PyTorch中的张量存储方式以及view()和reshape()操作
1. PyTorch张量的底层存储方式
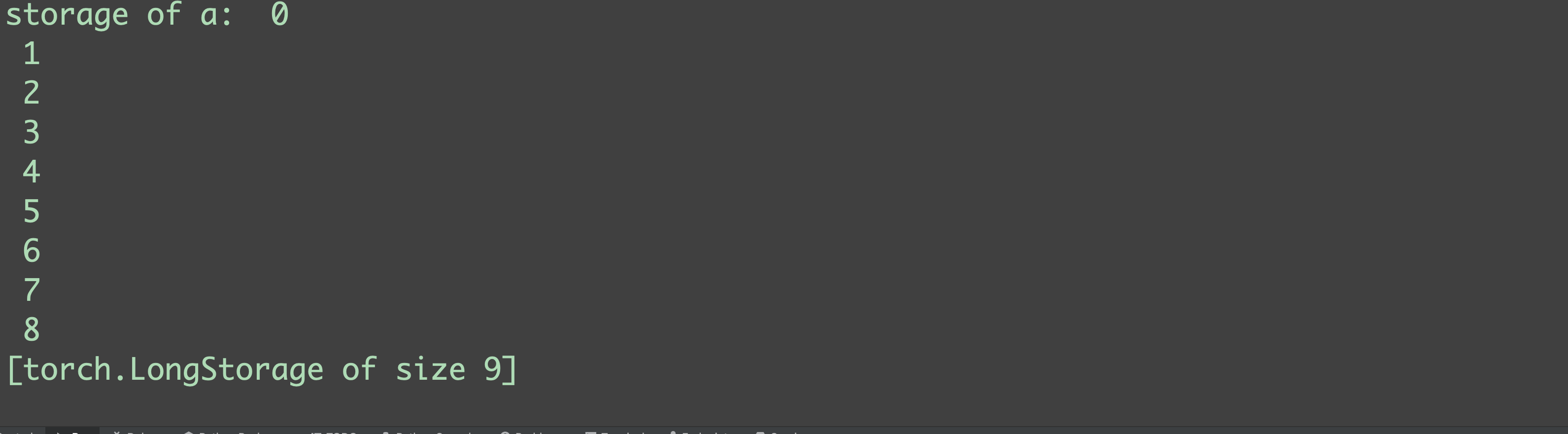
在PyTorch中,张量的头信息(包括张量名、形状等信息)和实际的数据是分开存储的。在数据区,无论张量的维度、形状如何,都是按照一维、连续的方式进行存储的,可以通过张量的storage()来查看张量的数据区:
import torch
a = torch.arange(9).view(3, 3)
print(f"storage of a: {a.storage()}")
1.1 张量的size属性和stride属性
张量的size指的是张量每一维度的大小,张量的步长属性stride可以理解为从索引中的一个维度跨到下一个维度中间的跨度:
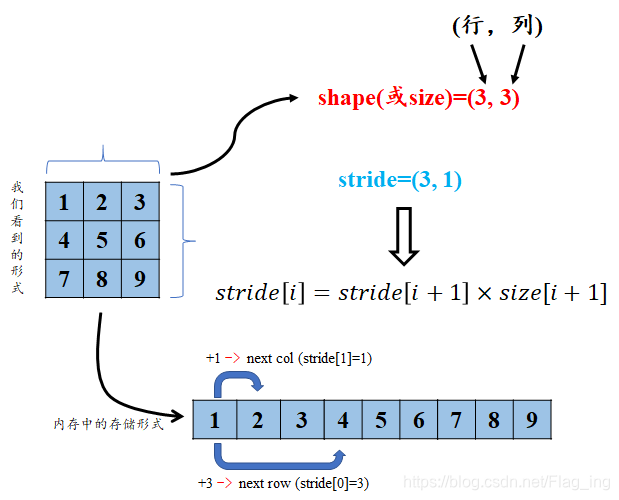
对于第一个维度(即行),从上一行跨越到下一行需要跨越三个元素,而第二个维度(即列),从前一列跨越到(同一行的)下一列只需跨越一个元素,故a的stride为(3,1)
1.2 连续性条件
张量是连续的是指张量满足以下条件:
stride[i] = stride[i + 1] * size[i + 1]
2. view()和reshape()
张量的view()和`reshape()的作用都是将张量转换为指定形状,然而,view()要求张量在装换前后满足连续型条件
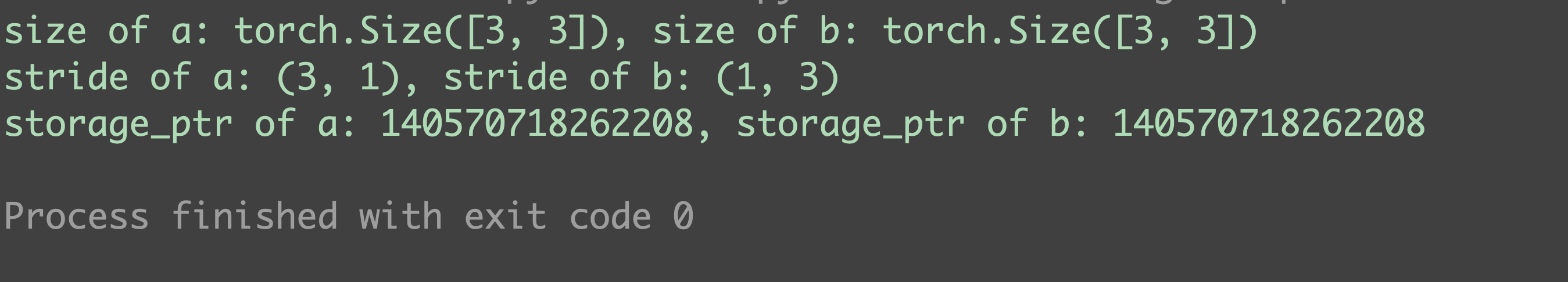
b = a.permute(1, 0) # b是a的转置,此时a和b共享存储区
print(f"size of a: {a.size()}, size of b: {b.size()}")
print(f"stride of a: {a.stride()}, stride of b: {b.stride()}") # b不满足连续型条件
print(f"storage_ptr of a: {a.storage().data_ptr()}, storage_ptr of b: {b.storage().data_ptr()}")
此时,若对b使用view(),则会因不满足连续性条件而报错:
b.view(1, 9)

解决方法是先使用contiguous()将其转换到满足连续性条件,该函数会开辟新的内存空间,对数据进行深拷贝:
b = b.contiguous()
print(f"storage_ptr of a: {a.storage().data_ptr()}, storage_ptr of b: {b.storage().data_ptr()}") # a, b的data_ptr不同
b = b.view(1, 9)
print(b)

reshape()也可以达到上述的效果:
- 当张量满足连续性条件时,等价于
b.view() - 当张量不满足连续性条件时,等价于
b.contiguous().view()
c = a.permute(1, 0)
c = c.reshape(1, 9)
print(c)
本文代码详见代码


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号