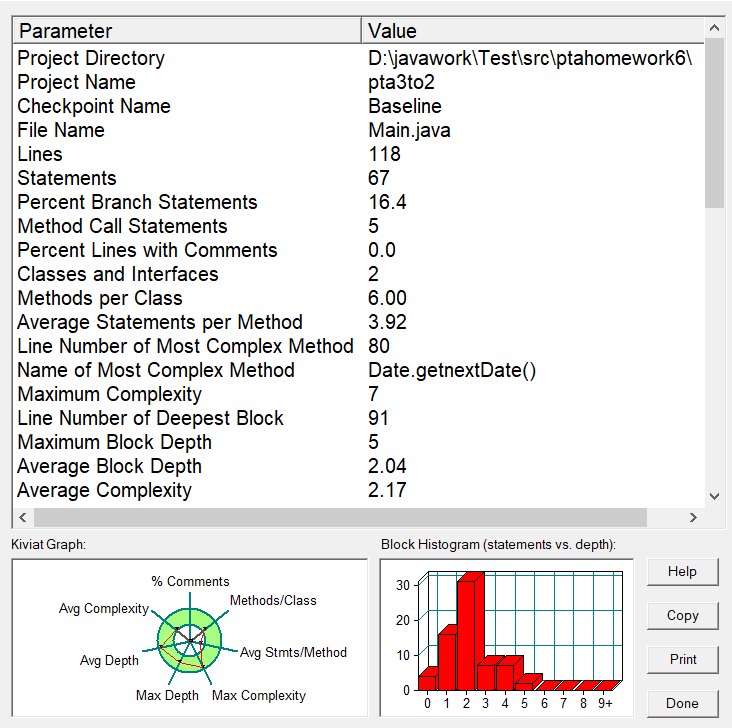
分析
这道题继续进行日期相关内容,并且给了日期类该需要的相关方法和属性。
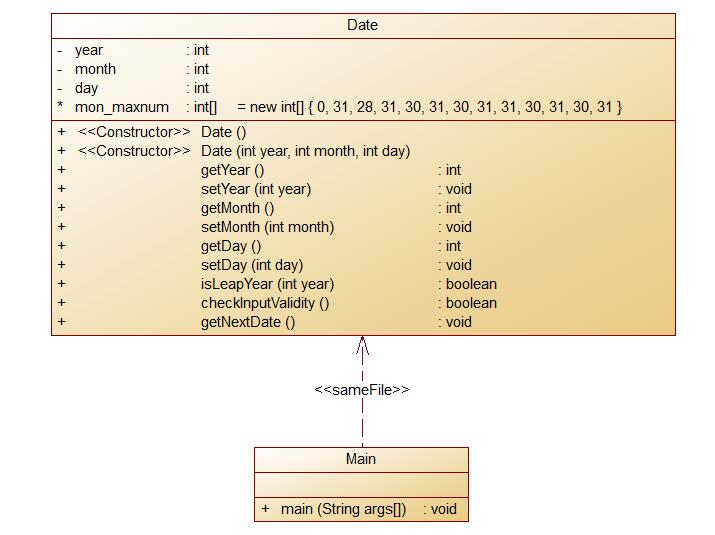
如题目所给的该类的相关要求,重点功能逻辑基本完全与上面两题所建的类的功能一样。因此我也基本直接使用了前面两题建好的类。补充了更规范发的类的要求结束。
因此其复杂度与前面两题相似。
第三次作业7-3
源代码
import java.math.BigInteger; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); String astr = scan.nextLine(); Item it = new Item(); String bstr = astr.replaceAll("\\s", ""); it.str1=astr; it.str2=bstr; if(it.checkInputValidity()==true) { it.splitstr(); it.compute(); it.connectShow(); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } class Item { String str1; String str2; ArrayList<String> alist = new ArrayList<String>(); ArrayList<String> blist = new ArrayList<String>(); public boolean checkInputValidity() { boolean result = true; int len1 = str1.length(); int i,path1,path2; //检测空格问题 for(i = 0; i < len1; i++) { /* if(str1.charAt(i)=='-') { j=i-1; path1=0; while(j>=0) { if(str1.charAt(j)==' ') j--; else { if( str1.charAt(j)>='0'&&str1.charAt(j)<='9' || str1.charAt(j)=='x' ) { path1=1; } break; } } if(path1==0) { i++; while(i<len1) { if(str1.charAt(i)>='0'&&str1.charAt(i)<='9') break; else { result = false; return result; } } } } */ if(str1.charAt(i)>='0'&&(str1.charAt(i)<='9')) { i++; path2=0; while(i<len1) { if(str1.charAt(i)==' ') { path2=1; i++; } else { if(str1.charAt(i)>='0'&&(str1.charAt(i)<='9')&&path2==1) { result = false; return result; } else break; } } } } String pa = "^(([+-]?[1-9]\\d*\\*(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?[1-9]\\d*))(([+-][1-9]\\d*\\*(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-](x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?[1-9]\\d*))*$"; result = str2.matches(pa); return result; } public void splitstr() { String pa = "[+-]?(([1-9]\\d*\\*)?(x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*|x)|([1-9]\\d*))"; Pattern p = Pattern.compile(pa); Matcher m = p.matcher(str2); while(m.find()) { //System.out.println(m.group()); alist.add(m.group()); } } public void compute() { int i,index; for(i=0;i<alist.size();i++) { index = alist.get(i).indexOf('x'); if(index!=-1) { if(alist.get(i).length() == index+1 ) { if(index>1) { if(alist.get(i).charAt(index-1)=='*') blist.add(alist.get(i).substring(0, index-1)); else blist.add(alist.get(i).substring(0, index)); } else if(index==1) { if(alist.get(i).charAt(0)=='-') blist.add("-1"); else if(alist.get(i).charAt(0)=='+') blist.add("1"); } else if(index==0) { blist.add("1"); } } else { String cstr; if(index==0) { cstr = "1*"+ alist.get(i); } else cstr = alist.get(i); String numdata[] = cstr.split("(\\*?)(x\\^)(\\+?)"); if(numdata[0].equals("-")) numdata[0]=new String("-1"); else if(numdata[0].equals("+")) numdata[0]=new String("1"); BigInteger xi = new BigInteger(numdata[0]); BigInteger zhi = new BigInteger(numdata[1]); BigInteger c = new BigInteger("1"); numdata[1]=String.valueOf(zhi.subtract(c)); numdata[0]=String.valueOf(xi.multiply(zhi)); if(numdata[1].equals("0")) blist.add(numdata[0]); else if(numdata[1].equals("1")) { if(numdata[0].equals("1")) blist.add("x"); else if(numdata[0].equals("-1")) blist.add("-x"); else blist.add(numdata[0]+"*x"); } else { if(numdata[0].equals("1")) blist.add("x^"+numdata[1]); else if(numdata[0].equals("-1")) blist.add("-x^"+numdata[1]); else blist.add(numdata[0]+"*x^"+numdata[1]); } } } } } public void connectShow() { if(blist.size() == 0) System.out.println('0'); else { String re[] = new String[blist.size()]; for(int j=0;j<blist.size();j++) { if(blist.get(j).charAt(0)!='+') re[j]=blist.get(j); else { re[j]=blist.get(j).substring(1); } } /* for(int t=0;t<blist.size();t++) { System.out.println(re[t]); } */ /* for(int i=0;i<blist.size();i++) { if(i==0) System.out.print(re[i]); else { if(re[i].charAt(0) == '-') System.out.print(re[i]); else System.out.print("+"+re[i]); } } */ /* if(re[0].charAt(0) == '-') { for(int i=0;i<blist.size();i++) { if(i==0) System.out.print(re[i]); else { if(re[i].charAt(0) == '-') System.out.print(re[i]); else System.out.print("+"+re[i]); } } } else { for(int i=0;i<blist.size();i++) { System.out.print(re[i]); } } */ /* int pat=0; for(int g=0;g<blist.size();g++) { if(re[g].charAt(0)=='-') { pat=1; break; } } if(pat==0) { for(int i=0;i<blist.size();i++) { System.out.print(re[i]); } } else { for(int i=0;i<blist.size();i++) { if(i==0) System.out.print(re[i]); else { if(re[i].charAt(0) == '-') System.out.print(re[i]); else System.out.print("+"+re[i]); } } } */ for(int g=1;g<blist.size();g++) { if(re[g].charAt(0)!='-'&&re[g].indexOf('x')!=-1) { re[g]="+"+re[g]; } } for(int g=0;g<blist.size();g++) { System.out.print(re[g]); } } } }
SourceMonitor 复杂度分析
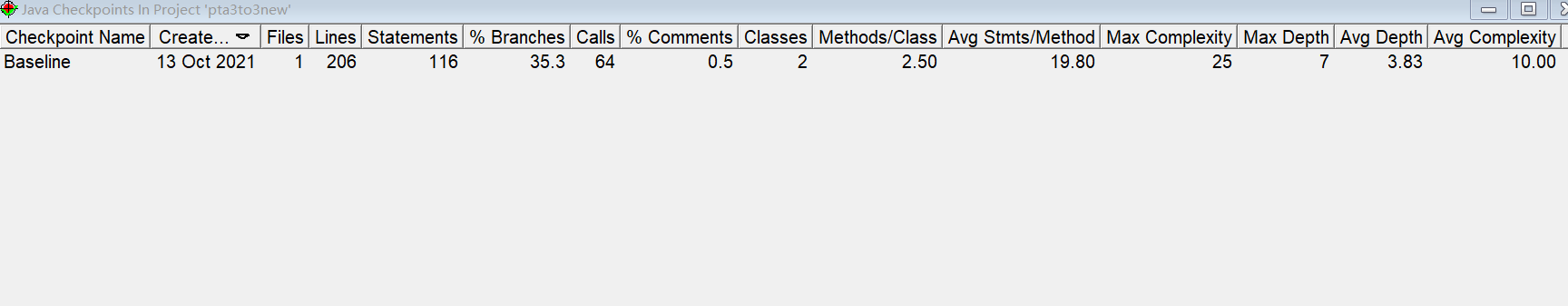
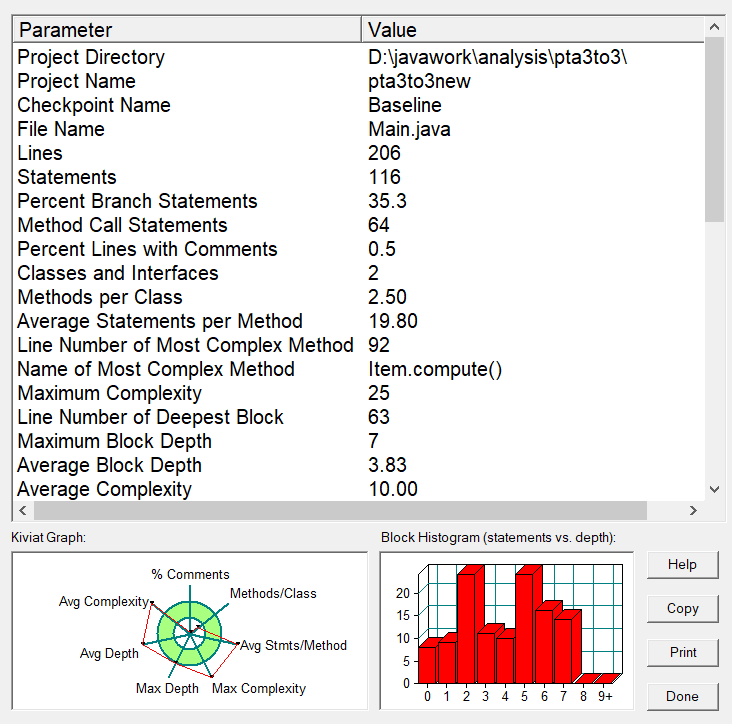
分析
本题多项式求导,其需考虑的内容就非常多了,主要分为四个方面,即各种输入格式的判断、分割、处理、输出。且我个人在写这道题的时候是边学其它新的内容如正则表达式、大数运算,边加深对它们的理解,边完成的。因此其实前面写的一些内容到后面快完成时其实已经理解了更好的方法代替,但从头修改工作量太大,而且对逻辑的改动过多,容易有新的遗漏,所以最后对开始和中间的内容没有重新做过多变动。
(1)输入格式的判断。
题目给出了相关要求:前导不为 0 的带符号整数,如果是正号,可以省略;带符号整数内不允许出现空白字符,其他位置均可以存在空白字符;由自变量 x(只支持小写)和指数组成,指数为一个带符号整 数,如 x^-2、x^+25,当指数为 1 时,可以省略指数;系数为 1 时的时候,可以省略系数或表示为正号开头的形式,如 x^-2;系数为-1 时的时候,可以表示为符号开头的形式,如-x^3;系数与指数均不能为 0。在开始的时候由于不清楚正则表达式,所以用循环判断各个字符中空格是否合法,若合法后再将空格去掉。
for(i = 0; i < len1; i++)
{
if(str1.charAt(i)>='0'&&(str1.charAt(i)<='9'))
{
i++;
path2=0;
while(i<len1)
{
if(str1.charAt(i)==' ')
{
path2=1;
i++;
}
else
{
if(str1.charAt(i)>='0'&&(str1.charAt(i)<='9')&&path2==1)
{
result = false;
return result;
}
else
break;
}
}
}
}
利用 String bstr = astr.replaceAll("\\s", ""); 去掉空格后,再用正则表达式比对。
String pa = "^(([+-]?[1-9]\\d*\\*(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?[1-9]\\d*))(([+-][1-9]\\d*\\*(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-](x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?[1-9]\\d*))*$";
result = str2.matches(pa);
由于此时刚刚接触正则表达式,其实上面pa字符串所展示的多种“或 | ”的情况其实可以合并。利用这里的这些内容即可完成对输入合法性的判断。
(2)多项式的分割。
对于多项式中不同格式的单项式的分割,同样可以运中正则表达式获取字符串。
public void splitstr() {
String pa = "[+-]?(([1-9]\\d*\\*)?(x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*|x)|([1-9]\\d*))";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(pa);
Matcher m = p.matcher(str2);
while(m.find()) {
//System.out.println(m.group());
alist.add(m.group());
}
}
按上面有0或1个+-号,最高位非0的任意整数去*x带或不带指数的各种格式,将分割的单项式存入列表alist中。
(3)运算处理
在获得分割好的各个单项式后,按照相关原则:为常数项,导数为0,不存,若最后列表为空输出0;系数=系数*指数,指数=指数-1,初始不带指数默认指数初始为1,求导后指数为0,x项可去掉……运用这些原则且用大数处理BigInterger完成运算,将运算结果存入列表中。
(4)输出
输出将多余的+号去掉,再按逻辑完成用+/-连接输出,即可完成求导。
如这道题前面分析所说的,因为开始时不知道使用正则表达式,所以使用for先进行空格判断,事实上可以融合入正则。处理的时候最后自己才分出7种单项式格式,导致修补后判断较乱,因此复杂度如SourceMonitor所示较高。
三、踩坑心得
1、第一次作业提交代码时一直有编译错误,开始的时候不清楚,后面知道pta题目主类public class Main,类名必须是Main。
2、对题7-8 判断三角形类型 ,关于判断等腰直角三角形的语句else if(a[0] == a[1] && a[0] * a[0] + a[1] * a[1] - a[2] * a[2] < 0.000001),如果我直接用等于号比较两平方之和则会出错无法通过。
3、在第二次作业各个判断日期合法性的题目中,判断语句if ( year>=1820 && year<=2020 && month>=1 && month<=12 && day<=a[month] && day>=1 ) 如果变成调换&&前后内容的顺序,变成从左往右为日、月、年,则会报错。
4、在7-5 求前N天中,如果天数过大出现跨年的情况,则需重新考虑闰年平年2月天数。
5、对一元多项式求导,处理分割好的各个单项式后要分清楚各个情况,真正编写理代码的时候极其容易混淆。
6、对一元多项式求导,最后一个测试点有bug,指数为1的单项式,求导后为常数,但题目输出时,会将结果常数用于与前面连接的单项式的+号莫名拿掉。
四、改进建议
首先是对于前面心得的第三点要注意,虽然现在还没有完全清楚原理,但以后做if的&&判断的时候要注意是否会因为顺序问题产生报错。
第二是在第二次作业中,7-5 求前N天中,如果天数过大出现跨年的情况,则需重新考虑闰年平年2月天数,这点其实在这次实验中没有考虑,但因为事实上pta的测试点连跨月的测试都没有,所以顺利通过了。
第三点是在最后对一元多项式的求导中,空格的for判断可以融入正则表达式中,用插入其中的\\s*完成判断。且第一个判断合法性的第一个括号里的两个或可以从
([+-]?[1-9]\\d*\\*(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?(x|x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*))|([+-]?[1-9]\\d*)
变为
[+-]?(([1-9]\\d*\\*)?(x\\^[+-]?[1-9]\\d*|x)|([1-9]\\d*))
另外对于各个单项式的处理,可以集中考虑系数和指数为空的情况,而不是分开考虑
第四点是面向对象的思想在做这几次作业的时候还没有很好的理解和运用,这也导致第三次作业的最后的题目处理的是否混乱复杂度较高。这几天对面向对象的理解亦有所加强,因此后续会更深入的应用面向对象的思想编程。
五、总结
总结前其实可以先提一下,那个第三次作业第三题的最后一个测试点的bug不要一代一代传下去。
这三次作业我个人对java的理解与运用有了很大的变化,从一开始不会import java.util.Scanner; Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); String astr = scan.nextLine(); 的输入,不会System.out.println();的输出,到能花一定时间前面几个做完第三次作业的第三题,对java的运用已经变的从完全不懂,到对基本类运用的相对熟悉了。在语法上面,在java这里学习了c语言之外的列表,大数处理等等,还有正则表达式从用来判断到获取字符串的不同使用方法。同时通过这轮作业和上课的讲解,我更加清楚的理解了类、属性、方法和对象。比如类中new出的新对象,其实是存放了该类对象的地址在此处,而变量则是直接存放在对象中。
三次作业从if else的基本语法使用,到方法的使用,再到创建新的类,对面向对象的分解管理的思想的理解也在逐步加深。但前几次作业中自己还没有掌握好类应该如何使用,到最近的几次课堂上相对简单的作业练习,才加强了一部分体会。对这里面向对象的思想的运用需要进一步加深。相信后面的编程会更好的运用面向对象的思想完成练习。
最后意见还是那个第三次作业第三题的最后一个测试点的bug确实应该改掉。我那一题代码里70多行的注释代码都是在测试越过这个bug。另外就是测试点其实覆盖不是很全面,不是多少的问题,就像那个日期题其实连跨月的测试点都没有更何况跨年的呢。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号